【Java数据结构】集合PriorityQueue及其背后的数据结构堆(优先级队列)
![]()
作者:渴望力量的土狗
博客主页:渴望力量的土狗的博客主页
专栏:数据结构与算法
工欲善其事必先利其器,给大家介绍一款超牛的斩获大厂offer利器——牛客网
点击免费注册和我一起刷题吧
目录
优先级队列(PriorityQueue)
优先级队列的概念
堆(Heap)
堆的概念
堆的性质
堆的存储方式
堆的创建:
调整方式:
大根堆实现代码:
小根堆实现代码:
建堆的时间复杂度
堆的插入与删除
堆的插入
堆的删除
用堆模拟实现优先级队列(完整代码)
常用接口介绍
PriorityQueue常用接口介绍
优先级队列(PriorityQueue)
优先级队列的概念
前面介绍过队列,队列是一种先进先出(FIFO)的数据结构,但有些情况下,操作的数据可能带有优先级,一般出队列时,可能需要优先级高的元素先出队列,该中场景下,使用队列显然不合适。在这种情况下,我们的数据结构应该提供两个最基本的操作,一个是返回最高优先级对象,一个是添加新的对象。这种数据结构就是优先级队列(Priority Queue)
JDK1.8中的PriorityQueue底层使用了堆的数据结构,而堆实际就是在完全二叉树的基础之上进行了一些元素的调整。
堆(Heap)
堆的概念
如果有一个关键码的集合K = {k0,k1, k2,…,kn-1},把它的所有元素按完全二叉树的顺序存储方式存储 在一个一维数组中,并满足:Ki <= K2i+1 且 Ki<= K2i+2 (Ki >= K2i+1 且 Ki >= K2i+2) i = 0,1,2…,则称为 小堆(或大堆)。将根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。
堆的性质
堆中某个节点的值总是不大于或不小于其父节点的值;
堆总是一棵完全二叉树。
堆的存储方式
从堆的概念可知,堆是一棵完全二叉树,因此可以层序的规则采用顺序的方式来高效存储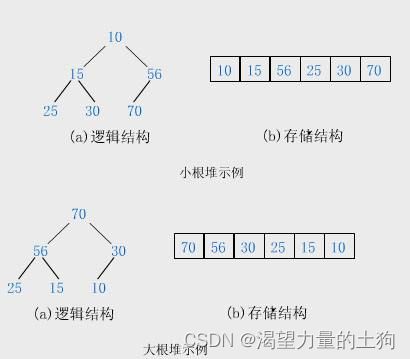
注意:对于非完全二叉树,则不适合使用顺序方式进行存储,因为为了能够还原二叉树,空间中必须要存储空节点,就会导致空间利用率比较低
堆的创建:
调整方式:
向下调整 是让调整的结点与其孩子节点进行比较
向上调整 是让调整的结点与其父亲结点进行比较
已知双亲的下标,则左孩子的下标为:left=2parent+1;
则右孩子的下标为:left=2parent+2;
已知孩子结点(不区分左右)的下标,则双亲的下标为:(child-1)/2
大根堆实现代码:
public class TestHeap {
public int[]elem;
public int usedSize;
public static final int DEFAULT_SIZE=10;
public TestHeap() {
elem=new int[DEFAULT_SIZE];
}
public void initElem(int[]arr){
for(int i=0;i=0;parent--){
//进行调整
shiftDown(parent,usedSize);
}
}
/**
*
* @param root 每颗子树的根
* @param len 每颗子树结束的位置
*/
public void shiftDown(int root,int len){
int child=2*root+1;
//保证有左孩子
while (childelem[root]){
int temp=elem[child];
elem[child]=elem[root];
elem[root]=temp;
root=child;
child=2*root+1;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
}
小根堆实现代码:
public class TestHeap {
public int[]elem;
public int usedSize;
public static final int DEFAULT_SIZE=10;
public TestHeap() {
elem=new int[DEFAULT_SIZE];
}
public void initElem(int[]arr){
for(int i=0;i=0;parent--){
//进行调整
shiftDown(parent,usedSize);
}
}
/**
*
* @param root 每颗子树的根
* @param len 每颗子树结束的位置
*/
public void shiftDown(int root,int len){
int child=2*root+1;
//保证有左孩子
while (childelem[child+1]){
//特别注意这个判断的条件(保证有右孩子才能执行下面的操作)
child++;//右移
}
//现在child下标一定是左右孩子的最小值的下标
//判断root下标的值和孩子的最大值
// if(elem[child]>elem[root]){
// int temp=elem[child];
// elem[child]=elem[root];
// elem[root]=temp;
// root=child;
// child=2*root+1;
// }else{
// break;
// }
//判断root下标的值和孩子的最小值
if(elem[child] 建堆的时间复杂度
因为堆是完全二叉树,而满二叉树也是完全二叉树,此处为了简化使用满二叉树来证明(时间复杂度本来看的就是近似值,多几个节点不影响最终结果):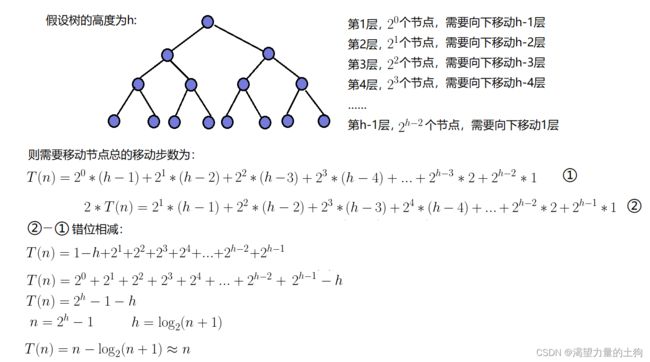 因此:建堆的时间复杂度为O(N)
因此:建堆的时间复杂度为O(N)
堆的插入与删除
堆的插入
堆的插入总共需要两个步骤:
1. 先将元素放入到底层空间中(注意:空间不够时需要扩容)
2. 将最后新插入的节点向上调整,直到满足堆的性质
/**
* 入队:仍然要保持是大根堆
* @param val
*/
public void push(int val) {
if(isFull()){
elem= Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
elem[usedSize]=val;
usedSize++;
shiftUp(usedSize-1);
}
private void shiftUp(int child) {
int parent=(child-1)/2;
while(child>0)
if(elem[child]>elem[parent]){
int temp=elem[child];
elem[child]=elem[parent];
elem[parent]=temp;
child=parent;
parent=(child-1)/2;
}else{
break;
}
}堆的删除
注意:堆的删除一定删除的是堆顶元素。具体如下:
1. 将堆顶元素对堆中最后一个元素交换
2. 将堆中有效数据个数减少一个
3. 对堆顶元素进行向下调整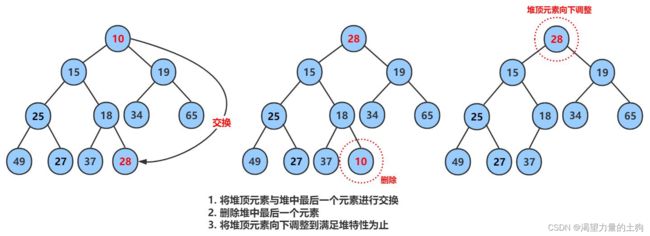
public void pollHeap() {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException();
}
int temp=elem[0];
elem[0]=elem[usedSize-1];
elem[usedSize-1]=temp;
usedSize--;
//保证依然是大根堆
shiftDown(0,usedSize);
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return usedSize==0;
}
/**
*
* @param root 是每棵子树的根节点的下标
* @param len 是每棵子树调整结束的结束条件
* 向下调整的时间复杂度:O(logn)
*/
private void shiftDown(int root,int len) {
int child=2*root+1;
while(child用堆模拟实现优先级队列(完整代码)
import java.util.Arrays;
public class PriorityQueue {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public static final int DEFAULT_INIT_USESZIE=10;
public PriorityQueue() {
elem=new int[DEFAULT_INIT_USESZIE];
}
/**
* 建堆的时间复杂度:O(n)
*
* @param array
*/
public void createHeap(int[] array) {
for(int i=0;i=0;parent--){
shiftDown(parent,usedSize);
}
}
/**
*
* @param root 是每棵子树的根节点的下标
* @param len 是每棵子树调整结束的结束条件
* 向下调整的时间复杂度:O(logn)
*/
private void shiftDown(int root,int len) {
int child=2*root+1;
while(child0)
if(elem[child]>elem[parent]){
int temp=elem[child];
elem[child]=elem[parent];
elem[parent]=temp;
child=parent;
parent=(child-1)/2;
}else{
break;
}
}
public boolean isFull() {
return usedSize== elem.length;
}
/**
* 出队【删除】:每次删除的都是优先级高的元素
* 仍然要保持是大根堆
*/
public void pollHeap() {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException();
}
int temp=elem[0];
elem[0]=elem[usedSize-1];
elem[usedSize-1]=temp;
usedSize--;
//保证依然是大根堆
shiftDown(0,usedSize);
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return usedSize==0;
}
/**
* 获取堆顶元素
* @return
*/
public int peekHeap() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return elem[0];
}
} 常用接口介绍
Java集合框架中提供了PriorityQueue和PriorityBlockingQueue两种类型的优先级队列,PriorityQueue是线程不安全的,PriorityBlockingQueue是线程安全的,本文主要介绍PriorityQueue。
关于PriorityQueue的使用要注意:
1. 使用时必须导入PriorityQueue所在的包,即:
import java.util.PriorityQueue;2. PriorityQueue中放置的元素必须要能够比较大小,不能插入无法比较大小的对象,否则会抛出
ClassCastException异常
3. 不能插入null对象,否则会抛出NullPointerException
4. 没有容量限制,可以插入任意多个元素,其内部可以自动扩容
5. 插入和删除元素的时间复杂度为
6. PriorityQueue底层使用了堆数据结构, (注意:此处大家可以不用管什么是堆,后文中有介绍)
7. PriorityQueue默认情况下是小堆---即每次获取到的元素都是最小的元素
PriorityQueue常用接口介绍
| 构造器 | 功能介绍 |
| PriorityQueue() | 创建一个空的优先级队列,默认容量是11 |
| PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity) |
创建一个初始容量为initialCapacity的优先级队列,注意: initialCapacity不能小于1,否则会抛IllegalArgumentException异 常 |
| PriorityQueue(Collection extends E> c) | 用一个集合来创建优先级队列 |
注意:默认情况下,PriorityQueue队列是小堆,如果需要大堆需要用户提供比较器
// 用户自己定义的比较器:直接实现Comparator接口,然后重写该接口中的compare方法即可
class IntCmp implements Comparator{
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2-o1;
}
}
public class TestPriorityQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue p = new PriorityQueue<>(new IntCmp()); 插入/删除/获取优先级最高的元素
| 函数名 | 功能介绍 |
| boolean offer(E e) |
插入元素e,插入成功返回true,如果e对象为空,抛出NullPointerException异常,时 间复杂度 ,注意:空间不够时候会进行扩容 |
| E peek() | 获取优先级最高的元素,如果优先级队列为空,返回null |
| E poll() | 移除优先级最高的元素并返回,如果优先级队列为空,返回null |
| int size() | 获取有效元素的个数 |
| void clear() |
清空 |
| boolean isEmpty() |
检测优先级队列是否为空,空返回true |
