QT信号槽实现-观察者模式架构
前面部分在这里–>(QT信号槽实现原理-观察者设计模式架构-QT源码)
三 、接下来把这些函数连接起来
思路:
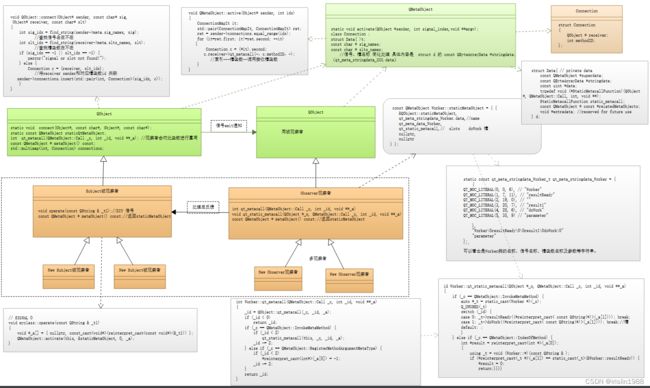
信号-槽QObjetc-QMetaObject-实现架构UML图
-
定义两个类: sender(被观察者)和recver(观察者) 均继承于QObject
-
recver(观察者),定义对某个处理函数比如按钮触发后处理函数。槽函数
-
sender(被观察者),定义一个数据结构,保持观察者对哪个事件id感兴趣,使用map建立对应关系。并调用(运行时)槽函数。
-
connect函数在QObject中可由 sender(被观察者)或recver(观察者) 调用
定义一个QObject类,有以下内容:
- qt_metacall调用观察者的槽函数用 虚函数重写形式实现 动态绑定实现 观察者模式的关键 在moc分析时将槽函数信号的信息写入 qt_static_metacall函数里 ,此函数在qt_metacall函数动态绑定时调用
- 成员变量 QMetaObject staticQtMetaObject;
QMetaObject 类实现moc, 有以下内容
关键数据信号和槽的信息都被分别存在此staticQtMetaObject变量里 ,
相关的宏定义 - 数据结构 存放观察者和被观察者信号绑定。std::multimap
- connect函数 将观察者和被观察者绑定 利用了上一步数据结构std::multimap进行存储。
对应代码
struct Connection
{
QObject * receiver;
int methodID;
};
class QObject
{
public:
...
static void connect(Object*, const char*, Object*, const char*);
...
private:
std::multimap<int, Connection> connections;
protected:
static const QMetaObject staticQtMetaObject;
**int qt_metacall(QMetaObject::Call _c, int _id, void **_a);** //观察者会对此函数进行重写
}
QMetaObject类内容:
1、 QMetaObject 里有active(发送者的信号函数里有 QMetaObject::activate,active是被信号函数emit时调用的)
2、 信号和槽函数对应的名称 const char * sig_names;
class QObject;
struct QMetaObject
{
const char * sig_names;
const char * slts_names;
//信号、槽名称 简化处理 具体内容是 struct d 的 const QByteArrayData *stringdata; (qt_meta_stringdata_XXX.data)
static void active(QObject * sender, int idx);
};
因为sender(被观察者)需要实现2件事
1 、添加观察者和感兴趣的事件id到容器map 中
程序运行时,connect借助两个字符串,即可将信号与槽的关联建立起来,那么,它是如果做到的呢?
void QObject::connect(Object* sender, const char* sig, Object* receiver, const char* slt)
{
int sig_idx = find_string(sender->meta.sig_names, sig);//查找信号名在不在
int slt_idx = find_string(receiver->meta.slts_names, slt);//查找槽函数在不在
if (sig_idx == -1 || slt_idx == -1) {
perror("signal or slot not found!");
} else {
Connection c = {receiver, slt_idx};//将receiver sender和对应槽函数id 关联
**sender->connections.insert(std::pair<int, Connection>(sig_idx, c));**
}
}
2 、通知事件函数执行逻辑:首先遍历map容器,有没有感兴趣的id
若有,则代表一系列观察者,对这个事件感兴趣,再次遍历观察者列表,让其执行相应的槽函数。
Active实现如下:
void QMetaObject::active(Object* sender, int idx)
{
ConnectionMapIt it;
std::pair<ConnectionMapIt, ConnectionMapIt> ret;
ret = sender->connections.equal_range(idx);
for (it=ret.first; it!=ret.second; ++it) {
Connection c = (*it).second;
c.receiver->qt_metacall(-,c.methodID,-); //索引---槽函数--调用接收槽函数
}
}
接下来到观察者这里 调用槽函数
直接调用槽函数我们都知道了,就一个普通函数
可现在通过索引调用了,那么我们必须定义一个接口函数
槽的索引和槽的调用关联起来
前面active通过receiver->qt_metacall调用,所以需要用到 C++的多态,动态多态 重写 虚函数QObject::qt_metacall,
int Worker::qt_metacall(QMetaObject::Call _c, int _id, void **_a)//重写了虚函数 QObject::qt_metacall 实现了运行时调用
{
_id = QObject::qt_metacall(_c, _id, _a);
if (_id < 0)
return _id;
if (_c == QMetaObject::InvokeMetaMethod) {
if (_id < 2)
qt_static_metacall(this, _c, _id, _a);
_id -= 2;
} else if (_c == QMetaObject::RegisterMethodArgumentMetaType) {
if (_id < 2)
*reinterpret_cast<int*>(_a[0]) = -1;
_id -= 2;
}
return _id;
}
然后查找槽函数的索引找到槽函数,调用槽函数
void Worker::qt_static_metacall(QObject *_o, QMetaObject::Call _c, int _id, void **_a)
{
if (_c == QMetaObject::InvokeMetaMethod) {
auto *_t = static_cast<Worker *>(_o);
Q_UNUSED(_t)
switch (_id) {
case 0: _t->resultReady((*reinterpret_cast< const QString(*)>(_a[1]))); break;
case 1: _t->doWork((*reinterpret_cast< const QString(*)>(_a[1]))); break;// 调用具体操作的槽函数
default: ;
}
} else if (_c == QMetaObject::IndexOfMethod) {
int *result = reinterpret_cast<int *>(_a[0]);
{
using _t = void (Worker::*)(const QString & );
if (*reinterpret_cast<_t *>(_a[1]) == static_cast<_t>(&Worker::resultReady)) {
*result = 0;
return;
}
}
}
}