【OpenCV】车道线检测原理与实现
文章目录
-
- 车道线检测原理
- 代码实现
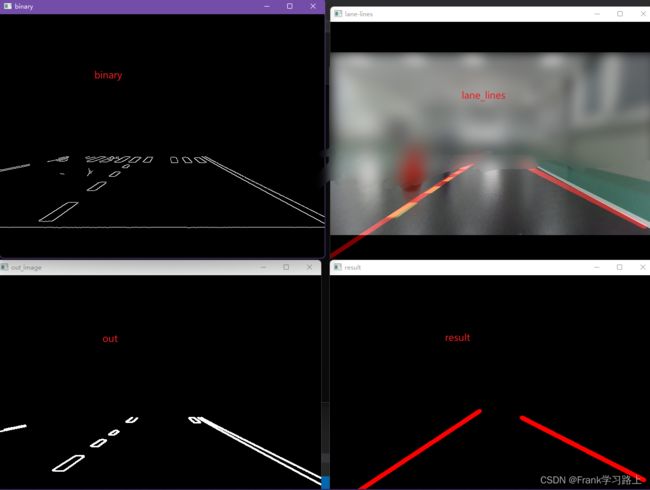
车道线检测原理
采用OpenCV读取视频,进行灰度化处理,然后用canny算子进行边缘检测,分析轮廓,然后进行直线拟合处理,最后对直线添加权重分析,得到最终的车道线检测结果。
代码实现
添加好opencv相关依赖后,写入:
//opencv454学习
#include 运行结果如下:
以上。