Yolov5-6.0官方源代码骨干解析,并使用TensorRT加速推理,最后封装成API
这里写目录标题
-
- YOLOV5模型源码的详细解析,先从模型结构开始,再到数据的预处理阶段,然后模型推理阶段Detect,最后使用TensorRT部署加速,基于Flask封装成api方便调用。
- 主要模型代码
- 数据预处理
- 模型推理阶段(Detect)
- TensorRT加速
- Flask API 封装
YOLOV5模型源码的详细解析,先从模型结构开始,再到数据的预处理阶段,然后模型推理阶段Detect,最后使用TensorRT部署加速,基于Flask封装成api方便调用。
主要模型代码
YOlOv5最新的官方代码是7.0版本,增添了很多内容。这里模型代码到推理代码的源代码解析使用的是6.0版本,tensorrt转换代码使用的是7.0版本。
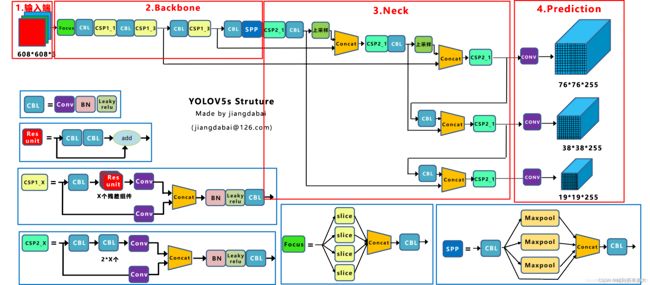
Yolov5模型的组成总体是图中的四块,每一块则使用不同的小组件搭建而成。这里以yolov5s.yaml举例:
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, C3, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 6, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, C3, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 3, C3, [1024]],
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]], # 9
]
# YOLOv5 v6.0 head
head:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 13
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
yolov5s.yaml的每一行内容代表:[连接哪一层或几层的输出,组件重复次数,组件名称,组件参数:(输出通道数数量,卷积核大小,填充大小,步长大小)] ,最后的注释代表的是:这层的位置-名称/压缩大小。
初始化组件的函数在yolo.py的 parse_model中:
def parse_model(d, ch): # model_dict, input_channels(3)
# 加载yolos.yaml的基础信息
LOGGER.info('\n%3s%18s%3s%10s %-40s%-30s' % ('', 'from', 'n', 'params', 'module', 'arguments'))
anchors, nc, gd, gw = d['anchors'], d['nc'], d['depth_multiple'], d['width_multiple']
na = (len(anchors[0]) // 2) if isinstance(anchors, list) else anchors # anchors对的数量
no = na * (nc + 5) # number of outputs = anchors * (classes + 4 + 1)
"""
layers:会按照顺序存放每一个层的结构,最后用于Sequential
save:存放不为-1的层
ch: 存放当前层的通道数
"""
'''通过配置文件初始化模型结构的逻辑是这样的:
comments中已经实现了每一个组件,从结构方面对于每一层,我们关心的是输入是什么,输出是什么,其中args自始至终都是每一层的输入/输出参数。
在每一层的里面,关心的是有什么组件,组件的数量和组件的连接顺序。其中m充当着组件类型,n充当着组件数量,最简单的顺序就是依次排列。
但对于跨越连接该如何处理呢,我们就需要通过索引获取上一层的输出,但是跨越链接两边相隔很远,且无法作为一层来操作,就用save把层数索引单独保存下来,放到后面处理。
'''
layers, save, c2 = [], [], ch[-1] # layers, savelist, ch out
for i, (f, n, m, args) in enumerate(d['backbone'] + d['head']): # from, number, module, args
m = eval(m) if isinstance(m, str) else m # eval strings
for j, a in enumerate(args):
try:
args[j] = eval(a) if isinstance(a, str) else a # eval strings
except NameError:
pass
'''控制深度,也就是控制重复次数,比如[-1, 9, C3, [512]], round(9*0.33) = 3'''
n = n_ = max(round(n * gd), 1) if n > 1 else n # depth gain
'''所有的组件匹配,实现代码在comments'''
if m in [Conv, GhostConv, Bottleneck, GhostBottleneck, SPP, SPPF, DWConv, MixConv2d, Focus, CrossConv,
BottleneckCSP, C3, C3TR, C3SPP, C3Ghost]:
# c1输入通道,c2输出通道
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != no: # if not output
'''控制宽度,控制当前层的输出通道数'''
c2 = make_divisible(c2 * gw, 8)
# args删掉了位置信息,增加了必要的输入输出
args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]
if m in [BottleneckCSP, C3, C3TR, C3Ghost]:
args.insert(2, n) # number of repeats
n = 1
elif m is nn.BatchNorm2d: #
args = [ch[f]]
elif m is Concat: # args的第一位是一个列表
c2 = sum([ch[x] for x in f])
elif m is Detect:# args的第一位是一个列表
args.append([ch[x] for x in f])
if isinstance(args[1], int): # number of anchors
args[1] = [list(range(args[1] * 2))] * len(f)
elif m is Contract:
c2 = ch[f] * args[0] ** 2
elif m is Expand:
c2 = ch[f] // args[0] ** 2
else:
c2 = ch[f]
# if n > 1 重复组件的次数
m_ = nn.Sequential(*[m(*args) for _ in range(n)]) if n > 1 else m(*args) # module
t = str(m)[8:-2].replace('__main__.', '') # module type
np = sum([x.numel() for x in m_.parameters()]) # number params
m_.i, m_.f, m_.type, m_.np = i, f, t, np # attach index, 'from' index, type, number params
LOGGER.info('%3s%18s%3s%10.0f %-40s%-30s' % (i, f, n_, np, t, args)) # print
save.extend(x % i for x in ([f] if isinstance(f, int) else f) if x != -1) # append to savelist
layers.append(m_)
if i == 0:
ch = []
ch.append(c2) # ch保存着每一层的输出通道数
return nn.Sequential(*layers), sorted(save)
模型的前向推理在yolo.py的Model.forward,其主要调用的是_forward_once:
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cfg='yolov5s.yaml', ch=3, nc=None, anchors=None): # model, input channels, number of classes
super().__init__()
'''就是加载yaml文件'''
if isinstance(cfg, dict):
self.yaml = cfg # model dict
else: # is *.yaml
import yaml # for torch hub
self.yaml_file = Path(cfg).name
with open(cfg, errors='ignore') as f:
self.yaml = yaml.safe_load(f) # model dict
# Define model
''''''
ch = self.yaml['ch'] = self.yaml.get('ch', ch) # input channels
if nc and nc != self.yaml['nc']:
LOGGER.info(f"Overriding model.yaml nc={self.yaml['nc']} with nc={nc}")
self.yaml['nc'] = nc # override yaml value
'''是否为自定义anchors'''
if anchors:
LOGGER.info(f'Overriding model.yaml anchors with anchors={anchors}')
self.yaml['anchors'] = round(anchors) # override yaml value
# self.model初始化的层,self.save保存着不为-1的连接层
self.model, self.save = parse_model(deepcopy(self.yaml), ch=[ch]) # model(Sequential), savelist(List)
self.names = [str(i) for i in range(self.yaml['nc'])] # default names,数字标签
self.inplace = self.yaml.get('inplace', True)
# Build strides, anchors
'''m对应这个 [[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)'''
m = self.model[-1] # Detect()
if isinstance(m, Detect):
s = 256 # 2x min stride
# 是否推理加速
m.inplace = self.inplace
# 计算下采样倍数,[8,16,32]
m.stride = torch.tensor([s / x.shape[-2] for x in self.forward(torch.zeros(1, ch, s, s))]) # forward
# 计算每个features map相对应的anchors大小,除以相对下采样倍数即可
m.anchors /= m.stride.view(-1, 1, 1)
check_anchor_order(m)
self.stride = m.stride
self._initialize_biases() # only run once
# Init weights, biases
initialize_weights(self)
self.info()
LOGGER.info('')
def forward(self, x, augment=False, profile=False, visualize=False):
# 推理的时候是否也需要数据增强
if augment:
return self._forward_augment(x) # augmented inference, None,推理时用不用数据增强
return self._forward_once(x, profile, visualize) # single-scale inference, train
def _forward_once(self, x, profile=False, visualize=False):
'''
m.f(m.from) != -1 有两种可能,一个正数或者一个列表,一个列表代表着需要前几层的输出。
self.save 保存着不为-1的所有下标,数量较少,用y保存相应层的实际输出。
'''
y, dt = [], [] # outputs
for m in self.model:
if m.f != -1: # if not from previous layer
x = y[m.f] if isinstance(m.f, int) else [x if j == -1 else y[j] for j in m.f] # from earlier layers
# 打印信息
if profile:
self._profile_one_layer(m, x, dt)
'''前面已经通过parse_model初始化完成了,这里直接forward'''
x = m(x) # run
y.append(x if m.i in self.save else None) # save output
# 可视化
if visualize:
feature_visualization(x, m.type, m.i, save_dir=visualize)
return x
'''
输出x为list:bartch_size=8,anchors=3*3=9,feature map大小不一,xywhc+80个类别
torch.Size([8, 3, 80, 80, 85])
torch.Size([8, 3, 40, 40, 85])
torch.Size([8, 3, 20, 20, 85])
'''
输出的结果是归一化的结果,怎样将得到的目标框转为原来相对应的尺寸?
https://blog.csdn.net/ogebgvictor/article/details/127481011 更加详细。
我们知道,COCO数据集有80个分类,每个anchor的对应的输出时xywhc+80,其中xy对应的是自身所处格子中心左上角的偏移。wh预测的也不时直接预测出的宽高,而是相对于目前的anchor值,预测值wh会乘上anchor值得到对应的宽高。
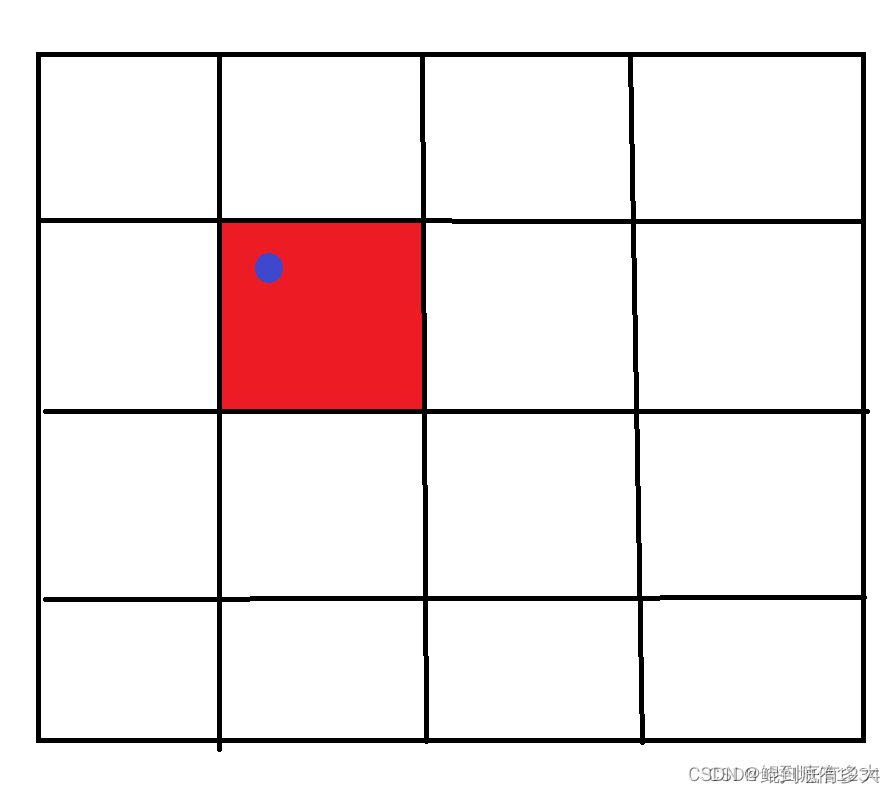
最后一层Detect是yolo.py中的Detect类:
class Detect(nn.Module):
stride = None # strides computed during build
onnx_dynamic = False # ONNX export parameter
def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), ch=(), inplace=True): # detection layer
super().__init__()
self.nc = nc # number of classes 80
self.no = nc + 5 # number of outputs per anchor 85
self.nl = len(anchors) # number of detection layers 3
self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2 # number of anchors 每一层的anchors对是3对
self.grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init grid 初始化格子的坐标
self.anchor_grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init anchor grid
self.register_buffer('anchors', torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2)) # shape(nl,na,2) (3,3,2)
self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
self.inplace = inplace # use in-place ops (e.g. slice assignment)
def forward(self, x):
z = [] # inference output
for i in range(self.nl): # 遍历每一层的输出
x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # conv
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85)
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
if not self.training: # inference
if self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4] or self.onnx_dynamic:
self.grid[i], self.anchor_grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny, i) # 初始化grid与anchor_grid
# 公式计算
y = x[i].sigmoid()
if self.inplace:
'''xy
y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 = 偏移量
self.grid[i] = 每个格子的中心坐标
self.stride[i] = 下采样率
'''
y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
''''wh
(y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] = 直接乘上相对应的anchor值,anchor值在在初始化是已经乘上了下采样倍数
'''
y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
else: # for YOLOv5 on AWS Inferentia https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2953
xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
y = torch.cat((xy, wh, y[..., 4:]), -1)
z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no))
return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1), x)
def _make_grid(self, nx=20, ny=20, i=0):
# 初始化每个小方格的坐标与对应的anchor值
d = self.anchors[i].device
yv, xv = torch.meshgrid([torch.arange(ny).to(d), torch.arange(nx).to(d)])
grid = torch.stack((xv, yv), 2).expand((1, self.na, ny, nx, 2)).float()
anchor_grid = (self.anchors[i].clone() * self.stride[i]) \
.view((1, self.na, 1, 1, 2)).expand((1, self.na, ny, nx, 2)).float()
return grid, anchor_grid
数据预处理
数据预处理流程从utils中的dataset.py 进入,部分数据增强的方法写在utils中的augmentations.py中。数据增强使用在dataset.py的LoadImagesAndLabels类的__getitem__中:
def __getitem__(self, index):
# 数据增强手段
index = self.indices[index] # linear, shuffled, or image_weights
hyp = self.hyp
# mosaic数据增强方式,load_mosaic将随机选取4张图片组合成一张图片
mosaic = self.mosaic and random.random() < hyp['mosaic']
if mosaic:
# Load mosaic
img, labels = load_mosaic(self, index)
shapes = None
# MixUp augmentation
if random.random() < hyp['mixup']:
img, labels = mixup(img, labels, *load_mosaic(self, random.randint(0, self.n - 1)))
else:
# Load image
img, (h0, w0), (h, w) = load_image(self, index)
# Letterbox
shape = self.batch_shapes[self.batch[index]] if self.rect else self.img_size # final letterboxed shape
# 自适应缩放过程
img, ratio, pad = letterbox(img, shape, auto=False, scaleup=self.augment)
shapes = (h0, w0), ((h / h0, w / w0), pad) # for COCO mAP rescaling
labels = self.labels[index].copy()
if labels.size: # normalized xywh to pixel xyxy format
labels[:, 1:] = xywhn2xyxy(labels[:, 1:], ratio[0] * w, ratio[1] * h, padw=pad[0], padh=pad[1])
if self.augment:
# 其他增强方法
img, labels = random_perspective(img, labels,
degrees=hyp['degrees'],
translate=hyp['translate'],
scale=hyp['scale'],
shear=hyp['shear'],
perspective=hyp['perspective'])
# 省略部分代码
# Convert
img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1] # HWC to CHW, BGR to RGB
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
# 注意输出结果:图片,标签,图片对应路径,图片大小
return torch.from_numpy(img), labels_out, self.img_files[index], shapes
mosaic 数据增强
# mosaic 数据增强
'''
将四张图片随机拼接成一整图片
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43799388/article/details/123830587 更加详细
'''
def load_mosaic(self, index):
# index get_item中图片的索引
# YOLOv5 4-mosaic loader. Loads 1 image + 3 random images into a 4-image mosaic
labels4, segments4 = [], []
s = self.img_size
# self.mosaic_border = [-img_size // 2, -img_size // 2]
# A(s/2, s/2)和点B(3s/2, 3s/2)限定的矩形内随机选择一点作为拼接点
yc, xc = [int(random.uniform(-x, 2 * s + x)) for x in self.mosaic_border] # mosaic center x, y
indices = [index] + random.choices(self.indices, k=3) # 3 additional image indices 随机取三张
random.shuffle(indices)
for i, index in enumerate(indices):
# Load image
img, _, (h, w) = load_image(self, index)
# place img in img4
if i == 0: # top left
'''初始化一幅尺寸为2s*2s的灰色大图,(1280,1280,3)'''
'''a为灰度图的待填充空间,b为图片的保留空间'''
img4 = np.full((s * 2, s * 2, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), max(yc - h, 0), xc, yc # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (large image)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), h - (y2a - y1a), w, h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (small image)
elif i == 1: # top right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, max(yc - h, 0), min(xc + w, s * 2), yc
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, h - (y2a - y1a), min(w, x2a - x1a), h
elif i == 2: # bottom left
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), yc, xc, min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), 0, w, min(y2a - y1a, h)
elif i == 3: # bottom right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, yc, min(xc + w, s * 2), min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, 0, min(w, x2a - x1a), min(y2a - y1a, h)
# 一张一张的填充到灰度图中
img4[y1a:y2a, x1a:x2a] = img[y1b:y2b, x1b:x2b] # img4[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
padw = x1a - x1b
padh = y1a - y1b
# Labels
labels, segments = self.labels[index].copy(), self.segments[index].copy()
if labels.size:
labels[:, 1:] = xywhn2xyxy(labels[:, 1:], w, h, padw, padh) # normalized xywh to pixel xyxy format
segments = [xyn2xy(x, w, h, padw, padh) for x in segments]
labels4.append(labels)
segments4.extend(segments)
# Concat/clip labels
# np.clip 限制标签在灰度图中,舍去超出的部分
labels4 = np.concatenate(labels4, 0)
for x in (labels4[:, 1:], *segments4):
np.clip(x, 0, 2 * s, out=x) # clip when using random_perspective()
# img4, labels4 = replicate(img4, labels4) # replicate
# Augment,不用管
img4, labels4, segments4 = copy_paste(img4, labels4, segments4, p=self.hyp['copy_paste'])
img4, labels4 = random_perspective(img4, labels4, segments4,
degrees=self.hyp['degrees'],
translate=self.hyp['translate'],
scale=self.hyp['scale'],
shear=self.hyp['shear'],
perspective=self.hyp['perspective'],
border=self.mosaic_border) # border to remove
return img4, labels4
cutout数据增强
'''随机遮盖部分区域
'''
def cutout(im, labels, p=0.5):
# Applies image cutout augmentation https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.04552
if random.random() < p:
h, w = im.shape[:2]
scales = [0.5] * 1 + [0.25] * 2 + [0.125] * 4 + [0.0625] * 8 + [0.03125] * 16 # image size fraction
for s in scales:
mask_h = random.randint(1, int(h * s)) # create random masks
mask_w = random.randint(1, int(w * s))
# box
xmin = max(0, random.randint(0, w) - mask_w // 2)
ymin = max(0, random.randint(0, h) - mask_h // 2)
xmax = min(w, xmin + mask_w)
ymax = min(h, ymin + mask_h)
# apply random color mask
im[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax] = [random.randint(64, 191) for _ in range(3)]
# return unobscured labels
# 删掉遮盖标签超过60%的标签
if len(labels) and s > 0.03:
box = np.array([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax], dtype=np.float32)
ioa = bbox_ioa(box, labels[:, 1:5]) # intersection over area
labels = labels[ioa < 0.60] # remove >60% obscured labels
return labels
Mixup数据增强
'''不同透明度的图片重叠在一起
'''
def mixup(im, labels, im2, labels2):
# Applies MixUp augmentation https://arxiv.org/pdf/1710.09412.pdf
r = np.random.beta(32.0, 32.0) # mixup ratio, alpha=beta=32.0
im = (im * r + im2 * (1 - r)).astype(np.uint8) # 将两张图片按照不同比例混合在一起
labels = np.concatenate((labels, labels2), 0) # 标签直接拼接
return im, labels
HSV色域变换数据增强
'''色域转换,三个通道的颜色分别处理'''
def augment_hsv(im, hgain=0.5, sgain=0.5, vgain=0.5):
# HSV color-space augmentation
if hgain or sgain or vgain:
r = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, 3) * [hgain, sgain, vgain] + 1 # random gains
hue, sat, val = cv2.split(cv2.cvtColor(im, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)) # HSV色域
dtype = im.dtype # uint8
x = np.arange(0, 256, dtype=r.dtype)
lut_hue = ((x * r[0]) % 180).astype(dtype)
lut_sat = np.clip(x * r[1], 0, 255).astype(dtype)
lut_val = np.clip(x * r[2], 0, 255).astype(dtype)
im_hsv = cv2.merge((cv2.LUT(hue, lut_hue), cv2.LUT(sat, lut_sat), cv2.LUT(val, lut_val)))
cv2.cvtColor(im_hsv, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR, dst=im) # no return needed
直方图均衡化数据增强
'''直方图均衡化
- 将BGR(或RGB)图像转换为YUV格式的图像。
- 若clahe=True,则采用自适应直方图均衡化,否则使用全局直方图均衡化,对Y通道进行直方图均衡化处理。
- 将处理后的YUV格式图像转换为BGR(或RGB)格式的图像,返回。
'''
def hist_equalize(im, clahe=True, bgr=False):
# Equalize histogram on BGR image 'im' with im.shape(n,m,3) and range 0-255
yuv = cv2.cvtColor(im, cv2.COLOR_BGR2YUV if bgr else cv2.COLOR_RGB2YUV)
if clahe:
c = cv2.createCLAHE(clipLimit=2.0, tileGridSize=(8, 8))
yuv[:, :, 0] = c.apply(yuv[:, :, 0])
else:
yuv[:, :, 0] = cv2.equalizeHist(yuv[:, :, 0]) # equalize Y channel histogram
return cv2.cvtColor(yuv, cv2.COLOR_YUV2BGR if bgr else cv2.COLOR_YUV2RGB) # convert YUV image to RGB
复制标签数据增强
'''复制标签区域'''
def replicate(im, labels):
# Replicate labels
h, w = im.shape[:2]
boxes = labels[:, 1:].astype(int)
x1, y1, x2, y2 = boxes.T
# 计算每个标签所对应的矩形的边长s。
s = ((x2 - x1) + (y2 - y1)) / 2 # side length (pixels)
# 对边长进行排序,并获取前50%最小的索引。
for i in s.argsort()[:round(s.size * 0.5)]: # smallest indices
# 遍历这些最小的索引,对每个标签进行复制操作。
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = boxes[i]
bh, bw = y2b - y1b, x2b - x1b
# 获取一个在图像内随机偏移的位置`(xc, yc)`。
yc, xc = int(random.uniform(0, h - bh)), int(random.uniform(0, w - bw)) # offset x, y
# 根据偏移位置和标签宽度和高度,计算出复制后的标签的坐标`[x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a]`。
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = [xc, yc, xc + bw, yc + bh]
im[y1a:y2a, x1a:x2a] = im[y1b:y2b, x1b:x2b] # im4[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
labels = np.append(labels, [[labels[i, 0], x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a]], axis=0)
return im, labels
自适应标签函数
'''自适应边框函数'''
def letterbox(im, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=True, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True, stride=32):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
# 保证缩小而不是放大图片
if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better val mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
# 计算需要添加的边框大小并设置填充比例。如果auto为True,则按照stride的大小计算边框。如果scaleFill为True,
# 则将图像拉伸以适应目标尺寸,而不是保留原始比例。
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if auto: # minimum rectangle
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, stride), np.mod(dh, stride) # wh padding
elif scaleFill: # stretch
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratios
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
仿射变换数据增强
'''仿射变换
- `targets`: 目标框的坐标信息,包括目标类别和坐标信息。
- `segments`: 目标分割区域的坐标信息。
- `degrees`: 旋转的角度范围。
- `translate`: 平移的比例范围。
- `scale`: 缩放的比例范围。
- `shear`: 剪切的角度范围。
- `perspective`: 透视变换的程度。
'''
def random_perspective(im, targets=(), segments=(), degrees=10, translate=.1, scale=.1, shear=10, perspective=0.0,
border=(0, 0)):
# torchvision.transforms.RandomAffine(degrees=(-10, 10), translate=(.1, .1), scale=(.9, 1.1), shear=(-10, 10))
# targets = [cls, xyxy]
height = im.shape[0] + border[0] * 2 # shape(h,w,c)
width = im.shape[1] + border[1] * 2
# Center
# 中心矩阵
C = np.eye(3)
C[0, 2] = -im.shape[1] / 2 # x translation (pixels)
C[1, 2] = -im.shape[0] / 2 # y translation (pixels)
# Perspective
# 透视矩阵P,并对P的第三维度进行随机调整
P = np.eye(3)
P[2, 0] = random.uniform(-perspective, perspective) # x perspective (about y)
P[2, 1] = random.uniform(-perspective, perspective) # y perspective (about x)
# Rotation and Scale
# 旋转缩放矩阵R,并对R的旋转角度和缩放比例进行随机调整
R = np.eye(3)
a = random.uniform(-degrees, degrees)
# a += random.choice([-180, -90, 0, 90]) # add 90deg rotations to small rotations
s = random.uniform(1 - scale, 1 + scale)
# s = 2 ** random.uniform(-scale, scale)
R[:2] = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(angle=a, center=(0, 0), scale=s)
# Shear
# 创建剪切矩阵S,并对S的两个维度进行随机调整
S = np.eye(3)
S[0, 1] = math.tan(random.uniform(-shear, shear) * math.pi / 180) # x shear (deg)
S[1, 0] = math.tan(random.uniform(-shear, shear) * math.pi / 180) # y shear (deg)
# Translation
# 平移矩阵T,并对T的两个维度进行随机调整
T = np.eye(3)
T[0, 2] = random.uniform(0.5 - translate, 0.5 + translate) * width # x translation (pixels)
T[1, 2] = random.uniform(0.5 - translate, 0.5 + translate) * height # y translation (pixels)
# Combined rotation matrix
# 将所有矩阵按照顺序乘起来,得到最终的变换矩阵M。
M = T @ S @ R @ P @ C # order of operations (right to left) is IMPORTANT
# 如果border参数不为0或者M不为单位矩阵,则对图像进行变换。
if (border[0] != 0) or (border[1] != 0) or (M != np.eye(3)).any(): # image changed
if perspective:
im = cv2.warpPerspective(im, M, dsize=(width, height), borderValue=(114, 114, 114))
else: # affine
im = cv2.warpAffine(im, M[:2], dsize=(width, height), borderValue=(114, 114, 114))
# Visualize
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 6))[1].ravel()
# ax[0].imshow(im[:, :, ::-1]) # base
# ax[1].imshow(im2[:, :, ::-1]) # warped
# Transform label coordinates
n = len(targets)
# 如果targets参数不为空,则对目标物体坐标进行相应的调整。
if n:
use_segments = any(x.any() for x in segments)
new = np.zeros((n, 4))
if use_segments:...
else: # warp boxes
xy = np.ones((n * 4, 3)) # 前两列表示对图像进行旋转、缩放和剪切的变换,第三列表示对图像进行平移的变换
xy[:, :2] = targets[:, [1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 4, 3, 2]].reshape(n * 4, 2) # x1y1, x2y2, x1y2, x2y1
xy = xy @ M.T # transform
xy = (xy[:, :2] / xy[:, 2:3] if perspective else xy[:, :2]).reshape(n, 8) # perspective rescale or affine
# create new boxes
x = xy[:, [0, 2, 4, 6]]
y = xy[:, [1, 3, 5, 7]]
new = np.concatenate((x.min(1), y.min(1), x.max(1), y.max(1))).reshape(4, n).T
# clip
new[:, [0, 2]] = new[:, [0, 2]].clip(0, width)
new[:, [1, 3]] = new[:, [1, 3]].clip(0, height)
# filter candidates
i = box_candidates(box1=targets[:, 1:5].T * s, box2=new.T, area_thr=0.01 if use_segments else 0.10)
targets = targets[i]
targets[:, 1:5] = new[i]
return im, targets
模型推理阶段(Detect)
detect.py 包含了对各种权重格式的加载、推理,非常的杂。这里看主要代码:
...
if pt and device.type != 'cpu':
model = torch.jit.load(w) if 'torchscript' in w else attempt_load(weights, map_location=device) # 加载权重
stride = int(model.stride.max()) # model stride
names = model.module.names if hasattr(model, 'module') else model.names # get class names
if half:
model.half() # to FP16
model(torch.zeros(1, 3, *imgsz).to(device).type_as(next(model.parameters()))) # run once,imgsz=640
...
...
# Dataloader
# 视频流/网页与单张图片,batch_size不同
if webcam:
view_img = check_imshow()
cudnn.benchmark = True # set True to speed up constant image size inference
dataset = LoadStreams(source, img_size=imgsz, stride=stride, auto=pt)
bs = len(dataset) # batch_size
else:
dataset = LoadImages(source, img_size=imgsz, stride=stride, auto=pt)
bs = 1 # batch_size
vid_path, vid_writer = [None] * bs, [None] * bs
for path, img, im0s, vid_cap in dataset:
t1 = time_sync()
if onnx:
img = img.astype('float32')
else:
img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(device)
img = img.half() if half else img.float() # uint8 to fp16/32 半精度更快
img = img / 255.0 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
if len(img.shape) == 3:
img = img[None] # expand for batch dim
t2 = time_sync()
# Inference
if pt:
visualize = increment_path(save_dir / Path(path).stem, mkdir=True) if visualize else False
"""
pred.shape=(1, num_boxes, 5+num_class)
h,w为传入网络图片的长和宽,注意dataset在检测时使用了矩形推理,所以这里h不一定等于w
num_boxes = h/32 * w/32 + h/16 * w/16 + h/8 * w/8
pred[..., 0:4]预测框坐标为xywh格式,通过yolo.py中的Detect类已经扩展成了原图的大小
pred[..., 4]objectness置信度
pred[..., 5:-1]分类结果
"""
pred = model(img, augment=augment, visualize=visualize)[0]
# NMS
# 非极大值抑制函数(重要)
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, conf_thres, iou_thres, classes, agnostic_nms, max_det=max_det)
# 画框,保存的操作
...
非极大值抑制函数
def non_max_suppression(prediction, conf_thres=0.25, iou_thres=0.45, classes=None, agnostic=False, multi_label=False,
labels=(), max_det=300):
"""Runs Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference results
Returns:
list of detections, on (n,6) tensor per image [xyxy, conf, cls]
"""
# 获取类别数量
nc = prediction.shape[2] - 5 # number of classes
# 获取所有置信度高于阈值的备选框
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates
# Checks
assert 0 <= conf_thres <= 1, f'Invalid Confidence threshold {conf_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
assert 0 <= iou_thres <= 1, f'Invalid IoU {iou_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
# Settings
min_wh, max_wh = 2, 4096 # 框的最小和最大宽度和高度
max_nms = 30000 # 最大需要输入 torchvision.ops.nms() 的框数
time_limit = 10.0 # 最大处理时间
redundant = True # 需要冗余检测结果
multi_label &= nc > 1 # 每个框可能有多个标签(添加0.5ms/图像的处理时间)
merge = False # 使用 merge-NMS 算法
t = time.time()
output = [torch.zeros((0, 6), device=prediction.device)] * prediction.shape[0]
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # 图像索引,图像检测结果
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # 保留置信度高于阈值的备选框
# 如果使用自动标注,则添加标签
if labels and len(labels[xi]):
l = labels[xi]
v = torch.zeros((len(l), nc + 5), device=x.device)
v[:, :4] = l[:, 1:5] # box
v[:, 4] = 1.0 # conf
v[range(len(l)), l[:, 0].long() + 5] = 1.0 # cls
x = torch.cat((x, v), 0)
# 如果没有备选框则处理下一张图像
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
# 计算置信度
x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # 置信度 = 目标置信度 * 类别置信度
# Box (center x, center y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
# 转换xywh2xyxy,左上右下
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4])
# 得到检测结果矩阵 nx6 (xyxy, 置信度, 类别)
if multi_label:
i, j = (x[:, 5:] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).T
x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, j + 5, None], j[:, None].float()), 1)
else: # 只保留最高置信度的类别
conf, j = x[:, 5:].max(1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float()), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes is not None:
x = x[(x[:, 5:6] == torch.tensor(classes, device=x.device)).any(1)]
# Apply finite constraint
# if not torch.isfinite(x).all():
# x = x[torch.isfinite(x).all(1)]
# Check shape
# 过滤框太少或太多
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
elif n > max_nms: # excess boxes
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # 框(加上类别的偏移量),置信度
i = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMS
if i.shape[0] > max_det: # 限制检测结果的数量
i = i[:max_det]
if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # 使用 merge-NMS 算法(使用加权平均数合并框)
# update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
x[i, :4] = torch.mm(weights, x[:, :4]).float() / weights.sum(1, keepdim=True) # merged boxes
if redundant:
i = i[iou.sum(1) > 1] # require redundancy
output[xi] = x[i]
if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:
print(f'WARNING: NMS time limit {time_limit}s exceeded')
break # time limit exceeded
return output
TensorRT加速
转换成tensorrt格式有两种方式,一种是pytorch -> engine ;另一种是pytorch -> onnx -> engine。
onnx现在作为通用的中间格式,已经支持许多格式的算子映射,pytorch自身封装了onnx,所以更为方便。
最新的官方代码已经支持tensorrt格式的转换,也是采用的第二种方式。
Format | `export.py --include` | Model
--- | --- | ---
PyTorch | - | yolov5s.pt
TorchScript | `torchscript` | yolov5s.torchscript
ONNX | `onnx` | yolov5s.onnx
OpenVINO | `openvino` | yolov5s_openvino_model/
**TensorRT | `engine` | yolov5s.engine**
CoreML | `coreml` | yolov5s.mlmodel
TensorFlow SavedModel | `saved_model` | yolov5s_saved_model/
TensorFlow GraphDef | `pb` | yolov5s.pb
TensorFlow Lite | `tflite` | yolov5s.tflite
TensorFlow Edge TPU | `edgetpu` | yolov5s_edgetpu.tflite
TensorFlow.js | `tfjs` | yolov5s_web_model/
PaddlePaddle | `paddle` | yolov5s_paddle_model/
def export_engine(model, im, file, half, dynamic, simplify, workspace=4, verbose=False, prefix=colorstr('TensorRT:')):
# YOLOv5 TensorRT export https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt
assert im.device.type != 'cpu', 'export running on CPU but must be on GPU, i.e. `python export.py --device 0`'
try:
import tensorrt as trt
except Exception:
if platform.system() == 'Linux':
check_requirements('nvidia-tensorrt', cmds='-U --index-url https://pypi.ngc.nvidia.com')
import tensorrt as trt
# 先转为onnx文件保存,再将onnx转为engine
if trt.__version__[0] == '7': # TensorRT 7 handling https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/issues/6012
grid = model.model[-1].anchor_grid
model.model[-1].anchor_grid = [a[..., :1, :1, :] for a in grid]
export_onnx(model, im, file, 12, dynamic, simplify) # opset 12
model.model[-1].anchor_grid = grid
else: # TensorRT >= 8
check_version(trt.__version__, '8.0.0', hard=True) # require tensorrt>=8.0.0
export_onnx(model, im, file, 12, dynamic, simplify) # opset 12
onnx = file.with_suffix('.onnx')
LOGGER.info(f'\n{prefix} starting export with TensorRT {trt.__version__}...')
assert onnx.exists(), f'failed to export ONNX file: {onnx}'
f = file.with_suffix('.engine') # TensorRT engine file 换个后缀
# trt日志设置
logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.INFO)
if verbose:
logger.min_severity = trt.Logger.Severity.VERBOSE
# 创建Tensor引擎对象
builder = trt.Builder(logger)
config = builder.create_builder_config()
# 设置引擎最大工作空间
# 表示向左移动30位,即乘以2的30次方即1G
config.max_workspace_size = workspace * 1 << 30 # 4G
# config.set_memory_pool_limit(trt.MemoryPoolType.WORKSPACE, workspace << 30) # fix TRT 8.4 deprecation notice
'''
在隐式批处理模式下,TensorRT可以在推理时动态地处理不同大小的批次。
而在显式批处理模式下,TensorRT需要在构建引擎时指定固定的批次大小,这可以提高引擎的性能。
'''
flag = (1 << int(trt.NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag.EXPLICIT_BATCH))
# 创建神经网络函数
network = builder.create_network(flag)
# 将onnx转化为engine
parser = trt.OnnxParser(network, logger)
if not parser.parse_from_file(str(onnx)):
raise RuntimeError(f'failed to load ONNX file: {onnx}')
inputs = [network.get_input(i) for i in range(network.num_inputs)] # 输入张量
outputs = [network.get_output(i) for i in range(network.num_outputs)] # 输出张量
for inp in inputs:
LOGGER.info(f'{prefix} input "{inp.name}" with shape{inp.shape} {inp.dtype}')
for out in outputs:
LOGGER.info(f'{prefix} output "{out.name}" with shape{out.shape} {out.dtype}')
'''
builder.create_optimization_profile() 函数创建一个优化配置,并使用 profile.set_shape() 函数为每个输入张量设置形状。
在这里,im 是输入数据,inputs 是 TensorRT 网络的输入张量列表。
'''
if dynamic:
if im.shape[0] <= 1:
LOGGER.warning(f'{prefix} WARNING ⚠️ --dynamic model requires maximum --batch-size argument')
profile = builder.create_optimization_profile()
'''
profile.set_shape() 函数有三个参数,分别是输入张量的名称、最小形状、最优形状和最大形状。
在这里,最小形状和最优形状都设置为 (1, *im.shape[1:]),即 batch size 为 1,其他维度与输入数据相同。
而最大形状则为 (max(1, im.shape[0] // 2), *im.shape[1:]),即 batch size 为输入数据的一半,其他维度与输入数据相同。
这样设置的目的是为了在 batch size 变化时,能够自适应调整输入张量的形状。
'''
for inp in inputs:
profile.set_shape(inp.name, (1, *im.shape[1:]), (max(1, im.shape[0] // 2), *im.shape[1:]), im.shape)
config.add_optimization_profile(profile)
LOGGER.info(f'{prefix} building FP{16 if builder.platform_has_fast_fp16 and half else 32} engine as {f}')
if builder.platform_has_fast_fp16 and half:
config.set_flag(trt.BuilderFlag.FP16)
with builder.build_engine(network, config) as engine, open(f, 'wb') as t:
# 序列化写入
t.write(engine.serialize())
return f, None
转成onnx的代码,可以用pytorch本身的torch.onnx.export
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/498425043 详解
def export_onnx(model, im, file, opset, dynamic, simplify, prefix=colorstr('ONNX:')):
# YOLOv5 ONNX export
check_requirements('onnx>=1.12.0')
import onnx
LOGGER.info(f'\n{prefix} starting export with onnx {onnx.__version__}...')
f = file.with_suffix('.onnx')
output_names = ['output0', 'output1'] if isinstance(model, SegmentationModel) else ['output0']
if dynamic:
dynamic = {'images': {0: 'batch', 2: 'height', 3: 'width'}} # shape(1,3,640,640)
if isinstance(model, SegmentationModel):
dynamic['output0'] = {0: 'batch', 1: 'anchors'} # shape(1,25200,85)
dynamic['output1'] = {0: 'batch', 2: 'mask_height', 3: 'mask_width'} # shape(1,32,160,160)
elif isinstance(model, DetectionModel):
dynamic['output0'] = {0: 'batch', 1: 'anchors'} # shape(1,25200,85)
torch.onnx.export(
model.cpu() if dynamic else model, # --dynamic only compatible with cpu
im.cpu() if dynamic else im,
f,
verbose=False,
opset_version=opset,
do_constant_folding=True, # WARNING: DNN inference with torch>=1.12 may require do_constant_folding=False
input_names=['images'], # 指定输入
output_names=output_names, # 指定输出
dynamic_axes=dynamic or None) # 指定输入输出张量的哪些维度是动态的。
# Checks
model_onnx = onnx.load(f) # load onnx model
onnx.checker.check_model(model_onnx) # check onnx model
# Metadata
d = {'stride': int(max(model.stride)), 'names': model.names}
for k, v in d.items():
meta = model_onnx.metadata_props.add()
meta.key, meta.value = k, str(v)
onnx.save(model_onnx, f)
# Simplify
if simplify:
try:
cuda = torch.cuda.is_available()
check_requirements(('onnxruntime-gpu' if cuda else 'onnxruntime', 'onnx-simplifier>=0.4.1'))
import onnxsim
LOGGER.info(f'{prefix} simplifying with onnx-simplifier {onnxsim.__version__}...')
model_onnx, check = onnxsim.simplify(model_onnx)
assert check, 'assert check failed'
onnx.save(model_onnx, f)
except Exception as e:
LOGGER.info(f'{prefix} simplifier failure: {e}')
return f, model_onnx
Export
会花费一会时间
onnx不需要GPU进行推理,但是tensorRT 需要 GPU 进行推理
# 要使用half,必须指定device
python export.py --data data/coco128.yaml --weights yolov5s.pt --include engine --half --int8 --device 0
# 输入输出
TensorRT: input "images" with shape(1, 3, 640, 640) DataType.HALF
TensorRT: output "output0" with shape(1, 25200, 85) DataType.HALF
TensorRT: building FP16 engine as yolov5s.engine
通过这句话就可以通过tensorrt加速了
python detect.py --weights yolov5s.engine --source data/images --half --device 0
Flask API 封装
创建client文件client.py,service文件service.py。
service的代码,传递图片的方式是base64编码,传递数据的方式是json,需要对detect.py做一点小改动,因为我们只需要处理一张图片。
from flask import Flask, jsonify #flask库
from flask import request
import base64
from datetime import datetime
from detect import run
'''api的调用返回
返回生成的结果图片,仅支持一张图片
'''
app = Flask(__name__) # 创建一个服务,赋值给APPflask
@app.route('/inference', methods=['Get',"Post"])
def inference():
source = request.json
uid = source.get('uid')
data = source.get("data")
# 解析一张图片
# 临时存储
with open("tmp.jpg", "wb") as f:
img = base64.b64decode(data["imgs"])
f.write(img)
# 将tmp_img_path传入检测函数中,每一次检测都要加载权重,影响较大
return_img = run(source="tmp.jpg",nosave=True) # numpy 格式,cv2可以直接保存
# return_img = return_img.tobytes() # 转bytes
return_img = base64.b64encode(return_img).decode('utf8') # str
# 赋值
response = {}
response["data"] = {}
response["uid"] = uid
response["data"]["imgs"] = return_img
response["data"]["response_date"] = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
return jsonify(response)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(host="127.0.0.1",port=8802,debug=True)
client代码
import requests
import base64
import cv2
import numpy as np
from datetime import datetime
'''模拟表单的提交
将图片转为base64格式传输
'''
if __name__ == "__main__":
url = "http://127.0.0.1:8802/inference" # api
require_data = {
"uid":1,
"data":{
"imgs":None,
"require_date":datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
}
}
with open("\data\images\R-C.jpg", "rb") as f:
base64_data = base64.b64encode(f.read()) # 使用base64进行加密
require_data["data"]["imgs"] = base64_data.decode('utf8') # str
# 处理返回数据
response = requests.get(url,json = require_data)
if response.ok:
print(response)
# 解码
img = response.json()["data"]["imgs"] # str
uid = response.json()["uid"]
img = base64.b64decode(img) # bytes
# 保存
with open("download.jpg","wb") as f:
f.write(img)
print("下载保存成功")
else:
print(response.status_code)
这中间可能会出现图片保存损坏的情况,可以在返回信息的时候用numpy.tolist格式返回图片内容。
最后相对应的文件夹中会有结果图片与一张临时图片。
需要对detect.py做个小小的改动,返回一张图片
# Process predictions 140行左右
for i, det in enumerate(pred): # per image
...
return im0 # numpy
