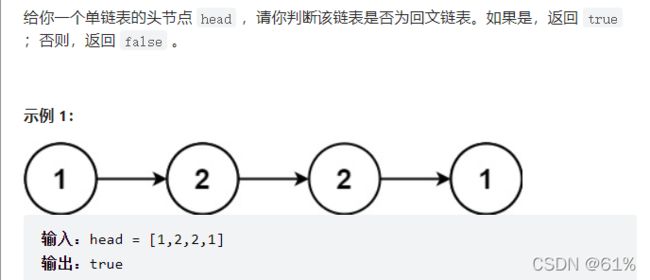
面试专题leetcode100题
目录
- 递归
-
- 70. 爬楼梯(简单)
-
- 递归(自顶向下)
- 递归+哈希表
- 循环解法(自底向上)
- 509. 斐波那契数(简单)
-
- 递归(自顶向下)
- 递归+哈希表
- 循环解法(自底向上)
- 哈希表
-
- 1. 两数之和(简单)
-
- 暴力
- 哈希表
- 数组
-
- 88. 合并两个有序数组(简单)
-
- 暴力
- 空间换时间
- 逆序遍历
- 283. 移动零(简单)
-
- 双指针
- 448. 找到所有数组中消失的数字(简单)
- 链表
-
- 21. 合并两个有序链表(简单)
- 83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素(简单)
- 141. 环形链表(简单)
- 142. 环形链表 II(中等)
- 160. 相交链表(简单)
- 206. 反转链表(简单)
- 234. 回文链表(简单)
- 876. 链表的中间结点(简单)
- 剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点(简单)
- 栈和队列
-
- 232. 用栈实现队列(简单)
- 394. 字符串解码(中等)
- 树
-
- 144. 二叉树的前序遍历(简单)
- 94. 二叉树的中序遍历(简单)
- 145. 二叉树的后序遍历(简单)
- 102. 二叉树的层序遍历(简单)
- 101. 对称二叉树(简单)
- 104. 二叉树的最大深度(简单)
- 110. 平衡二叉树(简单)
- 226. 翻转二叉树(简单)
- 二进制
-
- 136. 只出现一次的数字(简单)
- 338. 比特位计数(简单)
- 461. 汉明距离(简单)
- 字符串处理
-
- 20. 有效的括号(简单)
- 415. 字符串相加(简单)
- 动态规划
-
- 53. 最大子数组和(简单)
递归
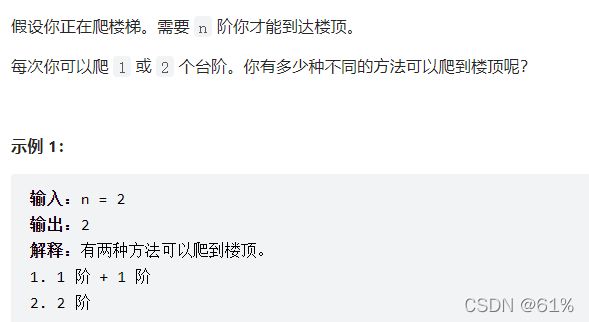
70. 爬楼梯(简单)
递归(自顶向下)
时空复杂度:n2,1
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if (n == 1) return 1;
if (n == 2) return 2;
return climbStairs(n - 1) + climbStairs(n - 2);
}
}
递归+哈希表
时空复杂度:n,n
class Solution {
private HashMap<Integer, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if (n == 1) return 1;
if (n == 2) return 2;
if (hashMap.get(n) != null) {
return hashMap.get(n);
} else {
int res = climbStairs(n - 1) + climbStairs(n - 2);
hashMap.put(n, res);
return res;
}
}
}
循环解法(自底向上)
时空复杂度:n,1
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if (n == 1) return 1;
if (n == 2) return 2;
int pre = 2, prePre = 1;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
res = pre + prePre;
prePre = pre;
pre = res;
}
return res;
}
}
509. 斐波那契数(简单)
递归(自顶向下)
时空复杂度:n2, 1
class Solution {
public int fib(int n) {
if(n==0) return 0;
if(n==1) return 1;
return fib(n-1)+fib(n-2);
}
}
递归+哈希表
时空复杂度:n,n
class Solution {
private HashMap<Integer, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
public int fib(int n) {
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1) return 1;
if (hashMap.get(n) != null) {
return hashMap.get(n);
} else {
int res = fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
hashMap.put(n, res);
return res;
}
}
}
循环解法(自底向上)
时空复杂度:n,1
class Solution {
public int fib(int n) {
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1) return 1;
int res = 0, pre = 1, prePre = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
res = pre + prePre;
prePre = pre;
pre = res;
}
return res;
}
}
哈希表
1. 两数之和(简单)
暴力
时空复杂度:n2, 1
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) return new int[]{i, j};
}
}
return null;
}
}
哈希表
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (hashMap.get(target - nums[i]) != null) {
return new int[]{hashMap.get(target - nums[i]), i};
} else {
hashMap.put(nums[i], i);
}
}
return null;
}
}
数组
88. 合并两个有序数组(简单)
暴力
时空复杂度:nlogn(快排),1
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
nums1[m + i] = nums2[i];
}
Arrays.sort(nums1);
}
}
空间换时间
时空复杂度:n,n
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int i = 0, j = 0;
for (; i < m && j < n; ) {//比较大小,除非某一方到头了
if (nums1[i] < nums2[j]) {
list.add(nums1[i++]);
} else {
list.add(nums2[j++]);
}
}
if (i != m) {//nums1到头了,把nums2直接接过来就行了,无需比较
for (int k = i; k < m; k++) {
list.add(nums1[k]);
}
}
if (j != n) {//nums2同理
for (int k = j; k < n; k++) {
list.add(nums2[k]);
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < nums1.length; k++) {//转移到nums1中
nums1[k] = list.get(k);
}
}
}
逆序遍历
时空复杂度:n,1
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int i = m - 1, j = n - 1, index = nums1.length - 1;
while (i >= 0 && j >= 0) {
if (nums1[i] < nums2[j]) {
nums1[index--] = nums2[j--];
} else {
nums1[index--] = nums1[i--];
}
}
if (i >= 0) {
while (index >= 0) {
nums1[index--] = nums1[i--];
}
}
if (j >= 0) {
while (index >= 0) {
nums1[index--] = nums2[j--];
}
}
}
}
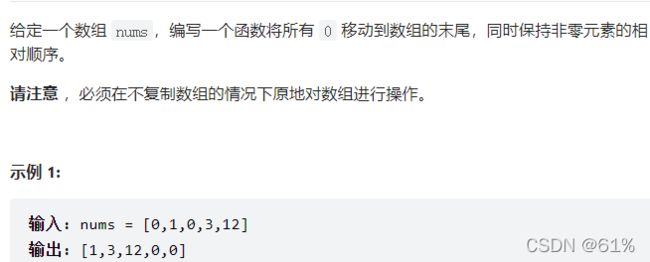
283. 移动零(简单)
双指针
时空复杂度:n,1
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] != 0) {
swap(nums, i, j);
j++;
}
}
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
}
448. 找到所有数组中消失的数字(简单)
时空复杂度:n,1
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers(int[] nums) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {//第一次便利,标记出现过的数字
int x = (nums[i]-1) % n;
nums[x] += n;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {//第二次便利,没有标记的下表就是结果
if (nums[i] <= n) list.add(i+1);
}
return list;
}
}
链表
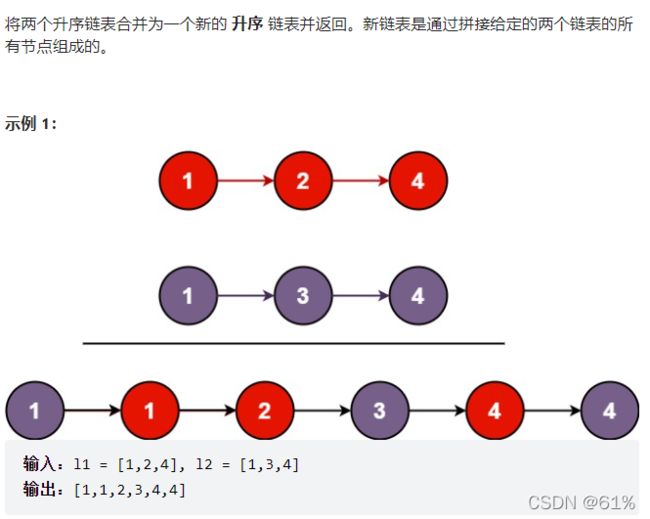
21. 合并两个有序链表(简单)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null) return list2;
if (list2 == null) return list1;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1), p = dummy, p1 = list1, p2 = list2;
while (null != p1 && null != p2) {
if (p1.val < p2.val) {
p.next = p1;
p = p.next;
p1 = p1.next;
} else {
p.next = p2;
p = p.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
}
if (null != p1) {
p.next = p1;
}
if (null != p2) {
p.next = p2;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素(简单)
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode p = head;
while (p.next != null) {
if (p.val == p.next.val) {
p.next = p.next.next;
} else {
p = p.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
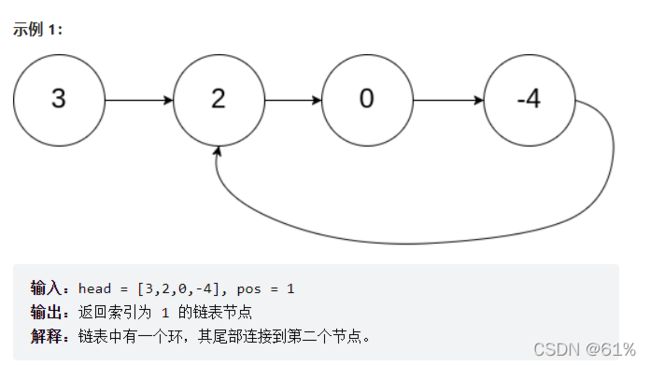
141. 环形链表(简单)
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return false;
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast!=null&&fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) return true;
}
return false;
}
}
142. 环形链表 II(中等)
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) break;
}
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) return null;
slow = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
160. 相交链表(简单)
时空复杂度:n,1

方法一:暴力
方法二:哈希表
方法三:双指针
方法四:长度统一
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode p1 = headA, p2 = headB;
while (p1 != p2) {
p1 = p1 == null ? headB : p1.next;
p2 = p2 == null ? headA : p2.next;
}
return p1;
}
}
206. 反转链表(简单)
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode p = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while (p != null) {
ListNode next = p.next;
p.next = pre;
pre = p;
p = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
234. 回文链表(简单)
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (head != null) {
list.add(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
for (int i = 0, j = list.size() - 1; i < j; i++, j--) {
if (list.get(i) != list.get(j)) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
876. 链表的中间结点(简单)
时空复杂度:n,1
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode p1 = head, p2 = head;
while (p2 != null && p2.next != null) {
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next.next;
}
return p1;
}
}
剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点(简单)
class Solution {
public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1), p1 = dummy, p2 = dummy;
dummy.next = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
p2 = p2.next;
}
while (p2 != null) {
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
return p1;
}
}
栈和队列
232. 用栈实现队列(简单)
public class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stack1;
Stack<Integer> stack2;
public MyQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stack1.add(x);
}
public int pop() {
if (stack2.isEmpty()) {
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
stack2.add(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (stack2.isEmpty()) {
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
stack2.add(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
if (stack2.isEmpty() && stack1.isEmpty()) return true;
return false;
}
}
394. 字符串解码(中等)
树
144. 二叉树的前序遍历(简单)
class Solution {
List<Integer> res;
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
res = new LinkedList<>();
traverse(root);
return res;
}
private void traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
res.add(root.val);
traverse(root.left);
traverse(root.right);
}
}
94. 二叉树的中序遍历(简单)
class Solution {
List<Integer> res;
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
res = new LinkedList<>();
traverse(root);
return res;
}
private void traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
traverse(root.left);
res.add(root.val);
traverse(root.right);
}
}
145. 二叉树的后序遍历(简单)
class Solution {
List<Integer> res;
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
res = new LinkedList<>();
traverse(root);
return res;
}
private void traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
traverse(root.left);
traverse(root.right);
res.add(root.val);
}
}
102. 二叉树的层序遍历(简单)
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return res;
traverse(root);
return res;
}
private void traverse(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode poll = queue.poll();
path.add(poll.val);
if (poll.left != null) queue.add(poll.left);
if (poll.right != null) queue.add(poll.right);
}
res.add(new LinkedList<>(path));
path.clear();
}
}
}
101. 对称二叉树(简单)
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
return traverse(root.left, root.right);
}
private boolean traverse(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if (root1 == null && root2 == null) return true;
if (root1 == null || root2 == null) return false;
return root1.val == root2.val && traverse(root1.left, root2.right) && traverse(root1.right, root2.left);
}
}
104. 二叉树的最大深度(简单)
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
return traverse(root);
}
private int traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return 1 + Math.max(traverse(root.left), traverse(root.right));
}
}
110. 平衡二叉树(简单)
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return traverse(root) != -1;
}
private int traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int left = traverse(root.left);
int right = traverse(root.right);
if (left == -1 || right == -1 ||
Math.abs(left - right) > 1) return -1;
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
}
}
226. 翻转二叉树(简单)
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
traverse(root);
return root;
}
private void traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
traverse(root.left);
traverse(root.right);
TreeNode temp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = temp;
}
}
二进制
常用位运算
按位与:1&1=1 0&0=0 1&0=0
Brian Kernighan 算法:对于任意整数 x,令 x=x& (x−1),该运算将 x 的二进制表示的最后一个 1 变成 0。
按位或: 1|1=1 0|0=0 1|0=1
按位非: ~1=0 ~0=1
按位异或:1^ 1=0 1^0=1 0 ^ 0=0, 相同为0,不同为1
1.任何数和 0 做异或运算,结果仍然是原来的数,即 a^ 0=a。
2.任何数和其自身做异或运算,结果是 0,即a^a=0。
3.异或运算满足交换律和结合律,即 a^b ^a=a ^ a ^ b=b.
有符号左移:<< (若正数,高位补0,负数,高位补1)
有符号右移:>>
无符号右移: >>>(无论正负,高位均补0)
位运算常用场景
判断奇偶数:n&(n-1),最后一位是1,是奇数,0,偶数
实现数字翻倍或减半:左乘右除
136. 只出现一次的数字(简单)
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int res = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
res ^= num;
}
return res;
}
}
338. 比特位计数(简单)
class Solution {
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] nums = new int[n+1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
nums[i] = countOne(i);
}
return nums;
}
private int countOne(int i) {
int cnt = 0;
while (i != 0) {
i &= i - 1;
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
}
461. 汉明距离(简单)
class Solution {
public int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
int k = x ^ y;
int cnt = 0;
while (k != 0) {
k &= k - 1;
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
}
字符串处理
20. 有效的括号(简单)
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == ')') {
if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.pop() != '(') return false;
} else if (s.charAt(i) == ']') {
if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.pop() != '[') return false;
} else if (s.charAt(i) == '}') {
if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.pop() != '{') return false;
} else stack.push(s.charAt(i));
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
415. 字符串相加(简单)
class Solution {
public String addStrings(String num1, String num2) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
int carry = 0;
for (int i = num1.length() - 1, j = num2.length() - 1; i >= 0 || j >= 0; i--, j--) {
int a = i >= 0 ? num1.charAt(i) - '0' : 0;
int b = j >= 0 ? num2.charAt(j) - '0' : 0;
int sum = a + b + carry;
sb.append(sum % 10);
carry = sum / 10;
}
if (carry != 0) sb.append('1');
return sb.reverse().toString();
}
}
动态规划
53. 最大子数组和(简单)
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int[] dp=new int[nums.length];//dp[i]代表以i为结尾的最大连续子数组和
//base case
dp[0]=nums[0];
for(int i=1; i<nums.length; i++){
dp[i]=Math.max(dp[i-1]+nums[i], nums[i]);
}
int max=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i=0; i<dp.length; i++){
max=Math.max(max,dp[i]);
}
return max;
}
}