SpringBoot 自动装配源码分析
文章目录
-
- @SpringBootApplication
- @EnableAutoConfiguration
- SpringApplication::run()
-
- prepareContext()
- refreshContext()
了解 SpringBoot 的自动装配得先了解下 SpringBoot 的启动流程
9千字长文带你了解SpringBoot启动过程–史上最详细 SpringBoot启动流程-图文并茂
@SpringBootApplication
从 @SpringBootApplication 注解开始分析,查看 @SpringBootApplication
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
// 标注在某个类上,表示这是一个springboot的配置类
@SpringBootConfiguration
// 开启自动配置功能,
@EnableAutoConfiguration
// 自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件或者bean,将这个bean定义加载到IOC容器中
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {}
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration 的作用:
开启自动配置,利用 AutoConfigurationImportSelector 给容器导入一些组件
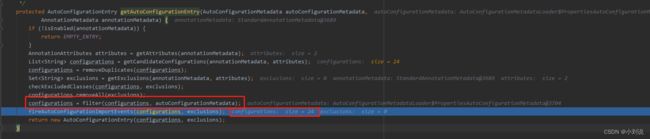
查看 AutoConfigurationImportSelector 的关键方法 getCandidateConfigurations()

会从 springboot-autoconfigure.jar 中的 /META-INF/spring.factories 获取 EnableAutoConfiguration 配置的全路径类,此时有124个,然后在 getAutoConfigurationEntry() 中去重与条件判断得到最后的24个需要自动装配的类
spring.factories

@Conditional:自动配置类在一定条件下才能生效
| @Conditional扩展注解 | 作用 |
| ------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------- |
| @ConditionalOnJava | 系统的java版本是否符合要求 |
| @ConditionalOnBean | 容器中存在指定Bean |
| @ConditionalOnMissingBean | 容器中不存在指定Bean |
| @ConditionalOnExpression | 满足SpEL表达式 |
| @ConditionalOnClass | 系统中有指定的类 |
| @ConditionalOnMissingClass | 系统中没有指定的类 |
| @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate | 容器中只有一个指定的Bean,或者是首选Bean |
| @ConditionalOnProperty | 系统中指定的属性是否有指定的值 |
| @ConditionalOnResource | 类路径下是否存在指定资源文件 |
| @ConditionOnWebApplication | 当前是web环境 |
| @ConditionalOnNotWebApplication | 当前不是web环境 |
| @ConditionalOnJndi | JNDI存在指定项 |
那么是什么时候进行获取调用这个应该自动装配的类的呢?
上述中 AutoConfigurationImportSelector 为关键的获取类,而该类由 @Import 注解导入
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
综合前面所学习的 spring 知识,所以应该看下对 @Import 注解的解析,下面从 springboot 启动流程开始分析
SpringApplication::run()
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
//1、创建并启动计时监控类
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
//2、初始化应用上下文和异常报告集合
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
//3、设置系统属性“java.awt.headless”的值,默认为true,用于运行headless服务器,进行简单的图像处理,多用于在缺少显示屏、键盘或者鼠标时的系统配置,很多监控工具如jconsole 需要将该值设置为true
configureHeadlessProperty();
//4、创建所有spring运行监听器并发布应用启动事件,简单说的话就是获取SpringApplicationRunListener类型的实例(EventPublishingRunListener对象),并封装进SpringApplicationRunListeners对象,然后返回这个SpringApplicationRunListeners对象。说的再简单点,getRunListeners就是准备好了运行时监听器EventPublishingRunListener。
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
//5、初始化默认应用参数类
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//6、根据运行监听器和应用参数来准备spring环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
//将要忽略的bean的参数打开
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//7、创建banner打印类
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//8、创建应用上下文,可以理解为创建一个容器
context = createApplicationContext();
//9、准备异常报告器,用来支持报告关于启动的错误
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
//10、准备应用上下文,该步骤包含一个非常关键的操作,将启动类注入容器,为后续开启自动化提供基础
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//11、刷新应用上下文
refreshContext(context);
//12、应用上下文刷新后置处理,做一些扩展功能
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
//13、停止计时监控类
stopWatch.stop();
//14、输出日志记录执行主类名、时间信息
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
//15、发布应用上下文启动监听事件
listeners.started(context);
//16、执行所有的Runner运行器
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
//17、发布应用上下文就绪事件
listeners.running(context);
}catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
//18、返回应用上下文
return context;
}
在上述代码中,我们了解springboot自动装配需要重点关注两个方法
prepareContext()
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
// 1.执行 ApplicationContextInitializer 的 initialize 方法
applyInitializers(context);
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
// 2.将启动类加载到上下文中
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
重点查看上面的两个方法
- applyInitializers(context)
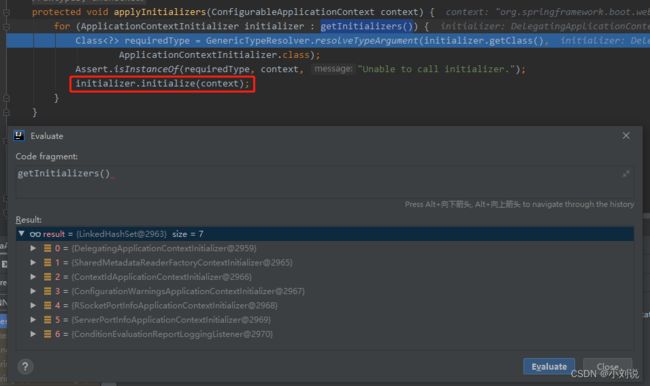
执行 ApplicationContextInitializer 的 initialize() 方法,而这些实现 ApplicationContextInitializer 接口的方法会在 SpringApplication 的构造方法中从 spring.factories 文件进行加载

- load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
跟踪源码,判断启动类是否由@Component标注,因为 @SpringBootApplication–>@SpringBootConfiguration–>@Configuration–>@Component,所以将启动类加入到 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 中,后续会进行实例化与初始化

refreshContext()
在 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors() 中存在注解解析的调用
02 Spring 源码总结 - invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()
通过debug一步一步进行查找,会发现最终会在ConfigurationClassParser类中,此类是所有配置类的解析类,所有的解析逻辑在 parser() 中

继续跟进 doProcessConfigurationClass() 方法,此方式是支持注解配置的核心逻辑,会看到对@Import注解的解析
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass, Predicate<String> filter)
throws IOException {
// @Configuration继承了@Component
if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) {
// Recursively process any member (nested) classes first
// 递归处理内部类,因为内部类也是一个配置类,配置类上有@configuration注解,该注解继承@Component,if判断为true,调用processMemberClasses方法,递归解析配置类中的内部类
processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
// 如果配置类上加了@PropertySource注解,那么就解析加载properties文件,并将属性添加到spring上下文中
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {
if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
else {
logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +
"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");
}
}
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations
// 处理@ComponentScan或者@ComponentScans注解,并将扫描包下的所有bean转换成填充后的ConfigurationClass
// 此处就是将自定义的bean加载到IOC容器,因为扫描到的类可能也添加了@ComponentScan和@ComponentScans注解,因此需要进行递归解析
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
// 解析@ComponentScan和@ComponentScans配置的扫描的包所包含的类
// 比如 basePackages = com.mashibing, 那么在这一步会扫描出这个包及子包下的class,然后将其解析成BeanDefinition
// (BeanDefinition可以理解为等价于BeanDefinitionHolder)
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
// 通过上一步扫描包com.mashibing,有可能扫描出来的bean中可能也添加了ComponentScan或者ComponentScans注解.
//所以这里需要循环遍历一次,进行递归(parse),继续解析,直到解析出的类上没有ComponentScan和ComponentScans
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
// 判断是否是一个配置类,并设置full或lite属性
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
// 通过递归方法进行解析
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
// Process any @Import annotations
// 处理@Import注解
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true);
// Process any @ImportResource annotations
// 处理@ImportResource注解,导入spring的配置文件
AnnotationAttributes importResource =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);
if (importResource != null) {
String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations");
Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader");
for (String resource : resources) {
String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource);
configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass);
}
}
// Process individual @Bean methods
// 处理加了@Bean注解的方法,将@Bean方法转化为BeanMethod对象,保存再集合中
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
// Process default methods on interfaces
// 处理接口的默认方法实现,从jdk8开始,接口中的方法可以有自己的默认实现,因此如果这个接口的方法加了@Bean注解,也需要被解析
processInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass);
// Process superclass, if any
// 解析父类,如果被解析的配置类继承了某个类,那么配置类的父类也会被进行解析
if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) {
String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName();
if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java") &&
!this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) {
this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass);
// Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recurse
return sourceClass.getSuperClass();
}
}
// No superclass -> processing is complete
return null;
}
