【Java进阶篇】—— File类与IO流
一、File类的使用
1.1 概述
-
File 类以及本章中的各种流都定义在 java.io 包下
-
一个File对象代表硬盘或网络中可能存在的一个文件或文件夹(文件目录)
-
File 能新建、删除、重命名 文件和目录,但 File不能访问文件内容本身。如果我们想要访问文件内容本身,就需要使用 输入/输出流
- 将 File 对象作为参数传递给流的构造器
-
在Java程序中表示一个真实存在的文件或目录用File对象,但定义的File对象不一定对应真实存在的文件或目录(file not found)
1.2 构造器
- public File(String pathname): 以pathname为路径创建File对象
- pathname是绝对路径或相对路径都可以
- 如果为相对路径,则默认的当前路径在系统属性 user.dir 中存储
- public File(String parent, String child): 以parent为父路径,child为子路径创建File对象 【将父子路径拼接到一起就是个完整路径】
- public File(File parent, String child): 根据一个父 File对象和子文件路径创建File对象【根据一个文件/目录的地址+child拼接新地址】
简述一下绝对路径和相对路径的概念:
- 绝对路径:属于一个从盘符开始的完整路径
- 相对路径:相对于项目目录的路径
- IDEA中,main中的文件的相对路径,是相对于"当前工程"
- IDEA中,单元测试方法中的文件的相对路径,是相对于"当前module"【模块】
代码演示:
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.File;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
public class FileObjectTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//通过pathname创建File对象
String path = "D:\\dataBase";
File file1 = new File(path);
//通过父路径+子路径创建File对象
String parent = "C:\\aaa";
String child = "bbb.txt";
File file2 = new File(parent, child);
//通过File对象+子路径创建File对象
File parentDir = new File("d:\\aaa");
String childFile = "bbb.txt";
File file3 = new File(parentDir, childFile);
//我们来打印一些File对象相关的信息
System.out.println("file1 = " + file1);
System.out.println("文件/目录的名称: " + file2.getName());
System.out.println("文件/目录的构造路径名: " + file3.getPath());
System.out.println("文件/目录的绝对路径名: " + file1.getAbsoluteFile());
System.out.println("文件/目录的父目录名: " + file2.getParent());
}
}
- 总结:
-
无论该路径下是否存在文件或者目录,都不影响File对象的创建
-
window的路径分隔符使用“\”,而Java程序中的“\”表示转义字符,所以在Windows中表示路径需要使用
\\或/,或者用File.separator常量值表示File file2 = new File(“d:” + File.separator + “atguigu” + File.separator + “info.txt”); -
当构造路径是绝对路径时,那么getPath和getAbsolutePath结果一样
-
当构造路径是相对路径时,那么getAbsolutePath的路径 = user.dir的路径 + 构造路径
-
1.3 常用方法
1、获取文件和目录的基本信息
- public String getName(): 获取名称
- public String getPath(): 获取路径
- public String getAbsolutePath(): 获取绝对路径
- public File getAbsoluteFile(): 获取绝对路径表示的文件
- public String getParent(): 获取上层目录路径;没有则返回null
- public long length(): 获取文件(不能是目录)的长度(字节数)
- public long lastModified(): 获取最后一次的修改时间,毫秒值
有一个值得我们注意的:
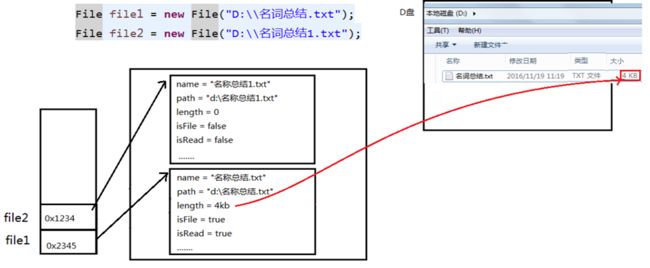
如果File对象代表的文件或目录存在,则File对象实例初始化时,就会用硬盘中对应文件或目录的属性信息(例如,时间、类型等)为File对象的属性赋值,否则除了路径和名称,File对象的其他属性将会保留默认值 【可以看下图辅助理解】
我来编写代码具体演示一下:file1存在、file2不存在
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.File;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
public class FileInfoMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//存在的文件
File file1 = new File("d:/小红书Java后端开发.png");
System.out.println("文件构造路径: " + file1.getPath());
System.out.println("文件名称: " + file1.getName());
System.out.println("文件长度: " + file1.length() + "字节");
System.out.println("文件最后修改时间: " + file1.lastModified());
System.out.println();
//虚构的文件
File file2 = new File("d:" + File.separator + "aaa.txt");
System.out.println("文件构造路径: " + file2.getPath());
System.out.println("文件名称: " + file2.getName());
System.out.println("文件长度: " + file2.length() + "字节");
System.out.println("文件最后修改时间: " + file2.lastModified());
}
}
2、列出目录的下一级
- public String [] list(): 返回一个String数组,表示该File目录中的所有子文件或目录
- public File[] listFiles(): 返回一个File数组,表示该File目录中的所有的子文件或目录
- 区别就在于返回的一个是字符串数组、一个是文件数组
- 字符串数组可以用于一些特征信息的提取
- 文件数组可以用于进一步加工成新的File对象
- 区别就在于返回的一个是字符串数组、一个是文件数组
代码演示一下:
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.File;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
public class DirListFiles {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file1 = new File("d:\\cfhd");
File file2 = new File("d:/DataBase");
//采用两种方式获取目录的子文件或子目录名,并打印输出
String [] list = file1.list();
File [] listFiles = file2.listFiles();
for(String child : list){
System.out.print(child + " ");
}
System.out.println();
for (File file : listFiles){
System.out.print(file + " ");
}
}
}
3、File 类的重命名功能
- public boolean renameTo(File dest): 把文件重命名为指定的文件路径
代码测试失败了
4、判断功能的方法
- public boolean exists(): 判断File表示的文件/目录是否真实存在
- public boolean isDirectory: 判断File表示的是不是目录
- public boolean isFile: 判断File表示的是不是文件
- public boolean canRead(): 判断是否可读
- public boolean canWrite(): 判断是否可写
- public boolean isHidden(): 判断是否隐藏
代码演示
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.File;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
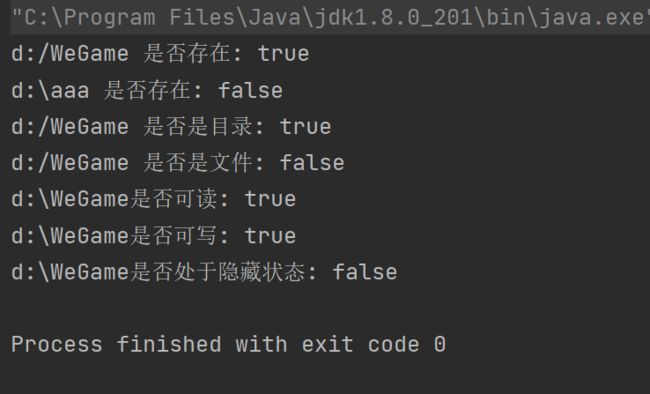
public class DirListFiles {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file1 = new File("d:\\WeGame");
System.out.println("d:/WeGame 是否存在: " + file1.exists());
System.out.println("d:\\aaa 是否存在: " + new File("d:\\aaa").exists());
System.out.println("d:/WeGame 是否是目录: " + file1.isDirectory());
System.out.println("d:/WeGame 是否是文件: " + file1.isFile());
System.out.println(file1 + "是否可读: " + file1.canRead());
System.out.println(file1 + "是否可写: " + file1.canWrite());
System.out.println(file1 + "是否处于隐藏状态: " + file1.isHidden());
}
}
5、创建、删除功能
- public boolean createNewFile(): 创建文件,文件已经存在则返回false(创建失败,不会覆盖文件)
- public boolean mkdir(): 创建目录,文件目录存在不创建或指定的文件目录上层目录不存在那么也不创建
- public boolean mkdirs(): 创建目录,上层目录不存在则一并创建 【可以理解为直接创建多级目录】
- public boolean delete(): 删除文件或文件夹
- 通过Java代码删除文件不会暂时保留到回收站中,直接从硬盘删除
- 如果删除的是文件目录,目录内不能包含子文件或子目录
代码演示
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
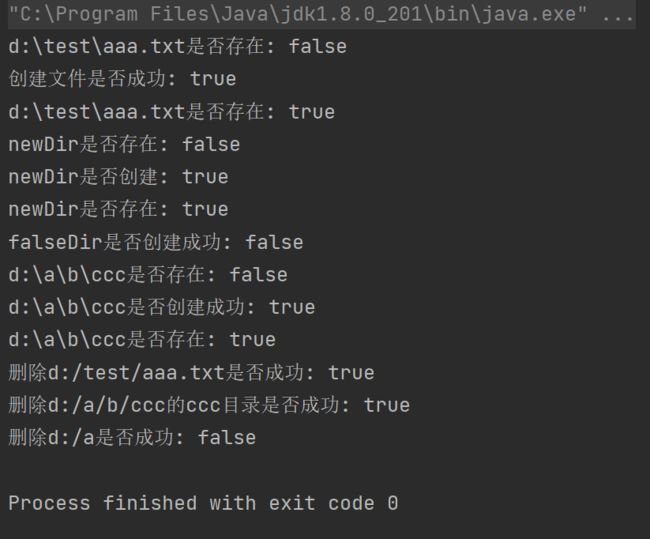
public class FileCreateDelete{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建一个本来不存在的文件
File f = new File("d:/test/aaa.txt");
System.out.println(f + "是否存在: " + f.exists());
System.out.println("创建文件是否成功: " + f.createNewFile());
System.out.println(f + "是否存在: " + f.exists());
//创建一个本来不存在的目录(上一级目录存在)
File f2 = new File("d:/test/newDir");
System.out.println("newDir是否存在: " + f2.exists());
System.out.println("newDir是否创建: " + f2.mkdir());
System.out.println("newDir是否存在: " + f2.exists());
//创建一个目录,但是他的上一级目录不存在
System.out.println("falseDir是否创建成功: " + new File("d:/dask/falseDir").mkdir());
//直接创建多级目录
File f3 = new File("d:/a/b/ccc");
System.out.println(f3 + "是否存在: " + f3.exists());
System.out.println(f3 + "是否创建成功: " + f3.mkdirs());
System.out.println(f3 + "是否存在: " + f3.exists());
//删除创建的文件
System.out.println("删除d:/test/aaa.txt是否成功: " + f.delete());
//删除目录,删除d:/a/b/ccc,它是一个空目录
System.out.println("删除d:/a/b/ccc的ccc目录是否成功: " + f3.delete());
//试图直接删除d:/a,删除失败,因为它有一个子目录b
System.out.println("删除d:/a是否成功: " + new File("d:/a").delete());
}
}
6、综合练习
(1)判断指定目录下是否有后缀名为 .jpg的文件。如果有,就输出该文件名称
- endWith 可以判断字符串是否以指定的片段结尾
- 一种通过 list() 方法获取所有子文件及子目录的String数组
- 另一种通过 listFiles() 方法获取所有子文件及子目录的File数组,调用File提供的getName()方法获取文件名
- 通过重写listFiles()方法的过滤器规则,也就是accept方法
- 返回的File数组都是满足要求的数组
public class FindJPGFileTest {
//方法1:
@Test
public void test1(){
File srcFile = new File("d:\\code");
String[] fileNames = srcFile.list();
for(String fileName : fileNames){
if(fileName.endsWith(".jpg")){
System.out.println(fileName);
}
}
}
//方法2:
@Test
public void test2(){
File srcFile = new File("d:\\code");
File[] listFiles = srcFile.listFiles();
for(File file : listFiles){
if(file.getName().endsWith(".jpg")){
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
//方法3:
/*
* File类提供了两个文件过滤器方法
* public String[] list(FilenameFilter filter)
* public File[] listFiles(FileFilter filter)
*/
@Test
public void test3(){
File srcFile = new File("d:\\code");
File[] subFiles = srcFile.listFiles(new FilenameFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
return name.endsWith(".jpg");
}
});
for(File file : subFiles){
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
(2)遍历指定目录所有文件名称,包括子文件目录中的文件
- 遇到目录就递归处理,否则就打印文件地址【参考下面两个方案】
public static void printSubFile(File dir) {
// 打印目录的子文件
File[] subfiles = dir.listFiles();
for (File f : subfiles) {
if (f.isDirectory()) {// 文件目录
printSubFile(f);
} else {// 文件
System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
public void listAllSubFiles(File file) {
if (file.isFile()) {
System.out.println(file);
} else {
File[] all = file.listFiles();
// 如果all[i]是文件,直接打印
// 如果all[i]是目录,接着再获取它的下一级
for (File f : all) {
listAllSubFiles(f);// 递归调用:自己调用自己就叫递归
}
}
}
(3)计算指定目录占用空间大小
public long getDirectorySize(File file) {
// file是文件,那么直接返回file.length()
// file是目录,把它的下一级的所有file大小加起来就是它的总大小
long size = 0;
if (file.isFile()) {
size = file.length();
} else {
File[] all = file.listFiles();// 获取file的下一级
// 累加all[i]的大小
for (File f : all) {
size += getDirectorySize(f);// f的大小;
}
}
return size;
}
(4)删除指定文件目录及其下的所有文件
public void deleteDirectory(File file) {
// 如果file是文件,直接delete
// 如果file是目录,先把它的下一级干掉,然后删除自己
if (file.isDirectory()) {
File[] all = file.listFiles();
// 循环删除的是file的下一级
for (File f : all) {// f代表file的每一个下级
deleteDirectory(f);
}
}
// 删除自己
file.delete();
}
二、IO流的原理及流的分类
2.1 Java IO原理
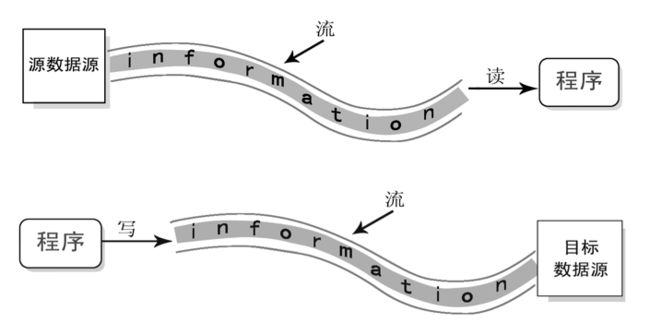
- Java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以"流(stream)"的方式进行,可以看做是一种数据的流动
- I/O流代表 Input/Output 的缩写,用于处理设备之间的数据传输【如读写文件、网络通讯】
- 输入input: 读取外部数据(磁盘、光盘等存储设备的数据)到程序(内存)中
- 输出 output:将程序(内存)数据输出到磁盘、光盘等存储设备中
2.2 流的分类
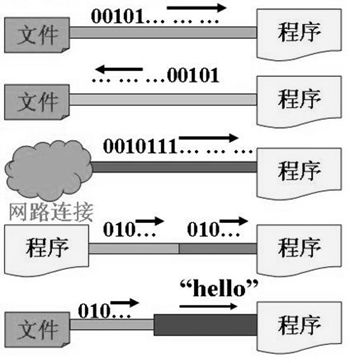
java.io 包下提供了各种"流"类和接口,用以获取不同种类的数据,并通过标准的方法输入或输出数据
-
按数据的流向不同分为:输入流和输出流
- 输入流:把数据从== 其他设备 读取到 内存 ==中的流
- 以 InputStream、Reader 结尾
- 输出流:把数据从 内存 中写出到 其他设备上的流
- 以 OutputStream、Writer 结尾
- 输入流:把数据从== 其他设备 读取到 内存 ==中的流
-
按操作数据单位的不同分为:字节流(8bit) 和 字符流(16bit)
- 字节流:以字节为单位,读写数据的流 【InputStream、OutputStream结尾】
- 字符流:以字符为单位,读写数据的流 【Reader、Writer结尾】
-
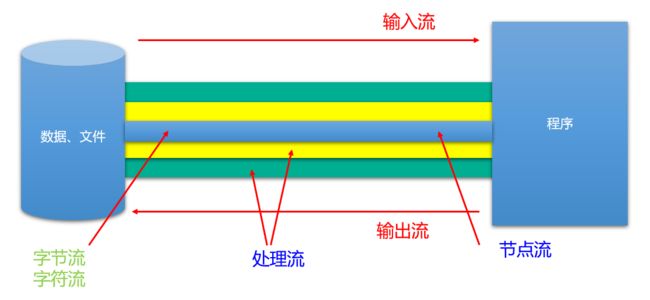
根据 IO 角色不同分为:节点流 和 处理流
一图总结:
2.3 流的API
- Java 由四个抽象基类派生出40多个IO流
- 派生出来的子类都以其父类名作为后缀
-
常见的字节流:
- 文件流: FileInputStream、FileOutputStream、FileReader、FileWriter
- 字节/字符数组流:ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream、CharArrayReader、CharArrayWriter
- 对数组进行处理的节点流(对应的不再是文件,而是内存中的一个数组)
-
常用处理流:
- 缓冲流:BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream、BufferedReader、BufferedWriter
- 作用:增加缓冲功能,避免频繁读写硬盘,进而提升读写效率
- 转换流:InputStreamReader、OutputStreamReader
- 作用:实现字节流和字符流的转换
- 对象流:ObjectInputStream、ObjectOutputStream
- 作用:提供直接读写Java对象功能
- 缓冲流:BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream、BufferedReader、BufferedWriter
三、 FileReader 和 FileWriter
3.1 Reader 与 Writer
- Java提供一些字符流类,以字符为单位读写数据,专门用于处理文本文件。
- .txt、.java、.c、.cpp、.py等都是文本文件
- 图片、视频、.doc、.xls、.ppt都不是文本文件
1、字符输入流:Reader
- java.io.Reader 抽象类是所有用于读取字符流的所有类的父类,可以读取字符信息到内存中,它定义了字符输入流的基本共性功能方法
- public int read(): 从输入流读取一个字符, 自动提升为 int,返回该字符的Unicode编码值,如果已经达到流末尾,则返回 -1
- public int read(char [] cbuf):从输入流读取一些字符,并将他们存储到字符数组 cbuf中,每次最多读取 cbuf.length个字符。返回实际读取的字符个数。如果已经到流末尾,没有数据可读,则返回 -1
- public int read(char [] cbuf, int off, int len): 从输入流中读取一些字符,并将它们存储到字符数组 cbuf中,从cbuf[off]开始的位置存储。每次最多读取len个字符。返回实际读取的字符个数。如果已经到达流末尾,没有数据可读,则返回-1
- public void close(): 关闭此流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源
It’s importent: 当完成流的操作时,必须调用close()方法,释放系统资源,否则会造成内存泄漏
2、字符输出流:Writer
- java.io.Writer 抽象类是表示用于写出字符流的所有类的超类,将指定的字符信息写到目的地。它定义了字节输出流的基本共性功能方法
-
public void write(int c): 写出单个字符
-
public void write(char [] cbuf): 写出字符数组
-
public void write(char [] cbuf, int off, int len): 写出字符数组的一部分
- off 是数组的开始索引
- len 是写出的字符个数
-
public void write(String str): 写出字符串
-
public void write(String str, int off, int len):写出字符串的某一部分
- off 是字符串的开始索引
- len 是写出的字符个数
-
public void flush(): 刷新该流的缓冲
-
public void close(): 关闭此流
-
和字符输入流一样,在完成流操作之后要调用 close 方法释放资源,否则可能会导致内存泄漏的问题
3.2 FileReader 与 FileWriter
1、FileReader
- java.io.FileReader 类用于读取字符文件,构造时使用系统默认的字符编码和默认字节缓冲区
- FileReader(File file): 创建一个新的FileReader,给定要读取的File对象
- FileReader(String fileName):创建一个新的FileReader,给定要读取的文件的名称
通过代码演示——如何从一个具体的文件中读取数据
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
public class FileReaderWriterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建文件类读取的对象
FileReader fr = null;
//捕获一下可能存在的IOException
try{
//创建File类的对象,对应着物理磁盘上的某个文件
File file = new File("d:/test/zbc.txt");
//创建FileReader流对象,将File类的对象作为参数传递到FileReader的构造器中
try{
fr = new FileReader(file);
}catch (FileNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
int data = 0;
//这里如果不将读取的字符赋值给data就会出现乱码,我还不知道为啥
while((data = fr.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)data);
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//4、关闭相关的流资源,避免出现内存泄漏
try{
if(fr != null){
fr.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
- 如果向一次读多个字符,那么就设置一个字符数组作为参数传递到 read()方法中
- 输出的时候用这个字符数组构造成字符串,然后再打印输出
2、FileWriter
- java.io.FileWriter 类用于写出字符到文件,构造时使用系统默认的字符编码和默认字符缓冲区
- FileWriter(File file): 创建一个新的FileWriter,给定要读取的 File 对象
- FileWriter(String fileName): 创建一个新的FileWriter,给定要读取的文件名称
- FileWriter(File file, boolean append): 创建一个新的 FileWriter,指明是否在现有文件末尾追加内容
代码演示:
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
public class FWWrite {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(new File("d:/test/zbc"));
char [] ch = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
String s = "zhenbucuo";
try{
fw.write("z");
fw.write(ch);
fw.write(ch, 1, 2);
fw.write(s);
fw.write(s, 2, 3);
//关闭资源
fw.close();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
总结:
-
因为出现流资源的调用,为了避免内存泄漏,需要使用try-catch-finally处理异常
-
对于输入流来说,File类的对象必须在物理磁盘上存在,否则执行就会报FileNotFoundException。如果传入的是一个目录,则会报IOException异常。
-
对于输出流来说,File类的对象是可以不存在的。
- 如果File类的对象不存在,则可以在输出的过程中,自动创建File类的对象
- 如果File类的对象存在,
- 如果调用FileWriter(File file)或FileWriter(File file,false),输出时会新建File文件覆盖已有的文件
- 如果调用FileWriter(File file,true)构造器,则在现有的文件末尾追加写出内容。
四、FileInputStream 和 FileOutputStream
- 对于Reader、Writer是对字符流进行操作的,也就是说不能处理非文本文件,那么我们如何使用字节流来读取、写入数据呢?
4.1 InputStream 与 OutputStream
1、字节输入流:InputStream
- java.io.InputStream 抽象类表示字节输入流的所有类的超类,可以读取字节信息到内存中,它定义了字节输入流的基本共性功能方法
- public int read(): 从输入流读取一个字节。返回读取的字节值。虽然读取了一个字节,但是会自动提升为int类型。如果已经到达流末尾,没有数据可读,则返回-1
- public int read(byte [] b): 从输入流中读取一些字节数,并将它们存储到字节数组 b中 。每次最多读取b.length个字节。返回实际读取的字节个数。如果已经到达流末尾,没有数据可读,则返回-1
- public int read(byte [] b, int off, int len): 从输入流中读取一些字节数,并将它们存储到字节数组 b中,从b[off]开始存储,每次最多读取len个字节 。返回实际读取的字节个数。如果已经到达流末尾,没有数据可读,则返回-1
- public void close(): 关闭次输入流,并释放与此流相关的任何系统资源 【完成流操作后必须调用此方法】
2、字节输出流:OutputStream
- java.io.OutputStream 抽象类是表示字节输出流的所有类的超类,将指定的字节信息写出到目的地,它定义了字节输出流的基本共性功能方法
- public void write(int b): 将指定的字节输出流写出。虽然参数为int类型四个字节,但是只会保留一个字节的信息写出
- public void write(byte [] b): 将 b.length字节从指定的字节数组写入此输出流
- public void write(byte [] b, int off, int len): 从指定的字节数组写入 len字节,从偏移量 off开始输出到此输出流
- public void flush(): 刷新此输出流并强制任何缓冲的输出字节被写出
- public void close(): 关闭此输出流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源 【完成流操作就调用】
4.2 FileInputStream 与 FileOutputStream
1、FileInputStreamStream
- java.io.FileInputStream 类是文件输入流,从文件中读取字节
- FileInputStream(File file): 通过打开与实际文件的连接来创建一个 FileInputStream,该文件由文件系统中File对象file命名
- FileInputStream(String name): 通过打开域实际文件的连接来创建一个FileInputStream,该文件由系统中的路径名 name 命名
通过代码演示字节流文件的读取操作:
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InvalidObjectException;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
public class FISRead {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//先准备一个文件
File f = new File("d:/test/abc.txt");
// f.createNewFile();//为了省事我直接抛出了
//演示几种以字节流的方式读取文件的操作
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);
FileInputStream fis2 = new FileInputStream(f);
FileInputStream fis3 = new FileInputStream(f);
FileInputStream fis4 = new FileInputStream(f);
//需要用read存一下,read()方法返回的是一个字节
int read = fis.read();
System.out.println((char)read);
fis.close();
System.out.println("*********************");
while((read = fis2.read()) != -1){
System.out.println((char)read);
}
fis2.close();
System.out.println("*********************");
//准备一个字节数组
byte [] b = new byte[2];
int len = 0;
while((len = fis3.read(b)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(b));
}
fis3.close();
System.out.println("*********************");
while((len = fis4.read(b)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(b, 0, len));
}
fis4.close();
}
}
2、FileOutputStream
- java.io.FileOutputStream 类是文件输出流,用于将数据写出到文件
- public FileOutpurStream(File file): 创建文件输出流,写出由指定的File对象表示的文件
- public FileOutputStream(String name): 创建文件输出流,指定的名称为写出文件
- public FIleOutputStream(File file, boolean append): 创建文件输出流,指明是否在现有文件末尾追加内容
通过代码来演示具体的用法:
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
public class FOSWrite {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//使用File对象创建流对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("d:/test/abc.txt"));
//写入一个字节
fos.write(97);
//写入一个字节数组
byte [] b = "abcd".getBytes();
fos.write(b);
//写入字节数组的一部分
fos.write(b, 1, 2); //bc
//使用FileInputStream读取一下文件
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:/test/abc.txt");
int data = 0;
while((data = fis.read()) != -1){
System.out.println((char)data);
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
//写入结果:aabcdbc,覆盖了原来的内容
}
}
(1)实现文件的copy功能,就是将一个文件的读取结果,写入到另一个文件中
- 我们以 d:/test/a.txt 和 d:/test/b.txt为例
- a.txt 中的内容为 I love China.
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
public class FIOSCopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try{
fis = new FileInputStream(new File("d:/test/a.txt"));
fos = new FileOutputStream("d:/test/b.txt");
//因为InputStream、OutputStream操作的是字节流
byte [] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){
fos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
System.out.println("内容复制成功!");
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
//最后我们要释放资源
try{
if(fis != null){
fis.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try{
if(fos != null){
fos.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//最后我们再检查一下是否写入成功
try{
FileInputStream fis2 = new FileInputStream("d:/test/b.txt");
int data = 0;
while((data = fis2.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)data);
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
加密提示:在Java中 ^ 代表异或操作;采用异或一个特定值加密,那么解密再次异或这个特定值就可以
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
* 图片的加密与解密
*/
public class FileSecretTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
encryption();
decryption();
}
//加密 [实际应该把加密的功能抽出来,但是我为了在一个类中实现
// 加密和解密,就把完整操作放在一个静态方法中了,通过主方法
// 调用来完成测试]
public static void encryption(){
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try{
fis = new FileInputStream(new File("d:/test/kun.jpg"));
fos = new FileOutputStream("d:/test/kun_secret.jpg");
//每次读取一个字节效率很低,所以采用1024字节数组读取
byte [] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){
//对每一个字节都进行加密
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
//需要强转,因为与5异或会自动将精度提升为int
buffer[i] = (byte)(buffer[i] ^ 5);
}
//写到字节输出流中
fos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
System.out.println("图片加密成功!");
}catch (IOException e){
//在实际开发中打印异常信息到控制台很少,大多采用抛出异常来提醒出问题了
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally{
//资源释放
try{
if(fis != null){
fis.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try{
if(fos != null){
fos.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
//图片的解密
public static void decryption(){
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try{
fis = new FileInputStream(new File("d:/test/kun_secret.jpg"));
fos = new FileOutputStream("d:/test/kun_unsecret.jpg");
int len = 0;
byte [] buffer = new byte[1024];
while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){
//解密
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
buffer[i] = (byte) (buffer[i] ^ 5);
}
//将解密后的字节数组写入到目标数据流中
fos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
System.out.println("图片解密成功!");
}catch (IOException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
try{
if (fos != null) {
fos.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try{
if (fis != null) {
fis.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
五、缓冲流
- 为了提供数据读写速度,Java API 提供了带缓冲功能的流类:缓冲流
- 缓冲流要 “套接” 在相应的节点流之上,根据数据操作单位可以把缓冲流分为:
- 字节缓冲流: BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream
- 字符缓冲流:BufferedReader、BufferedWriter
- 缓冲流的基本原理:在创建流对象时,内部会创建一个缓冲区数组(缺省使用8192个字节(8Kb)的缓冲区),通过缓冲区读写,减少系统IO次数,从而提高读写的效率
5.1 构造器
- 字节缓冲流构造器:
- public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in): 创建一个新的字节型的缓冲输入流
- public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out ):创建一个新的字节型的缓冲输出流
代码演示:
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("abc.jpg"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("abc_copy.jpg"));
- 字符缓冲流构造器
- public BufferedReader(Reader in):创建一个新的字符型的缓冲输入流
- public BufferedWriter(Writer out): 创建一个新的字符型的缓冲输出流
代码演示
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("br.txt));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("bw.txt));
5.2 效率测试
查询API,缓冲流读写方法与基本的流是一致的,我们通过复制大文件测试他们的读写效率
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
* 比较普通流和缓冲流的复制文件速度
*/
public class CopyFileWithFileStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String srcPath = "d:/test/Flutter.rar";
String destPath = "d:/test/copy_Flutter.rar";
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
ordinaryStream(srcPath, destPath);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("ordinary流完成复制花费的时间为: " + (end - start));
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
bufferedStream(srcPath, "d:/test/copy2_Flutter.rar");
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("bufferedStream流完成复制花费的时间为: " + (end - start));
}
//普通流完成文件copy
public static void ordinaryStream(String srcPath, String destPath){
//创建字节流文件读取的对象
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try{
fis = new FileInputStream(new File(srcPath));
fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(destPath));
//复制操作
byte [] buffer = new byte[100];
int len = 0;
while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){
fos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
System.out.println("复制成功!");
}catch (IOException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally{
try{
if (fis != null) {
fis.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try{
if (fos != null) {
fos.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
public static void bufferedStream(String srcPath, String destPath){
//字节输入输出流对象,以及字节缓冲输入输出流对象
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try{
fis = new FileInputStream(new File(srcPath));
fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(destPath));
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//copy
int len = 0;
byte [] buffer = new byte[100];
while((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1){
bos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
System.out.println("复制成功!");
}catch (IOException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally{
try{
if (bos != null) {
bos.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try{
if(bis != null){
bis.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
5.3 字符缓冲流特有方法
- 字符缓冲流的基本方法与普通字符流调用方法一致,以下为特有方法
- BufferedReader: public String readLine(): 读一行文字
- BufferedWriter: public void newLine(): 写一行行分隔符,由系统属性定义符号
通过代码演示一下具体的用法:
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
public class BufferedIOLine {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示readLine
try{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File("d:/test/cc.txt")));
//定义一个字符串保存读取的一行文字
String line = "";
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//演示写入换行
try{
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(new File("d:/test/cc.txt")));
bw.write("奇衡三");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("可以");
bw.write("召唤");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("魁拔的脉兽");
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 我们可以发现中华文化博大精深没有了,因为被新写入的文件覆盖掉了
- 还有一个重点内容我们需要知道:
- 涉及到嵌套的多个流时,如果都显式关闭的话,需要先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流
- 其实在开发中,只需要关闭最外层的流即可,因为在关闭外层流时,内层的流也会被关闭
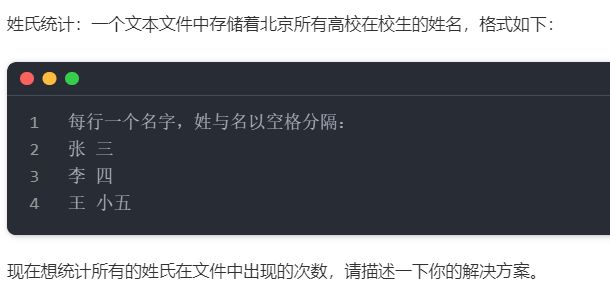
我们通过一个练习来进一步数据缓冲流:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//key对应姓,value为出现次数
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
//之所以要选取字符缓冲流,是因为要用它特有的readLine()读取一行数据
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File("e:/name.txt")));
String value = null; // 临时接收文件中的字符串变量
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
flag:
while ((value = br.readLine()) != null) { // 开始读取文件中的字符
char[] c = value.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
//拼接姓到buffer里,注意姓可能不是一个字
if (c[i] != ' ') {
buffer.append(String.valueOf(c[i]));
} else {
//我用了HashMap的getOrDefault优化了一下
if(map != null){
map.put(buffer.toString(), map.getOrDefault(buffer.toString(), 0) + 1);
}else{
map.put(buffer.toString(), 1)
/*
if (map.containsKey(buffer.toString())) {
int count = map.get(buffer.toString());
map.put(buffer.toString(), count + 1);
} else {
map.put(buffer.toString(), 1);
}
*/
//目的是将buffer重置为空串
buffer.delete(0, buffer.length());
continue flag;
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (br != null) {
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//排序
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> set = map.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> it = set.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, Integer> end = (Map.Entry<String, Integer>) it.next();
System.out.println(end);
}
}
六、转换流
- 针对文本文件,现在使用一个字节流进行数据的读入,希望将数据显示在控制台上,对于其中的中文数据可能会出现乱码
- 使用FileReader读取项目中的文本文件,由于IDEA设置中针对项目设置了UTF-8编码,当读取Windows系统中创建的文本文件时,如果Windows系统默认的是GBK编码,则读入内存会出现乱码
- 那么有没有什么办法可以解决以上的问题呢?
- 转换流是字节与字符之间的桥梁
6.1 InputStreamReader 与 OutputStreamReader
1、InputStreamReader
- 转换流 java.io.InputStreamReader,是Reader的子类,是从字节流到字符流的桥梁。 它读取字节,并使用指定的字符集将其解码为字符。它的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以接受平台的默认字符集
- 构造器:
- InputStreamReader(InputStream int): 创建一个使用默认字符集的字符流
- InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName):创建一个指定字符集的字符流
//两种构造方法演示
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("in.txt"));
OutputStreamReader osr = new OutputStreamReader(new FileOutputStream("out.txt"));
通过代码演示具体的用法
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
public class InputStreamReaderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建转换流的对象,指定编码字符集
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(new File("d:/test/a.txt")), "GBK");
int data = 0;
while((data = isr.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)data);
}
System.out.println();
if (isr != null) {
isr.close();
}
//创建字节流到字符流的转换流对象,不设置编码
InputStreamReader isr2 = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("d:/test/a.txt"));
int charData = 0;
while((charData = isr2.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)charData);
}
if (isr2 != null) {
isr2.close();
}
}
}
- 因为我的这个文件时UTF-8编码的,为了演示出乱码的效果,我就将转换流的编码设置成GBK
2、OutputStreamWriter
- 转换流: java.io.OutputStreamWriter,是Writer的子类,从字符流到字节流的桥梁,使用指定的字符集将字符编码为字节。它的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以接受平台的默认字符集
- 构造器:
- OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream in): 创建一个使用默认字符集的字符流
- OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charserName):创建一个指定字符集的字符流
OutputStreamWriter isr = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("out.txt"));
OutputStreamWriter isr2 = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("out.txt"), "GBK");
通过代码演示具体的使用方法:
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InvalidObjectException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
* 从字符流到字节流转换的桥梁
*/
public class OutputStreamWriterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String FileName = "d:/test/a.txt";
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(FileName));
osw.write("你好");//一个汉字在UTF-8里占3个字节
osw.close();
OutputStreamWriter osw2 = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("d:/test/aaa.txt"), "GBK");
osw2.write("你好");//一个汉字在GBK里占两个字节
osw2.close();
}
}
6.2 字符编码和字符集
1、编码和解码的概念
-
计算机中存储的信息都是用二进制数表示的
- 按照某种规则,将字符存储到计算机中,称之为编码
- 将存储在计算机中的二进制数按照某种规则解析显示出来,称之为解码
-
字符编码(Character Encoding):就是一套自然语言的字符与二进制数之间的对应规则
-
编码表:生活中文字和计算机中二进制的对应规则
-
什么情况下会出现乱码的现象呢?
- 用不同的规则进行存储和解析
2、各种字符集的介绍
-
字符集Charset:也叫编码表。是一个系统支持的所有字符的集合,包括各国家文字、标点符号、图形符号、数字等。
-
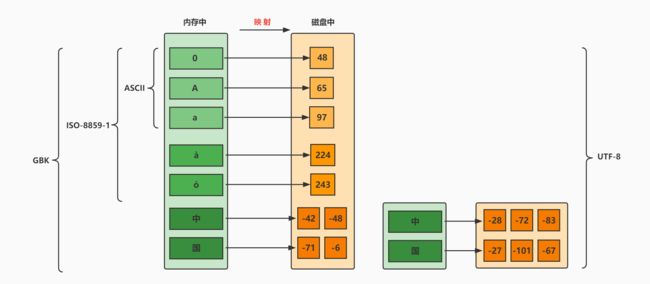
计算机要准确的存储和识别各种字符集符号,需要进行字符编码,一套字符集必然至少有一套字符编码。常见字符集有ASCII字符集、GBK字符集、Unicode字符集等
-
可见,当指定了编码,它所对应的字符集自然就指定了,所以编码才是我们最终要关心的
(1)ASCII字符集 :
- ASCII码(American Standard Code for Information Interchange,美国信息交换标准代码):上个世纪60年代,美国制定了一套字符编码,对英语字符与二进制位之间的关系,做了统一规定。这被称为ASCII码。
- ASCII码用于显示现代英语,主要包括控制字符(回车键、退格、换行键等)和可显示字符(英文大小写字符、阿拉伯数字和西文符号)。
- 基本的ASCII字符集,使用7位(bits)表示一个字符(最前面的1位统一规定为0),共128个字符。比如:空格“SPACE”是32(二进制00100000),大写的字母A是65(二进制01000001)。
- 缺点:不能表示所有字符。
(2)ISO-8859-1字符集:
- 拉丁码表,别名Latin-1,用于显示欧洲使用的语言,包括荷兰语、德语、意大利语、葡萄牙语等
- ISO-8859-1使用单字节编码,兼容ASCII编码。
(3)GBxxx字符集:
- GB就是国标的意思,是为了显示中文而设计的一套字符集。
- GB2312:简体中文码表。一个小于127的字符的意义与原来相同,即向下兼容ASCII码。但两个大于127的字符连在一起时,就表示一个汉字,这样大约可以组合了包含7000多个简体汉字,此外数学符号、罗马希腊的字母、日文的假名们都编进去了,这就是常说的"全角"字符,而原来在127号以下的那些符号就叫"半角"字符了。
- GBK:最常用的中文码表。是在GB2312标准基础上的扩展规范,使用了双字节编码方案,共收录了21003个汉字,完全兼容GB2312标准,同时支持繁体汉字以及日韩汉字等。
- GB18030:最新的中文码表。收录汉字70244个,采用多字节编码,每个字可以由1个、2个或4个字节组成。支持中国国内少数民族的文字,同时支持繁体汉字以及日韩汉字等。
(4)Unicode字符集 :
- Unicode编码为表达任意语言的任意字符而设计,也称为统一码、标准万国码Unicode 将世界上所有的文字用2个字节统一进行编码,为每个字符设定唯一的二进制编码,以满足跨语言、跨平台进行文本处理的要求。
- Unicode 的缺点:这里有三个问题:
- 第一,英文字母只用一个字节表示就够了,如果用更多的字节存储是极大的浪费
- 第二,如何才能区别Unicode和ASCII?计算机怎么知道两个字节表示一个符号,而不是分别表示两个符号呢?
- 第三,如果和GBK等双字节编码方式一样,用最高位是1或0表示两个字节和一个字节,就少了很多值无法用于表示字符,不够表示所有字符。
- Unicode在很长一段时间内无法推广,直到互联网的出现,为解决Unicode如何在网络上传输的问题,于是面向传输的众多 UTF(UCS Transfer Format)标准出现。具体来说,有三种编码方案,UTF-8、UTF-16和UTF-32。
(5)UTF-8字符集:
- Unicode是字符集,UTF-8、UTF-16、UTF-32是三种将数字转换到程序数据的编码方案。顾名思义,UTF-8就是每次8个位传输数据,而UTF-16就是每次16个位。其中,UTF-8 是在互联网上使用最广的一种 Unicode 的实现方式。
- 互联网工程工作小组(IETF)要求所有互联网协议都必须支持UTF-8编码。所以,我们开发Web应用,也要使用UTF-8编码。UTF-8 是一种变长的编码方式。它使用1-4个字节为每个字符编码,编码规则:
- 128个US-ASCII字符,只需一个字节编码。
- 拉丁文等字符,需要二个字节编码。
- 大部分常用字(含中文),使用三个字节编码。
- 其他极少使用的Unicode辅助字符,使用四字节编码。
在中文操作系统上,ANSI(美国国家标准学会、AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARDS INSTITUTE: ANSI)编码即为GBK;在英文操作系统上,ANSI编码即为ISO-8859-1
七、数据流、对象流
7.1 数据流与对象流的说明
-
如果需要将内存中定义的变量(包括基本数据类型或引用数据类型)保存在文件中,那怎么办呢?
- Java提供了数据流和对象流来处理这些类型的数据
-
数据流: DataOutputStream、DataInputStream
- DataOutputStream: 允许应用程序将基本数据类型、String类型的变量写入输出流中
- DataInputStream:允许应用程序以与机器无关的方式从底层输入流中读取基本数据类型、String类型的变量
-
数据输入流和数据输出流的方法类似:【read-write相互替换即可】
- 数据输入、输出流存在弊端:就是只支持基本数据类型和String类的读写
然而对象流既支持基本数据类型的读写,又支持Java对象的读写
- 对象流:ObjectOutputStream、ObjectInputStream
- ObjectOutputStream: 将Java基本数据类型和对象写入字节输出流中, 通过在流中使用文件可以实现Java各种基本数据类型的==数据以及对象的持久化存储 ==
- ObjectInputStream: 对以前使用 ObjectOutputStream写出的基本数据类型的数据和对象进行读入操作,保存在内存中
对象流最大的优势就是:可以把Java对象写入到数据源中,也可以把对象从数据源中还原回来
7.2 对象流API
1、ObjectOutputStream 的构造器与常用方法:
- ObjectOutputStream中的构造器:
public ObejectOutputStream(OutputStream out):创建一个指定的ObjectOutputStream
ObjectOutputStream 中的常用方法:
- public void writeBoolean(boolean val):写出一个 boolean 值。
- public void writeByte(int val):写出一个8位字节
- public void writeShort(int val):写出一个16位的 short 值
- public void writeChar(int val):写出一个16位的 char 值
- public void writeInt(int val):写出一个32位的 int 值
- public void writeLong(long val):写出一个64位的 long 值
- public void writeFloat(float val):写出一个32位的 float 值。
- public void writeDouble(double val):写出一个64位的 double 值
- public void writeUTF(String str):将两个字节的长度信息写入输出流,其后是字符串 s中每个字符的s 。 如果s是null ,则抛出一个NullPointerException 。 字符串s中的每个字符根据字符的值s为一个,两个或三个字节的组
- public void writeObject(Object obj):写出一个obj对象
- public void close() :关闭此输出流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源
2、ObjectInputStream 的构造器与常用方法:
- ObjectInputStream中的构造器:
public ObjectInputStream(InputStream in):创建一个指定的ObjectInputStream
ObjectInputStream 中的常用方法:
- public boolean readBoolean():读取一个 boolean 值
- public byte readByte():读取一个 8 位的字节
- public short readShort():读取一个 16 位的 short 值
- public char readChar():读取一个 16 位的 char 值
- public int readInt():读取一个 32 位的 int 值
- public long readLong():读取一个 64 位的 long 值
- public float readFloat():读取一个 32 位的 float 值
- public double readDouble():读取一个 64 位的 double 值
- public String readUTF():读取 UTF-8 修改版格式的 String
- public void readObject(Object obj):读入一个obj对象
- public void close() :关闭此输入流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源
7.3 认识对象序列化机制
1、什么是对象序列化机制?
-
对象序列化机制:允许把内存中的Java对象转化成与平台无关的二进制流。从而把这种二进制流持久地保存在磁盘上,或通过网络将这种二进制流传输到另一个网络节点。
-
序列化机制包括两个过程:
- 序列化过程:用一个字节序列可以表示一个对象,该字节序列包括该 对象的类型 和 对象中存储的属性 等信息。字节序列写出到文件之后,相当于文件中 持久保存 了一个对象的信息
- 反序列化过程:该字节序列还可以从文件中读取回来,重构对象,对它进行反序列化。其中对象的数据、对象的类型和对象中存储的数据信息,都可以用来在内存中创建对象
-
序列化是 RMI(Remote Method Invoke、远程方法调用)过程的参数和返回值都必须实现的机制,而 RMI 是 JavaEE 的基础。因此序列化机制是 JavaEE 平台的基础。
-
序列化的好处,在于可将任何实现了Serializable接口的对象转化为字节数据,使其在保存和传输时可被还原
3、序列化机制的实现原理是什么?
- 序列化:用ObjectOutputStream类保存基本类型数据或对象的机制。方法为:
- public final void writeObject (Object obj) : 将指定的对象写出。
- 反序列化:用ObjectInputStream类读取基本类型数据或对象的机制。方法为:
- public final Object readObject () : 读取一个对象。
4、如何实现序列化机制?
如果我们想让某个对象支持序列化机制,就必须让其所属类实现 java.io.Serializable 接口
- 通过代码来演示如何完成序列化和反序列化
- 如果有多个对象需要序列化,可以将对象放到集合中,再序列化集合对象即可
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
public class ReadWriteObject {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建学生类对象
Student s = new Student("042040133", "JiaSiting", 21);
//序列化
try{
//创建对象输入流,将我们的Java对象写入到指定的文件中
File f = new File("d:/test/student.txt");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f));
oos.writeObject(s);
oos.close();
System.out.println("Serialized data is saved");
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//反序列化
try{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("d:/test/student.txt")));
try{
Student stu = (Student) ois.readObject();
ois.close();
System.out.println(stu);
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//创建学生类让它实现Serializable接口,使其对象支持序列化机制
class Student implements Serializable {
private String sno;
private String sname;
private int age;
public Student(String sno, String sname, int age) {
this.sno = sno;
this.sname = sname;
this.age = age;
}
public String getSno() {
return sno;
}
public void setSno(String sno) {
this.sno = sno;
}
public String getSname() {
return sname;
}
public void setSname(String sname) {
this.sname = sname;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"sno='" + sno + '\'' +
", sname='" + sname + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
7.5 反序列化失败问题
1、反序列化失败的两种情况:
-
对于JVM可以反序列化对象,他必须是能够遭到 class 文件的类。否则会抛出 CLassNotFoundException 异常
-
能够找到class文件,但是在序列化对象之后发生了修改,那么反序列化操作也会失败,会抛出 InvalidClassException 异常
- 有可能是该类的序列版本号与从流中读取的类描述符的版本号不匹配
- 该类包含未知数据类型
2、那么如何解决上面的问题呢?
- Serializable 接口给需要序列化的类,提供了一个序列化版本号:serialVersionUID
- 凡是实现 Serializable 接口的类都应该有一个表示序列化版本标识符的静态变量
static final long serialVersionUID = 234242343243L; //它的值由程序员随意指定即可。
- serialVersionUID用来表明类的不同版本间的兼容性。
简单来说,Java 的序列化机制是通过在运行时判断类的serialVersionUID来验证版本一致性的。
在进行反序列化时,JVM会把传来的字节流中的serialVersionUID与本地相应实体类的serialVersionUID进行比较,如果相同就认为是一致的,可以进行反序列化,否则就会出现序列化版本不一致的异常(InvalidCastException)。
- 如果类没有显示定义这个静态常量,它的值是Java运行时环境根据类的内部细节自动生成的。若类的实例变量做了修改,serialVersionUID 可能发生变化。因此,建议显式声明
- 如果声明了serialVersionUID,即使在序列化完成之后修改了类导致类重新编译,则原来的数据也能正常反序列化,只是新增的字段值是默认值而已。
package com.atguigu.object;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Employee implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1324234L; //增加serialVersionUID
}
3、综合练习
(1)谈谈你对java.io.Serializable接口的理解,我们知道它用于序列化,是空方法接口,还有其它认识吗?
实现了Serializable接口的对象,可将它们转换成一系列字节,并可在以后完全恢复回原来的样子。这一过程亦可通过网络进行。这意味着序列化机制能自动补偿操作系统间的差异。换句话说,可以先在Windows机器上创建一个对象,对其序列化,然后通过网络发给一台Unix机器,然后在那里准确无误地重新“装配”。不必关心数据在不同机器上如何表示,也不必关心字节的顺序或者其他任何细节。
由于大部分作为参数的类如String、Integer等都实现了java.io.Serializable的接口,也可以利用多态的性质,作为参数使接口更灵活。
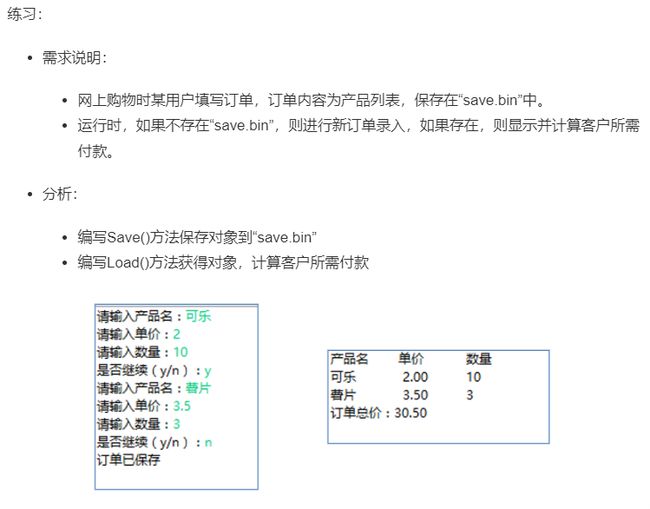
(2)要求如图:
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.operations.Or;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
* 需求说明:
* 网上购物时某用户填写订单,订单内容为产品列表,保存在“save.bin”中。
* 运行时,如果不存在“save.bin”,则进行新订单录入,如果存在,则显示并计算客户所需付款。
* 分析:
* 编写Save()方法保存对象到“save.bin”
* 编写Load()方法获得对象,计算客户所需付款
*/
public class OrderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<OrderInformation> lists = new ArrayList<OrderInformation>();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
char op = 'y';
while(op == 'y'){
System.out.print("请输入产品名:");
String name = sc.next();
System.out.print("请输入单价:");
Double price = sc.nextDouble();
System.out.print("请输入数量:");
int count = sc.nextInt();
//创建商品订单对象
OrderInformation order = new OrderInformation(name, price, count);
lists.add(order);
//是否继续操作
System.out.print("是否继续(y/n):");
op = sc.next().charAt(0);
}
System.out.println("订单已保存");
//将完整订单写到目标文件中
save(lists);
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
load();
}
//存储订单信息
public static void save(ArrayList<OrderInformation> o){
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try{
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("d:/test/save.bin")));
oos.writeObject(o);
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try{
if (oos != null) {
oos.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//加载订单信息,获取总金额
public static void load(){
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try{
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("d:/test/save.bin")));
//计算客户需要支付的总金额
Double countMoney = 0.0;
ArrayList<OrderInformation> lists = (ArrayList<OrderInformation>)ois.readObject();
System.out.println("产品名" + "\t" + "单价" + "\t\t" + "数量");
for(OrderInformation order : lists){
countMoney += order.getPrice() * order.getCount();
System.out.println(order.getOrderName() + "\t\t" + order.getPrice() + "\t\t" + order.getCount());
}
System.out.println("您需要支付的金额为: " + countMoney);
}catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class OrderInformation implements Serializable {
//定义一个序列号
private static final long serialVersionUID = 123456789L;
//订单属性
private String orderName;
private Double price;
private int count;
public OrderInformation(){}
public OrderInformation(String orderName, double price, int count) {
this.orderName = orderName;
this.price = price;
this.count = count;
}
public String getOrderName() {
return orderName;
}
public void setOrderName(String orderName) {
this.orderName = orderName;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "OrderInformation{" +
"orderName='" + orderName + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", count=" + count +
'}';
}
}
八、其他流的使用
8.1 标准输入、输出流
- System.in和System.out分别代表了系统标准的输入和输出设备
- 默认输入设备是:键盘,输出设备是:显示器
- System.in的类型是InputStream
- System.out的类型是PrintStream,其是OutputStream的子类FilterOutputStream 的子类
- 重定向:通过System类的setIn、setOut 方法对默认设备进行改变
- public static void setIn(InputStream in)
- public static void setOut(PrintStream out)
1、 通过案例来分析如何使用标准输入、输出流
- 从键盘输入字符串,要求将读取到的整行字符串转成大写输出。然后继续进行输入操作,直至当输入“e”或者“exit”时,退出程序
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
* 从键盘输入字符串,要求将读取到的整行字符串转成大写输出。
* 然后继续进行输入操作,直至当输入“e”或者“exit”时,退出程序
*/
public class SystemTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入信息(退出输入e 或 exit):");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
String s = null;
try{
while((s = br.readLine()) != null){
//判断输入的是否为跳出操作
if(s.equalsIgnoreCase("e") || s.equalsIgnoreCase("exit")){
break;
}
pw.println(s.toUpperCase());
pw.flush();
System.out.println("继续输入信息");
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try{
//释放连接
if (br != null) {
br.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2、System类中有三个常量对象:System.out、System.in、System.err
public final static InputStream in = null;
public final static PrintStream out = null;
public final static PrintStream err = null;
- 这三个常量对象有final声明,但是却初始化为null。final声明的常量一旦赋值就不能修改,那么null不会空指针异常吗?
- 这三个常量对象为什么要小写?final声明的常量按照命名规范不是应该大写吗?
- 这三个常量的对象有set方法?final声明的常量不是不能修改值吗?set方法是如何修改它们的值的?
final声明的常量,表示在Java的语法体系中它们的值是不能修改的,而这三个常量对象的值是由C/C++等系统函数进行初始化和修改值的,所以它们故意没有用大写,也有set方法。
public static void setOut(PrintStream out) {
checkIO();
setOut0(out);
}
public static void setErr(PrintStream err) {
checkIO();
setErr0(err);
}
public static void setIn(InputStream in) {
checkIO();
setIn0(in);
}
private static void checkIO() {
SecurityManager sm = getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPermission(new RuntimePermission("setIO"));
}
}
private static native void setIn0(InputStream in);
private static native void setOut0(PrintStream out);
private static native void setErr0(PrintStream err);
3、练习
Create a program named MyInput.java: Contain the methods for reading int, double, float, boolean, short, byte and String values from the keyboard.
package com.atguigu.java;
// MyInput.java: Contain the methods for reading int, double, float, boolean, short, byte and
// string values from the keyboard
import java.io.*;
public class MyInput {
// Read a string from the keyboard
public static String readString() {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// Declare and initialize the string
String string = "";
// Get the string from the keyboard
try {
string = br.readLine();
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex);
}
// Return the string obtained from the keyboard
return string;
}
// Read an int value from the keyboard
public static int readInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(readString());
}
// Read a double value from the keyboard
public static double readDouble() {
return Double.parseDouble(readString());
}
// Read a byte value from the keyboard
public static double readByte() {
return Byte.parseByte(readString());
}
// Read a short value from the keyboard
public static double readShort() {
return Short.parseShort(readString());
}
// Read a long value from the keyboard
public static double readLong() {
return Long.parseLong(readString());
}
// Read a float value from the keyboard
public static double readFloat() {
return Float.parseFloat(readString());
}
}
8.2 打印流
- 实现将基本数据类型的数据格式转化为字符串输出
- 打印流:PrintStream、PrintStream
- 提供了一系列重载的print()和println()方法,用于多种数据类型的输出

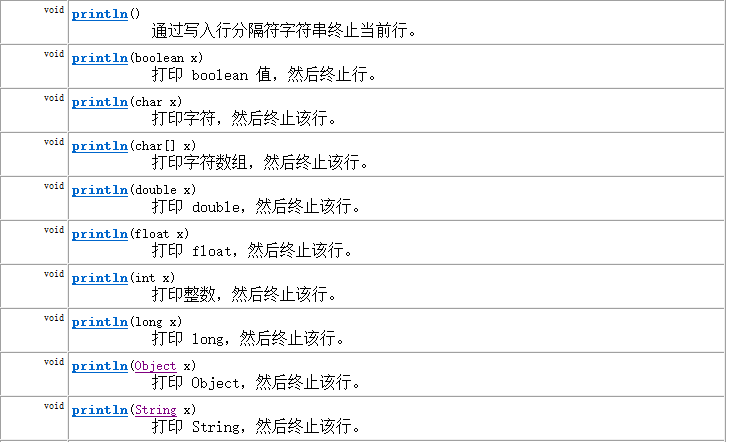
- PrintStream和PrintWriter的输出不会抛出IOException异常
- PrintStream和PrintWriter有自动flush功能
- PrintStream 打印的所有字符都使用平台的默认字符编码转换为字节。在需要写入字符而不是写入字节的情况下,应该使用 PrintWriter 类。
- System.out返回的是PrintStream的实例
- 构造器
- PrintStream(File file) :创建具有指定文件且不带自动行刷新的新打印流
- PrintStream(File file, String csn):创建具有指定文件名称和字符集且不带自动行刷新的新打印流。
- PrintStream(OutputStream out) :创建新的打印流。
- PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush):创建新的打印流。 autoFlush如果为 true,则每当写入 byte 数组、调用其中一个 println 方法或写入换行符或字节 (‘\n’) 时都会刷新输出缓冲区。
- PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush, String encoding) :创建新的打印流。
- PrintStream(String fileName):创建具有指定文件名称且不带自动行刷新的新打印流。
- PrintStream(String fileName, String csn) :创建具有指定文件名称和字符集且不带自动行刷新的新打印流。
通过代码演示具体用法:自定义一个日志工具
package com.zwh.shangguigu.fileandio_;
import java.io.*;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
public class LoggerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Logger.log("调用了System类的gc()方法,建议启动垃圾回收");
Logger.log("调用了TeamView的addMember()方法");
Logger.log("用户尝试进行登录,验证失败");
}
}
class Logger{
public static void log(String msg){
try{
// 指向一个日志文件
PrintStream out = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("log.txt"), true);
// 改变输出方向
System.setOut(out);
// 日期当前时间
Date nowTime = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS");
String strTime = sdf.format(nowTime);
System.out.println(strTime + ": " + msg);
}catch (FileNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
8.3 Scanner 类
-
构造方法:
- Scanner(File source): 构造一个新的 Scanner,它生成的值是从指定文件扫描的
- Scanner(File source, String charsetName): 构造一个新的 Scanner,它生成的值是从指定文件扫描的
- Scanner(InputStream source):构造一个新的 Scanner,它生成的值是从指定的输入流扫描的
- Scanner(InputStream source, String charsetName) :构造一个新的 Scanner,它生成的值是从指定的输入流扫描的
-
常用方法:
- boolean hasNextXxx(): 如果通过使用nextXxx() 方法,此扫描器输入信息中的下一个标记可以解释为默认基数中的一个Xxx值,则返回true
- hasNextXxx():是否还有下一个输入项,其中Xxx可以是Int、Long等代表基本数据类型的字符串。如果需要判断是否包含下一个字符串,可以省略Xxx.
- Xxx nextXxx(): 将输入信息的下一个标记扫描为一个Xxx
- nextXxx():获取下一个输入项。Xxx的含义与前一个方法中Xxx相同。
- boolean hasNextXxx(): 如果通过使用nextXxx() 方法,此扫描器输入信息中的下一个标记可以解释为默认基数中的一个Xxx值,则返回true
通过代码演示具体用法:
package com.atguigu.systemio;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestScanner {
@Test
public void test01() throws IOException {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("1.txt");
while(true){
System.out.print("请输入一个单词:");
String str = input.nextLine();
if("stop".equals(str)){
break;
}
ps.println(str);
}
input.close();
ps.close();
}
@Test
public void test2() throws IOException {
Scanner input = new Scanner(new FileInputStream("1.txt"));
while(input.hasNextLine()){
String str = input.nextLine();
System.out.println(str);
}
input.close();
}
}
九、apache-common包的使用
- IO技术开发中,代码量很大,而且代码的重复率较高,为此Apache软件基金会,开发了IO技术的工具类commonsIO,大大简化了IO开发【需要添加jar包】
- 在导入commons-io-2.5.jar包之后,内部的API都可以使用
IOUtils类的使用
- 静态方法:IOUtils.copy(InputStream in,OutputStream out)传递字节流,实现文件复制。
- 静态方法:IOUtils.closeQuietly(任意流对象)悄悄的释放资源,自动处理close()方法抛出的异常。
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
//- 静态方法:IOUtils.copy(InputStream in,OutputStream out)传递字节流,实现文件复制。
IOUtils.copy(new FileInputStream("E:\\Idea\\io\\1.jpg"),new FileOutputStream("E:\\Idea\\io\\file\\柳岩.jpg"));
//- 静态方法:IOUtils.closeQuietly(任意流对象)悄悄的释放资源,自动处理close()方法抛出的异常。
/* FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter("day21\\io\\writer.txt");
fw.write("hahah");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
IOUtils.closeQuietly(fw);
}*/
}
}
FileUtils类的使用:
- 静态方法:void copyDirectoryToDirectory(File src,File dest):整个目录的复制,自动进行递归遍历
参数:
src:要复制的文件夹路径
dest:要将文件夹粘贴到哪里去
- 静态方法:void writeStringToFile(File file,String content):将内容content写入到file中
- 静态方法:String readFileToString(File file):读取文件内容,并返回一个String
- 静态方法:void copyFile(File srcFile,File destFile):文件复制
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//- 静态方法:void copyDirectoryToDirectory(File src,File dest);
FileUtils.copyDirectoryToDirectory(new File("E:\\Idea\\io\\aa"),new File("E:\\Idea\\io\\file"));
//- 静态方法:writeStringToFile(File file,String str)
FileUtils.writeStringToFile(new File("day21\\io\\commons.txt"),"柳岩你好");
//- 静态方法:String readFileToString(File file)
String s = FileUtils.readFileToString(new File("day21\\io\\commons.txt"));
System.out.println(s);
//- 静态方法:void copyFile(File srcFile,File destFile)
FileUtils.copyFile(new File("io\\yangm.png"),new File("io\\yangm2.png"));
System.out.println("复制成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}