编程题(二)
一、N皇后 II
n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
给你一个整数 n ,返回 n 皇后问题 不同的解决方案的数量。
示例 1:
输入:n = 4
输出:2
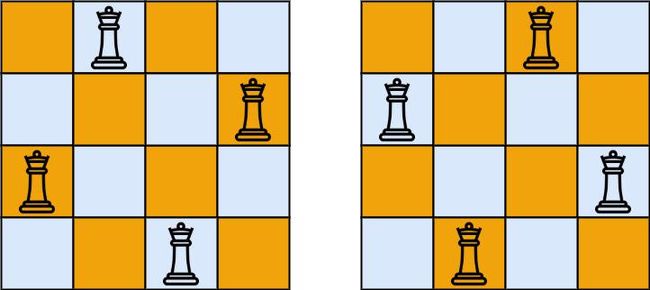
解释:如上图所示,4 皇后问题存在两个不同的解法。
示例 2:
输入:n = 1
输出:1
提示:
- 1 <= n <= 9
- 皇后彼此不能相互攻击,也就是说:任何两个皇后都不能处于同一条横行、纵行或斜线上。
public class S1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(totalNQueens(1));
System.out.println(totalNQueens(4));
}
private static boolean col[];
private static boolean dia1[];
private static boolean dia2[];
public static int totalNQueens(int n) {
col = new boolean[n];
dia1 = new boolean[2 * n - 1];
dia2 = new boolean[2 * n - 1];
return putQueen(n, 0);
}
private static int putQueen(int n, int index) {
int res = 0;
if (index == n) {
return 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!col[i] && !dia1[i - index + n - 1] && !dia2[i + index]) {
col[i] = true;
dia1[i - index + n - 1] = true;
dia2[i + index] = true;
res += putQueen(n, index + 1);
col[i] = false;
dia1[i - index + n - 1] = false;
dia2[i + index] = false;
}
}
return res;
}
}
二、编辑距离
给你两个单词 word1 和 word2,请你计算出将 word1 转换成 word2 所使用的最少操作数 。
你可以对一个单词进行如下三种操作:
- 插入一个字符
- 删除一个字符
- 替换一个字符
示例 1:
输入:word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros"
输出:3
解释:horse -> rorse (将 'h' 替换为 'r')rorse -> rose (删除 'r')rose -> ros (删除 'e')
示例 2:
输入:word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution"
输出:5
解释:intention -> inention (删除 't')inention -> enention (将 'i' 替换为 'e')enention -> exention (将 'n' 替换为 'x')exention -> exection (将 'n' 替换为 'c')exection -> execution (插入 'u')
提示:
- 0 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 500
- word1 和 word2 由小写英文字母组成
public class S2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String word1 = "horse";
String word2 = "ros";
System.out.println(minDistance(word1, word2));
String word3 = "intention";
String word4 = "execution";
System.out.println(minDistance(word3, word4));
}
public static int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int len1 = word1.length();
int len2 = word2.length();
if (len1 * len2 == 0)
return len1 + len2;
String longerStr = len1 > len2 ? word1 : word2;
String shorterStr = len1 > len2 ? word2 : word1;
int shorterOne = Math.min(len1, len2);
int[] dp = new int[shorterOne + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < shorterOne + 1; i++) {
dp[i] = i;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= longerStr.length(); j++) {
int left = j;
for (int i = 1; i <= shorterStr.length(); i++) {
int updateDown = dp[i] + 1;
int updateLeft = left + 1;
int updateLeftDown = dp[i - 1];
if (longerStr.charAt(j - 1) != shorterStr.charAt(i - 1)) {
updateLeftDown++;
}
int min = Math.min(updateLeft, Math.min(updateDown, updateLeftDown));
dp[i - 1] = left;
if (i == dp.length - 1) {
dp[i] = min;
} else {
left = min;
}
}
}
return dp[shorterOne];
}
}
三、串联所有单词的子串
给定一个字符串 s 和一些长度相同的单词 words。找出 s 中恰好可以由 words 中所有单词串联形成的子串的起始位置。
注意子串要与 words 中的单词完全匹配,中间不能有其他字符,但不需要考虑 words 中单词串联的顺序。
示例 1:
输入: s = "barfoothefoobarman", words = ["foo","bar"]
输出:[0,9]
解释:从索引 0 和 9 开始的子串分别是 "barfoo" 和 "foobar" 。输出的顺序不重要, [9,0] 也是有效答案。
示例 2:
输入: s = "wordgoodgoodgoodbestword", words = ["word","good","best","word"]
输出:[]
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
public class S3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "barfoothefoobarman";
String[] words = { "foo", "bar" };
System.out.println(findSubstring(s, words));
String s1 = "wordgoodgoodgoodbestword";
String[] words1 = { "word", "good", "best", "word" };
System.out.println(findSubstring(s1, words1));
}
public static List findSubstring(String s, String[] words) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
if (s == null || s.length() == 0 || words == null || words.length == 0)
return res;
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
int one_word = words[0].length();
int word_num = words.length;
int all_len = one_word * word_num;
for (String word : words) {
map.put(word, map.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < one_word; i++) {
int left = i, right = i, count = 0;
HashMap tmp_map = new HashMap<>();
while (right + one_word <= s.length()) {
String w = s.substring(right, right + one_word);
right += one_word;
if (!map.containsKey(w)) {
count = 0;
left = right;
tmp_map.clear();
} else {
tmp_map.put(w, tmp_map.getOrDefault(w, 0) + 1);
count++;
while (tmp_map.getOrDefault(w, 0) > map.getOrDefault(w, 0)) {
String t_w = s.substring(left, left + one_word);
count--;
tmp_map.put(t_w, tmp_map.getOrDefault(t_w, 0) - 1);
left += one_word;
}
if (count == word_num)
res.add(left);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
四、打家劫舍
你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋。每间房内都藏有一定的现金,影响你偷窃的唯一制约因素就是相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警。
给定一个代表每个房屋存放金额的非负整数数组,计算你 不触动警报装置的情况下 ,一夜之内能够偷窃到的最高金额。
示例 1:
输入:[1,2,3,1]
输出:4
解释:偷窃 1 号房屋 (金额 = 1) ,然后偷窃 3 号房屋 (金额 = 3)。
偷窃到的最高金额 = 1 + 3 = 4 。
示例 2:
输入:[2,7,9,3,1]
输出:12
解释:偷窃 1 号房屋 (金额 = 2), 偷窃 3 号房屋 (金额 = 9),接着偷窃 5 号房屋 (金额 = 1)。
偷窃到的最高金额 = 2 + 9 + 1 = 12 。
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 100
0 <= nums[i] <= 400
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums1 = { 1, 2, 3, 1 };
int[] nums2 = { 2, 7, 9, 3, 1 };
System.out.println(rob(nums1));
System.out.println(rob(nums2));
}
public static int rob(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0)
return 0;
if (nums.length == 1)
return nums[0];
int result[] = new int[nums.length];
result[0] = nums[0];
result[1] = Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
for (int i = 2; i < result.length; i++) {
result[i] = Math.max(result[i - 1], result[i - 2] + nums[i]);
}
return result[result.length - 1];
}
}