Python教程:while 循环用法讲解
1.while 循环
Python 中 while 语句的一般形式:
while 判断条件(condition):
执行语句(statements)……
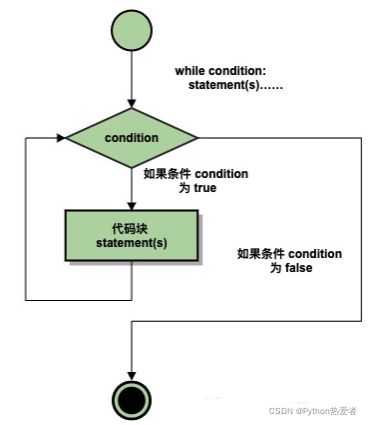
执行流程图如下:
同样需要注意冒号和缩进。另外,在 Python 中没有 do…while 循环。
以下实例使用了 while 来计算 1 到 100 的总和:
n = 100
sum = 0
count = 1
while count <= n:
sum = sum + count
count = count + 1
print("1加到100的和为%d" % sum)
执行结果:
1加到100的和为5050
2.无限循环
我们可以通过设置条件表达式永远不为 false 来实现无限循环,实例如下:
while True:
num = int(input("请输入一个数字:"))
print("您输入的数字是%d" % num)
执行结果:
请输入一个数字:1
您输入的数字是1
请输入一个数字:3
您输入的数字是3
请输入一个数字:4
您输入的数字是4
请输入一个数字:
你可以使用 CTRL+C 来退出当前的无限循环。
无限循环在服务器上客户端的实时请求非常有用。
3、while 循环使用 else 语句
如果 while 后面的条件语句为 false 时,则执行 else 的语句块。
语法格式如下:
while <expr>:
<statement(s)>
else:
<additional_statement(s)>
expr 条件语句为 true 则执行 statement(s) 语句块,如果为 false,则执行 additional_statement(s)。
循环输出数字,并判断大小:
'''
学习中遇到问题没人解答?小编创建了一个Python学习交流QQ群:857662006
寻找有志同道合的小伙伴,互帮互助,群里还有不错的视频学习教程和PDF电子书!
'''
count = 0
while count <5:
print("count小于5:", count)
count = count + 1
else:
print("count大于5了:", count)
执行结果:
count小于5: 0
count小于5: 1
count小于5: 2
count小于5: 3
count小于5: 4
count大于5了 5
4、简单语句组
类似if语句的语法,如果你的while循环体中只有一条语句,你可以将该语句与while写在同一行中, 如下所示:
flag = 1
while (flag):
print("hello.yin")
print("hello.yin! good bye~")
执行结果:
hello.yin
hello.yin
hello.yin
hello.yin
hello.yin
hello.yin
.......