Linux网络编程基础API
为何需要半关闭
考虑以下情况:
- 一旦客户端连接到服务器,服务器将约定的文件传输给客户端,客户端收到后发送字符串「Thank you」给服务器端。
此处「Thank you」的传递是多余的,这只是用来模拟客户端断开连接前还有数据要传输的情况。此时程序实现的难度并不小,因为传输文件的服务器端只需连续传输文件数据即可,而客户端无法知道需要接收数据到何时。客户端也没办法无休止的调用输入函数,因为这有可能导致程序阻塞。
- 是否可以让服务器和客户端约定一个代表文件尾的字符?
这种方式也有问题,因为这意味这文件中不能有与约定字符相同的内容。为了解决该问题,服务端应最后向客户端传递 EOF 表示文件传输结束。客户端通过函数返回值接受 EOF ,这样可以避免与文件内容冲突。那么问题来了,服务端如何传递 EOF?
- 断开输出流时向主机传输 EOF。
当然,调用 close 函数的同时关闭 I/O 流,这样也会向对方发送 EOF 。但此时无法再接受对方传输的数据。换言之,若调用 close 函数关闭流,就无法接受客户端最后发送的字符串「Thank you」。这时需要调用 shutdown 函数,只关闭服务器的输出流。这样既可以发送 EOF ,同时又保留了输入流。下面实现收发文件的服务器端/客户端。
基于TCP的半关闭
#include- __fd:需要断开的套接字文件描述符。
- __how:传递断开方式信息。
- SHUT_RD =不再接收;
- SHUT_WR =不再传输;
- SHUT_RDWR =不再接收和传输。
TCP数据读写
/* Send N bytes of BUF to socket FD. Returns the number sent or -1.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern ssize_t send (int __fd, const void *__buf, size_t __n, int __flags);
/* Read N bytes into BUF from socket FD.
Returns the number read or -1 for errors.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern ssize_t recv (int __fd, void *__buf, size_t __n, int __flags);
- recv读取sockfd上的数据,buf和len参数分别指定读缓冲区的位置和大小,flags参数通常设置为0即可。recv 成功时返回实际读取到的数据的长度,它可能小于我们期望的长度len。因此我们可能要多次调用recv,才能读取到完整的数据。recv 可能返回0,这意昧着通信对方已经关闭连接了。recv 出错时返回-1并设置errno。
- send往sockfd上写入数据,buf和len参数分别指定写缓冲区的位置和大小。send成功时返回实际写人的数据的长度,失败则返回-1并设置ermo。
flags参数为数据收发提供了额外的控制,它可以取表所示选项中的一个或几个的逻辑或。
UDP数据读写
/* Send N bytes of BUF on socket FD to peer at address ADDR (which is
ADDR_LEN bytes long). Returns the number sent, or -1 for errors.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern ssize_t sendto (int __fd, const void *__buf, size_t __n,
int __flags, __CONST_SOCKADDR_ARG __addr,
socklen_t __addr_len);
/* Read N bytes into BUF through socket FD.
If ADDR is not NULL, fill in *ADDR_LEN bytes of it with tha address of
the sender, and store the actual size of the address in *ADDR_LEN.
Returns the number of bytes read or -1 for errors.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern ssize_t recvfrom (int __fd, void *__restrict __buf, size_t __n,
int __flags, __SOCKADDR_ARG __addr,
socklen_t *__restrict __addr_len);
- recvfrom读取sockfd上的数据,buf 和len参数分别指定读缓冲区的位置和大小。因为UDP通信没有连接的概念,所以我们每次读取数据都需要获取发送端的socket地址,即参数src_ addr 所指的内容,addrlen 参数则指定该地址的长度。
- sendto往sockfd.上写人数据,buf 和len参数分别指定写缓冲区的位置和大小。dest addr参数指定接收端的socket地址,addrlen 参数则指定该地址的长度。这两个系统调用的flags参数以及返回值的含义均与send/recv系统调用的flags 参数及返回值相同。值得一提的是,recvfrom/sendto 系统调用也可以用于面向连接(STREAM)的socket的数据读写,只需要把最后两个参数都设置为NULL以忽略发送端/接收端的socket地址(因为我们已经和对方建立了连接,所以已经知道其socket地址了)。
通用数据读写函数
/* Structure for scatter/gather I/O. */
struct iovec
{
void *iov_base; /* Pointer to data. */
size_t iov_len; /* Length of data. */
};
/* Structure describing messages sent by
`sendmsg' and received by `recvmsg'. */
struct msghdr
{
void *msg_name; /* Address to send to/receive from. */
socklen_t msg_namelen; /* Length of address data. */
struct iovec *msg_iov; /* Vector of data to send/receive into. */
size_t msg_iovlen; /* Number of elements in the vector. */
void *msg_control; /* Ancillary data (eg BSD filedesc passing). */
size_t msg_controllen; /* Ancillary data buffer length.
!! The type should be socklen_t but the
definition of the kernel is incompatible
with this. */
int msg_flags; /* Flags on received message. */
};
/* Receive a message as described by MESSAGE from socket FD.
Returns the number of bytes read or -1 for errors.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern ssize_t recvmsg (int __fd, struct msghdr *__message, int __flags);
- msg_name成员指向–个socket地址结构变量。它指定通信对方的socket地址。对于面向连接的TCP协议,该成员没有意义,必须被设置为NULL,这是因为对数据流socket而言,对方的地址已经知道。
- msg_namelen成员则指定了msg_name 所指socket地址的长度。
- 由上可见,iovec结构体封装了一块内存的起始位置和长度。msg_iovlen指定这样的iovec结构对象有多少个。对于recvmsg而言,数据将被读取并存放在msg_ jiovlen 块分散的内存中,这些内存的位置和长度则由msg_iov指向的数组指定,这称为分散读(satter read);对于sendmsg而言,msg_iovlen 块分散内存中的数据将被-并发送,这称为集中写(gather write)。
- msg_ control 和msg_ controllen 成员用于辅助数据的传送。
- msg_ fags成员无须设定,它会复制recvmsg/sendmsg的flags参数的内容以影响数据读写过程。recvmsg 还会在调用结束前,将某些更新后的标志设置到msg. flags 中。recvmsg/sendmsg的flags 参数以及返回值的含义均与send/recv的flags参数及返回值相同。
外带标记
在实际应用中,我们通常无法预期带外数据何时到来。好在Linux内核检测到TCP紧急标志时,将通知应用程序有带外数据需要接收。内核通知应用程序带外数据到达的两种常见方式是: 1O复用产生的异常事件和SIGURG信号。但是,即使应用程序得到了有带外数据需要接收的通知,还需要知道带外数据在数据流中的具体位置,才能准确接收带外数据。这- -点可通过如下系统调用实现:
#ifdef __USE_XOPEN2K
/* Determine whether socket is at a out-of-band mark. */
extern int sockatmark (int __fd) __THROW;
#endif
sockatmark判断sockfd是否处于带外标记,即下一个被读取到的数据是否是带外数据。如果是,sockatmark 返回I,此时我们就可以利用带MSG_0OB标志的reev调用来接收带外数据。如果不是,则sockatmark返回0。
地址信息函数
/* Put the local address of FD into *ADDR and its length in *LEN. */
extern int getsockname (int __fd, __SOCKADDR_ARG __addr,
socklen_t *__restrict __len) __THROW;
/* Put the address of the peer connected to socket FD into *ADDR
(which is *LEN bytes long), and its actual length into *LEN. */
extern int getpeername (int __fd, __SOCKADDR_ARG __addr,
socklen_t *__restrict __len) __THROW;
- getsockname获取sockfd对应的本端socket地址,并将其存储于address参数指定的内存中,该socket地址的长度则存储于address_len参数指向的变量中。如果实际socket地址的长度大于address所指内存区的大小,那么该socket地址将被截断。getsockname 成功时返回0,失败返回-1并设置errno。
- getpeemame获取sockfd对应的远端socket地址,其参数及返回值的含义与getsockname的参数及返回值相同。
socket选项
/* Put the current value for socket FD's option OPTNAME at protocol level LEVEL
into OPTVAL (which is *OPTLEN bytes long), and set *OPTLEN to the value's
actual length. Returns 0 on success, -1 for errors. */
extern int getsockopt (int __fd, int __level, int __optname,
void *__restrict __optval,
socklen_t *__restrict __optlen) __THROW;
/* Set socket FD's option OPTNAME at protocol level LEVEL
to *OPTVAL (which is OPTLEN bytes long).
Returns 0 on success, -1 for errors. */
extern int setsockopt (int __fd, int __level, int __optname,
const void *__optval, socklen_t __optlen) __THROW;
//成功时返回0,失败时返回-1并设置error
sockfd参数指定被操作的目标socket。level 参数指定要操作哪个协议的选项(即属性),比如IPv4、IPv6、 TCP等。option_ name 参数则指定选项的名字。我们在表中列举了socket通信中几个比较常用的socket 选项。option_ value 和option_ len 参数分别是被操作选项的值和长度。不同的选项具有不同类型的值,如表中“数据类型”一列所示。
值得指出的是,对服务器而言,有部分socket选项只能在调用listen系统调用前针对业听socket设置才有效。这是因为连接socket只能由accept调用返回,而accept从listen听队列中接受的连接至少已经完成了TCP三次握手的前两个步骤(因为listen监听队列的连接至少已进入SYN_ RCVD状态,这说明服务器已经往接受连接上发送出了TCP同步报文段。但有的socket选项却应该在TCP同步报文段中设置,比如TCP最大报文段选项。对这种情况,Linux给开发人员提供的解决方案是:对监听socket设置这些socket选项,那么accept返回的连接socket将自动继承这些选项。这些socket选项包括: SO_DEBUG、SO_DONTROUTE、SO_KEEPALIVE、SO_LINGER、SO_OOBINLINE、SO_RCVBUF、SO_RCVLOWAT、sO_SNDBUF、SO_SNDLOWAT、TCP_MAXSEG和TCP_NODELAY。而对客户端而言,这些socket选项则应该在调用connect函数之前设置,因为connect调用成功返回之后,TCP三次握手已完成。
网络信息API
利用域名获取IP地址
IP地址比域名发生变更的概率要高,所以利用IP地址编写程序并非上策。
#include- h_name:该变量中存有官方域名(Official domain name)。官方域名代表某一主页,但实际上,一些著名公司的域名并没有用官方域名注册。
- h_aliases:可以通过多个域名访问同一主页。同一IP可以绑定多个域名,因此,除官方域名外还可以指定其他域名。这些信息可以通过 h_aliases 获得。
- h_addrtype:gethostbyname 函数不仅支持 IPV4 还支持 IPV6 。因此可以通过此变量获取保存在- - h_addr_list 的IP地址族信息。若是 IPV4 ,则此变量中存有 AF_INET。
- h_length:保存IP地址长度。若是 IPV4 地址,因为是 4 个字节,则保存4;IPV6 时,因为是 16 个字节,故保存16。
- h_addr_list:这个是最重要的的成员。通过此变量以整数形式保存域名相对应的IP地址。另外,用户比较多的网站有可能分配多个IP地址给同一个域名,利用多个服务器做负载均衡,此时可以通过此变量获取IP地址信息。
- __name:传入的域名。
调用 gethostbyname 函数后,返回的结构体变量如图:
利用IP地址获取域名
/* Return entry from host data base which address match ADDR with
length LEN and type TYPE.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern struct hostent *gethostbyaddr (const void *__addr, __socklen_t __len,int __type);
//成功时返回 hostent 结构体地址,失败时返回 NULL 指针。
- addr: 含有IP地址信息的 in_addr 结构体指针。为了同时传递 IPV4 地址之外的全部信息,该变量的类型声明为 char 指针;
- len: 向第一个参数传递的地址信息的字节数,IPV4时为 4 ,IPV6 时为16;
- family: 传递地址族信息,ipv4 是 AF_INET ,IPV6是 AF_INET6。
getaddrinfo
getaddrinfo函数既能通过主机名获得IP地址(内部使用的是gethostbyname函数),也能通过服务名获得端口号(内部使用的是getservbyname函数)。它是否可重人取决于其内部调用的gethostbyname和getservbyname函数是否是它们的可重人版本。该函数的定义如下:
/* Extension from POSIX.1:2001. */
#ifdef __USE_XOPEN2K
/* Structure to contain information about address of a service provider. */
struct addrinfo
{
int ai_flags; /* Input flags. */
int ai_family; /* Protocol family for socket. */
int ai_socktype; /* Socket type. */
int ai_protocol; /* Protocol for socket. */
socklen_t ai_addrlen; /* Length of socket address. */
struct sockaddr *ai_addr; /* Socket address for socket. */
char *ai_canonname; /* Canonical name for service location. */
struct addrinfo *ai_next; /* Pointer to next in list. */
};
/* Translate name of a service location and/or a service name to set of
socket addresses.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int getaddrinfo (const char *__restrict __name,
const char *__restrict __service,
const struct addrinfo *__restrict __req,
struct addrinfo **__restrict __pai);
hostname参数可以接收主机名,也可以接收字符串表示的IP地址(IPv4 采用点分十进制字符串,IPv6则采用十六进制字符串)。同样,service 参数可以接收服务名,也可以接收字符串表示的十进制端口号。hints参数是应用程序给getaddrinfo的一个提示,以对getaddrinfo的输出进行更精确的控制。hints 参数可以被设置为NULL,表示允许getaddrinfo反馈任何可用的结果。result 参数指向一个链表,该链表用于存储getaddrinfo 反馈的结果。
addrinfo结构体中,ai_ protocol 成员是指具体的网络协议,其含义和socket系统调用的第三个参数相同,它通常被设置为0。ai_fags 成员可以取表中的标志的按位或。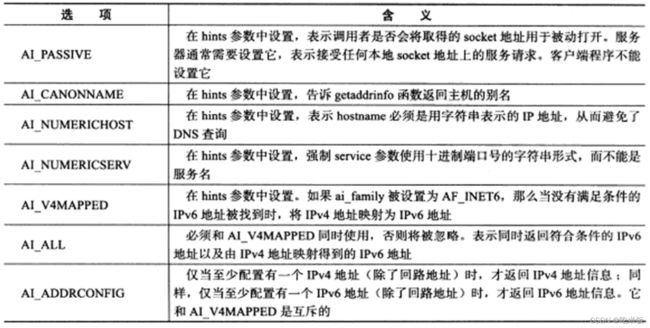 当我们使用hints参数的时候,可以设置其ai_flags,ai_family,ai_socktype和ai_protocol四个字段,其他字段则必须被设置为NULL。
当我们使用hints参数的时候,可以设置其ai_flags,ai_family,ai_socktype和ai_protocol四个字段,其他字段则必须被设置为NULL。
getaddrinfo 将隐式地分配堆内存(可以通过valgrind等工具查看),因为res指针原本是没有指向一块合法内存的,所以,getaddrinfo 调用结束后,我们必须使用如下配对函数来释放这块内存。
/* Free `addrinfo' structure AI including associated storage. */
extern void freeaddrinfo (struct addrinfo *__ai) __THROW;
getnameinfo
/* Translate a socket address to a location and service name.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int getnameinfo (const struct sockaddr *__restrict __sa,
socklen_t __salen, char *__restrict __host,
socklen_t __hostlen, char *__restrict __serv,
socklen_t __servlen, int __flags);
#endif /* POSIX */
getnameinfo函数能通过socket地址同时获得以字符串表示的主机名(内部使用的是gethostbyaddr函数)和服务名(内部使用的是getservbyport函数)。它是否可重人取决于其内部调用的gethostbyaddr和getservbyport 函数是否是它们的可重人版本。该函数的定义getnameinfo将返回的主机名存储在host参数指向的缓存中,将服务名存储在serv参数指向的缓存中,hostlen和servlen参数分别指定这两块缓存的长度。flags参数控制getnameinfo的行为,它可以接收表的选项。

getnameinfo和getaddrinfo函数成功时返回0,失败时返回错误码,可能的错误码如表:
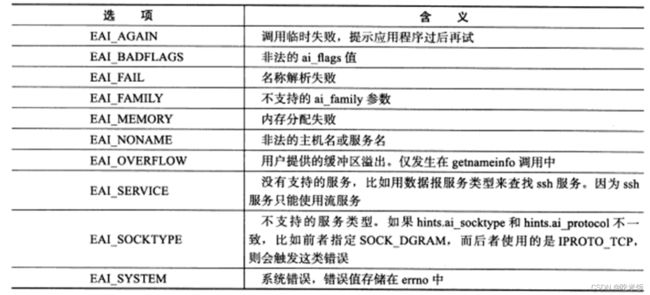
Linux下strerror函数能将数值错误码error转换成易读的字符串形式,同样下面的函数可将表错误码转换成字符串形式。
/* Convert error return from getaddrinfo() to a string. */
extern const char *gai_strerror (int __ecode) __THROW;
代码
#include \n" , argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
// 把参数传递给函数,返回结构体
host = gethostbyname(argv[1]);
if (!host)
error_handling("gethost... error");
// 输出官方域名
printf("Official name: %s \n", host->h_name);
// Aliases 解析的 cname 域名
for (i = 0; host->h_aliases[i]; i++)
printf("Aliases %d: %s \n", i + 1, host->h_aliases[i]);
//看看是不是ipv4
printf("Address type: %s \n",
(host->h_addrtype == AF_INET) ? "AF_INET" : "AF_INET6");
// 输出ip地址信息
for (i = 0; host->h_addr_list[i]; i++)
printf("IP addr %d: %s \n", i + 1,
inet_ntoa(*(struct in_addr *)host->h_addr_list[i]));
return 0;
}
void error_handling(char *message)
{
fputs(message, stderr);
fputc('\n', stderr);
exit(1);
}
#include \n" , argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
memset(&addr, 0, sizeof(addr));
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[1]);
host = gethostbyaddr((char *)&addr.sin_addr, 4, AF_INET);
if (!host)
{
error_handling("gethost... error");
}
printf("Official name: %s \n", host->h_name);
for (int i = 0; host->h_aliases[i]; i++)
{
printf("Aliases %d:%s \n", i + 1, host->h_aliases[i]);
}
printf("Address type: %s \n",(host->h_addrtype == AF_INET) ? "AF_INET" : "AF_INET6");
for (int i = 0; host->h_addr_list[i]; i++)
{
printf("IP addr %d: %s \n", i + 1,inet_ntoa(*(struct in_addr *)host->h_addr_list[i]));
}
return 0;
}
void error_handling(char *message)
{
fputs(message, stderr);
fputc('\n', stderr);
exit(1);
}