react+ts+router+redux+node+hooks+antd项目搭建
之前有写过react项目模块但是没有系统性的学过react,过一遍。ts,es6不会介绍语法,自行百度。
Ts初始化项目
yarn create react-app 项目名称 --template=typescript
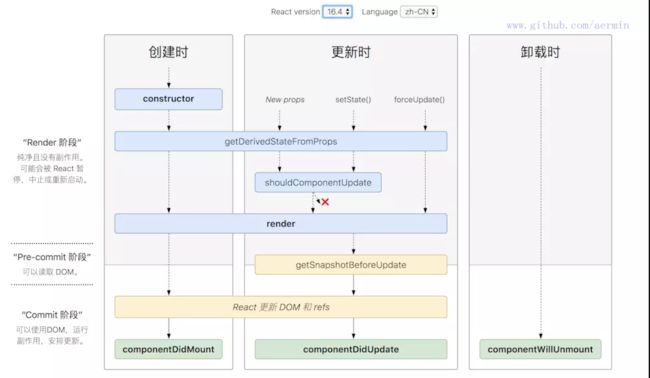
组件的基础写法以及通信
// App.tsx
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import './App.css';
import Home from './Home/Home'
import Counter from './Counter/index'
class App extends Component<any, any>{
getInfo = (info:string) => {
console.log(`来自组件的回调:${info}`)
}
render(): React.ReactNode {
return (
<>
<Home name="这是一个组件" callBack={this.getInfo}></Home>
<Counter></Counter>
<UserList></UserList>
</>
)
}
}
export default App;
// Home.tsx
import { Component, ReactNode } from "react";
interface IProps {
name: string,
age?: number,
user?: User,
callBack: (info: string) => void
}
interface User {
sex: boolean,
address: string
}
class Home extends Component<IProps, any>{
send = () => {
this.props.callBack('执行')
}
render(): ReactNode {
return (
<div className="box">
<h1>这是一个组件</h1>
<span onClick={this.send}>{this.props.name}</span>
</div>
)
}
}
class Home extends Component<IProps, any>{
render(): ReactNode {
return (
<>
<h1>这是一个组件</h1>
<span>{this.props.name}</span>
</>
)
}
}
export default Home
// Counter.tsx
import { Component, ReactNode } from "react";
interface IState {
counter: number
}
let timer:any = null
export default class Counter extends Component<any,IState>{
constructor(props:any, context: any){
super(props, context)
this.state = {
counter: 0
}
}
componentDidMount() {
// state更新是异步的 通过setState来更新值 不允许this.state.xx = xx写法
// state的更新会导致组件重新更新(重新render)
timer = setInterval(() => {
this.setState({
counter: this.state.counter + 1
})
},2000)
}
componentWillUnmount() {
clearInterval(timer)
}
render(): ReactNode {
return (
<>
计数器: {this.state.counter}
</>
)
}
}
路由
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import './App.css';
import Home from './Home/Home'
import Counter from './Counter/index'
import {
BrowserRouter as Router,
Routes,
Route
} from 'react-router-dom'
/**
* React Router v6
* Router: 用于包装不同的路线,它使用HTML5 historyAPI来跟踪React应用程序中的路由历史记录
* Routes: v5版本Switch组件的升级版,它包括相对路由和链接、自动路由排名、嵌套路由和布局等功能
* Route: 负责渲染React组件的UI。
它有一个称为path的属性,该属性始终与应用程序的当前URL匹配。
第二个需要的属性叫做element,当遇到当前的URL时,会告诉Route组件要渲染哪个React组件(v5中则是使用component属性)
* Link: 避免刷新页面
*/
class App extends Component<any, any>{
constructor(props: any, context: any){
super(props, context)
this.state = {
id: 1
}
}
render(): React.ReactNode {
return (
<div>
<Router>
<nav style={{ margin: 10 }}>
<Link to="/" style={{ padding: 5 }}>
Home
</Link>
<Link to={`/counter/${this.state.id}`} style={{ padding: 5 }}>
About
</Link>
// 类组件中this.props.history, this.props.match获取到的都是undefined
// v5中是支持这么取参数的,v6下得用window.location来取
// 查了下说v6主要拥抱hooks,放弃了之前的取法。有其他取参方案的希望大佬可以提供下。
</nav>
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<Home name="这是传递给组件的值"/>} />
<Route path="/counter/*" element={<Counter />} />
</Routes>
</Router>
{/* v5中使用switch 后续demo中使用的是v5
*/}
// 非根路由中可以使用withRouter 进行this.props.history.push('/*')跳转
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
写一个简单的路由控制
// App.tsx
import React, { Component, ReactNode, Suspense } from 'react';
import './App.css';
import { router } from './router/index'
import { Layout, Menu } from 'antd';
import {
PieChartOutlined,
MailOutlined,
} from '@ant-design/icons';
import {
BrowserRouter as Router,
Link,
Route,
Switch
} from 'react-router-dom';
const { SubMenu } = Menu;
const { Footer, Sider, Content } = Layout;
interface IRouter {
id: number,
path: string,
title: string,
exact: boolean,
component: ReactNode,
children?: IRouter[]
}
class App extends Component<any, any>{
constructor(props: any, context: any) {
super(props, context)
this.state = {}
}
componentDidMount = () => {
}
render(): React.ReactNode {
return (
<Router>
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<Layout>
<Sider>
<Menu
defaultSelectedKeys={['1']}
defaultOpenKeys={['sub1']}
mode="inline"
theme="dark"
>
{
router.map((r: IRouter) => {
if (r.children) {
return (
<SubMenu key={r.id} icon={<MailOutlined />} title={r.title}>
{
r.children.map((v: IRouter) => {
return (
<Menu.Item key={v.id}>
<Link to={v.path}>{v.title}</Link>
</Menu.Item>
)
})
}
</SubMenu>
)
} else {
return (
<Menu.Item key={r.id} icon={<PieChartOutlined />}>
<Link to={r.path}>{r.title}</Link>
</Menu.Item>
)
}
})
}
</Menu>
</Sider>
<Layout>
<Content>
{
router.map((r: IRouter) => {
if (r.children) {
return (
<Switch key={r.id}>
{
r.children.map((v: IRouter) => {
return (
<Route key={v.id} path={v.path} exact={v.exact}>{v.component}</Route>
)
})
}
</Switch>
)
} else {
return (
<Switch key={r.id}>
<Route path={r.path} exact={r.exact}>
{r.component}
</Route>
</Switch>
)
}
})
}
</Content>
<Footer>Footer</Footer>
</Layout>
</Layout>
</Suspense>
</Router>
)
}
}
export default App;
// touter/index.tsx
import { ReactNode, lazy } from "react"
const Home = lazy(() => import('../pages/Home/Home'))
const User = lazy(() => import('../pages/User/index'))
const UserDetail = lazy(() => import('../pages/User/comp/detail'))
interface IRouter{
id: number,
path: string,
title: string,
exact: boolean,
component: ReactNode,
children?: IRouter[]
}
export const router:IRouter[] = [
{
id: 1,
path: '/',
title: 'Home page',
exact: true,
component: () => (<Home name="这是传递给组件的值"></Home>)
},
{
id:2,
path: '/User',
title: 'User page',
exact: true,
component: () => (<User/>),
children: [
{
id: 3,
path: '/user/detail',
title: 'user detail',
exact: true,
component: () => (<UserDetail/>)
}
]
}
]
Redux
yarn add redux
你需要action这个普通对象来描述发生了生命,而不是直接改变state。然后,编写一个名为reducer的特殊函数,来决定如何基于action来更新整个应用的状态树。
在典型的Redux应用程序中,只有一个store以及一个根reducer函数。随着应用程序的增长,您可以将根reducer拆分为较小的reducer,分别在状态树的不同部分上进行操作。这就像在React应用程序中只有一个根组件一样,但是它是由许多小组件组成的。
- state:驱动应用的真实数据源头
- view:基于当前状态的UI声明性描述
- actions:根据用户输入在应用程序中发生的事件,并触发状态更新(记录改变的动作由reducer来改变)
用state来描述应用程序在特定时间点的状况
基于state来渲染View
当发生某些事情时,state会根据发生的事情进行更新,生成新的state
基于新的state重新渲染View
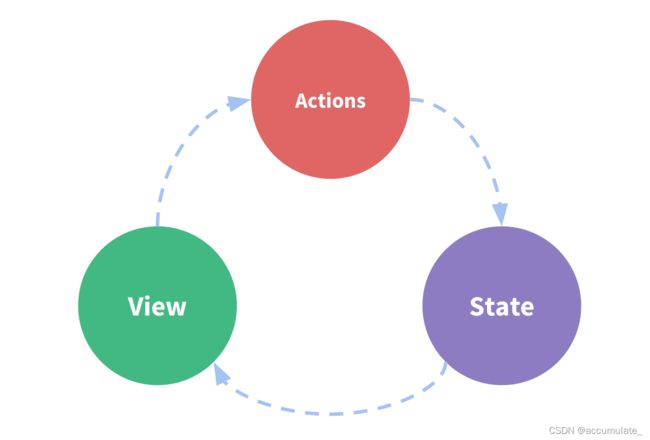
- Redux使用’单项数据流’
State描述了应用程序在某个时间点的状态,UI基于该状态渲染
当应用程序中发生某些事情时:
- UI dispatch 一个action
- store调用reducer,随后根据发生的事情来更新state
- store通知UI state发生变化
UI 基于新state重新渲染
// 目录结构
-src
-store
-aciton
index.tsx
-reducer
index.tsx
index.tsx
//store/index.tsx
import { createStore } from "redux";
import { reducer } from "./reducer";
const store = createStore(reducer)
export default store
// aciton/index.tsx
// 需要执行的操作
export const sendAction = () => {
return {
type: 'send_type',
value: 'this is action'
}
}
// reducer/index.tsx
interface IAction {
type: string,
value: any
}
const initState = {
value: 'init'
}
export const reducer = (state = initState, action: IAction) => {
// 修改数据
switch (action.type) {
case 'send_type':
return Object.assign({key: '改变'}, state, action)
default:
return state
}
}
// Home.tsx
import { Button } from "antd";
import { Component, ReactNode } from "react";
import './Home.css'
import store from '../../store'
import { sendAction } from '../../store/action'
interface IProps {
name: string,
age?: number,
user?: User
}
interface User {
sex: boolean,
address: string
}
class Home extends Component<IProps, any>{
clickBtn = () => {
const action = sendAction()
store.dispatch(action)
}
componentDidMount(){
store.subscribe(() => {
console.log(store.getState())
})
}
render(): ReactNode {
return (
<div className="box">
<h1>这是一个组件</h1>
<span>{this.props.name}</span>
<Button type="primary" onClick={this.clickBtn}>Home</Button>
</div>
)
}
}
export default Home
Hooks
React组件创建方式,一种是类组件,一种是纯函数组件。前面都是以类组件形式写的不再介绍。
纯函数组件相对于类组件有以下几点不足:
- 纯函数组件没有状态
- 纯函数组件没有生命周期
- 纯函数组件没有this
- 只能是纯函数
React Hooks就是加强版的函数组件,可以完全不使用class,就能写出一个全功能的组件
useState():状态钩子
import { Button } from 'antd'
import React, { useState } from 'react'
interface IProps {
num: number
}
const AddCount = (props: IProps) => {
// useState(state, setState)
const [state, setState] = useState({
count: props.num
});
const updateCount = () => {
setState({ ...state, count: state.count + 1 });
};
return <>
<p>{state.count}</p>
<Button type="primary" onClick={updateCount}>Home</Button>
</>
}
export default AddCount
useContext():共享状态钩子
该钩子的作用是,在组件之间共享状态。
import { Button } from 'antd'
import React, { createContext, useContext, useState } from 'react'
interface IProps {
num: number
}
const AppContext = createContext({text: ''})
const AddCount = (props: IProps) => {
// useState(state, setState)
const [state, setState] = useState({
count: props.num,
});
const updateCount = () => {
setState({ ...state, count: state.count + 1 });
};
return <>
<p>{state.count}</p>
<Button type="primary" onClick={updateCount}>点击</Button>
{/* 在下发状态组件内修改text值时,子组件内状态也会更改 */}
<AppContext.Provider value={{text: state.count.toString()}} >
<Add></Add>
<Del></Del>
</AppContext.Provider>
</>
}
// 在子组件中修改text值时候,在其他子组件内是不会发生改变的
const Add = () => {
const {text} = useContext(AppContext)
return <>
{`这里是Add组件${text}`}
</>
}
const Del = () => {
const {text} = useContext(AppContext)
return <>
{`这里是Del组件${text}`}
</>
}
export default AddCount
useReducer():Action钩子
前面有提到redux中是页面出发action然后通过reducer来修改state。useReducer()中是这样
const [state,dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialState)
/**
它接收reducer函数和状态的初始值作为参数,返回一个数组,其中第一项为当前的状态值,第二项为发送action的dispatch函数。
*/
import { Button } from "antd"
import { useReducer } from "react"
const initialState = {
count: 0,
}
const reducer = (state: any, action: any) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'a':
return { ...state, count: state.count + 1 };
case 'b':
return { ...state, count: state.count - 1 };
default:
return { ...state, count: state.count };
}
}
const A = () => {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialState)
return <>
我是A组件--{state.count}---
<Button type="primary" onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'a' })}>a</Button>
<Button type="primary" onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'b' })}>b</Button>
<Button type="primary" onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'c' })}>c</Button>
</>
}
export default A
// 这写法感觉和redux一毛一样...
useEffect():副作用钩子
useEffect可以是看作componentDidMount、componentDidUpdate、componentwillUnmount三者结合。
useEffect( cllback, [source] )
useEffect(() => {
// source参数不传时,则第一次渲染之后和每次更新之后都会执行
})
useEffect(() => {
// source参数传[]时, 则外部的函数只会在初始化时调用一次,
// 返回的那个函数也只会最终在组件卸载时调用一次
console.log('componentDidMount')
return () => {
console.log('componentwillUnmount')
}
},[])
useEffect(() => {
// source参数有值时,则只会监听到数组中的值发生改变后,才优先调用返回的那个函数,再调用外部的函数
}, [count])
代理、请求、环境配置
- 代理
yarn run eject可以把配置文件显示出来 在webpack.config.js中配置代理也可以。
这里推荐另外一种
yarn add http-proxy-middleware
src下新增setupProxy.js文件 不需要再做引入操作,这个webapck会自动读取
const { createProxyMiddleware } = require('http-proxy-middleware');
module.exports = function(app) {
app.use('/api', createProxyMiddleware({
// 这里路径我配的node启的地址
target: 'xxxxx',
changeOrigin: true,
pathRewrite: { //路径替换
'^/api': '',
}
}));
app.use('/api2', createProxyMiddleware({
target: 'http://xxx.com',
changeOrigin: true,
pathRewrite: { //路径替换
'^/api2': '/api', // axios 访问/api2 == target + /api
}
}));
};
- 请求
yarn add axios
-src/api/axios.ts request.ts
// axios.ts
import { notification } from 'antd';
import axios from 'axios'
axios.defaults.headers.post['Content-Type'] = 'application/json' // post请求头设置
let config = {
// baseURL: process.env.VUE_APP_API_BASE_URL || '', //请求地址
baseURL: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'? '/' : '/api', //请求地址
timeout: 60 * 1000, //超时时间
withCredentials: true, //axios请求开启cookie,支持跨域请求携带cookie
};
const _axios = axios.create(config);
// 请求拦截
_axios.interceptors.request.use(
function (config) {
// config.headers[ 'AccessToken' ] = getToken()
return config;
},
function (error) {
return Promise.reject(error);
}
);
// 响应拦截
_axios.interceptors.response.use(
function (response) {
const { data } = response
if (data.code !== 200){
notification.error({ message: data.message || data.error || '服务器异常', duration: 4})
}
return data;
},
function (error) {
let response = error.response
if (response){
let data = response.data
let status = response.status
switch (status) {
case 401:
// removeToken()
// router.go(0)
break
default:
notification.error({
message: '系统提示',
description: data.message || data.error || data || '服务器异常',
duration: 4
})
break
}
}
return Promise.reject(error);
}
);
export default _axios
import request from './axios'
//post
export function POST(url: string, parameter?: any) {
return request({
url: url,
method: 'post',
data: parameter
})
}
//get
export function GET(url: string, parameter?: any) {
return request({
url: url,
method: 'get',
params: parameter
})
}
//put
export function PUT(url: string, parameter?: any) {
return request({
url: url,
method: 'put',
data: parameter
})
}
//delete
export function DELETE(url: string, parameter?:any) {
return request({
url: url,
method: 'delete',
params: parameter
})
}
// 请求
import {GET} from '../../api/request'
GET('/users').then((res:any) => {
if(res.success){
}
})
- 开发环境配置
这个就没提供了dev环境 pro环境 ······
在更新中···