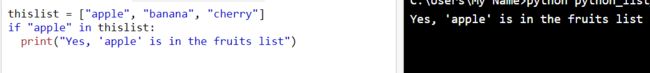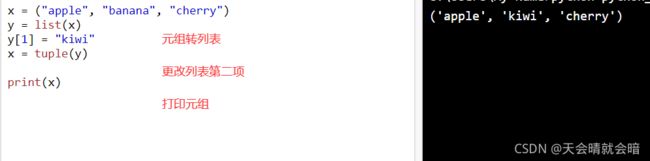浅谈python四种集合数据类型—【列表、元组、集合、字典】
浅谈python四种集合数据类型—【列表、元组、集合、字典】
- 一、python列表
-
- 1、基本认识
- 2、python列表
- 二、python元组
- 三、python集合
- 四、python字典
一、python列表
1、基本认识
python编程语言中有四种集合数据类型:
- 列表(List):是一种有序和可更改的集合。允许重复的成员
- 元组(Tuple):是一种有序且不可更改的集合。允许重复成员
- 集合(Set):是一种无序和无索引的集合。没有重复的成员
- 词典(Dictionary):是一个无序,可变和有索引的集合。没有重复的成员
为特定数据集合选择正确的类型可能意味着保留含义,并且可能意味着提高效率或安全性。
2、python列表
列表是一个有序且可更改的集合,在python中,列表用方括号[ ]
表示
创建列表
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
print(thislist)
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
print(thislist[1])
负索引表示从末尾开始,-1 表示最后一个项目,-2 表示倒数第二个项目,依此类推.
索引范围
- 通过指定范围的起点和终点来指定索引范围;
- 指定范围后,返回值将是包含指定项目的新列表。
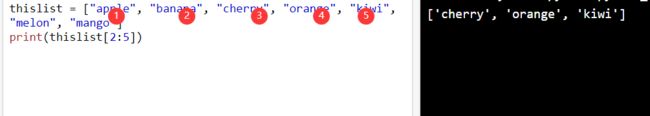
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "orange", "kiwi", "melon", "mango"]
print(thislist[2:5])
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
thislist[1] = "mango"
print(thislist)
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
for x in thislist:
print(x)
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
if "apple" in thislist:
print("Yes, 'apple' is in the fruits list")
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
print(len(thislist))
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
thislist.append("orange")
print(thislist)
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
thislist.insert(1, "orange")
print(thislist)
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
thislist.remove("banana")
print(thislist)
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
thislist.pop()
print(thislist)
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
del thislist[0]
print(thislist)
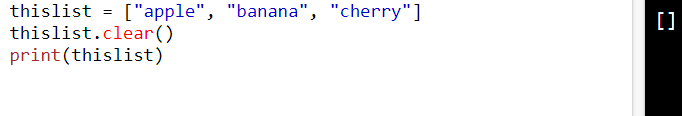
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
thislist.clear()
print(thislist)
通过键入 list2 = list1 来复制列表,因为:list2 将只是对 list1 的引用,list1 中所做的更改也将自动在 list2 中进行
使用copy() 复制列表
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
mylist = thislist.copy()
print(mylist)
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
mylist = list(thislist)
print(mylist)
在 Python 中,有几种方法可以连接或串联两个或多个列表。
最简单的方法之一是使用+运算符
合并两个列表
list1 = ["a", "b" , "c"]
list2 = [1, 2, 3]
list3 = list1 + list2
print(list3)
连接两个列表的另一种方法是将 list2 中的所有项一个接一个地追加到 list1 中.
把list2追加到list1中
list1 = ["a", "b" , "c"]
list2 = [1, 2, 3]
for x in list2:
list1.append(x)
print(list1)

使用extend()方法,其目的是将一个列表中的元素添加到另一个列表中
将list2添加到list1的末尾
list1 = ["a", "b" , "c"]
list2 = [1, 2, 3]
list1.extend(list2)
print(list1)
List()构造函数
使用List()构造函数创建一个新列表
thislist = list(("apple", "banana", "cherry")) # 请注意双括号
print(thislist)
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
append() |
在列表的末尾添加一个元素 |
clear() |
删除列表中的所有元素 |
copy() |
返回列表的副本 |
count() |
返回具有指定值的元素数量 |
extend() |
将列表元素(或任何可迭代的元素)添加到当前列表的末尾 |
index() |
返回具有指定值的第一个元素的索引 |
insert() |
在指定位置添加元素 |
pop() |
删除指定位置的元素 |
remove() |
删除具有指定值的项目 |
reverse() |
颠倒列表顺序 |
sort() |
对列表进行排序 |
二、python元组
元组是有序且不可更改的集合。在python中,元组是用圆括号()编写的
创建元组
thistuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")
print(thistuple)
thistuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")
print(thistuple[1])
负索引
负索引表示从末尾开始,-1 表示最后一个项目,-2 表示倒数第二个项目,依此类推
thistuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")
print(thistuple[-1])
- 通过指定范围的起点和终点来指定索引范围。
- 指定范围后,返回值将是带有指定项目的新元组
返回第三、第四、第五个项目
thistuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry", "orange", "kiwi", "melon", "mango")
print(thistuple[2:5])
搜索将从索引 2(包括)开始,到索引 5(不包括)结束。
请记住,第一项的索引为 0
负索引范围
从元组的末尾开始搜索,请指定负索引
将返回从索引 -4(包括)到索引 -1(排除)的项目
thistuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry", "orange", "kiwi", "melon", "mango")
print(thistuple[-4:-1])
创建元组后,您将无法更改其值。元组是不可变的,或者也称为恒定的。
但是有一种解决方法。可以将元组转换为列表,更改列表,然后将列表转换回元组
把元组转换为列表即可进行更改
x = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")
y = list(x)
y[1] = "kiwi"
x = tuple(y)
print(x)
thistuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")
for x in thistuple:
print(x)
检查项目是否存在
确定元组中是否存在指定的项,请使用 in 关键字
thistuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")
if "apple" in thistuple:
print("Yes, 'apple' is in the fruits tuple")
元组长度
确定元组有多少项,请使用len()方法
thistuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")
print(len(thistuple))
添加项目
元组一旦创建,无法向其添加项目。元组是不可改变的
thistuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")
thistuple[3] = "orange" # 会引发错误
print(thistuple)

创建有一个项目的元组
创建仅包含一个项目的元组,您必须在该项目后添加一个逗号,否则 Python 无法将变量识别为元组
thistuple = ("apple",)
print(type(thistuple))
#不是元组
thistuple = ("apple")
print(type(thistuple))
元组是不可更改的,因此无法从中删除项目,但可以完全删除元组
del·关键字可以完全删除元组
thistuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")
del thistuple
print(thistuple) # 这会引发错误,因为元组已不存在。
合并两个元组
连接两个或多个元组,可以使用 + 运算符
tuple1 = ("a", "b" , "c")
tuple2 = (1, 2, 3)
tuple3 = tuple1 + tuple2
print(tuple3)
tuple()构造函数
使用tuple()构造函数来创建元组
thistuple = tuple(("apple", "banana", "cherry")) # 请注意双括号
print(thistuple)
元组方法
python提供两个可以在元组上使用的内建方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
count() |
返回元组中指定值出现的次数 |
index() |
在元组中搜索指定的值并返回它被找到的位置 |
三、python集合
集合是无序和无索引的集合,在python中,集合用
花括号{ }编写
创建集合
thisset = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
print(thisset)
集合是无序的,因此无法确定项目的显示顺序。
访问项目
使用
for循环遍历set项目,或者使用关键词in查询集合中是否存在指定值。
遍历集合 ,并打印值
thisset = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
for x in thisset:
print(x)
thisset = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
print("banana" in thisset)
集合一旦创建,无法更改项目,但是可以添加新项目。
添加项目
- 要将一个项添加到集合,使用
add()方法; - 要向集合中添加多个项目。使用
updata()方法
使用add()向set添加项目
thisset = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
thisset.add("orange")
print(thisset)
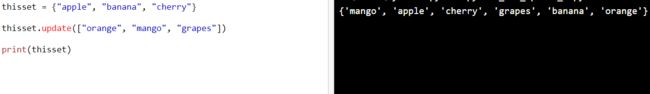
thisset = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
thisset.update(["orange", "mango", "grapes"])
print(thisset)
thisset = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
print(len(thisset))
删除项目
要删除集合中的项目,使用
remove()和discard()方法
使用remove()删除“banana”【删除项目必须存在于集合,否则报错】
thisset = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
thisset.remove("banana")
print(thisset)
使用discard()删除“banana”【集合不存在删除项目,不会引发报错】
thisset = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
thisset.discard("banana")
print(thisset)
使用pop()删除项目,将删除最后一项,【集合无序,无法确知删除项,返回值是被删除的项目】
thisset = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
x = thisset.pop()
print(x)
print(thisset)
thisset = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
thisset.clear()
print(thisset)
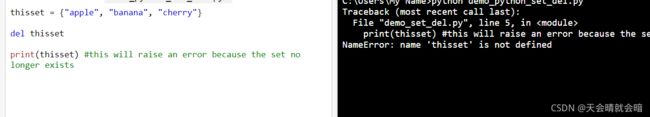
thisset = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
del thisset
print(thisset)
使用
union()方法返回包含两个集合中所有项目的新集合,也可以使用update()方法将一个集合中的所有项目插入另一个集合中:
使用union()方法返回一个新集合,其中包含两个集合的所有项目
set1 = {"a", "b" , "c"}
set2 = {1, 2, 3}
set3 = set1.union(set2)
print(set3)
set1 = {"a", "b" , "c"}
set2 = {1, 2, 3}
set1.update(set2)
print(set1)
union()和update()都将排除任何重复项
set()构造函数
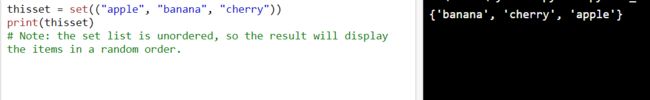
使用set()构造函数来创建集合
thisset = set(("apple", "banana", "cherry")) # 请留意这个双括号
print(thisset)
Set方法
python拥有一套能够在集合(set)上使用的内建方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
add() |
向集合添加元素 |
clear() |
删除集合中的所有元素 |
copy() |
返回集合的副本 |
difference() |
返回包含两个或更多集合之间差异的集合 |
difference_updata() |
删除此集合中也包含在另一个指定集合中的项目 |
discard() |
删除指定集合 |
intersection() |
返回为两个其他集合的交集的集合 |
intersection_update() |
删除此集合中不存在于其他指定集合中的项目 |
isdisjoint() |
返回两个集合是否有交集 |
issubset() |
返回另一个集合是否包含此集合 |
issuperset() |
返回此集合是否包含另一个集合 |
pop() |
从集合中删除一个元素 |
remove() |
删除指定元素 |
symmetric_difference() |
返回具有两组集合的对称差集的集合 |
symmetric_difference_update() |
插入此集合和另一个集合的对称差集 |
union() |
返回包含集合并集的集合 |
update() |
用此集合和其他集合的并集来更新集合 |
四、python字典
字典是一个无序,可变和有索引的集合,在python中,字典用
花括号{}编写,拥有键和值。
创建并打印字典
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
print(thisdict)
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
x = thisdict["model"]
print(x)
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
x = thisdict.get("model")
print(x)
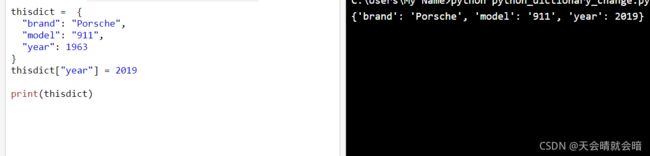
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
thisdict["year"] = 2019
print(thisdict)
使用
for循环遍历字典。
循环遍历字典时,返回值是字典的键,但也有返回值的方法
逐个打印字典中的所有键名
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
for x in thisdict:
print(x)
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
for x in thisdict:
print(thisdict[x])
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
for x in thisdict.values():
print(x)
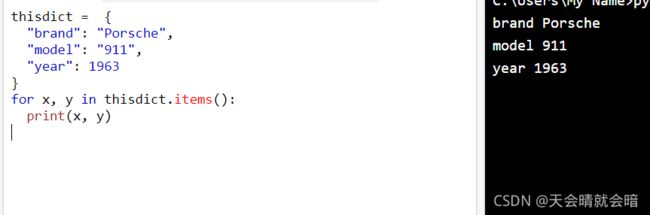
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
for x, y in thisdict.items():
print(x, y)
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
if "model" in thisdict:
print("Yes, 'model' is one of the keys in the thisdict dictionary")
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
print(len(thisdict))
添加项目
通过使用新的索引键并为其赋值,可以将项目添加到字典中
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
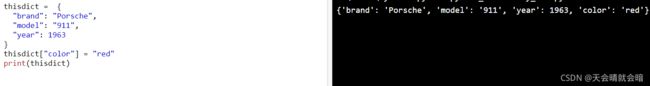
thisdict["color"] = "red"
print(thisdict)
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
thisdict.pop("model")
print(thisdict)
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
thisdict.popitem()
print(thisdict)
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
del thisdict["model"]
print(thisdict)
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
del thisdict
print(thisdict) #this 会导致错误,因为 "thisdict" 不再存在。
clear()关键字清空字典
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
thisdict.clear()
print(thisdict)
不能通过键入 dict2 = dict1 来复制字典,因为:dict2 只是对 dict1 的引用,而 dict1 中的更改也将自动在 dict2 中进行.
使用copy() 方法来复制字典
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
mydict = thisdict.copy()
print(mydict)
thisdict = {
"brand": "Porsche",
"model": "911",
"year": 1963
}
mydict = dict(thisdict)
print(mydict)
myfamily = {
"child1" : {
"name" : "Phoebe Adele",
"year" : 2002
},
"child2" : {
"name" : "Jennifer Katharine",
"year" : 1996
},
"child3" : {
"name" : "Rory John",
"year" : 1999
}
}
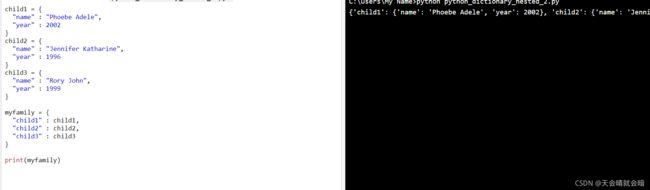
创建三个字典,然后创建一个包含其他三个字典的字典
child1 = {
"name" : "Phoebe Adele",
"year" : 2002
}
child2 = {
"name" : "Jennifer Katharine",
"year" : 1996
}
child3 = {
"name" : "Rory John",
"year" : 1999
}
myfamily = {
"child1" : child1,
"child2" : child2,
"child3" : child3
}
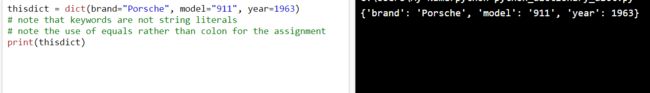
thisdict = dict(brand="Porsche", model="911", year=1963)
# 请注意,关键字不是字符串字面量
# 请注意,使用了等号而不是冒号来赋值
print(thisdict)
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
clear() |
删除字典中的所有元素 |
copy() |
返回字典的副本 |
fromkeys() |
返回拥有指定键和值的字典 |
get() |
返回指定键的值 |
items() |
返回包含每个键值对的元组的列表 |
keys() |
返回包含字典键的列表 |
pop() |
删除拥有指定键的元素 |
popitem() |
删除最后插入的键值对 |
setdefault() |
返回指定键的值。如果该键不存在,则插入具有指定值的键。 |
update() |
使用指定的键值对字典进行更新 |
values() |
返回字典中所有值的列表 |