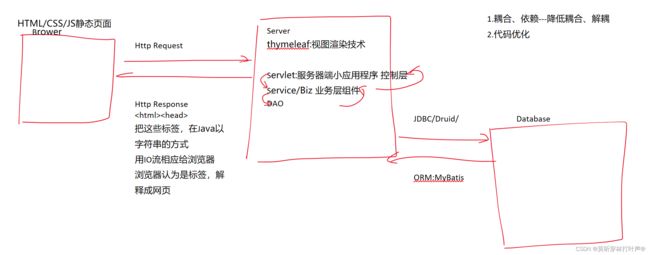
JDBC---Java连接数据库
- 第一章 JDBC概述
1.1 JDBC概述
jdbc是(Java Database Connectivity)单词的缩写,翻译为java连接数据库。是Java程序连接数据库的技术总称。
JDBC由两个部分组成:
①java语言的规范(接口)
②各个数据库厂商的实现驱动(jar)组成
所以不一定只连接MySQL,Java API中提供的是接口规范,导入不同数据库厂商的jar包,从不同的实现类里获取连接,就连接上了不同的数据库。
1.2 JDBC使用步骤
0.添加jar
1.注册驱动
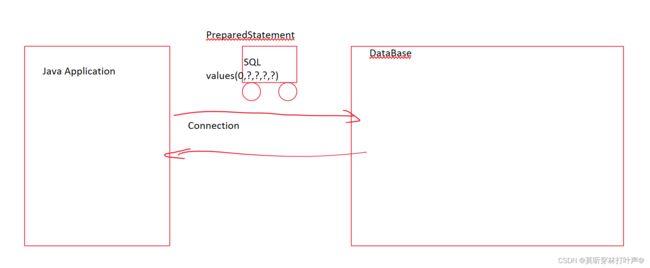
2.获取连接Connection
3.编写SQL语句
4.创建预处理命令对象PreparedStatement
5.填参数
6.执行SQL语句,并返回结果(“增删改”返回影响行数,“查”返回结果集,解析结果集)
7.释放连接
- 第二章 使用PreparedStatement处理CRUD
2.0简单的CRUD:
先提供一个实体类pojo:里面生成必要的方法
public class Fruit {
private Integer fid;
private String fname;
private Integer price;
private Integer fcount;
private String remark;
public Fruit(){
}
public Fruit(Integer fid, String fname, String remark) {
this.fid = fid;
this.fname = fname;
this.remark = remark;
}
public Fruit(Integer fid, String fname, Integer price, Integer fcount, String remark) {
this.fid = fid;
this.fname = fname;
this.price = price;
this.fcount = fcount;
this.remark = remark;
}
public Integer getFid() {
return fid;
}
public void setFid(Integer fid) {
this.fid = fid;
}
public String getFname() {
return fname;
}
public void setFname(String fname) {
this.fname = fname;
}
public Integer getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Integer price) {
this.price = price;
}
public Integer getFcount() {
return fcount;
}
public void setFcount(Integer fcount) {
this.fcount = fcount;
}
public String getRemark() {
return remark;
}
public void setRemark(String remark) {
this.remark = remark;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Fruit{" +
"fid=" + fid +
", fname='" + fname + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", fcount=" + fcount +
", remark='" + remark + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
添加数据:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//2.通过驱动管理器获取连接对象
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/fruitdb?user=root&password=0630");
//3.编写SQL语句
String sql="insert into t_fruit values(0,?,?,?,?)";
//4.创建预处理命令对象
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.填充参数
preparedStatement.setString(1,"榴莲");
preparedStatement.setString(2,"15");
preparedStatement.setString(3,"100");
preparedStatement.setString(4,"榴莲是一种神奇的水果");
//6.执行更新(增删改),返回影响行数
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(i>0?"添加成功":"添加失败");
//7.释放资源
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
更新数据:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Fruit fruit=new Fruit(33,"猕猴桃","猕猴桃营养价值很高");
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/fruitdb?user=root&password=0630");
String sql="update t_fruit set fname=?,remark=? where fid=?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1,fruit.getFname());
preparedStatement.setString(2,fruit.getRemark());
preparedStatement.setInt(3,fruit.getFid());
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(i>0?"修改成功":"修改失败");
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
删除数据:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Fruit fruit=new Fruit(33,"猕猴桃","猕猴桃营养价值很高");
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/fruitdb?user=root&password=0630");
String sql="delete from t_fruit where fid=?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1,fruit.getFid());
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(i>0?"删除成功":"删除失败");
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
查询数据:把每一行的每一列都取出来,一次放一行数据到List中,最后将list打印。
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/fruitdb?user=root&password=0630");
String sql="select * from t_fruit";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.执行查询 返回结果集
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//6.解析结果集
List<Fruit> fruitList=new ArrayList<>();
//resultSet.next()返回的是一个布尔值
//第一层循环返回的是第一行
while (resultSet.next()){
//1表示读取当前行的第一列的数据
//getInt 因为这一列是int类型,所以使用getInt
//所以这次循环得到的就是第一行的第一列
//放编号 和列名都是可以的(结果集的列名 有别名加别名)
int fid = resultSet.getInt(1);
String fname = resultSet.getString(2);
int price = resultSet.getInt(3);
int fcount = resultSet.getInt(4);
String remark = resultSet.getString(5);
Fruit fruit = new Fruit(fid, fname, price, fcount, remark);
fruitList.add(fruit);
}
resultSet.close();
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
fruitList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
查询指定的数据:查询一条数据就不用List了,直接用实体类对象就OK
这里用了集合,不用的话去掉集合声明,直接输出实体类对象
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/fruitdb?user=root&password=0630");
String sql="select fid,fname,price,fcount,remark from t_fruit where fid=?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1,2);
List<Fruit> fruitList=new ArrayList<>();
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()){
String fidStr = resultSet.getString("fid");
Integer fid = Integer.parseInt(fidStr);
String fname = resultSet.getString("fname");
String priceStr = resultSet.getString("price");
Integer price = Integer.parseInt(priceStr);
String fcountStr = resultSet.getString("fcount");
Integer fcount=Integer.parseInt(fcountStr);
String remark = resultSet.getString("remark");
//不要集合 直接在这里输出也可以 只有一条记录
Fruit fruit = new Fruit(fid, fname, price, fcount, remark);
fruitList.add(fruit);
}
fruitList.forEach(System.out::println);
resultSet.close();
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
查询总记录条数:结果集就只有一行一列
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/fruitdb?user=root&password=0630");
String sql="select count(fid) from t_fruit";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//这个结果集只有一行一列
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()){
int anInt = resultSet.getInt(1);
System.out.println(anInt);
}
resultSet.close();
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
2.1通过PreparedStatement解决Statement的问题
Statement使用字符串拼接的方式,会有SQL注入的问题。使用PreparedStatement。
面试题: 如何避免SQL注入?
1.使用PreparedStatement
2.使用正则表达式过滤传入的参数
3.字符串过滤
4.JSP中调用该函数检查是否包非法字符
5.JSP页面判断代码
2.2获取自增长键值
为什么要获得自增长的主键值,当主表添加数据的时候,主键自增长了。从表要添加新数据的时候,外键和主表的主键相关联,此时需要知道主表自增长的主键值是什么,就需要将自增长的主键值回显。
如何解决?在第四步创建预处理命令对象PreparedStatement时传入第二个参数Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS,告知SQL取数据的时候将自增长的主键值带回来,以后要用
代码:只有在插入的时候进行主键回显,判断一下SQL语句是以INSERT开始,使用主键回显
protected int executeUpdate(String sql,Object... params){
boolean insertFlag=false;
insertFlag=sql.trim().toUpperCase().startsWith("INSERT");
try {
connection=getConnection();
if (insertFlag){
connection.prepareStatement(sql,Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
}else {
preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
}
setParams(preparedStatement,params);
int count= preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
resultSet= preparedStatement.getGeneratedKeys();
if (resultSet.next()){
return ((Long)resultSet.getLong(1)).intValue();
}
return count;
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(resultSet,preparedStatement,connection);
}
return 0;
}
2.3批处理
为了加快插入的速度,设置URL属性rewriteBatchedStatement=true
原理:将插入的数据统一追加到values后面,一批添加
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//2.通过驱动管理器获取连接对象 如果要执行批处理任务 需要添加一个参数 rewriteBatchedStatement=true
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/fruitdb?rewriteBatchedStatement=true&user=root&password=0630");
//3.编写SQL语句
String sql="insert into t_fruit values(0,?,?,?,?)";
//4.创建预处理命令对象
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.填充参数
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
preparedStatement.setString(1,"榴莲"+i);
preparedStatement.setString(2,"15");
preparedStatement.setString(3,"100");
preparedStatement.setString(4,"榴莲是一种神奇的水果");
//追加到values 追加 放到一批处理
preparedStatement.addBatch();
//如果任务较多 可以分批次执行 每次执行完 清空任务队列
if (i%1000==0){
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
preparedStatement.clearBatch();
}
}
//6.执行更新(增删改),返回影响行数
//剩下的批处理用这条执行
int[] count = preparedStatement.executeBatch();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(count));
//7.释放资源
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
2.4事务
数据库事务就是一种SQL语句执行的缓存机制,不会单条执行完毕就更新数据库数据,最终根据缓存内的多条语句执行结果统一判定。
一个事务内所有语句都成功及事务成功,我们可以触发commit提交事务来结束事务,更新数据。
一个事务内任意一条语句失败,及事务失败,我们可以触发rollback回滚结束事务,数据回到事务之前状态。
事务的ACID特性
- 原子性(Atomicity)原子性是指事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中的操作要么都发生,要么都不发生。
- 一致性(Consistency)事务必须使数据库从一个一致性状态变换到另外一个一致性状态。
- 隔离性(Isolation)事务的隔离性是指一个事务的执行不能被其他事务干扰,即一个事务内部的操作及使用的数据对并发的其他事务是隔离的,并发执行的各个事务之间不能互相干扰。
- 持久性(Durability)持久性是指一个事务一旦被提交,它对数据库中数据的改变就是永久性的,接下来的其他操作和数据库故障不应该对其有任何影响。
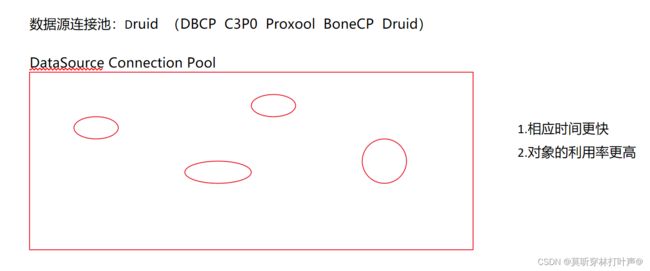
- 第三章 数据库连接池—Druid数据源连接技术
连接Connection用的时候创建,用完了再销毁太过浪费。使用数据源连接技术,提供一个连接池,里面存放连接,使用的时候从连接池取,使用完后放回连接池。
步骤:
1.导入jar
2.硬编码方式和软编码方式(推荐)
硬编码连接方式 代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/fruitdb?user=root&password=0630");
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
//1.被close()的连接对象,并没有真正关闭,而是将状态重新设置为空闲状态,然后放回池中。这样下次获取连接对象,这个对象可以被重复使用
//2.没有被close()的连接对象会被一直被占用
}
软编码连接方式 代码:
首先要提供一个配置文件:里面的key是固定的
driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/fruitdb
username=root
password=0630
initialSize=2
maxActive=5
maxWait=5000
使用Druid工厂创建连接池:
Properties读的是输入流,使用当前类的类加载器将配置文件变成一个输入流,再使用Properties对象加载,就能获取到配置文件的key-value
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//切换jar包修改配置文件就可以了
Properties properties = new Properties();
//类加载器
InputStream resourceAsStream = DemoDruid2.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc2.properties");
properties.load(resourceAsStream);
//key是固定的
DataSource dataSource= DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
}
- 第四章 代码封装
DAO(Data Access Object数据访问对象)层是用来操作数据库的,要有一个DAO接口来规范:
表中的一条记录就对应实体类的一个对象。所有的记录放在List中,即List中的数据就是一个一个的Fruit对象。
public interface FruitDAO {
/**
* 查询库存列表
* @return
*/
List<Fruit> getFruitList();
/**
* 新增库存
*/
boolean addFruit(Fruit fruit);
/**
* 修改库存
*/
boolean updateFruit(Fruit fruit);
/**
* 根据名称查询指定库存
*/
Fruit getFruitByFname(String fname);
/**
* 删除特定库存记录
*/
boolean delFruit(String fname);
}
未封装前的代码:
实现类:实现的是上面DAO接口
public class FruitDaoImpl implements FruitDAO {
Connection connection;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement;
ResultSet resultSet;
final String DRIVER="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
final String URL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/fruitdb?user=root&password=0630";
@Override
public List<Fruit> getFruitList() {
List<Fruit> fruitList=new ArrayList<>();
try {
Class.forName(DRIVER);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL);
String sql="select * from t_fruit";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//解析结果集
while (resultSet.next()){
int fid=resultSet.getInt(1);
String fname=resultSet.getString(2);
int price=resultSet.getInt(3);
int fcount=resultSet.getInt(4);
String remark=resultSet.getString(5);
Fruit fruit = new Fruit(fid, fname, price, fcount, remark);
fruitList.add(fruit);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
try {
if (resultSet!=null){
resultSet.close();
}
if (preparedStatement!=null){
preparedStatement.close();
}
if (connection!=null&&!connection.isClosed()){
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return fruitList;
}
@Override
public boolean addFruit(Fruit fruit) {
try {
Class.forName(DRIVER);
connection= DriverManager.getConnection(URL);
String sql="insert into t_fruit values(0,?,?,?,?)";
preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1,fruit.getFname());
preparedStatement.setInt(2,fruit.getPrice());
preparedStatement.setInt(3,fruit.getFcount());
preparedStatement.setString(4,fruit.getRemark());
return preparedStatement.executeUpdate()>0;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
if (preparedStatement!=null){
preparedStatement.close();
}
if (connection!=null&&!connection.isClosed()){
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean updateFruit(Fruit fruit) {
try {
Class.forName(DRIVER);
connection= DriverManager.getConnection(URL);
String sql="update t_fruit set fcount=? where fid=?";
preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1,fruit.getFcount());
preparedStatement.setInt(2,fruit.getFid());
return preparedStatement.executeUpdate()>0;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
if (resultSet!=null){
resultSet.close();
}
if (preparedStatement!=null){
preparedStatement.close();
}
if (connection!=null&&!connection.isClosed()){
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
@Override
public Fruit getFruitByFname(String fname) {
try {
Class.forName(DRIVER);
connection= DriverManager.getConnection(URL);
String sql="select * from t_fruit where fname like ?";
preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1,fname);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()){
int fid=resultSet.getInt(1);
int price=resultSet.getInt(3);
int fcount=resultSet.getInt(4);
String remark=resultSet.getString(5);
return new Fruit(fid,fname,price,fcount,remark);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean delFruit(String fname) {
try {
Class.forName(DRIVER);
connection= DriverManager.getConnection(URL);
String sql="delete from t_fruit where fname like ?";
preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1,fname);
return preparedStatement.executeUpdate()>0;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
if (preparedStatement!=null){
preparedStatement.close();
}
if (connection!=null&&!connection.isClosed()){
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
对代码进行封装:
查询中:要先设法获取到泛型的类型,是Fruit。拿到泛型的类型后,通过反射创建一个实例,得到fruit对象。每取出一行一列的数据,给fruit对象赋值,然后将这个fruit对象追加到list中。
public abstract class BaseDAO<T> {
public final String DRIVER="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
public final String URL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/fruitdb?user=root&password=0630";
protected Connection connection;
protected PreparedStatement preparedStatement;
protected ResultSet resultSet;
/**
* 获取T的Class对象
* 怎么获取?
*/
private Class entityClass;
public BaseDAO(){
//getClass()获取实现类(FruitDAOImpl)的Class,创建的是FruitDAOImpl的实例
//那么子类构造方法内部首先会调用父类BaseDAO的无参构造方法
//因此此处的getClass()会执行,但是getClass获取的是FruitDAOImpl的Class
//getGenericSuperclass()获取的是BaseDAO的Class
Type genericType=getClass().getGenericSuperclass();
//ParameterizedType参数化类型 获取实际的类型参数 实际传入的类型是什么 就可以获取到
Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType) genericType).getActualTypeArguments();
//获取到的中的T的真实的类型
Type actualType = actualTypeArguments[0];
try {
//得到泛型的类型名 就是Fruit
entityClass=Class.forName(actualType.getTypeName());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
protected Connection getConnection(){
try {
Class.forName(DRIVER);
return DriverManager.getConnection(URL);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
protected void close(ResultSet resultSet, PreparedStatement preparedStatement, Connection connection){
try {
if (resultSet!=null){
resultSet.close();
}
if (preparedStatement!=null){
preparedStatement.close();
}
if (connection!=null&&!connection.isClosed()){
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/**
* 给预处理命令对象设置参数
* @param preparedStatement
* @param params
* @throws SQLException
*/
private void setParams(PreparedStatement preparedStatement,Object... params) throws SQLException {
if (params!=null&¶ms.length>0){
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1,params[i]);
}
}
}
/**
* 执行更新,返回影响行数
*/
protected int executeUpdate(String sql,Object... params){
boolean insertFlag=false;
insertFlag=sql.trim().toUpperCase().startsWith("INSERT");
try {
connection=getConnection();
if (insertFlag){
connection.prepareStatement(sql,Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
}else {
preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
}
setParams(preparedStatement,params);
int count= preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
resultSet= preparedStatement.getGeneratedKeys();
if (resultSet.next()){
return ((Long)resultSet.getLong(1)).intValue();
}
return count;
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(resultSet,preparedStatement,connection);
}
return 0;
}
/**
* 通过反射技术给obj对象的property属性赋propertyValue值
*/
private void setValue(Object obj,String property,Object propertyValue){
Class clazz = obj.getClass();
try {
//获取property这个字符串对应的属性名,比如"fid"去找obj对象中的fid属性
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(property);
if (field!=null){
field.setAccessible(true);
//propertyValue值赋给obj对象的属性
field.set(obj,propertyValue);
}
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/**
* 执行查询:返回的是List
*/
protected List<T> executeQuery(String sql, Object... params){
List<T> list=new ArrayList<>();
try {
connection = getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
setParams(preparedStatement,params);
//保存的是行数据
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//获取结果集的元数据
//元数据:描述结果集数据的数据,就是这个结果集有那些列、什么类型等等
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
int count = metaData.getColumnCount();
//解析结果集
while (resultSet.next()){
//得到fruit对象
T entity= (T) entityClass.newInstance();
//第一行 第一列 第二列 第三列...
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
//得到列名
String columnName = metaData.getColumnName(i + 1);
//得到列的值
Object columnValue = resultSet.getObject(i + 1);
setValue(entity,columnName,columnValue);
}
list.add(entity);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
close(resultSet,preparedStatement,connection);
}
return list;
}
/**
* 执行查询 返回单个实体对象
*/
protected T load(String sql,Object... params){
try {
connection = getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
setParams(preparedStatement,params);
//保存的是行数据
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//获取结果集的元数据
//元数据:描述结果集数据的数据,就是这个结果集有那些列、什么类型等等
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
int count = metaData.getColumnCount();
//解析结果集
if (resultSet.next()){
//得到fruit对象
T entity= (T) entityClass.newInstance();
//第一行 第一列 第二列 第三列...
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
//得到列名
String columnName = metaData.getColumnName(i + 1);
//得到列的值
Object columnValue = resultSet.getObject(i + 1);
setValue(entity,columnName,columnValue);
}
return entity;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
close(resultSet,preparedStatement,connection);
}
return null;
}
/**
* 执行复杂查询,返回例如统计结果 行和列所有的值
*/
protected Object[] executeComplexQuery(String sql,Object...params){
try {
connection = getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
setParams(preparedStatement,params);
//保存的是行数据
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//获取结果集的元数据
//元数据:描述结果集数据的数据,就是这个结果集有那些列、什么类型等等
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
int count = metaData.getColumnCount();
Object[] columnValueArr=new Object[count];
//解析结果集
if (resultSet.next()){
//第一行 第一列 第二列 第三列...
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
//得到列的值
Object columnValue = resultSet.getObject(i + 1);
columnValueArr[i]=columnValue;
}
return columnValueArr;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(resultSet,preparedStatement,connection);
}
return null;
}
}
实现类中:只需要提供SQL语句、调用方法即可
public class FruitDaoImpl extends BaseDAO<Fruit> implements FruitDAO {
@Override
public List<Fruit> getFruitList() {
String sql="select * from t_fruit";
return super.executeQuery(sql);
}
@Override
public boolean addFruit(Fruit fruit) {
String sql="insert into t_fruit values(0,?,?,?,?)";
//insert语句返回的是自增列的值 而不是影响行数 自增主键回显
int count = super.executeUpdate(sql,fruit.getFname(),fruit.getPrice(),fruit.getFcount(),fruit.getRemark());
System.out.println(count);
return count>0;
}
@Override
public boolean updateFruit(Fruit fruit) {
String sql="update t_fruit set fcount=? where fid=?";
return super.executeUpdate(sql,fruit.getFcount(),fruit.getFid())>0;
}
@Override
public Fruit getFruitByFname(String fname) {
String sql="select * from t_fruit where fname like ?";
return super.load(sql,fname);
}
@Override
public boolean delFruit(String fname) {
String sql="delete from t_fruit where fname like ?";
//影响行数大于0就表示删除成功了
return super.executeUpdate(sql,fname)>0;
}
}