元学习之《Siamese Neural Networks for One-shot Image Recognition》代码解读
元学习系列文章
- optimization based meta-learning
- 《Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning for Fast Adaptation of Deep Networks》 论文翻译笔记
- 元学习方向 optimization based meta learning 之 MAML论文详细解读
- MAML 源代码解释说明 (一)
- MAML 源代码解释说明 (二)
- 元学习之《On First-Order Meta-Learning Algorithms》论文详细解读
- 元学习之《OPTIMIZATION AS A MODEL FOR FEW-SHOT LEARNING》论文详细解读
- metric based meta-learning
- 元学习之《Matching Networks for One Shot Learning》代码解读
- 元学习之《Siamese Neural Networks for One-shot Image Recognition》代码解读
- model based meta-learning: 待更新…
文章目录
-
-
- 前言
- Siamese Neural Networks
-
- 网络结构实现
- 训练及测试数据
- 总结
- 实验结果
- 参考资料
-
前言
此篇是 metric-based metalearning 的第二篇,所谓 metric-based 即通过某种度量方式来判断测试样本和训练集中的哪个样本最相似,进而把最相似样本的 label 作为测试样本的 label,总体思想有点类似于 KNN。
Siamese Neural Networks
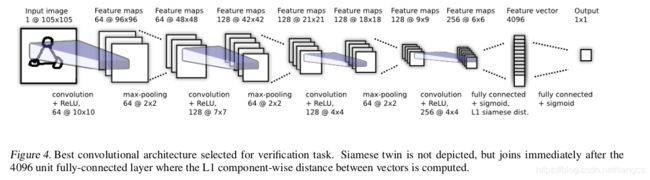
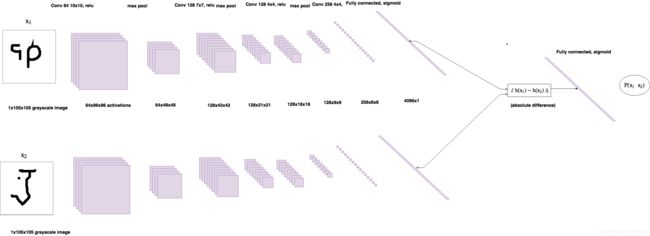
Siamese Neural Networks 中文翻译叫孪生网络,下图是孪生网络的草图,所谓孪生,就体现在该网络的卷积网络部分,网络每次接收一个 pair 的图片作为输入,分别通过同一个卷积网络进行 Encode,将每个图片Encode后的全连接层特征进行 L1 距离计算,结算结果输入到 sigmoid 全连接层,然后输出两个概率值,表示两个图片是同一类的概率。
网络结构实现
官方的论文代码在这里,其中关于网络结构的实现和解释如下:
def W_init(shape,name=None):
"""Initialize weights as in paper"""
values = rng.normal(loc=0,scale=1e-2,size=shape)
return K.variable(values,name=name)
#//TODO: figure out how to initialize layer biases in keras.
def b_init(shape,name=None):
"""Initialize bias as in paper"""
values=rng.normal(loc=0.5,scale=1e-2,size=shape)
return K.variable(values,name=name)
input_shape = (105, 105, 1)
# pair 输入
left_input = Input(input_shape)
right_input = Input(input_shape)
#build convnet to use in each siamese 'leg'
# keras 构造网络结构
convnet = Sequential()
# 卷积网络部分,共享网络权值
convnet.add(Conv2D(64,(10,10),activation='relu',input_shape=input_shape,
kernel_initializer=W_init,kernel_regularizer=l2(2e-4)))
convnet.add(MaxPooling2D())
convnet.add(Conv2D(128,(7,7),activation='relu',
kernel_regularizer=l2(2e-4),kernel_initializer=W_init,bias_initializer=b_init))
convnet.add(MaxPooling2D())
convnet.add(Conv2D(128,(4,4),activation='relu',kernel_initializer=W_init,kernel_regularizer=l2(2e-4),bias_initializer=b_init))
convnet.add(MaxPooling2D())
convnet.add(Conv2D(256,(4,4),activation='relu',kernel_initializer=W_init,kernel_regularizer=l2(2e-4),bias_initializer=b_init))
convnet.add(Flatten())
# 最后一层是 4096 维的全连接
convnet.add(Dense(4096,activation="sigmoid",kernel_regularizer=l2(1e-3),kernel_initializer=W_init,bias_initializer=b_init))
#call the convnet Sequential model on each of the input tensors so params will be shared
# 两个图片,分别输入到同一个卷积网络中进行特征提取,得到 4096 维的特征向量
encoded_l = convnet(left_input)
encoded_r = convnet(right_input)
#layer to merge two encoded inputs with the l1 distance between them
# 计算两个图片 4096 维向量的 L1 距离,其实就是对应位置元素相减的绝对值
L1_layer = Lambda(lambda tensors:K.abs(tensors[0] - tensors[1]))
#call this layer on list of two input tensors.
L1_distance = L1_layer([encoded_l, encoded_r])
# L1 向量输入到 Dense 全连接层,单元数只有1,激活函数是 sigmoid。输出值表示两个图片是同一类别的概率
prediction = Dense(1,activation='sigmoid',bias_initializer=b_init)(L1_distance)
siamese_net = Model(inputs=[left_input,right_input],outputs=prediction)
optimizer = Adam(0.00006)
#//TODO: get layerwise learning rates and momentum annealing scheme described in paperworking
siamese_net.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy",optimizer=optimizer)
训练及测试数据
数据构造的代码如下,对关键部分进行了注释:
class Siamese_Loader:
"""For loading batches and testing tasks to a siamese net"""
def __init__(self, path, data_subsets = ["train", "val"]):
self.data = {}
self.categories = {}
self.info = {}
for name in data_subsets:
file_path = os.path.join(path, name + ".pickle")
print("loading data from {}".format(file_path))
with open(file_path,"rb") as f:
(X,c) = pickle.load(f)
self.data[name] = X
self.categories[name] = c
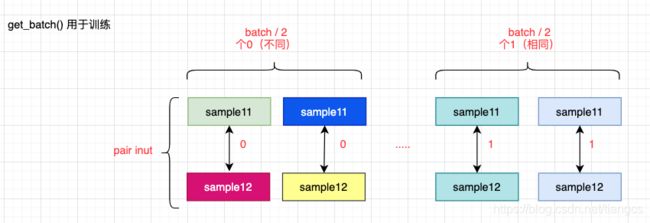
def get_batch(self,batch_size,s="train"):
"""Create batch of n pairs, half same class, half different class"""
X=self.data[s]
n_classes, n_examples, w, h = X.shape
#randomly sample several classes to use in the batch
# 共有 n_classes 个类别,每个 batch 从中随机选取 batch_size 个类别
categories = rng.choice(n_classes,size=(batch_size,),replace=False)
#initialize 2 empty arrays for the input image batch
# pairs 输入数组,[[left], [right]],其中 left 有 batch_size 个,right有batch_size个
pairs=[np.zeros((batch_size, h, w,1)) for i in range(2)]
#initialize vector for the targets, and make one half of it '1's, so 2nd half of batch has same class
# target数组,长度是 batch_size,前一半标签是0表示对应pair不是同一个类别,后一半标签是1,表示对应pair输入是同一个类别
targets=np.zeros((batch_size,))
targets[batch_size//2:] = 1
for i in range(batch_size):
# 训练抽样到的每个具体类别
category = categories[i]
# 每个类别共有 n_examples 个样本,随机抽取该类别的一个样本,作为 left
idx_1 = rng.randint(0, n_examples)
pairs[0][i,:,:,:] = X[category, idx_1].reshape(w, h, 1)
# 随机抽取第二个样本编号,作为 right
idx_2 = rng.randint(0, n_examples)
#pick images of same class for 1st half, different for 2nd
# 如果是后半部分,则 right的类别是left类别一样
if i >= batch_size // 2:
category_2 = category
else:
# 如果是前半部分,则right样本的类别要从非 left 类别中随机选择一个 class
#add a random number to the category modulo n classes to ensure 2nd image has
# ..different category
category_2 = (category + rng.randint(1,n_classes)) % n_classes
# 取出 right 样本放到对应位置,和 left 位置相对应
pairs[1][i,:,:,:] = X[category_2,idx_2].reshape(w, h,1)
return pairs, targets
def generate(self, batch_size, s="train"):
"""a generator for batches, so model.fit_generator can be used. """
while True:
pairs, targets = self.get_batch(batch_size,s)
yield (pairs, targets)
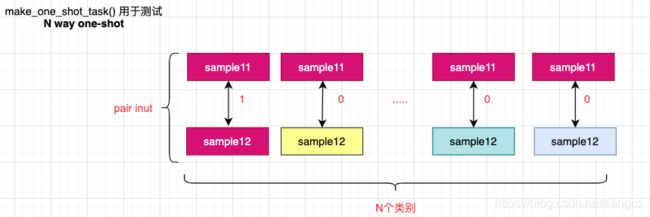
def make_oneshot_task(self,N,s="val",language=None):
"""Create pairs of test image, support set for testing N way one-shot learning. """
# 目的是构造 N way one-shot 的测试样本,一共有N个 pair,test_image 是某个类中未出现过的一个样本
X=self.data[s]
n_classes, n_examples, w, h = X.shape
# 每个类都有 n_examples 个样本,随机选择 indices 个样本编号
indices = rng.randint(0,n_examples,size=(N,))
if language is not None:
low, high = self.categories[s][language]
if N > high - low:
raise ValueError("This language ({}) has less than {} letters".format(language, N))
categories = rng.choice(range(low,high),size=(N,),replace=False)
else:#if no language specified just pick a bunch of random letters
# 共有 n_classes 个类别,随机选取 categories 个类别索引
categories = rng.choice(range(n_classes),size=(N,),replace=False)
# 将抽样到的第一个类别作为 test_image 的类别
true_category = categories[0]
# 随机抽取两个样本编号 ex1, ex1
ex1, ex2 = rng.choice(n_examples,replace=False,size=(2,))
# true_category 类的第 ex1 个样本作为 test_image
test_image = np.asarray([X[true_category,ex1,:,:]]*N).reshape(N, w, h,1)
# 抽取训练集,N个class,每个class只有1个样本
support_set = X[categories,indices,:,:]
# true_category 类的第 ex2 个样本作为训练集的第一个样本,意思就是训练集的的第一个样本和test_iamge是同一个类别,其他样本都是不同类别
support_set[0,:,:] = X[true_category,ex2]
support_set = support_set.reshape(N, w, h,1)
# one-shot任务的 target,只有第一个位置是1表示同一个类别,其它位置都是0表示不同类别
targets = np.zeros((N,))
targets[0] = 1
# 同时 shuffle
targets, test_image, support_set = shuffle(targets, test_image, support_set)
pairs = [test_image,support_set]
return pairs, targets
不同颜色代表不同类别,上边是 left样本,下边是right样本。
同样也是不同颜色代表不同类别,上边是 left样本,下边是right样本,由于是one-shot,所以 test image 只有一个,但是要和每个 train 样本组成 pair。
总结
论文整体比较简单,孪生网络的 idea 以前也有,用在 one-shot 的少样本学习中应该是第一次吧。因为是构造 pair 数据,所以反倒使得训练用的样本量增加了,不太容易出现过拟合现象。假设训练用的数据集有 E 个类别,每个类别有 C 个样本,一共有 C*E个样本,则总共可以构造的 pair 数为:
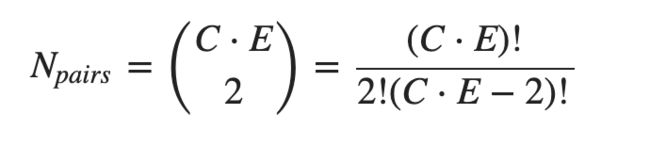
实验结果
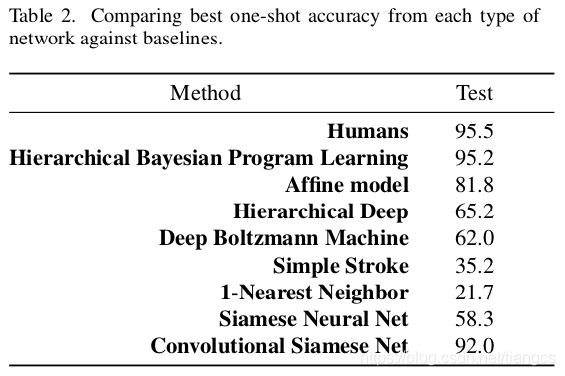
证明作者的卷积孪生网络在 one-shot 任务上可以达到 92% 的准确率,只落后于人类的 95% 准确率。
参考资料
- https://github.com/sorenbouma/keras-oneshot/blob/master/SiameseNet.ipynb
- https://sorenbouma.github.io/blog/oneshot/
- http://www.sohu.com/a/169212370_473283