Ansible自动化运维
目录
一、简介
二、部署
1.环境
2.安装ansible服务器
3.免密ssh-key(可做可不做)
三、Ansible基础
1.定义主机清单
2.测试连通性
3.简介输出
四、Inventory-主机清单
1.增加主机组
2.增加用户名 密码
3.增加端口
4.组:变量
5.子分组
五、Ad-Hoc-点对点模式
1.shell模块
2.复制模块
3.用户模块
4.软件包管理
5.服务模块
6.文件模块
7.收集模块
六、YAML-非标记语言
1.语法
2.示例
七、Role-角色扮演
1.目录结构
2.编写任务
3.准备配置文件
4.编写变量
5.编写处理程序
6.编写剧本
7.实施
一、简介
ansible是新出现的自动化运维工具,基于Python开发,集合了众多运维工具(puppet、cfengine、chef、func、fabric)的优点,实现了批量系统配置、批量程序部署、批量运行命令等功能。
ansible是基于模块工作的,本身没有批量部署的能力。真正具有批量部署的是ansible所运行的模块,ansible只是提供一种框架。主要包括:
(1)、连接插件connection plugins:负责和被监控端实现通信;
(2)、host inventory:指定操作的主机,是一个配置文件里面定义监控的主机;
(3)、各种模块核心模块、command模块、自定义模块;
(4)、借助于插件完成记录日志邮件等功能;
(5)、playbook:剧本执行多个任务时,非必需可以让节点一次性运行多个任务。
二、部署
1.环境
一台服务器,四台客户机
ansible服务器做域名解析,客户机不需要配置
vim /etc/hosts
192.168.172.141 ansible
192.168.172.142 host1
192.168.172.143 host2
192.168.172.145 host3
192.168.172.146 host42.安装ansible服务器
[root@localhost ~]# yum install -y epel-release (安装epel源,使用的是阿里云的yum源)
[root@localhost ~]# yum install -y ansible(检查部署是否完成)
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -ql ansible(列出所有文件)
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -qc ansible(查看配置文件)
[root@localhost ~]# ansible --help(查看ansible帮助)
[root@localhost ~]# ansible-doc -l(看所有模块(A10,华为,docker,EC2,aws等等广大厂商设备))
[root@localhost ~]# ansible-doc -s yum(看yum模块,理解其功能)
3.免密ssh-key(可做可不做)
ssh-keygen
ssh-copy-id 192.168.172.142 (推送公钥,四台都要做)
ssh [email protected](登录测试)
三、Ansible基础
1.定义主机清单
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
host1
host2
host3
host42.测试连通性
ansible localhost -m ping(测试连通性,-m指定模块,什么功能,ping只是其中一个模块,还有shell,yum等等)3.简洁输出
ansible host1 -m ping -o(简洁输出)
ansible host1 -m ping -u root -k -o(成功不提示)四、Inventory-主机清单
1.增加主机组
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[webserver]
host1
host2
host3
host4
absible webserver -m ping -o2.增加用户名 密码
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[webserver]
#如果主机和主机的用户名密码不同,一个一个设置
host[1:4] ansible_ssh_user='root' ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
ansible webserver -m ping -o (免用户名和密码成功)
3.增加端口
将host1的sshd端口修改为222
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Port 222
systemctl restart sshd#在ansible上测试一下
ssh [email protected] -p 222
ansible webserver -m ping -o (失败,因为默认端口已更改)vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[webserver]
host1 ansible_ssh_user='root' ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
ansible_ssh_port='222'
host[2:4] ansible_ssh_user='root' ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
ansible webserver -m ping -o (此时可以看到连接成功)
#测试完成之后把端口号恢复原状4.组:变量
ansible内部变量可以帮助我们简化主机清单的设置
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[webserver]
host[1:4]
[webserver:vars]
ansible_ssh_user='root'
ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
ansible weserver -m ping -o| 参数 | 用途 | 例子 |
| ansible_ssh_host | 定义hosts ssh地址 | ansible_ssh_host=192.168.172.142 |
| ansible_ssh_port | 定义hosts ssh端口 | ansible_ssh_port=222 |
| ansible_ssh_user | 定义hosts ssh认证用户 | ansible_ssh_user=user |
| ansible_ssh_pass | 定义hosts ssh认证密码 | ansible_ssh_pass=pass |
| ansible_sudo | 定义hosts sudo用户 | ansible_sudo=www |
| ansible_sudo_pass | 定义hosts sudo密码 | ansible_sudo_pass=pass |
| ansible_sudo_exe | 定义hosts sudo路径 | ansible_sudo_exe=/usr/bin/sudo |
| ansible_connection | 定义hosts 连接方式 | ansible_connection=local |
| ansible_ssh_private_key_file | 定义hosts 私钥 | ansible_ssh_private_key_file=/root/key |
| ansible_ssh_shell_type | 定义hosts shell类型 | ansible_ssh_shell_type=bash |
| ansible_python_interpreter | 定义hosts 任务执行python路径 | ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python2.6 |
| ansible_*_interpreter | 定义hosts 其他语言解析路径 | ansible_*_interpreter=/usr/bin/ruby |
5.子分组
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[webserver1]
host[1:2]
[webserver2]
host[3:4]
[webserver:vars]
ansible_ssh_user='root'
ansible_ssh_pass='123456'五、Ad-Hoc-点对点模式
简介:临时的,在ansible中是指需要快速执行的单条命令,并且不需要保持的命令。
1.shell模块
ansible-doc shell (帮助)
ansible webserver -m shell -a 'hostname' -o
ansible webserver -m shell -a 'hostname' -o -f 2 (-f 2指定线程数)
ansible host1 -m -a 'yum -y install httpd' -o
ansible host1 -m shell -a 'uptime' -o (查询系统负载)2.复制模块
ansible-doc copy
ansible webserver -m copy -a 'src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/1.txt owner=root group=root mode=777'
ls /tmp/ -l3.用户模块
ansible-doc user(帮助)
ansible webserver -m user -a 'name=user1 state=persent'(创建用户)
echo '512050951' | openssh passwd -l -stdin (生成加密密码值)
ansible webserver -m user -a 'name=user1 password='加密密码值''
ssh user1@ip地址
ansible webserver -m user -a 'name=user1 shell=/sbin/nologin append='yes''(追加)
ansible webserver -m user -a 'name=user1 state=absent'(删除用户)
4.软件包管理
ansible-doc yum
ansible webserver -m yum -a 'name="*" state=latest' (升级所有包)
ansible webserver -m yum -a 'name="httpd" state=latest'(安装apache)5.服务模块
ansible-doc service (帮助)
ansible host2 -m service -a 'name=httpd state=started'(启动)
ansible host2 -m service -a 'name=httpd state=started enabled=yes'(开机自启动)
ansible host2 -m service -a 'name=httpd state=stopped'(停止)
ansible host2 -m service -a 'name=httpd state=restarted'(重启)
ansible host2 -m service -a 'name=httpd state=started enabled=no'(开机禁止启动)
6.文件模块
ansible-doc file
ansible host2 -m file -a 'path=/tmp/1.txt mode=777 state=touch'(创建文件)
ansible host2 -m file -a 'path=/tmp/99 mode=777 state=directory'7.收集模块
ansible-doc setup
ansible host1 -m setup
ansible host1 -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_all_ipv4_addresses'(调用的信息模块)六、YAML-非标记语言
1.语法
列表
fruits:
-Apple
-Orange
-Strawberry
-Mango
字典
martin:
name:Martin D'vloper
job:Developer
skill:Elite
2.示例
需求:通过YAML编写一个简单的剧本,完成web部署、配置、启动的全过程
准备工作
ansible all -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=removed' -o
yum install -y httpd (准备配置文件)
mkdir apache
cd apache
cp -ef /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf .
grep '^Listen' httpd.conf
vim httpd.conf
Liaten80改为Listen 8080编写剧本
vim apache.yaml
- hosts: webserver #-后面要加空格,:后面也要有空格,格式不能有错
tasks:
- name: install apache packages
yum: name=httpd state=present
- name: copy apache conf
copy: src=./httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- name: ensure apache is running
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes测试
ansible-playbook apache.yaml --syntax-check (检查是否有语法错误)
ansible-playbook apache.yaml --list-tasks (列出任务)
ansible-playbook apache.yaml --list-hosts (列出主机)
ansible-playbook apache.yaml (执行)
http://192.168.172.142:8080/ #不要忘记关闭防火墙,systemctl stop firewalld.service
http://192.168.172.143:8080/
http://192.168.172.144:8080/
http://192.168.172.145:8080/七、Role-角色扮演
简介:roles则是在ansible中,playbooks的目录组织结构。将代码或文件进行模块化,成为roles的文件目录组织结构,易读、代码可重用、层次清晰。
目标:通过role远程部署nginx并配置
1.目录结构
mkdir roles/nginx/{files,handlers,tasks,templates,vars} -p
touch roles/site.yaml roles/nginx/{handlers,tasks,vars}/main.yaml
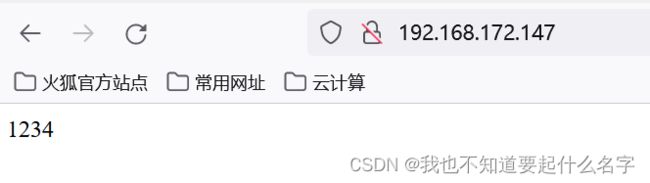
echo 1234 > roles/nginx/files/index.html
tree roles
nginx 角色名
files 普通文件
handlers 触发器程序
tasks 主任务
templates 金甲模式(有变量的文件)
vars 自定义变量
yum install -y nginx && cp /etc/nginx/nginx.conf roles/nginx/templates/nginx.conf.j22.编写任务
vim roles/nginx/tasks/main.yaml
---
- name: install epel-release packge
yum: name=epel-release state=latest
- name: install nginx packge
yum: name=nginx state=latest
- name: copy index.html
copy: src=index.html dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
- name: copy nginx.conf template
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify: restart nginx
- name: make sure nginx service running
service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes
3.准备配置文件
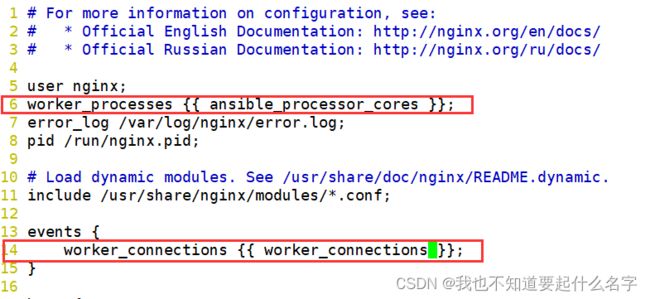
vim roles/nginx/templates/nginx.conf.j2
#找到文件中的worker_processes auto
worker_processes {{ ansible_processor_cores }};(ansible内置变量,调用cpu的数量)
worker_connections {{ worker_connections }};(自定义变量)
4.编写变量
vim roles/nginx/vars/main.yaml
worker_connection:10240
5.编写处理程序
vim roles/nginx/handlers/main.yaml
---
- name: restart nginx
service: name=nginx state=restarted6.编写剧本
vim /roles/site.yaml
- hosts: webserver
roles:
- nginx7.实施
cd roles
ansible-playbook site.yaml --syntax-check (测试)
ansible-playbook site.yaml (实施剧本)
http://192.168.172.142 (验证)
http://192.168.172.143
http://192.168.172.144
http://192.168.172.145
#根据自己实际的IP来