【应用】SpringBoot -- Shiro 实现认证与鉴权
Shiro
- Shiro 核心框架
- SpringBoot 中 Shiro 的配置使用
-
- 引入 Shiro 依赖
- 自定义 Realm
- 配置 Redis 缓存管理器
- 配置类 ShiroConfig 实现各个组件的拼装
- 编写控制层代码用于验证测试
- 测试使用
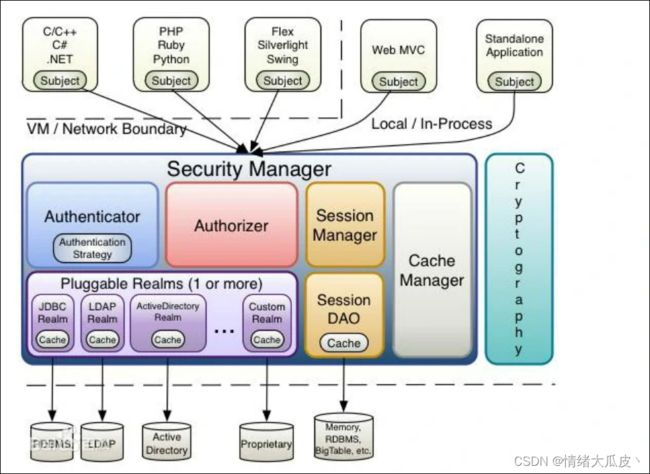
Shiro 核心框架
| 名称 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
subject |
subject 是主体,记录了当前操作用户的主体,外部的程序通过 subject 与 Security Manager 交互从而进行认证和授权 |
Security Manager |
Security Manager 是安全管理器,对全部的 subject 进行管理,是 Shiro 的核心。在安全管理器中,通过 Authenticator 进行认证,通过 Authorizer 进行授权,通过 Session Manager 进行会话管理,通过 Cache Manager 进行缓存管理,通过 Cryptography 进行密码管理 |
Authenticator |
Authenticator 是认证器,对用户进行身份的认证 |
Authorizer |
Authorizer 是授权器,对用户进行权限的授予和鉴别 |
Realm |
Realm 是领域,安全管理器通过 Realm 获取用户的权限数据,一般在 Realm 中查询数据库获取用户信息 |
Session Manager |
Session Manager 是和会话管理器,Shiro 自定义了一套会话管理器,不需要依赖于 Web 容器的 session,因此它可以在非 Web 应用中使用 |
SessionDAO |
管理会话操作的一套接口,可以将 session 保存到数据库等 |
Cache Manager |
Cache Manager 是缓存管理器,可以将用户的认证数据、权限数据保存在缓存中,提高性能 |
Cryptography |
Cryptography 是密码管理器,Shiro 提供了加密解密的组件,方便开发使用 |
SpringBoot 中 Shiro 的配置使用
引入 Shiro 依赖
创建 Maven 项目,引入相应的依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shirogroupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring-boot-web-starterartifactId>
<version>1.9.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
自定义 Realm
自定义 Realm 实现 AuthorizingRealm,将用户认证、鉴权信息提供给认证管理器以及权限管理器
-
在
doGetAuthorzationInfo()方法中,可以实现对账号的授权,授予权限或者角色 -
在
doGetAuthenticationInfo()方法中,将用户的信息加密后交由 Shiro 执行认证
/**
* @author zqf
*/
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
/**
* 授权
* @param principalCollection
* @return
*/
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
System.out.println("执行了授权=>doGetAuthorizationInfo");
SimpleAuthorizationInfo authorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
// 此处应为获取当前用户信息并根据信息查询其拥有的权限的逻辑
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// 权限赋予:demo测试写成固定权限,应查询数据库获得
authorizationInfo.addStringPermission("user:add");
// 角色赋予:demo测试写成固定角色,应查询数据库获得
authorizationInfo.addRole("tourist");
// 由shiro执行权限鉴别
return authorizationInfo;
}
/**
* 认证
* @param authenticationToken
* @return
* @throws AuthenticationException
*/
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("执行了认证=>doGetAuthenticationInfo");
// 在 token 中获得用户名
UsernamePasswordToken token = (UsernamePasswordToken) authenticationToken;
String principal = (String) token.getPrincipal();
// 此处应该为从数据库中查询用户信息的逻辑
// demo测试写成固定用户
if (!"[email protected]".equals(token.getUsername())) {
return null;
}
// 构造加密后的密码
Md5Hash md5Hash = new Md5Hash("123456", "salt", 1024);
// 由shiro执行密码的认证
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, md5Hash.toHex(), new MySimpleByteSource("salt"), this.getName());
}
}
上述过程中,对于“盐”的传递需要我们自定义一个类继承 ByteSource 和 Serializable 接口,因为 Shiro 提供的 ByteSource 接口没有实现序列化,故在使用 Redis 作为缓存时将产生序列化错误
MySimpleByteSource 代码如下:
/**
* @author zqf
*/
public class MySimpleByteSource implements ByteSource, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private byte[] bytes;
private String cachedHex;
private String cachedBase64;
public MySimpleByteSource(){
}
public MySimpleByteSource(byte[] bytes) {
this.bytes = bytes;
}
public MySimpleByteSource(char[] chars) {
this.bytes = CodecSupport.toBytes(chars);
}
public MySimpleByteSource(String string) {
this.bytes = CodecSupport.toBytes(string);
}
public MySimpleByteSource(ByteSource source) {
this.bytes = source.getBytes();
}
public MySimpleByteSource(File file) {
this.bytes = (new MySimpleByteSource.BytesHelper()).getBytes(file);
}
public MySimpleByteSource(InputStream stream) {
this.bytes = (new MySimpleByteSource.BytesHelper()).getBytes(stream);
}
public static boolean isCompatible(Object o) {
return o instanceof byte[] || o instanceof char[] || o instanceof String || o instanceof ByteSource || o instanceof File || o instanceof InputStream;
}
public void setBytes(byte[] bytes) {
this.bytes = bytes;
}
@Override
public byte[] getBytes() {
return this.bytes;
}
@Override
public String toHex() {
if(this.cachedHex == null) {
this.cachedHex = Hex.encodeToString(this.getBytes());
}
return this.cachedHex;
}
@Override
public String toBase64() {
if(this.cachedBase64 == null) {
this.cachedBase64 = Base64.encodeToString(this.getBytes());
}
return this.cachedBase64;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.bytes == null || this.bytes.length == 0;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.toBase64();
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return this.bytes != null && this.bytes.length != 0? Arrays.hashCode(this.bytes):0;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if(o == this) {
return true;
} else if(o instanceof ByteSource) {
ByteSource bs = (ByteSource)o;
return Arrays.equals(this.getBytes(), bs.getBytes());
} else {
return false;
}
}
private static final class BytesHelper extends CodecSupport {
private BytesHelper() {
}
public byte[] getBytes(File file) {
return this.toBytes(file);
}
public byte[] getBytes(InputStream stream) {
return this.toBytes(stream);
}
}
}
配置 Redis 缓存管理器
使用中一般集成 Redis 实现缓存,配置文件中配置 Redis 服务的地址
spring:
redis:
host: >
port: 6379
database: 0
自定义 RedisCache 继承 Cache 接口实现缓存的存取
/**
* Redis 缓存
* @param key
* @param value
*
* @author zqf
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class RedisCache<K, V> implements Cache<K, V> {
private String cacheName;
public RedisCache() {
}
public RedisCache(String cacheName) {
this.cacheName = cacheName;
}
/**
* 获取 redisTemplate 实例
*
* 因为没有交由容器管理,故无法直接注入
*
* @return redisTemplate
*/
private RedisTemplate getRedisTemplate() {
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = (RedisTemplate) ApplicationContextUtil.getBean("redisTemplate");
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
return redisTemplate;
}
@Override
public V get(K k) throws CacheException {
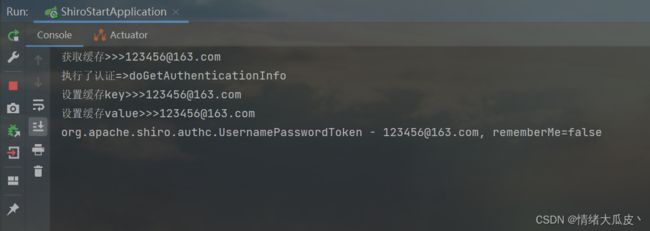
System.out.println("获取缓存>>>" + k);
return (V) getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().get(this.cacheName, k.toString());
}
@Override
public V put(K k, V v) throws CacheException {
System.out.println("设置缓存key>>>" + k);
System.out.println("设置缓存value>>>" + v);
getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().put(this.cacheName, k.toString(), v);
return null;
}
@Override
public V remove(K k) throws CacheException {
return (V) getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().delete(this.cacheName, k.toString());
}
@Override
public void clear() throws CacheException {
getRedisTemplate().delete(this.cacheName);
}
@Override
public int size() {
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().size(this.cacheName).intValue();
}
@Override
public Set<K> keys() {
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().keys(this.cacheName);
}
@Override
public Collection<V> values() {
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().values(this.cacheName);
}
}
获取 RedisTemplate 实例对象时,因为该类不能交由容器管理,故需要使用 spring 上下文工具类进行对象的获取
ApplicationContextUtil 代码如下:
/**
* spring 上下文工具类
*/
@Component
public class ApplicationContextUtil implements ApplicationContextAware {
/**
* 上下文对象实例
*/
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
ApplicationContextUtil.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
/**
* 获取applicationContext
*
* @return
*/
public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return applicationContext;
}
/**
* 通过name获取 Bean.
*
* @param name
* @return
*/
public static Object getBean(String name) {
return getApplicationContext().getBean(name);
}
/**
* 通过class获取Bean.
*
* @param clazz
* @param
* @return
*/
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz) {
return getApplicationContext().getBean(clazz);
}
/**
* 通过name,以及Clazz返回指定的Bean
*
* @param name
* @param clazz
* @param
* @return
*/
public static <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> clazz) {
return getApplicationContext().getBean(name, clazz);
}
}
自定义 RedisCacheManager 即 Redis 缓存管理器,继承 CacheManager 接口进行缓存管理
/**
* Redis 缓存管理
*
* @author zqf
*/
public class RedisCacheManager implements CacheManager {
@Override
public <K, V> Cache<K, V> getCache(String cacheName) throws CacheException {
System.out.println("缓存名称>>>"+ cacheName);
return new RedisCache<K,V>(cacheName);
}
}
配置类 ShiroConfig 实现各个组件的拼装
编写 ShiroConfig 类,对我们自定义的组件进行配置,配置类中主要需要完成三步工作
-
创建自定义的 Realm 对象
-
实现凭证匹配器的设置,设置加密算法,hash 次数等;
-
实现缓存管理器的设置,开启全局缓存,开启认证、鉴权缓存
-
-
创建 DefaultWebSecurityManager 安全管理器
- 实现安全管理器对 Realm 的关联
-
配置 ShiroFilterFactoryBean 用于拦截所有请求,进行认证与鉴权
-
为 filter 配置安全管理器
-
为 filter 配置资源审查的规则
-
为 filter 配置失败跳转页
-
/**
* @author zqf
*/
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
/**
* 创建自定义 Realm 对象
*/
@Bean
public UserRealm getUserRealm() {
// 创建 Realm
UserRealm userRealm = new UserRealm();
// 为 Realm 设置凭证匹配器
HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
// 设置凭证匹配器加密算法
credentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("md5");
// 设置凭证匹配器的 hash 次数
credentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024);
// 为 userRealm 配置凭证匹配器
userRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(credentialsMatcher);
// 为 userRealm 配置自定义的 RedisCacheManager 缓存管理器
userRealm.setCacheManager(new RedisCacheManager());
// 开启全局缓存
userRealm.setCachingEnabled(true);
// 开启认证缓存
userRealm.setAuthenticationCachingEnabled(true);
// 开启授权缓存
userRealm.setAuthorizationCachingEnabled(true);
return userRealm;
}
/**
* 创建 DefaultWebSecurityManager 安全管理器
*/
@Bean
public DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager(UserRealm userRealm) {
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
// 关联 Realm
securityManager.setRealm(userRealm);
return securityManager;
}
/**
* 配置 ShiroFilterFactoryBean,用于拦截所有请求
*
* anon:无需认证就可以访问
* authc:必须认证才可以访问
* user: 必须拥有记住我功能才能用
* roles:拥有某个角色权限才能访问
* perms:拥有对某个资源的权限才能访问
*/
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean(DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager) {
ShiroFilterFactoryBean factoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
// 为filter配置安全管理器
factoryBean.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
Map<String, String> filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// 为filter配置资源审查规则
// 必须登录之后才可以访问/user/* 下的所有请求
filterMap.put("/start/*", "authc");
// 鉴权,必须有相应的权限才能访问某接口
filterMap.put("/user/add", "perms[user:add]");
filterMap.put("/user/update", "perms[user:update]");
filterMap.put("/user/delete", "roles[admin]");
filterMap.put("/user/get", "roles[tourist]");
factoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap);
// 如果未登录,就跳转到登录页
factoryBean.setLoginUrl("/unLogin");
// 设置未授权请求
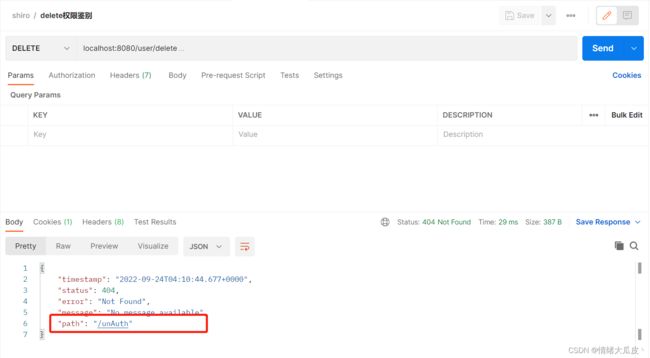
factoryBean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/unAuth");
return factoryBean;
}
}
编写控制层代码用于验证测试
登录登出控制层
/**
* @author zqf
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/start")
public class StartController {
@GetMapping("/login/{username}/{password}")
public String login(@PathVariable("username") String username,
@PathVariable("password") String password) {
// 获取当前用户
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// 执行登陆操作
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password);
try {
currentUser.login(token);
System.out.println(token);
return "登陆成功~";
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return "登陆失败~";
}
}
@GetMapping("/logout")
public String logout() {
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
currentUser.logout();
return "登出成功~";
}
}
操作控制层
/**
* @author zqf
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@PostMapping("/add")
public String add() {
return "执行新增成功~";
}
@DeleteMapping("/delete")
public String delete() {
return "执行删除成功~";
}
@PutMapping("/update")
public String update() {
return "执行更新成功~";
}
@GetMapping("/get")
public String get() {
return "查询到对应信息~";
}
}
相应的认证逻辑逻辑和方法所需的权限配置在前文已经介绍
测试使用
启动项目,访问登录接口,首先会尝试获取认证缓存执行认证,然后对缓存进行设置或更新
访问 /add 接口,首先尝试获取授权缓存进行鉴权,然后进行设置
访问 /delete 接口,此时直接村缓存中读取账号权限,鉴权失败,没有对应权限,故跳转"/unAuth"
退出登录直接访问 /add 接口,显示未登录,跳转“unLogin”