Qt中信号槽的概念和部分应用
目录
1. 信号槽的概念
2. 函数原型
2.1 自带信号 → 自带槽
2.2 自带信号 → 自定义槽
2.3 自定义信号
3. 参数传递
3.1 全局参数
3.2 信号槽传参
4. 对应关系
4.1 一对多
4.2 多对一
1. 信号槽的概念
如果让按钮能在用户点击后执行某个代码,就需要用到Qt中的信号槽机制。
信号槽是Qt基于C++语法上新增的特性,可以实现对象之间的通信,形成一定因果关系。
使用信号槽的对象需要具备两个条件:
- 通信的对象必须继承自QObject
- 类中要有Q_OBJECT宏
2. 函数原型
QObject类是所有Qt对象的基类,此类中有一个静态成员函数connect,用于连接信号槽之间的因果关系,函数原型如下:
参数1:发射者,通信的对象,此对象是信号槽触发的来源,例如:按钮对象(n.)
参数2:信号函数,使用SIGNAL()包裹,表示发射者触发的效果,例如:点击(v.)
参数3:接收者,通信对象,此对象是执行结果代码的主体(n.)
参数4:槽函数,使用SLOT()包裹,表示接收者要执行的函数(v.)
为了方便讲解各种场景下使用信号槽的不同方式,分别使用三种类型进行讲解:
- 自带信号 → 自带槽
- 自带信号 → 自定义槽
- 自定义信号 → 槽函数
2.1 自带信号 → 自带槽
这是最简单的一种连接方式,因为信号函数和槽函数都在Qt中预设了,只需要通过connect函数“连线”即可。
【例子】点击按钮,关闭窗口。
分析:
参数1,按钮对象;
参数2,点击函数;
参数3,窗口对象;
参数4:关闭函数。
dialog.h
#ifndef DIALOG_H
#define DIALOG_H
#include
#include
class Dialog : public QDialog
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
Dialog(QWidget *parent = 0);
~Dialog();
private:
QPushButton* btn;
};
#endif // DIALOG_H dialog.cpp
#include "dialog.h"
Dialog::Dialog(QWidget *parent)
: QDialog(parent)
{
resize(300,300);
btn = new QPushButton("关闭",this);
btn->move(100,100);
// 参数1,按钮对象 btn
// 参数2,点击函数 void clicked()
// 参数3,窗口对象 this
// 参数4:关闭函数 bool close()
connect(btn,SIGNAL(clicked()),this,SLOT(close()));
}
Dialog::~Dialog()
{
delete btn;
}
2.2 自带信号 → 自定义槽
这种方式是使用频率最高的一种连接方式,因为Qt源代码中不可能囊括所有要执行的代码。实际上槽函数是一种特殊的成员函数,编写方式基本等同成员函数。
【例子】点击按钮,左下角移动窗口并输出移动后的窗口坐标。
dialog.h
#ifndef DIALOG_H
#define DIALOG_H
#include
#include
#include
class Dialog : public QDialog
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
Dialog(QWidget *parent = 0);
~Dialog();
private:
QPushButton* btn;
// 私有槽函数
private slots:
// 声明自定义槽函数
void mySlot();
};
#endif // DIALOG_H dialog.cpp
#include "dialog.h"
Dialog::Dialog(QWidget *parent)
: QDialog(parent)
{
resize(300,300);
btn = new QPushButton("移动并输出",this);
btn->move(100,100);
// 连接信号槽
connect(btn,SIGNAL(clicked()),this,SLOT(mySlot()));
}
void Dialog::mySlot()
{
// 获得当前坐标
int x = this->x();
int y = this->y();
// 移动窗口
move(x+10,y+10);
// 输出
qDebug() << x << y;
}
Dialog::~Dialog()
{
delete btn;
}
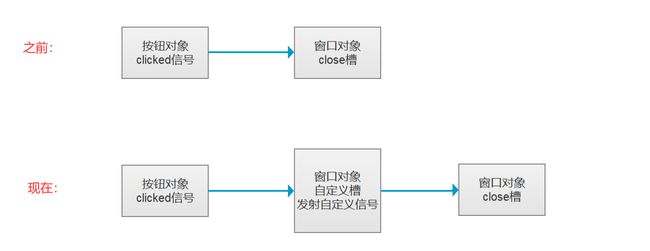
2.3 自定义信号
自定义信号主要用于后期一些相对复杂的通信场景,本次学习强行使用,并不是功能实现的最优解。
信号函数是非常特殊的一种函数,只有声明,没有定义,且不能在代码中直接调用,可以配合emit关键字进行发射。
【例子】点击按钮,关闭窗口。
dialog.h
#ifndef DIALOG_H
#define DIALOG_H
#include
#include
class Dialog : public QDialog
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
Dialog(QWidget *parent = 0);
~Dialog();
private:
QPushButton *btn;
// 自定义槽函数
private slots:
void mySlot();
// 声明信号函数,只声明
signals:
void mySignal();
};
#endif // DIALOG_H dialog.cpp
#include "dialog.h"
Dialog::Dialog(QWidget *parent)
: QDialog(parent)
{
resize(500,500);
btn = new QPushButton("关闭",this);
btn->move(200,300);
connect(btn,SIGNAL(clicked()),this,SLOT(mySlot()));
connect(this,SIGNAL(mySignal()),this,SLOT(close()));
}
// 自定义槽函数
void Dialog::mySlot()
{
// 发射自定义信号
emit mySignal();
}
Dialog::~Dialog()
{
delete btn;
}
3. 参数传递
【例子】点击按钮,按钮上显示点击的次数。
提示:
QPushButton显示文字的属性:
- text : QString
getter:QString text() const
setter:void setText(const QString & text)
3.1 全局参数
本次使用成员变量作为一个对象内部的全局参数,根据实际情况也可以使用静态变量。
dialog.h
#ifndef DIALOG_H
#define DIALOG_H
#include
#include
class Dialog : public QDialog
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
Dialog(QWidget *parent = 0);
~Dialog();
private:
int count; // 记录点击的次数
QPushButton* btn;
private slots:
void btnClickedSlot(); // 按钮点击的槽函数
};
#endif // DIALOG_H
dialog.cpp
#include "dialog.h"
Dialog::Dialog(QWidget *parent)
: QDialog(parent)
{
count = 0; // 属性赋予初始值
resize(300,400);
btn = new QPushButton("0",this);
btn->move(100,250);
connect(btn,SIGNAL(clicked()),
this,SLOT(btnClickedSlot()));
}
void Dialog::btnClickedSlot()
{
// 计数+1
count++;
// int → QString
QString text = QString::number(count);
// 设置显示
btn->setText(text);
}
Dialog::~Dialog()
{
delete btn;
}
3.2 信号槽传参
使用信号槽也可以进行参数传递,但是这种方式通常用户后面较为复杂的情况,本次讲解的代码也不是最优解。
dialog.h
#ifndef DIALOG_H
#define DIALOG_H
#include
#include
class Dialog : public QDialog
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
Dialog(QWidget *parent = 0);
~Dialog();
private:
QPushButton *btn;
private slots:
void mySlot1(); // 自定义槽函数1
void mySlot2(int); // 自定义槽函数2
signals:
// 带参数的自定义信号函数
void mySignal(int);
};
#endif // DIALOG_H
dialog.cpp
#include "dialog.h"
Dialog::Dialog(QWidget *parent)
: QDialog(parent)
{
resize(300,300);
btn = new QPushButton("0",this);
connect(btn,SIGNAL(clicked()),this,SLOT(mySlot1()));
connect(this,SIGNAL(mySignal(int)),this,SLOT(mySlot2(int)));
}
Dialog::~Dialog()
{
delete btn;
}
void Dialog::mySlot1()
{
// 静态局部变量
static int count = 0;
// 发射自定义信号
emit mySignal(++count);
}
void Dialog::mySlot2(int count)
{
// int → QString
QString text = QString::number(count);
// 设置显示
btn->setText(text);
}
需要注意的是:
1. 理论上可以通过信号槽发送任意多个参数
2. 信号函数的参数个数必须大于等于槽函数的参数个数
3. 参数类型必须一致
4. 对应关系
4.1 一对多
同一个信号可以同时连接多个槽函数,也可以把这多个槽函数合并为一个槽函数。
dialog.h
#ifndef DIALOG_H
#define DIALOG_H
#include
#include
#include
class Dialog : public QDialog
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
Dialog(QWidget *parent = 0);
~Dialog();
private:
QPushButton* btn1;
QPushButton* btn2;
private slots:
void mySlot1();
void mySlot2();
void mySlot3();
};
#endif // DIALOG_H dialog.cpp
#include "dialog.h"
Dialog::Dialog(QWidget *parent)
: QDialog(parent)
{
resize(300,600);
btn1 = new QPushButton("一对多",this);
btn1->move(100,200);
connect(btn1,SIGNAL(clicked()),this,SLOT(mySlot1()));
connect(btn1,SIGNAL(clicked()),this,SLOT(mySlot2()));
btn2 = new QPushButton("一对一",this);
btn2->move(100,400);
connect(btn2,SIGNAL(clicked()),this,SLOT(mySlot3()));
}
void Dialog::mySlot1()
{
qDebug() << "A";
}
void Dialog::mySlot2()
{
qDebug() << "B";
}
void Dialog::mySlot3()
{
// 槽函数也是成员函数,可以直接调用槽函数1和槽函数2
mySlot1();
mySlot2();
}
Dialog::~Dialog()
{
delete btn1;
delete btn2;
}
4.2 多对一
多个信号可以连接到同一个槽函数。
dialog.h
#ifndef DIALOG_H
#define DIALOG_H
#include
#include
#include
class Dialog : public QDialog
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
Dialog(QWidget *parent = 0);
~Dialog();
private:
QPushButton *btn1;
QPushButton *btn2;
private slots:
void mySlot();
};
#endif // DIALOG_H
dialog.cpp
#include "dialog.h"
Dialog::Dialog(QWidget *parent)
: QDialog(parent)
{
resize(600,200);
btn1 = new QPushButton("1",this);
btn1->move(200,100);
btn2 = new QPushButton("2",this);
btn2->move(400,100);
connect(btn1,SIGNAL(clicked()),this,SLOT(mySlot()));
connect(btn2,SIGNAL(clicked()),this,SLOT(mySlot()));
}
void Dialog::mySlot()
{
qDebug() << "自定义槽函数";
}
Dialog::~Dialog()
{
delete btn1;
delete btn2;
}