MyBatis-小葵花宝典
文章摘要
- 前言
-
-
- 什么是框架?
-
- 第一部分:MyBatis基础
-
- 一、MyBatis介绍
-
- 1、MyBatis简介
- 2、MyBatis开发流程:
- 二、MyBatis基本使用
- 1、MyBatis环境配配置
- 2、SqlSessionFactory、Sqlssession
- 三、MyBatis使用案例
- 四、SQL传参
-
- 1、MyBatis 获取 多表关联查询结果
- 2、ResultMap结果映射
- 五、MyBtis的数据写入
-
- selectKey 与 useGeneratedKeys 的区别
- 六、SQL注入
- 七、第一部分总结:
- 第二部分:MyBatis 进阶
-
- 一、MyBatis日志管理与动态SQL
-
- 1、MyBatis 日志管理
- 1、动态SQL
- 二、MyBatis二级缓冲
-
- 级缓存运行规则
- 三、MyBatis 对象关联查询
- 四、分页插件 PageHelper
- 五、MyBtis 配置C3P0连接池
- 六、MyBtis 批量处理
- 七、MyBtis 注解开发
- 总结
前言
此文分成两部分,第一部分是MyBatis基础。首先介绍mybatis框架。然后是MyBatis的开发流程,其中涉及到六步的开发流程等。第二部分是MyBatis进阶。日志管理、动态SQL、缓冲机制、多表级联查询、PageHelper插件、还有MyBatis的使用细节,工作流程等。
什么是框架?
生活中: 本文的目录、电脑主板、大楼的骨架、=>这些都是框架。框架提供了整体的结构,和底层的支撑。例:一栋大楼的框架建设完成后,每套房的大小、设计、装修、开发商可以设计。但不可能有大的更改,因为大楼的框架已经确定。
开发中: 框架是可被开发者定制的应用骨架。框架是一种规则,保证开发者遵循相同的方式开发程序。框架提倡“不要重复造轮子”,对基础功能进行封装。
SSM开发框架: Spring 对象容器框架(框架的框架)。SpringMVC框架 一种架构模式。MyBatis框架 简化数据库和程序的交互。总结:Spring提供了底层的对象管理,SpringMVC提供了web上的交互,MyBatis 提供了数据库的便捷操作。
框架的优点: 提高开发效率,统一的编码规则,灵活配置应用,维护性高。
第一部分:MyBatis基础
一、MyBatis介绍
1、MyBatis简介
◆MyBatis是优秀的持久层框架,持久就是将内存中的数据保存到数据库中。
◆MyBatis使用 XML 将 SQL 与程序 降低耦合度,方便程序的维护。
◆执行高效,基于JDBC对数据库进行操作。MyBatis官方地址:“ https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/ ”。
2、MyBatis开发流程:
① 引入MyBatis依赖
② 创建XML核心配置文件
③ 创建实体(Entity)类
④ 创建Mapper映射文件
⑤ 初始化SeesionFactory
⑥ 利用SqlSession对象操作数据
二、MyBatis基本使用
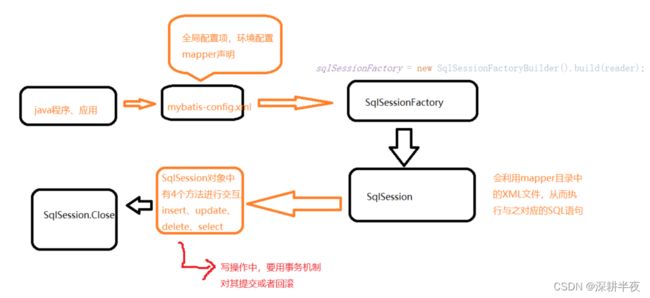
MyBatis采用XML文件,来保存环境配置信息。 其中用到
SqlSessionFactory (SQL会话工厂)是MyBatis的核心对象。 SqlSessionFactory在应用中是 唯一 的。 用于初始化MyBatis,创建SqlSession对象。
SqlSession是MyBatis操作数据库的核心对象,SqlSession使用JDBC的方式与数据库交互。 SqlSession对象还提供了,数据表的CRUD对应方法。
1、MyBatis环境配配置
环境配置 不同环境不同id名
<environment id="dev">
说明数据库的事务 通过调用JDBC的commit 或 rollback方法提交
<transactionManager type="JDBC">transactionManager>
数据源 采用连接池方式管理数据库连接(这里用的是MyBatis自带的连接池)
<dataSource type="POOLED">
属性
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true">
<property name="username" value="root">
<property name="password" value="root">
dataSource>
environment>
实际案例演示:⚓️⚓️⚓️
① pom.xml中 添加 MyBatis依赖、数据库驱动、等
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>org.examplegroupId>
<artifactId>testWeb-serletartifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8maven.compiler.target>
properties>
镜像仓库
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>aliyunid>
<name>aliyunname>
<url>https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/publicurl>
repository>
repositories>
添加依赖:MyBatis、MySQL驱动
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatisgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatisartifactId>
<version>3.5.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>5.1.47version>
dependency>
project>
② 在resources目录下,创建MyBatis的
mybatis-config.xml核心配置文件
DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/teat?......"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
dataSource>
environment>
environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/example/BlogMapper.xml"/>
mappers>
configuration>
2、SqlSessionFactory、Sqlssession
SqlSessionFactory创建案例:⚓️⚓️⚓️
public class MyBatisTestor {
@Test
public void testSqlSessionFactor() throws IOException {
* 利用Reader 加载lasspath下的 mybatis-config.xml 核心文件
// 资源 按照字符流进行读取
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
* 初始化SqlsessionFactory对象,同时解析mybatis.xml文件
// 构造者模式 初始化SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
* 创建Sqlssion对象,Sqlsession是JDBC的扩展类,用于与数据库交互
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//获取底层的 数据库连接对象|(测试用,实际开发MyBatis自动完成)
Connection coon = sqlSession.getConnection();
System.out.println(coon);
}
}
有开就有关,上面案例的 资源关闭 代码如下:
public class MyBatisTestor {
@Test
public void testSqlSessionFactor() throws IOException {
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try{
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
Connection coon = sqlSession.getConnection();
System.out.println(coon);
}catch(Exception){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(sqlSession != null){
sqlsession.close();
}
}
}
}
上面的代码很复杂,可以对其封装。 封装成 : MyBatisUtils工具类。 同时也能保证SqlSessionFactory的全局唯一性。在主包下创建utils包,在该包中创建此工具类。
public class MyBatisUtils {
//利用static 属于类不属于对象,且全局唯一
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory=null;
//利用静态块在初始化类时,实例化sqlsessionFactory
static {
Reader reader = null;
try {
reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 在类的初始化的过程中,产生的错误
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);
}
}
// 创建新的 Sqlsession 对象
public static SqlSession openSession(){
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
// 关闭或释放 Sqlsession 对象
public static void closeSession(SqlSession sqlSession){
if (sqlSession != null){
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
===========================下面代码测试用例==========================
// MyBatisUtils 的测试
@Test
public void testMyBatisUtils(){
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
Connection connection = sqlSession.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(sqlSession);
}
}
}
三、MyBatis使用案例
MyBatis数据查询使用案例:⚓️⚓️⚓️
第1️⃣步:创建实体类(Entity),存放查询结果。
在主包下创建entity包,在该包中创建此 实体类。
public class Goods {
private Integer goodsId;//商品编号
private String title;//标题
private String subTitle;//子标题
private Float originalCost;//原始价格
private Float currentPrice;//当前价格
private Float discount;//折扣率
private Integer isFreeDelivery;//是否包邮
private Integer categoryId;//分类编号
······
······
//以省略 get、set 方法
······
······
}
第2️⃣步:创建Mapper XML
目的:说明上面的实体类,和哪个数据库的表对应,表中的属性和哪个字段对应。
在resources目录下,创建 mappers包。 此包保存的都是XML文件 (MyBatis映射文件) 。
此处创建的是 goods.xml 文件
DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="goods">
mapper>
第3️⃣步:编写 < select > SQL 标签
DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="goods">
<select id="selectAll" resultType="com.XXXX.mybatis.entity.Goods">
select * from t_goods order by goods_id limt 10
select>
mapper>
完成 2、3 两步。就是完整的 Mapper XML了。 Mybatis 要认识 该Mapper XML文件,就需要在mybatis-config.xml中 对其进行声明。
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mappers/goods.xml" />
mappers>
书写以上标签后,MyBatis 启动时会自动加载,goods.xml文件
然后可以对,2、3 两步进行测试: SqlSession执行 select 语句
//测试 selectAll(设置的一个sql语句的别称(也就是设置了sql语句的id))sql语句
@Test
public void testSelectAll() throws Exception{
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
//作为SqlSession对象来说,最核心执行SQL查询语句的方法是:select();/select...();
// 因为selectAllsql语句 返回的是多条数据 这里选择:selectList();
//其中selectList();里面的参数是=》selectList("命名空间.SQL语句的id");
List<Goods> list = sqlSession.selectList("goods.selectAll");
//执行完sql语句过后,list集合就包含了查询结果。下面可以遍历看一下
for (Goods g:list){
System.out.println(g.getTitle());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw e;
}finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(sqlSession);
}
}
数据库底层的 goods_id 和实体类 goodsId 是无法对应的,所以需要开启 驼峰命名映射
}
第4️⃣步:开启驼峰命名映射
在 mybatis-config.xml中 添加< settings > 标签
<settings>
驼峰命名 转换 例:goods_id => goodsId
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
settings>
四、SQL传参
在用户界面动态输入数据,然后把用户的数据编成SQL语句,进行处理。
需要编写 Mapper 目录下的 xml 文件,改变 select标签。
<select id="selectById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="com.XXXX.mybatis.Goods">
下面这个就代表从外侧 传进来的Integer数据
select * from t_goods order by goods_id = #{value}
select>
下面是 代码对比:
之前的 数据查询 SQL:
<select id="selectAll" resultType="com.xxxx.mybatis.entity.Goods">
select * from t_goods order by goods_id desc limit 10
select>
SQL传参的 代码:
<select id="selectByid" parameterType="Integer" resultType="com.xxxx.mybatis.entity.Goods">
select * from t_goods where goods_id = #{value}
select>
测试使用案例:⚓️⚓️⚓️
动态查询 一条数据
public void testSlectById(){
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
根据编写的 select标签 只返回一条数据,所以选择selectOne(命名空间.SQL语句的id ,外侧传入的参数)方法
Goods goods = sqlSession.selectOne("goods.selectByid", 1888);
System.out.println(goods.getTitle());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
测试使用案例二: 动态传入多条数据 ⚓️⚓️⚓️
因为在Mybatis中 goods.xml文件里的select标签 ,只支持一个parameterType=" xxxx ",所以要传递多参,还是需要 改变 select标签。=> parameterType="java.util.Map"
goods.xml 文件中的 select标签
<select id="selectBypriceRange" parameterType="java.util.Map" resultType="com.xxxx.mybatis.entity.Goods">
select * from t_goods where current_price between #{min} and #{max} order by current_price limit 0,#{limt}
</select>
=======================改完上面的标签后,下面是测试代码===========================
public void testSelectByPriceRange(){
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
// 因为 goods.xml中的 select标签 内部设置Map 所以下面创建Map
Map param = new HashMap();
param.put("min",100);
param.put("max",500);
param.put("limt",10);
List<Goods> goods = sqlSession.selectList("goods.selectBypriceRange", param);
for (Goods g : goods){
System.out.println(g.getTitle());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
1、MyBatis 获取 多表关联查询结果
如果 获取 多表关联查询结果,使用一个表的实体类存放结果,肯定是不行的。把select标签中的,resultType属性改一下 ,不让它在返回到某一个实体类里,返回到Map集合里面去。
想让返回的字段有序 也可以使用LinkedHashMap
<select id="selectGoodsMap" resultType="java.util.Map">
select g.* ,c.category_name from t_goods g ,t_category c where g.category_id = c.category_id
</select>
=======================配置完上面的select标签后,下面是测试======================
public void selectGoodsMap(){
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
List<Map> list = sqlSession.selectList("goods.selectGoodsMap");
for (Map map :list){
System.out.println(map);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
从上面可以看出,利用LinkedHashMap保存多表关联结果.MyBatis会将每一条记录包装成为LinkedHashMap对象。Kye 是字段名、value 是字段值,字段类型根据表结构进行自动判断。使用这种方式的好处:易于扩展,易于使用。缺点:无法在编译时检查,太过灵活。
因为开发中使用Map使用体验并不是很好,但不使用Map,又如何用对象的方式保存关联查询的结果呢?可以使用 => ResultMap结果映射。
2、ResultMap结果映射
ResultMap可以将查询结果映射为复杂类型的java对象。适用于java对象保存多表关联结果。
在entity包同级目录下,创建dto包。是一个特殊的java bin包。该包 作为数据传输对象,都是对原始的对象进行扩展。用于数据保存和传递。
实际使用案例: ⚓️⚓️⚓️
dto包下的DTO类
//对于原始实体类Goods 进行扩展
public class GoodsDTO {
private Goods goods = new Goods();
private String categoryName;
private String test;
······
······
//以省略 get、set 方法
······
······
}
goods.xml 里的resultMap 标签
添加resultMap 的标签 type是 设置转换成哪一个DTO
<resultMap id="rmGoods" type="com.xxxx.mybatis.dto.GoodsDTO">
里面的属性: id代表主键 property是dao类里的属性名的意思 column是字段名
<id property="goods.goodsId" column="goods_id"></id>
设置完上面的主键,还有其他属性 除了主键以外,其他的字段还有哪些?
<result property="goods.title" column="title"></result>
<result property="goods.originalCost" column="original_cost"></result>
······
<result property="categoryName" column="category_name"></result>
</resultMap>
这里的映射要和上面的id相同
<select id="selectGoodsDTO" resultMap="rmGoods">
select g.* ,c.category_name from t_goods g ,t_category c where g.category_id = c.category_id
</select>
====================================测试用例=====================================
public void testSelectGoodsDTO(){
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
// 泛型里的要和 resultMap标签中 type里设置的类要一致
List<GoodsDTO> list = sqlSession.selectList("goods.selectGoodsDTO");
for (GoodsDTO g :list){
System.out.println(g.getGoods().getTitle());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
五、MyBtis的数据写入
插入功能 添加< insert>标签
指向要传入的原始数据
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.xxxx.mybtis.entity.Goods">
INSERT INTO `shujuku`.`t_goods`(`title`,`sub_title`,`xxxx`,`zzz`)
VALUES(#{title},#{subTitle},#{originalCost},#{xxxx})
让原始的Goods对象得到新插入数据的编号
SQL的返回值类型是什么 dao类里的属性名 执行顺序 说明先执行上面的
<selectKey resultType="int" KeyProperty="goodsld" order="AFTER">
当前连接中最后产生的id号
select last_insert_id()
selectKey>
insert>
插入使用案例: ⚓️⚓️⚓️
<insert> 标签
<!-- parameterType是用来指定参数类型,插入数据的时候往往插入封装的对象 insert标签没有返回对象的-->
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.xxxx.mybatis.entity.Goods">
INSERT INTO t_goods(title,sub_title,original_cost,current_price,discount,is_free_delivery,category_id)
VALUE (#{title},#{subTitle},#{originalCost},#{currentPrice},#{discount},#{isFreeDelivery},#{categoryId})
<!-- 上面完成插入,不知道插入到哪里了,下面操作看一下-->
<!-- 如何插入成功以后获取到自动生成的主键-->
<selectKey resultType="Integer" keyProperty="goodsId" order="AFTER">
-- 当执行完上面的SQL语句,会自动的执行下面语句。将下面得到的值回填到goodsId中
select last_insert_id()
</selectKey>
</insert>
=====================================测试案例======================================
public void testInsert(){
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
Goods goods = new Goods();
goods.setTitle("测试商品2");goods.setSubTitle("测试商品子标题");goods.setOriginalCost(200f);goods.setCurrentPrice(100f);goods.setDiscount(0.5f);goods.setIsFreeDelivery(1);goods.setCategoryId(43);
// insert(SQL语句的id,要保存的数据) 返回 本次成功插入的总数
int num = sqlSession.insert("goods.insert", goods);
sqlSession.commit();
System.out.println(goods.getGoodsId()+" "+num);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("出现错误");
if (sqlSession != null){
sqlSession.rollback();
}
}
}
}
selectKey 与 useGeneratedKeys 的区别
selecKey用于在数据插入以后,把最新的主键值进行返回。useGeneratedKeys 也是用于获取最新的主键。
selectKey标签用法
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.xxxx.mybtis.entity.Goods">
INSERT INTO SQL语句
说明主键的类型 说明主键对应哪个属性 下面语句执行的顺序
<selectKey resultType="int" KeyProperty="goodsld" order="AFTER">
下面获取的主键值,回填到com.xxxx.mybtis.entity.Goods对象的goodsId中
select last_insert_id()
selectKey>
insert>
useGeneratedKeys标签用法
<insert id="insert"
parameterType="com.xxxx.mybtis.entity.Goods">
useGeneratedKeys="true" 开启自动生成的主键
keyProperty="goodsId" 代表主键的属性(哪个属性代表了主键)
keyColumn="goods_id" 对应底层字段的名字(表中主键的字段名)
INSERT INTO SQL语句
insert>
selectKey标签需要明确写上select last_insert_id()语句。useGeneratedKeys根据数据库驱动自动生成,不需要写前面的SQL语句。selectKey通用方案,但编写麻烦。useGeneratedKeys只支持“自增主键”类型的数据库。
更新 添加< update>标签
指明插入包含更新数据的实体对象
<update id="update" paramenterType="com.xxxx.mybaits.entity.Goods">
UPDATE SQL语句
update>
更新使用案例: ⚓️⚓️⚓️
<update id="update" parameterType="com.xxxx.mybatis.entity.Goods">
UPDATE t_goods SET title = #{title} where goods_id = #{goodsId}
</update>
===================================测试代码===================================
public void testUpdate(){
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
因为更改,所以先使用之前设置的查询,先查询商品Id 获取商品,后更改
Goods goods = sqlSession.selectOne("goods.selectByid", 739);
goods.setTitle("测试商品aaaa");
int num = sqlSession.update("goods.update", goods);
System.out.println(num);
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
}
}
删除 添加< delete>标签
说明插入数据的 基本的数据类型
<delete id="delete" paramenterType="Inetger">
delete SQL语句
delete>
删除使用案例: ⚓️⚓️⚓️
<!-- 大多数删除 根据传入的主键 来删除数据 这是声明主键的类型-->
<delete id="delete" parameterType="Integer">
DELETE from t_goods where goods_id = #{value}
</delete>
</mapper>
===================================测试代码===================================
public void testDelete(){
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
int num = sqlSession.delete("goods.delete", 739);
System.out.println(num);
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
}
}
六、SQL注入
其实在上面XML文件的标签中,已经使用到了 #{xxxx} 该方式已经预编译了传入的SQL语句。 ${xxxx} 该方式是 原文传值 的意思 => 会产生SQL攻击。
七、第一部分总结:
第二部分:MyBatis 进阶
一、MyBatis日志管理与动态SQL
1、MyBatis 日志管理
日志:系统运行的历史记录。 也就是记录系统操作事件的记录文件或者文件集合。是诊断问题以及理解系统活动的重要依据。
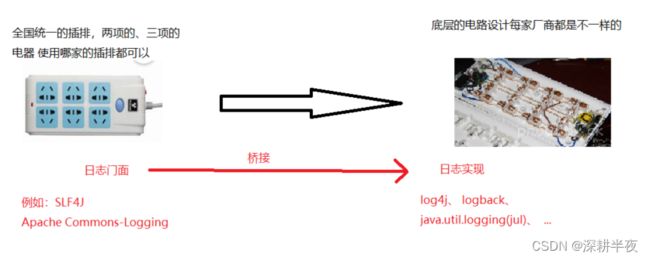
如何让MyBatis 和 logback 协同输出日志?
pom.xml 中添加依赖。然后运行程序就会有日志输出了。
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logbackgroupId>
<artifactId>logback-classicartifactId>
<version>1.2.3version>
dependency>
上面运行程序以后,出来一大堆,可以自定义日志输出的内容吗?logback 是支持 日志输出的内容自定义化的。 在resources目录下 创建 logback.xml 配置文件 ,该文件名 是强制要求的。
官网中有使用帮助文档的,可以复制。
<configuration>
appender输出器:指明在什么地方进行输出日志
<appender name="console" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
日志输出的格式
<pattern>%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%npattern>
encoder>
appender>
日志输出级别:
error:错误 - 系统的故障日志
warn:警告 — 存在风险或使用不当的日志
info:一般性消息
debug:程序内部调试信息
trace:程序运行的跟踪信息
通过设置的level 可以确定当前输出的日志最低级别。开发环境适合debug。生产环境适合info
<root level="debug">
<appender-ref ref="console" />
root>
configuration>
1、动态SQL
应用场景举例:
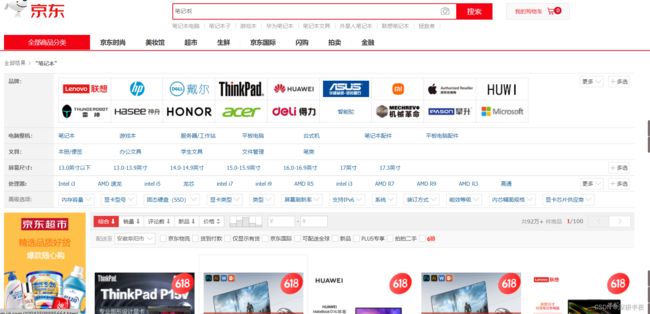
上面京东页面中,搜索框搜索:“笔记本”。出现一堆笔记本。下面会出现一些品牌、使用场景、处理器等等的筛选条件。当点击 某些筛选条件后,它会自动的把筛选条件增加上。然后显示相应的产品。对于在指定的“笔记本”搜索页面,动态组织条件的SQL语句,称为:动态SQL。
例:
<select id="selectSQL" parameterType="java.util.Map" resultType="com...mybatis.entity.Goods">
select * from t_goods
<where>
如果Map中包含了categoryId属性的话,就增加if tset标签里面的SQL语句
<if test="categoryId != null">
and category_id = #{categoryId}
if>
where>
select>
使用案例: ⚓️⚓️⚓️
<select id="dongTaiSQL" parameterType="java.util.Map" resultType="com.imooc.mybatis.entity.Goods">
select * from t_goods
where
1=1
<if test="categoryId != null">
and category_id = #{categoryId}
</if>
<if test="currentPrice != null">
and current_price < #{currentPrice}
</if>
</select>
从控制太可以看到SQL语句为:
select * from t_goods where and category_id = ? and current_price < ?
很显然,where 和 and 之间是空白的 所以填个1=1 使SQL语法 保持正确
如果有强迫症可以去掉1=1,把where 改成 <where>标签 也能解决此问题
================================测试代码=======================================
public void testDongTaiSql(){
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
Map m = new HashMap();
m.put("categoryId",44);
m.put("currentPrice",500);
如果只填写selectList("goods.dongTaiSQL"),则会出现所有商品。这是动态SQL特性
或者 注释 掉一个Map中的属性 结果一样会发生变化
List<Goods> goods = sqlSession.selectList("goods.dongTaiSQL",m);
for (Goods g : goods){
System.out.println(g.getTitle()+"|"+g.getCategoryId()+"|"+g.getCurrentPrice());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
}finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(sqlSession);
}
}
二、MyBatis二级缓冲
如果使用SQL语句查询一件商品,从数据库获取到了。如果第二次在查询该商品,又要从数据库获取。众所周知,数据库是在硬盘上的。硬盘提取数据并不快。因为第一次和第二次返回的记录是相同的。解决方法就出来了。可以第一次查询的结果放在内存中,第二次再有相同查询直接在内存中获取。存到内存的方式就是 缓存最基础最底层的实现。
MyBatis中 有两级缓存: 第一级:默认开启的,缓存范围在SqlSession会话。第二级:需要手动开启,属于范围Mapper Namespace。
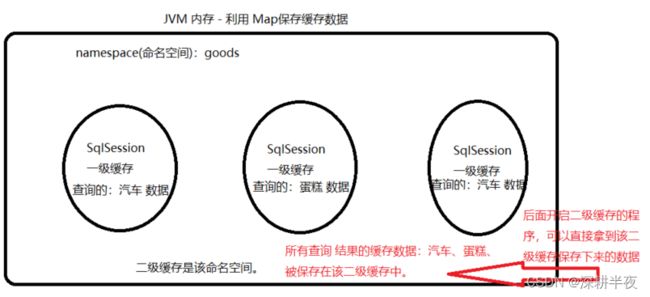
根据上面的表述,肯定涉及二级缓存的开启、
级缓存运行规则
二级缓存开启后,默认所有查询操作均 使用 缓存 。
写操作commit提交时,该namespace(命名空间)所有的缓存强制清空。保证数据的一致性。
可以设置某个select 标签 不适用缓存:设置useCache=false。
设置flushCache=true代表执行完某条select标签后,强制清空该namespace所有缓存。
cache(缓存)
注:缓存命中率 例:开启二级缓存后,第一次查询某个商品,数据库获取。第二次相同查询,直接二级缓存中获取。在两次操作中只是用到了一次改缓存。用到该缓存的次数/查询次数=> 1/2=0.5。
开启二级缓存:
在goods.xml文件中。根 标签内 添加< cache >标签
<cache eviction="LRU" flushInterval="6000000" size="512" readOnly="true"/>
cache属性详细说明:
eviction:缓存的清除策略,当缓存对象达到上限后,会触发对应算法对缓存对象清楚。
1. LRU - 移除最长时间不被使用的对象
2. FIFO - 先进先出:按照对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们
3. SOFT - 软引用:
4. WEAK - 弱引用
flushInterval 属性详细说明:
代表间隔多长时间自动清除缓存,单位是毫秒
size 属性详细说明:
缓存存储上限,用于保存对象或集合(1个集合算1个对象)的数量上限
readOnly属性详细说明:
true:代表返回只读缓存,每次从缓存取出的是缓存对象本身。执行效率高
false:代表每次取出的是缓存对象的“副本”,每一次取出的对象都是不同的,这种方式安全性高。
三、MyBatis 对象关联查询
之前的多表关联查询指:两个表通过主外键,在一条SQL中进行查询。
现在的多表级联(对象关联)查询:通过一个对象,来获取与它关联的另外一个对象。执行的SQL语句是分为多条的。
开发中往往要理清楚数据之间的关系。有助于数据表的设计,也影响未来程序的实现。
例:
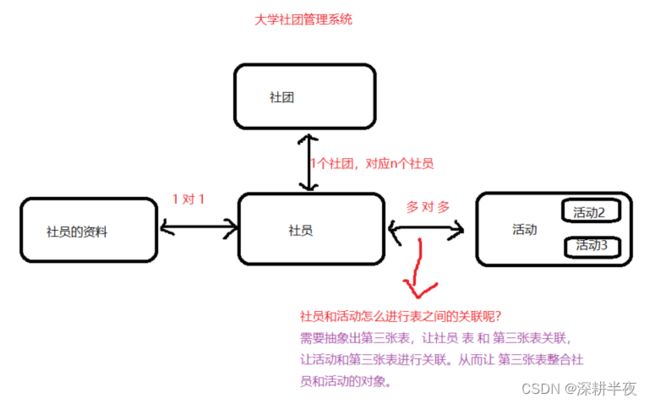
再例:

上面 商品 案例: ⚓️⚓️⚓️
1、在entity目录下,创建商品详情的实体类
public class GoodsDetail {
private Integer gdId;
private Integer goodsId;
private String gdPicUrl;
private Integer gdOrder;
······
······
//以省略 get、set 方法
······
······
}
2、在mappers目录下,创建商品详情实体类的XML文件 用于SQL查询。
DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="goodsDetail">
<select id="selectBYGoodsId" parameterType="Integer" resultType="com.xxxx.mybatis.entity.GoodsDetail">
select * from t_goods_detail where goods_id =#{value}
select>
mapper>
出现新的xml文件,就要在mybatis-config.xml文件中进行注册。
添加如下:
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mappers/goods.xml" />
<mapper resource="mappers/goods_detail.xml"/>
mappers>
3、在对象关联时,分析 商品 和 商品详情 之间的关系,两者之间应该是 1 对 多 的关系。如果用对象表达,那么 1 的一方 如何 持有多的一方呢?改造下原来的 Goods 这个实体类。
public class Goods {
private Integer goodsId;//商品编号
private String title;//标题
private String subTitle;//子标题
private Float originalCost;//原始价格
private Float currentPrice;//当前价格
private Float discount;//折扣率
private Integer isFreeDelivery;//是否包邮
private Integer categoryId;//分类编号
下面添加一个变量,用来存放GoodsDetail 对象。这样一个Doods下可以有多个GoodsDetail对象
private List<GoodsDetail> goodsDetail;
······
······
//以省略 get、set 方法
······
······
}
4、编写goods.xml文件
<resultMap id="rmGoods1" type="com.imooc.mybatis.entity.Goods">
<id column="goods_id" property="goodsId">id>
<collection property="goodsDetails" select="goodsDetail.selectBYGoodsId" column="goods_id">collection>
resultMap>
<select id="selectOneToMany" resultMap="rmGoods1">
select * from t_goods limit 0,1
select>
5、测试代码:
public void testOneToMany(){
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
List<Goods> goods = sqlSession.selectList("goods.selectOneToMany");
for (Goods g : goods){
System.out.println(g.getTitle()+"|"+g.getGoodsDetails().size());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
}finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(sqlSession);
}
}
上面案例反转,多的一方获取 1 的一方: ⚓️⚓️⚓️
1、在多的一方 添加 1 的 对象
public class GoodsDetail {
private Integer gdId;
private Integer goodsId;
private String gdPicUrl;
private Integer gdOrder;
添加Goods 对象,但MyBatis并不知道该数据是从哪来的,所以需要goods_detail.xml 进行配置
private Goods goods;
······
······
//以省略 get、set 方法
······
······
}
2、在goods_detail.xml文件中 添加SQL
<select id="selectAll" resultType="com.xxxx.mybatis.entity.Goods">
select * from t_goods order by goods_id desc limit 0,1
select>
<resultMap id="rmGoodsDetail" type="com.xxxx.mybatis.entity.GoodsDetail">
<id column="gd_id" property="gdId"/>
<association property="goods" select="goodsDetail.selectAll" column="goods_id">association>
resultMap>
<select id="selectManyToOne" resultMap="rmGoodsDetail">
select * from t_goods_detail limit 0,1
select>
3、测试代码
public void tsetManyToOne(){
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
List<GoodsDetail> goods = sqlSession.selectList("goodsDetail.selectManyToOne");
for (GoodsDetail g : goods){
System.out.println(g.getGdPicUrl()+"|"+g.getGoods().getTitle());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
}finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(sqlSession);
}
}
四、分页插件 PageHelper
能自动完成分页查询的工作。因为表的分页操作起来很麻,所以该插件就孕育而生了。该插件在哪呢?浏览器直接:pageHelper就可以进入官方网站。
使用流程如下: 完成姿势 官方 有 帮助文档
1、maven 引入 pageHelper与jsplparser依赖
pom.xml文件中
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelpergroupId>
<artifactId>pagehelperartifactId>
<version>5.1.10version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.jsqlparsergroupId>
<artifactId>jsqlparserartifactId>
<version>2.0version>
dependency>
2、mybatis-config.xml增加Plugin(插件)配置
要写在 settings 标签的下面
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor">
<property name="helperDialect" value="mysql"/>
<property name="reasonable" value="ture"/>
plugin>
plugins>
3、代码中使用pageHelper.startPage() 自动分页
使用前,要写SQL语句吧!!!goods.xml 最普通的SQL 查询语句了
<select id="selectPage" resultType="com.imooc.mybatis.entity.Goods">
select * from t_goods where current_price < 1000
</select>
===============================测试代码========================================
public void tsetSelectPage(){
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
// startPage(要查询第几页的数据,设置每页多少行) 该方法会自动将下一次查询进行分页
PageHelper.startPage(2,10);
// 这里返回的不再是List集合,而是Page对象
Page<Goods> goods = (Page)sqlSession.selectList("goods.selectPage");
System.out.println("总页数:"+goods.getPages());
System.out.println("总记录数:"+goods.getTotal());
System.out.println("开始行号:"+goods.getStartRow());
System.out.println("结束行号:"+goods.getEndRow());
System.out.println("当前页码:"+goods.getPageNum());
// 当前页的数据包含在了Result属性中 使用Result 可以获取当前页面的属性
List<Goods> result = goods.getResult();
for (Goods g : result){
System.out.println(g.getTitle());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(sqlSession);
}
}
五、MyBtis 配置C3P0连接池
使用流程: ⚓️⚓️⚓️
1、pom.xml中,加入C3P0依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mchangegroupId>
<artifactId>c3p0artifactId>
<version>0.9.5.4version>
dependency>
如果让MyBatis对其连接池支持,还需额外的扩展一个类
2、和entity 同级目录下创建 datasource包,用于保存数据源。
// C3P0与MyBatis兼容使用的数据源工厂类
//C3P0的数据源工厂,通过继承UnpooledDataSourceFactory 可以完成C3P0的嵌入工作
public class C3P0DataSourceFactory extends UnpooledDataSourceFactory {
public C3P0DataSourceFactory(){
// 让该类初始化的时候 让数据源由 C3P0 进行创建
this.dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
}
}
3、更改mybatis-config.xml文件
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/...">
<property name="username" value="root">
<property name="password" value="root">
dataSource>
更改成下面的
<dataSource type="com.xxxx.mybatis.datasource.C3P0DataSourceFactory">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/..."/>
<property name="user" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="yhl05711"/>
<property name="initialPoolSize" value="5"/>
<property name="minPoolSize" value="5"/>
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="20"/>
dataSource>
六、MyBtis 批量处理
利用集合保存批量处理的数据,再利用批量处理SQL一次性完成。
使用案例: ⚓️⚓️⚓️
goods.xml 文件中 别写SQL语句
INSERT INTO TABLE VALUE ("A","A2","A3"),("A","A2","A3"),("A","A2","A3")...
关系型数据库都可以这样插入多条数据
<insert id="batchInsert" parameterType="java.util.List">
INSERT INTO
遍历读取List 集合 collection:迭代的数据源从哪来t_goods(title,sub_title,original_cost,current_price,discount,is_free_delivery,category_id)
VALUE
<foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" separator=",">
(#{item.title},#{item.subTitle},#{item.originalCost},#{item.currentPrice},#{item.discount},#{item.isFreeDelivery},#{item.categoryId})
</foreach>
</insert>
===============================测试代码========================================
public void testBatchInsert(){
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
List list = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++){
Goods goods = new Goods();
goods.setTitle("测试测试");
goods.setSubTitle("Test子标题");
goods.setOriginalCost(200f);
goods.setCurrentPrice(1000f);
goods.setDiscount(0.5f);
goods.setIsFreeDelivery(1);
goods.setCategoryId(43);
list.add(goods);
}
//之前的话应该是 创建一个对象 调用一次Insert 语句。
//这里 是 所有对象都创建好,放入一个集合中,执行一次Insert语句,传入集合
sqlSession.insert("goods.batchInsert",list);
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
}finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(sqlSession);
}
}
七、MyBtis 注解开发
注解可以替代掉,原有的XML标签。
| 注解 | 对应XML标签 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| @Insert | < insert> | 新增SQL |
| @Upadte | < update> | 更新SQL |
| @Delete | < delete> | 删除SQL |
| @Select | < select> | 查询SQL |
| @Param | - - | 参数映射 |
| @Results | < resultMap> | 结果映射 |
| @Result | < id>< result> | 字段映射 |
总结
码字不易,如果对您有所帮助不妨点个赞赞吧~
我爱你 ~ 希望有一天,你能把这三个字还给我。
愿: 宇宙的尽头没有 Mybatis。