nacos2.0配置中心源码解析
文章目录
- 前言
- 前置说明
- springboot中如何装配nacos
- 从服务端加载配置内容
- 服务端处理gRpc请求
- 客户端监听机制
- 总结
前言
nacos作为目前较为主流的服务注册和动态配置的组件,目前已有很多公司在内部使用,本文以nacos的springboot集成版本进行分析下动态配置中心实现原理
本文以nacos2.0.2版本进行源码分析,对应nacos-config-spring-boot-starter版本为0.2.10
nacos 2.0.2在1.x版本上做了重大的重构,具体可看官网
本文只讨论nacos作为动态配置中心相关的分析,首先了解一个动态配置中心应该实现哪些必须的功能
- 客户端从远程服务端获取配置
- spring环境中,肯定会把远程加载的数据源加载到environment中,实现@Value注解的属性注入
- 客户端动态感知功能,服务端修改配置可以实现客户端动态修改
前置说明
pom.xml文件内容
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<artifactId>nacos-spring-boot-example</artifactId>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>8</source>
<target>8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<groupId>com.alibaba.nacos</groupId>
<version>0.2.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<properties>
<nacos-config-spring-boot.version>0.2.1</nacos-config-spring-boot.version>
<spring-boot.version>2.0.3.RELEASE</spring-boot.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>nacos-config-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>0.2.10</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>
application.properties文件内容
spring.application.name=example
# 开启nacos.config配置
nacos.config.bootstrap.enable=true
# 主配置服务器地址
nacos.config.server-addr=127.0.0.1:8848
nacos.config.namespace=first
nacos.config.group=pro
nacos.config.data-id=myDemo.properties
nacos.config.type=properties
## 主配置 最大重试次数
nacos.config.max-retry=1
## 主配置 开启自动刷新
nacos.config.auto-refresh=true
## 主配置 重试时间
nacos.config.config-retry-time=2333
# 配置扩展的配置,因为很多情况项目都需要使用一些公共的配置,比如微服务之间很多公共配置项
nacos.config.ext-config[0].namespace=common
nacos.config.ext-config[0].data-id=redisCommon
nacos.config.ext-config[0].group=test
nacos.config.ext-config[0].max-retry=1
nacos.config.ext-config[0].type=properties
nacos.config.ext-config[0].auto-refresh=true
nacos.config.ext-config[0].config-retry-time=2333
nacos.config.ext-config[0].config-long-poll-timeout=46000
nacos.config.ext-config[0].enable-remote-sync-config=true
nacos.config.ext-config[1].namespace=first
nacos.config.ext-config[1].data-id=myDemo.properties
nacos.config.ext-config[1].group=test
nacos.config.ext-config[1].max-retry=1
nacos.config.ext-config[1].type=properties
nacos.config.ext-config[1].auto-refresh=true
nacos.config.ext-config[1].config-retry-time=2333
nacos.config.ext-config[1].config-long-poll-timeout=46000
nacos.config.ext-config[1].enable-remote-sync-config=true
需要从远处加载三个配置文件,其中两个的namespace都是first
springboot中如何装配nacos
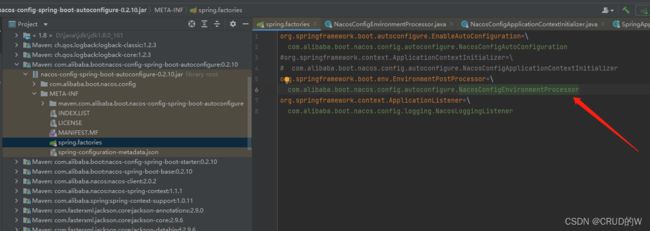
首先看springboot的spi机制
在nacos-config-spring-boot-autoconfigure jar中META-INF/spring.factories文件
看org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor,这个在spring环境的预加载时会通过spi被调用到,然后执行postProcessEnvironment方法
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplication application) {
// 核心
application.addInitializers(new NacosConfigApplicationContextInitializer(this));
nacosConfigProperties = NacosConfigPropertiesUtils
.buildNacosConfigProperties(environment);
if (enable()) {
System.out.println(
"[Nacos Config Boot] : The preload log configuration is enabled");
loadConfig(environment);
}
}
往spring上下文添加了一个NacosConfigApplicationContextInitializer,这个类实现了spring的ApplicationContextInitializer,在spring刷新上下文时会调用到initialize,所以直接看initialize方法
public class NacosConfigApplicationContextInitializer
implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(NacosConfigApplicationContextInitializer.class);
private final NacosConfigEnvironmentProcessor processor;
private final CacheableEventPublishingNacosServiceFactory singleton = CacheableEventPublishingNacosServiceFactory
.getSingleton();
private final Function<Properties, ConfigService> builder = properties -> {
try {
return singleton.createConfigService(properties);
}
catch (NacosException e) {
throw new NacosBootConfigException(
"ConfigService can't be created with properties : " + properties, e);
}
};
private ConfigurableEnvironment environment;
private NacosConfigProperties nacosConfigProperties;
public NacosConfigApplicationContextInitializer(
NacosConfigEnvironmentProcessor configEnvironmentProcessor) {
this.processor = configEnvironmentProcessor;
}
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
singleton.setApplicationContext(context);
environment = context.getEnvironment();
nacosConfigProperties = NacosConfigPropertiesUtils
.buildNacosConfigProperties(environment);
final NacosConfigLoader configLoader = new NacosConfigLoader(
nacosConfigProperties, environment, builder);
if (!enable()) {
logger.info("[Nacos Config Boot] : The preload configuration is not enabled");
}
else {
// If it opens the log level loading directly will cache
// DeferNacosPropertySource release
if (processor.enable()) {
processor.publishDeferService(context);
configLoader
.addListenerIfAutoRefreshed(processor.getDeferPropertySources());
}
else {
// 核心1
configLoader.loadConfig();
// 核心2
configLoader.addListenerIfAutoRefreshed();
}
}
final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory factory = context.getBeanFactory();
if (!factory
.containsSingleton(NacosBeanUtils.GLOBAL_NACOS_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
factory.registerSingleton(NacosBeanUtils.GLOBAL_NACOS_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME,
configLoader.buildGlobalNacosProperties());
}
}
private boolean enable() {
return processor.enable() || nacosConfigProperties.getBootstrap().isEnable();
}
}
从服务端加载配置内容
核心1,加载配置,进入NacosConfigLoader的loadConfig
public void loadConfig() {
Properties globalProperties = buildGlobalNacosProperties();
MutablePropertySources mutablePropertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
// 核心1
List<NacosPropertySource> sources = reqGlobalNacosConfig(globalProperties,
nacosConfigProperties.getType());
// 核心2
for (NacosConfigProperties.Config config : nacosConfigProperties.getExtConfig()) {
// 核心3
List<NacosPropertySource> elements = reqSubNacosConfig(config,
globalProperties, config.getType());
sources.addAll(elements);
}
if (nacosConfigProperties.isRemoteFirst()) {
// 核心4
for (ListIterator<NacosPropertySource> itr = sources.listIterator(sources.size()); itr.hasPrevious();) {
mutablePropertySources.addAfter(
StandardEnvironment.SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, itr.previous());
}
} else {
// 核心5
for (NacosPropertySource propertySource : sources) {
mutablePropertySources.addLast(propertySource);
}
}
}
核心1,看名字,请求公共的nacos配置
核心2、3请求所有扩展的配置文件,因为一个项目可以添加多个扩展的配置文件,并且加到一起保存到sources
核心4、核心5就是根据有没有配置nacos.config.remote-first=true,如果配置了则从nacos加载的配置加载到一个名称为systemEnvironment的PropertySources后面,但是会在application配置文件前面,如果没配置则默认加到最后面,在application配置文件后面
这里的mutablePropertySources是spring环境对象environment中的所有配置源,这里把nacos远程加载到的也加进去,那么在spring处理@Value注入时就能拿到了,到这里为止,大逻辑已经看懂了
然后看一下核心1是如何从远程加载配置的,核心3和核心1类似,就不看了
private List<NacosPropertySource> reqGlobalNacosConfig(Properties globalProperties,
ConfigType type) {
List<String> dataIds = new ArrayList<>();
// Loads all data-id information into the list in the list
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(nacosConfigProperties.getDataId())) {
final String ids = environment
.resolvePlaceholders(nacosConfigProperties.getDataIds());
dataIds.addAll(Arrays.asList(ids.split(",")));
}
else {
dataIds.add(nacosConfigProperties.getDataId());
}
final String groupName = environment
.resolvePlaceholders(nacosConfigProperties.getGroup());
final boolean isAutoRefresh = nacosConfigProperties.isAutoRefresh();
// 核心
return new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(reqNacosConfig(globalProperties,
dataIds.toArray(new String[0]), groupName, type, isAutoRefresh)));
}
拿到dataId、group、type、isAutoRefresh(nacos上修改了属性,客户端是否需要动态修改),调用reqNacosConfig
private NacosPropertySource[] reqNacosConfig(Properties configProperties,
String[] dataIds, String groupId, ConfigType type, boolean isAutoRefresh) {
final NacosPropertySource[] propertySources = new NacosPropertySource[dataIds.length];
for (int i = 0; i < dataIds.length; i++) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(dataIds[i])) {
continue;
}
// Remove excess Spaces
final String dataId = environment.resolvePlaceholders(dataIds[i].trim());
// 核心1
final String config = NacosUtils.getContent(builder.apply(configProperties),
dataId, groupId);
final NacosPropertySource nacosPropertySource = new NacosPropertySource(
dataId, groupId,
buildDefaultPropertySourceName(dataId, groupId, configProperties),
config, type.getType());
nacosPropertySource.setDataId(dataId);
nacosPropertySource.setType(type.getType());
nacosPropertySource.setGroupId(groupId);
nacosPropertySource.setAutoRefreshed(isAutoRefresh);
logger.info("load config from nacos, data-id is : {}, group is : {}",
nacosPropertySource.getDataId(), nacosPropertySource.getGroupId());
propertySources[i] = nacosPropertySource;
DeferNacosPropertySource defer = new DeferNacosPropertySource(
nacosPropertySource, configProperties, environment);
nacosPropertySources.add(defer);
}
return propertySources;
}
核心1处就是拿到远程的文件内容,然后后面包装为propertySources返回
这里的builder.apply(configProperties)返回了一个ConfigService,这个也很关键
builder是在NacosConfigApplicationContextInitializer中初始化的,所以会调用这个lambda的createConfigService创建ConfigService
private final Function<Properties, ConfigService> builder = properties -> {
try {
return singleton.createConfigService(properties);
}
catch (NacosException e) {
throw new NacosBootConfigException(
"ConfigService can't be created with properties : " + properties, e);
}
};
这里创建ConfigService的过程中会有很多逻辑,这个后面看,先把主逻辑看完
看NacosUtils.getContent
public static String getContent(ConfigService configService, String dataId,
String groupId) {
String content = null;
try {
// 核心
content = configService.getConfig(dataId, groupId, DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
}
catch (NacosException e) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Can't get content from dataId : " + dataId + " , groupId : "
+ groupId, e);
}
}
return content;
}
看NacosConfigService的getConfig,这个方法已经属于nacos-client包的代码了,和spring无关,是属于nacos的核心代码,从远程获取配置
@Override
public String getConfig(String dataId, String group, long timeoutMs) throws NacosException {
return getConfigInner(namespace, dataId, group, timeoutMs);
}
这里新拿到了ConfigService的namespace
private String getConfigInner(String tenant, String dataId, String group, long timeoutMs) throws NacosException {
group = blank2defaultGroup(group);
ParamUtils.checkKeyParam(dataId, group);
ConfigResponse cr = new ConfigResponse();
cr.setDataId(dataId);
cr.setTenant(tenant);
cr.setGroup(group);
// use local config first
// 核心1
String content = LocalConfigInfoProcessor.getFailover(worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant);
if (content != null) {
LOGGER.warn("[{}] [get-config] get failover ok, dataId={}, group={}, tenant={}, config={}",
worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant, ContentUtils.truncateContent(content));
cr.setContent(content);
String encryptedDataKey = LocalEncryptedDataKeyProcessor
.getEncryptDataKeyFailover(agent.getName(), dataId, group, tenant);
cr.setEncryptedDataKey(encryptedDataKey);
configFilterChainManager.doFilter(null, cr);
content = cr.getContent();
return content;
}
try {
// 核心2
ConfigResponse response = worker.getServerConfig(dataId, group, tenant, timeoutMs, false);
cr.setContent(response.getContent());
cr.setEncryptedDataKey(response.getEncryptedDataKey());
configFilterChainManager.doFilter(null, cr);
content = cr.getContent();
return content;
} catch (NacosException ioe) {
if (NacosException.NO_RIGHT == ioe.getErrCode()) {
throw ioe;
}
LOGGER.warn("[{}] [get-config] get from server error, dataId={}, group={}, tenant={}, msg={}",
worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant, ioe.toString());
}
LOGGER.warn("[{}] [get-config] get snapshot ok, dataId={}, group={}, tenant={}, config={}",
worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant, ContentUtils.truncateContent(content));
// 核心3
content = LocalConfigInfoProcessor.getSnapshot(worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant);
cr.setContent(content);
String encryptedDataKey = LocalEncryptedDataKeyProcessor
.getEncryptDataKeyFailover(agent.getName(), dataId, group, tenant);
cr.setEncryptedDataKey(encryptedDataKey);
configFilterChainManager.doFilter(null, cr);
content = cr.getContent();
return content;
}
这里代码比较长,主代码分为三个逻辑
- 从本地缓存文件拿,没拿到则走2,window下目录为:C:\Users\admin\nacos\config\config_rpc_client_nacos\data\config-data-tenant\first\pro\myDemo.properties,看了一下代码并没有保存到这个目录的代码,而且我即使启动了客户端这个目录也没有文件,猜测是为了让我们在某些情况可以手动增加吧,算是一种预留的机制吧
- 从远程调用拿,没拿到则走3
- 从本地快照文件目录拿,快照的目录为C:\Users\admin\nacos\config\config_rpc_client_nacos\snapshot-tenant,这个目录项目起来之后看到是有的,可以类似于本地缓存文件
那么这里核心的逻辑就是2,从远程调用获取
ClientWorker的getServerConfig,这里的代码和dubbo1.x已经完全不同了,nacos1.x是直接使用http请求来实现获取远程配置的,nacos2.0采用了grpc来实现客户端与服务端的交互
public ConfigResponse getServerConfig(String dataId, String group, String tenant, long readTimeout, boolean notify)
throws NacosException {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(group)) {
group = Constants.DEFAULT_GROUP;
}
return this.agent.queryConfig(dataId, group, tenant, readTimeout, notify);
}
queryConfig
@Override
public ConfigResponse queryConfig(String dataId, String group, String tenant, long readTimeouts, boolean notify)
throws NacosException {
ConfigQueryRequest request = ConfigQueryRequest.build(dataId, group, tenant);
request.putHeader(NOTIFY_HEADER, String.valueOf(notify));
RpcClient rpcClient = getOneRunningClient();
if (notify) {
CacheData cacheData = cacheMap.get().get(GroupKey.getKeyTenant(dataId, group, tenant));
if (cacheData != null) {
rpcClient = ensureRpcClient(String.valueOf(cacheData.getTaskId()));
}
}
// 核心代码
ConfigQueryResponse response = (ConfigQueryResponse) requestProxy(rpcClient, request, readTimeouts);
ConfigResponse configResponse = new ConfigResponse();
......
}
这里的核心代码内部就是会发起一个gRpc的请求到服务端获取配置,内部就不分析了,比较复杂
服务端处理gRpc请求
这里我把本地的nacos服务端启动起来了,然后客户端连接本地的服务端进行了测试,在nacos1.x版本是实用http请求获取数据的,2.x版本改为了实用grpc请求
服务端接受请求的核心类是BaseRpcServer,在bean初始化完成后会调用start方法
@PostConstruct
public void start() throws Exception {
String serverName = getClass().getSimpleName();
Loggers.REMOTE.info("Nacos {} Rpc server starting at port {}", serverName, getServicePort());
// 核心
startServer();
Loggers.REMOTE.info("Nacos {} Rpc server started at port {}", serverName, getServicePort());
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
Loggers.REMOTE.info("Nacos {} Rpc server stopping", serverName);
try {
BaseRpcServer.this.stopServer();
Loggers.REMOTE.info("Nacos {} Rpc server stopped successfully...", serverName);
} catch (Exception e) {
Loggers.REMOTE.error("Nacos {} Rpc server stopped fail...", serverName, e);
}
}
});
}
startServer
@Override
public void startServer() throws Exception {
final MutableHandlerRegistry handlerRegistry = new MutableHandlerRegistry();
// server interceptor to set connection id.
ServerInterceptor serverInterceptor = new ServerInterceptor() {
@Override
public <T, S> ServerCall.Listener<T> interceptCall(ServerCall<T, S> call, Metadata headers,
ServerCallHandler<T, S> next) {
Context ctx = Context.current()
.withValue(CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_ID, call.getAttributes().get(TRANS_KEY_CONN_ID))
.withValue(CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_REMOTE_IP, call.getAttributes().get(TRANS_KEY_REMOTE_IP))
.withValue(CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_REMOTE_PORT, call.getAttributes().get(TRANS_KEY_REMOTE_PORT))
.withValue(CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_LOCAL_PORT, call.getAttributes().get(TRANS_KEY_LOCAL_PORT));
if (REQUEST_BI_STREAM_SERVICE_NAME.equals(call.getMethodDescriptor().getServiceName())) {
Channel internalChannel = getInternalChannel(call);
ctx = ctx.withValue(CONTEXT_KEY_CHANNEL, internalChannel);
}
return Contexts.interceptCall(ctx, call, headers, next);
}
};
// 核心
addServices(handlerRegistry, serverInterceptor);
。。。。。。
addServices
private void addServices(MutableHandlerRegistry handlerRegistry, ServerInterceptor... serverInterceptor) {
// unary common call register.
final MethodDescriptor<Payload, Payload> unaryPayloadMethod = MethodDescriptor.<Payload, Payload>newBuilder()
.setType(MethodDescriptor.MethodType.UNARY)
.setFullMethodName(MethodDescriptor.generateFullMethodName(REQUEST_SERVICE_NAME, REQUEST_METHOD_NAME))
.setRequestMarshaller(ProtoUtils.marshaller(Payload.getDefaultInstance()))
.setResponseMarshaller(ProtoUtils.marshaller(Payload.getDefaultInstance())).build();
// 核心1
final ServerCallHandler<Payload, Payload> payloadHandler = ServerCalls
.asyncUnaryCall((request, responseObserver) -> {
grpcCommonRequestAcceptor.request(request, responseObserver);
});
final ServerServiceDefinition serviceDefOfUnaryPayload = ServerServiceDefinition.builder(REQUEST_SERVICE_NAME)
.addMethod(unaryPayloadMethod, payloadHandler).build();
handlerRegistry.addService(ServerInterceptors.intercept(serviceDefOfUnaryPayload, serverInterceptor));
// bi stream register.
final ServerCallHandler<Payload, Payload> biStreamHandler = ServerCalls.asyncBidiStreamingCall(
(responseObserver) -> grpcBiStreamRequestAcceptor.requestBiStream(responseObserver));
final MethodDescriptor<Payload, Payload> biStreamMethod = MethodDescriptor.<Payload, Payload>newBuilder()
.setType(MethodDescriptor.MethodType.BIDI_STREAMING).setFullMethodName(MethodDescriptor
.generateFullMethodName(REQUEST_BI_STREAM_SERVICE_NAME, REQUEST_BI_STREAM_METHOD_NAME))
.setRequestMarshaller(ProtoUtils.marshaller(Payload.newBuilder().build()))
.setResponseMarshaller(ProtoUtils.marshaller(Payload.getDefaultInstance())).build();
final ServerServiceDefinition serviceDefOfBiStream = ServerServiceDefinition
.builder(REQUEST_BI_STREAM_SERVICE_NAME).addMethod(biStreamMethod, biStreamHandler).build();
handlerRegistry.addService(ServerInterceptors.intercept(serviceDefOfBiStream, serverInterceptor));
}
核心1的payloadHandler就是处理gRpc请求的,当收到请求后进入了grpcCommonRequestAcceptor.request
进入GrpcRequestAcceptor的request
@Override
public void request(Payload grpcRequest, StreamObserver<Payload> responseObserver) {
......
Request request = (Request) parseObj;
try {
Connection connection = connectionManager.getConnection(CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_ID.get());
RequestMeta requestMeta = new RequestMeta();
requestMeta.setClientIp(connection.getMetaInfo().getClientIp());
requestMeta.setConnectionId(CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_ID.get());
requestMeta.setClientVersion(connection.getMetaInfo().getVersion());
requestMeta.setLabels(connection.getMetaInfo().getLabels());
connectionManager.refreshActiveTime(requestMeta.getConnectionId());
// 核心1
Response response = requestHandler.handleRequest(request, requestMeta);
Payload payloadResponse = GrpcUtils.convert(response);
traceIfNecessary(payloadResponse, false);
responseObserver.onNext(payloadResponse);
responseObserver.onCompleted();
} catch (Throwable e) {
Loggers.REMOTE_DIGEST
.error("[{}] Fail to handle request from connection [{}] ,error message :{}", "grpc", connectionId,
e);
Payload payloadResponse = GrpcUtils.convert(buildErrorResponse(
(e instanceof NacosException) ? ((NacosException) e).getErrCode() : ResponseCode.FAIL.getCode(),
e.getMessage()));
traceIfNecessary(payloadResponse, false);
responseObserver.onNext(payloadResponse);
responseObserver.onCompleted();
}
}
RequestHandler的handleRequest
public Response handleRequest(T request, RequestMeta meta) throws NacosException {
for (AbstractRequestFilter filter : requestFilters.filters) {
try {
Response filterResult = filter.filter(request, meta, this.getClass());
if (filterResult != null && !filterResult.isSuccess()) {
return filterResult;
}
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
Loggers.REMOTE.error("filter error", throwable);
}
}
// 核心1
return handle(request, meta);
}
ConfigQueryRequestHandler的handle
@Override
@TpsControl(pointName = "ConfigQuery", parsers = {ConfigQueryGroupKeyParser.class, ConfigQueryGroupParser.class})
@Secured(action = ActionTypes.READ, parser = ConfigResourceParser.class)
public ConfigQueryResponse handle(ConfigQueryRequest request, RequestMeta meta) throws NacosException {
try {
return getContext(request, meta, request.isNotify());
} catch (Exception e) {
return ConfigQueryResponse
.buildFailResponse(ResponseCode.FAIL.getCode(), e.getMessage());
}
}
getContext
private ConfigQueryResponse getContext(ConfigQueryRequest configQueryRequest, RequestMeta meta, boolean notify)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String dataId = configQueryRequest.getDataId();
String group = configQueryRequest.getGroup();
String tenant = configQueryRequest.getTenant();
String clientIp = meta.getClientIp();
String tag = configQueryRequest.getTag();
ConfigQueryResponse response = new ConfigQueryResponse();
final String groupKey = GroupKey2
.getKey(configQueryRequest.getDataId(), configQueryRequest.getGroup(), configQueryRequest.getTenant());
String autoTag = configQueryRequest.getHeader(com.alibaba.nacos.api.common.Constants.VIPSERVER_TAG);
String requestIpApp = meta.getLabels().get(CLIENT_APPNAME_HEADER);
// 核心1
int lockResult = tryConfigReadLock(groupKey);
boolean isBeta = false;
boolean isSli = false;
if (lockResult > 0) {
//FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
String md5 = Constants.NULL;
long lastModified = 0L;
CacheItem cacheItem = ConfigCacheService.getContentCache(groupKey);
if (cacheItem != null) {
if (cacheItem.isBeta()) {
if (cacheItem.getIps4Beta().contains(clientIp)) {
isBeta = true;
}
}
String configType = cacheItem.getType();
response.setContentType((null != configType) ? configType : "text");
}
File file = null;
ConfigInfoBase configInfoBase = null;
PrintWriter out = null;
if (isBeta) {
md5 = cacheItem.getMd54Beta();
lastModified = cacheItem.getLastModifiedTs4Beta();
if (PropertyUtil.isDirectRead()) {
configInfoBase = persistService.findConfigInfo4Beta(dataId, group, tenant);
} else {
file = DiskUtil.targetBetaFile(dataId, group, tenant);
}
response.setBeta(true);
} else {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(tag)) {
if (isUseTag(cacheItem, autoTag)) {
if (cacheItem != null) {
if (cacheItem.tagMd5 != null) {
md5 = cacheItem.tagMd5.get(autoTag);
}
if (cacheItem.tagLastModifiedTs != null) {
lastModified = cacheItem.tagLastModifiedTs.get(autoTag);
}
}
if (PropertyUtil.isDirectRead()) {
configInfoBase = persistService.findConfigInfo4Tag(dataId, group, tenant, autoTag);
} else {
file = DiskUtil.targetTagFile(dataId, group, tenant, autoTag);
}
response.setTag(URLEncoder.encode(autoTag, Constants.ENCODE));
} else {
// 核心2
md5 = cacheItem.getMd5();
lastModified = cacheItem.getLastModifiedTs();
// 核心3
if (PropertyUtil.isDirectRead()) {
configInfoBase = persistService.findConfigInfo(dataId, group, tenant);
} else {
file = DiskUtil.targetFile(dataId, group, tenant);
}
if (configInfoBase == null && fileNotExist(file)) {
// FIXME CacheItem
// No longer exists. It is impossible to simply calculate the push delayed. Here, simply record it as - 1.
ConfigTraceService.logPullEvent(dataId, group, tenant, requestIpApp, -1,
ConfigTraceService.PULL_EVENT_NOTFOUND, -1, clientIp, false);
// pullLog.info("[client-get] clientIp={}, {},
// no data",
// new Object[]{clientIp, groupKey});
response.setErrorInfo(ConfigQueryResponse.CONFIG_NOT_FOUND, "config data not exist");
return response;
}
}
} else {
if (cacheItem != null) {
if (cacheItem.tagMd5 != null) {
md5 = cacheItem.tagMd5.get(tag);
}
if (cacheItem.tagLastModifiedTs != null) {
Long lm = cacheItem.tagLastModifiedTs.get(tag);
if (lm != null) {
lastModified = lm;
}
}
}
if (PropertyUtil.isDirectRead()) {
configInfoBase = persistService.findConfigInfo4Tag(dataId, group, tenant, tag);
} else {
file = DiskUtil.targetTagFile(dataId, group, tenant, tag);
}
if (configInfoBase == null && fileNotExist(file)) {
// FIXME CacheItem
// No longer exists. It is impossible to simply calculate the push delayed. Here, simply record it as - 1.
ConfigTraceService.logPullEvent(dataId, group, tenant, requestIpApp, -1,
ConfigTraceService.PULL_EVENT_NOTFOUND, -1, clientIp, false);
// pullLog.info("[client-get] clientIp={}, {},
// no data",
// new Object[]{clientIp, groupKey});
response.setErrorInfo(ConfigQueryResponse.CONFIG_NOT_FOUND, "config data not exist");
return response;
}
}
}
response.setMd5(md5);
if (PropertyUtil.isDirectRead()) {
response.setLastModified(lastModified);
response.setContent(configInfoBase.getContent());
response.setResultCode(ResponseCode.SUCCESS.getCode());
} else {
//read from file
String content = null;
try {
// 核心4
content = readFileContent(file);
response.setContent(content);
response.setLastModified(lastModified);
response.setResultCode(ResponseCode.SUCCESS.getCode());
} catch (IOException e) {
response.setErrorInfo(ResponseCode.FAIL.getCode(), e.getMessage());
return response;
}
}
......
return response;
}
核心1,groupKey=dataid+group+namespace,服务端对每一个配置文件都有服务端的内存缓存,这里使用读写锁获取锁,为了避免并发修改的情况
核心2,上面一大堆逻辑,判断是不是预发、有没有使用tag,最常规的都是走到核心2这里开始
核心3
public static boolean isDirectRead() {
return EnvUtil.getStandaloneMode() && isEmbeddedStorage();
}
EnvUtil.getStandaloneMode()是指当前启动模式是不是单机模式
isEmbeddedStorage()读取当前成员变量embeddedStorage,embeddedStorage的值默认是等于EnvUtil.getStandaloneMode()的,但是当存储方案是数据库时有这样一行代码,使用mysql数据库存储数据时修改为了false,也就是说只有单机模式并且不使用mysql,使用默认的内嵌数据库时才走第一个if
if (isUseExternalDB()) {
setEmbeddedStorage(false);
}
第一个if,从数据库查询,如果是嵌入式数据库则从嵌入式数据库查询即可
@Override
public ConfigInfoWrapper findConfigInfo(final String dataId, final String group, final String tenant) {
final String tenantTmp = StringUtils.isBlank(tenant) ? StringUtils.EMPTY : tenant;
try {
return this.jt.queryForObject(
"SELECT ID,data_id,group_id,tenant_id,app_name,content,md5,type FROM config_info WHERE data_id=? AND group_id=? AND tenant_id=?",
new Object[] {dataId, group, tenantTmp}, CONFIG_INFO_WRAPPER_ROW_MAPPER);
} catch (EmptyResultDataAccessException e) { // Indicates that the data does not exist, returns null.
return null;
} catch (CannotGetJdbcConnectionException e) {
LogUtil.FATAL_LOG.error("[db-error] " + e.toString(), e);
throw e;
}
}
else,从磁盘读取,因为如果每次都从数据库查询则性能肯定会降低,所以设计了本地磁盘存储文件,我这里读取的文件目录为:C:\Users\admin\nacos\data\tenant-config-data\first\pro\myDemo.properties
public static File targetFile(String dataId, String group, String tenant) {
File file;
if (StringUtils.isBlank(tenant)) {
file = new File(EnvUtil.getNacosHome(), BASE_DIR);
} else {
file = new File(EnvUtil.getNacosHome(), TENANT_BASE_DIR);
file = new File(file, tenant);
}
file = new File(file, group);
file = new File(file, dataId);
return file;
}
核心4处,读取文件获取文件内容,把当前文件lastModified、md5、content都设置到response中,然后返回
到这里客户端就从服务端拿到配置文件的内容了,并且加载到了spring的environment中,后续使用@Value注入属性时即可使用到远程拿到的配置了
客户端监听机制
接下来就要看之前还没看的逻辑,看一下客户端是如何动态感知服务端的配置更改的
回到NacosConfigApplicationContextInitializer类创建ConfigService的代码
private final Function<Properties, ConfigService> builder = properties -> {
try {
return singleton.createConfigService(properties);
}
catch (NacosException e) {
throw new NacosBootConfigException(
"ConfigService can't be created with properties : " + properties, e);
}
};
public ConfigService createConfigService(Properties properties)
throws NacosException {
Properties copy = new Properties();
copy.putAll(properties);
return (ConfigService) createWorkerManager.get(ServiceType.CONFIG).run(copy,
null);
}
run方法进入ConfigCreateWorker的run
@Override
public ConfigService run(Properties properties, ConfigService service)
throws NacosException {
// 核心0
String cacheKey = identify(properties);
ConfigService configService = configServicesCache.get(cacheKey);
if (configService == null) {
if (service == null) {
// 核心1
service = NacosFactory.createConfigService(properties);
}
// 核心2
configService = new EventPublishingConfigService(service, properties,
getSingleton().context,
getSingleton().nacosConfigListenerExecutor);
configServicesCache.put(cacheKey, configService);
}
return configService;
}
核心0处也是一个关键点
public static String identify(Map<?, ?> properties) {
String namespace = (String) properties.get(NAMESPACE);
String serverAddress = (String) properties.get(SERVER_ADDR);
String contextPath = (String) properties.get(CONTEXT_PATH);
String clusterName = (String) properties.get(CLUSTER_NAME);
String endpoint = (String) properties.get(ENDPOINT);
String accessKey = (String) properties.get(ACCESS_KEY);
String secretKey = (String) properties.get(SECRET_KEY);
String encode = (String) properties.get(ENCODE);
return build(namespace, clusterName, serverAddress, contextPath, endpoint,
accessKey, secretKey, encode);
}
这个cacheKey和namespace和serverAddress有关,和groupid和dataid无关,也就是相同namespace不同的group和dataid的文件,都公用一个ConfigService,然后存储到了configServicesCache中
我这里加载三个配置文件,两个的namespace都是first,所以会创建两个ConfigService
然后看核心1创建configService
核心2把configService包装到EventPublishingConfigService中,并且放到缓存configServicesCache中
看核心1做了什么
public static ConfigService createConfigService(Properties properties) throws NacosException {
return ConfigFactory.createConfigService(properties);
}
public static ConfigService createConfigService(Properties properties) throws NacosException {
try {
Class<?> driverImplClass = Class.forName("com.alibaba.nacos.client.config.NacosConfigService");
Constructor constructor = driverImplClass.getConstructor(Properties.class);
ConfigService vendorImpl = (ConfigService) constructor.newInstance(properties);
return vendorImpl;
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new NacosException(NacosException.CLIENT_INVALID_PARAM, e);
}
}
调用NacosConfigService的带Properties的构造器实例化对象
public NacosConfigService(Properties properties) throws NacosException {
ValidatorUtils.checkInitParam(properties);
initNamespace(properties);
this.configFilterChainManager = new ConfigFilterChainManager(properties);
ServerListManager serverListManager = new ServerListManager(properties);
serverListManager.start();
// 核心1
this.worker = new ClientWorker(this.configFilterChainManager, serverListManager, properties);
// will be deleted in 2.0 later versions
agent = new ServerHttpAgent(serverListManager);
}
核心1的ClientWorker主要是处理客户端与服务端交互的,很关键
public ClientWorker(final ConfigFilterChainManager configFilterChainManager, ServerListManager serverListManager,
final Properties properties) throws NacosException {
this.configFilterChainManager = configFilterChainManager;
init(properties);
agent = new ConfigRpcTransportClient(properties, serverListManager);
ScheduledExecutorService executorService = Executors
.newScheduledThreadPool(ThreadUtils.getSuitableThreadCount(1), r -> {
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.setName("com.alibaba.nacos.client.Worker");
t.setDaemon(true);
return t;
});
agent.setExecutor(executorService);
// 核心1
agent.start();
}
看start方法
public void start() throws NacosException {
if (securityProxy.isEnabled()) {
securityProxy.login(serverListManager.getServerUrls());
this.executor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
securityProxy.login(serverListManager.getServerUrls());
}
}, 0, this.securityInfoRefreshIntervalMills, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// 核心
startInternal();
}
startInternal方法
public void startInternal() throws NacosException {
executor.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (!executor.isShutdown() && !executor.isTerminated()) {
try {
// 核心1
listenExecutebell.poll(5L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (executor.isShutdown() || executor.isTerminated()) {
continue;
}
// 核心2
executeConfigListen();
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("[ rpc listen execute ] [rpc listen] exception", e);
}
}
}
// 核心2
}, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
创建了一个定时任务,每隔0秒循环,相当于死循环,但是核心1处从一个阻塞队列listenExecutebell调用poll方法,然后超时时间是5秒
也就是没有其他干预下,这里是每隔5秒会执行到一次核心2的executeConfigListen
@Override
public void executeConfigListen() {
Map<String, List<CacheData>> listenCachesMap = new HashMap<String, List<CacheData>>(16);
Map<String, List<CacheData>> removeListenCachesMap = new HashMap<String, List<CacheData>>(16);
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
boolean needAllSync = now - lastAllSyncTime >= ALL_SYNC_INTERNAL;
// 核心1
for (CacheData cache : cacheMap.get().values()) {
......
}
}
这里的cacheMap刚启动是是空的,所以这里的代码晚一点再看
先看之前没看的NacosConfigApplicationContextInitializer中的initialize方法里面的核心2,addListenerIfAutoRefreshed
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
singleton.setApplicationContext(context);
environment = context.getEnvironment();
nacosConfigProperties = NacosConfigPropertiesUtils
.buildNacosConfigProperties(environment);
final NacosConfigLoader configLoader = new NacosConfigLoader(
nacosConfigProperties, environment, builder);
if (!enable()) {
logger.info("[Nacos Config Boot] : The preload configuration is not enabled");
}
else {
// If it opens the log level loading directly will cache
// DeferNacosPropertySource release
if (processor.enable()) {
processor.publishDeferService(context);
configLoader
.addListenerIfAutoRefreshed(processor.getDeferPropertySources());
}
else {
// 核心1
configLoader.loadConfig();
// 核心2
configLoader.addListenerIfAutoRefreshed();
}
}
final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory factory = context.getBeanFactory();
if (!factory
.containsSingleton(NacosBeanUtils.GLOBAL_NACOS_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
factory.registerSingleton(NacosBeanUtils.GLOBAL_NACOS_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME,
configLoader.buildGlobalNacosProperties());
}
}
核心1已经看过了,会从远程读取配置,看核心2
public void addListenerIfAutoRefreshed() {
addListenerIfAutoRefreshed(nacosPropertySources);
}
public void addListenerIfAutoRefreshed(
final List<DeferNacosPropertySource> deferNacosPropertySources) {
for (DeferNacosPropertySource deferNacosPropertySource : deferNacosPropertySources) {
NacosPropertySourcePostProcessor.addListenerIfAutoRefreshed(
deferNacosPropertySource.getNacosPropertySource(),
deferNacosPropertySource.getProperties(),
deferNacosPropertySource.getEnvironment());
}
}
public static void addListenerIfAutoRefreshed(
final NacosPropertySource nacosPropertySource, final Properties properties,
final ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
if (!nacosPropertySource.isAutoRefreshed()) { // Disable Auto-Refreshed
return;
}
final String dataId = nacosPropertySource.getDataId();
final String groupId = nacosPropertySource.getGroupId();
final String type = nacosPropertySource.getType();
final NacosServiceFactory nacosServiceFactory = getNacosServiceFactoryBean(
beanFactory);
try {
// 核心1
ConfigService configService = nacosServiceFactory
.createConfigService(properties);
// 核心2
Listener listener = new AbstractListener() {
@Override
public void receiveConfigInfo(String config) {
String name = nacosPropertySource.getName();
NacosPropertySource newNacosPropertySource = new NacosPropertySource(
dataId, groupId, name, config, type);
newNacosPropertySource.copy(nacosPropertySource);
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment
.getPropertySources();
// replace NacosPropertySource
propertySources.replace(name, newNacosPropertySource);
}
};
if (configService instanceof EventPublishingConfigService) {
// 核心3
((EventPublishingConfigService) configService).addListener(dataId,
groupId, type, listener);
}
else {
configService.addListener(dataId, groupId, listener);
}
}
catch (NacosException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"ConfigService can't add Listener with properties : " + properties,
e);
}
}
核心1前面看过了,创建ConfigService,并且会判断缓存是否已存在,保证只创建一次,并且类型是EventPublishingConfigService
核心2处的逻辑就是根据config的文本内容,重新创建PropertySource,替代spring environment中的PropertySource,这个listener现在没有被调用到,后面肯定是会被触发的
核心3
public void addListener(String dataId, String group, String type, Listener listener)
throws NacosException {
Listener listenerAdapter = new DelegatingEventPublishingListener(configService,
dataId, group, type, applicationEventPublisher, executor, listener);
// 核心
addListener(dataId, group, listenerAdapter);
}
把listener包装为了DelegatingEventPublishingListener
addListener
public void addListener(String dataId, String group, Listener listener)
throws NacosException {
// 核心1
configService.addListener(dataId, group, listener);
publishEvent(new NacosConfigListenerRegisteredEvent(configService, dataId, group,
listener, true));
}
NacosConfigService的addListener
@Override
public void addListener(String dataId, String group, Listener listener) throws NacosException {
worker.addTenantListeners(dataId, group, Arrays.asList(listener));
}
ClientWorker的addTenantListeners
public void addTenantListeners(String dataId, String group, List<? extends Listener> listeners)
throws NacosException {
group = blank2defaultGroup(group);
String tenant = agent.getTenant();
// 核心1
CacheData cache = addCacheDataIfAbsent(dataId, group, tenant);
synchronized (cache) {
for (Listener listener : listeners) {
// 核心2
cache.addListener(listener);
}
cache.setSyncWithServer(false);
// 核心3
agent.notifyListenConfig();
}
}
先看核心2,把listener加到了CacheData中,CacheData也就是对应一个dataid,也就是配置文件,这里后面会用到,到这里为止每一个需要自动刷新的配置文件类CacheData都绑定了一个listener,这个listener触发时会修改environment中对应的PropertiesSource
核心3
public void notifyListenConfig() {
listenExecutebell.offer(bellItem);
}
往之前的定时任务使用的阻塞队列中加了个数据,那么相当于强制唤醒那个定时任务了
然后看核心1
public CacheData addCacheDataIfAbsent(String dataId, String group, String tenant) throws NacosException {
CacheData cache = getCache(dataId, group, tenant);
if (null != cache) {
return cache;
}
String key = GroupKey.getKeyTenant(dataId, group, tenant);
synchronized (cacheMap) {
CacheData cacheFromMap = getCache(dataId, group, tenant);
// multiple listeners on the same dataid+group and race condition,so
// double check again
// other listener thread beat me to set to cacheMap
if (null != cacheFromMap) {
cache = cacheFromMap;
// reset so that server not hang this check
cache.setInitializing(true);
} else {
// 核心1
cache = new CacheData(configFilterChainManager, agent.getName(), dataId, group, tenant);
// 核心2
int taskId = cacheMap.get().size() / (int) ParamUtil.getPerTaskConfigSize();
cache.setTaskId(taskId);
// fix issue # 1317
if (enableRemoteSyncConfig) {
ConfigResponse response = getServerConfig(dataId, group, tenant, 3000L, false);
cache.setContent(response.getContent());
}
}
Map<String, CacheData> copy = new HashMap<String, CacheData>(this.cacheMap.get());
copy.put(key, cache);
cacheMap.set(copy);
}
LOGGER.info("[{}] [subscribe] {}", agent.getName(), key);
MetricsMonitor.getListenConfigCountMonitor().set(cacheMap.get().size());
return cache;
}
核心1处就是按照每一个namespace+group+dataId创建一个对应的CacheData,并且放到cacheMap中,记住每一个CacheData中默认都有一个DelegatingEventPublishingListener
核心2处,ParamUtil.getPerTaskConfigSize()的值是3000,也就是按照3000进行了分片,每3000个配置文件的taskId是一样的
然后这里的逻辑就完成了,之前的定时线程池的cacheMap就能拿到数据了,继续看那里的executeConfigListen方法
这个方法特别长,只关注核心的逻辑,每一个NacosConfigService都会执行executeConfigListen
@Override
public void executeConfigListen() {
Map<String, List<CacheData>> listenCachesMap = new HashMap<String, List<CacheData>>(16);
Map<String, List<CacheData>> removeListenCachesMap = new HashMap<String, List<CacheData>>(16);
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
boolean needAllSync = now - lastAllSyncTime >= ALL_SYNC_INTERNAL;
// 核心1,遍历当前NacosConfigService所有的CacheData
for (CacheData cache : cacheMap.get().values()) {
synchronized (cache) {
//check local listeners consistent.
// 关键的控制代码逻辑,后面分析
if (cache.isSyncWithServer()) {
cache.checkListenerMd5();
if (!needAllSync) {
continue;
}
}
// 核心2,因为直接给每一个CacheData都加了一个默认的DelegatingEventPublishingListener,所以这里肯定有值
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(cache.getListeners())) {
//get listen config
// 这里貌似是1.x的代码,后面没改吧,看了下可以设置这个值的方法,已经没有任何地方调用了,也就是这个if一定为true
if (!cache.isUseLocalConfigInfo()) {
List<CacheData> cacheDatas = listenCachesMap.get(String.valueOf(cache.getTaskId()));
if (cacheDatas == null) {
cacheDatas = new LinkedList<CacheData>();
// 按照taskid进行合并放到listenCachesMap中
listenCachesMap.put(String.valueOf(cache.getTaskId()), cacheDatas);
}
cacheDatas.add(cache);
}
// 核心3,上面的if走完,就相当于把所有的CacheData按照taskid进行合并转移到了listenCachesMap中
} else if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(cache.getListeners())) {
if (!cache.isUseLocalConfigInfo()) {
List<CacheData> cacheDatas = removeListenCachesMap.get(String.valueOf(cache.getTaskId()));
if (cacheDatas == null) {
cacheDatas = new LinkedList<CacheData>();
removeListenCachesMap.put(String.valueOf(cache.getTaskId()), cacheDatas);
}
cacheDatas.add(cache);
}
}
}
}
boolean hasChangedKeys = false;
// 核心4,上面转移了,所以这里会有值
if (!listenCachesMap.isEmpty()) {
for (Map.Entry<String, List<CacheData>> entry : listenCachesMap.entrySet()) {
String taskId = entry.getKey();
List<CacheData> listenCaches = entry.getValue();
ConfigBatchListenRequest configChangeListenRequest = buildConfigRequest(listenCaches);
configChangeListenRequest.setListen(true);
try {
// 核心4.1,这个方法后面还要分析,这里可以看到相同的taskid的CacheData只会创建一个RpcClient,一起发送给服务端
RpcClient rpcClient = ensureRpcClient(taskId);
// 核心5,构造了grpc客户端和请求对象,发起请求
ConfigChangeBatchListenResponse configChangeBatchListenResponse = (ConfigChangeBatchListenResponse) requestProxy(
rpcClient, configChangeListenRequest);
if (configChangeBatchListenResponse != null && configChangeBatchListenResponse.isSuccess()) {
Set<String> changeKeys = new HashSet<String>();
//handle changed keys,notify listener
// 核心6,如果有更改的配置,那么继续往下走
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configChangeBatchListenResponse.getChangedConfigs())) {
hasChangedKeys = true;
for (ConfigChangeBatchListenResponse.ConfigContext changeConfig : configChangeBatchListenResponse
.getChangedConfigs()) {
// 核心7,这里可以判断上面的请求,只能拿到哪个文件修改了,而不能直接拿到更改的内容
// 也就是说我一次发送多个我想监听的dataid给服务端,如果其中有改变的,那么服务端告诉我哪些改变了
String changeKey = GroupKey
.getKeyTenant(changeConfig.getDataId(), changeConfig.getGroup(),
changeConfig.getTenant());
changeKeys.add(changeKey);
boolean isInitializing = cacheMap.get().get(changeKey).isInitializing();
// 核心8,下面分析
refreshContentAndCheck(changeKey, !isInitializing);
}
}
//handler content configs
for (CacheData cacheData : listenCaches) {
String groupKey = GroupKey
.getKeyTenant(cacheData.dataId, cacheData.group, cacheData.getTenant());
if (!changeKeys.contains(groupKey)) {
//sync:cache data md5 = server md5 && cache data md5 = all listeners md5.
synchronized (cacheData) {
if (!cacheData.getListeners().isEmpty()) {
// 控制循环的逻辑,后面分析
cacheData.setSyncWithServer(true);
continue;
}
}
}
cacheData.setInitializing(false);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("Async listen config change error ", e);
try {
Thread.sleep(50L);
} catch (InterruptedException interruptedException) {
//ignore
}
}
}
}
// 不关注
if (!removeListenCachesMap.isEmpty()) {
for (Map.Entry<String, List<CacheData>> entry : removeListenCachesMap.entrySet()) {
String taskId = entry.getKey();
List<CacheData> removeListenCaches = entry.getValue();
ConfigBatchListenRequest configChangeListenRequest = buildConfigRequest(removeListenCaches);
configChangeListenRequest.setListen(false);
try {
RpcClient rpcClient = ensureRpcClient(taskId);
boolean removeSuccess = unListenConfigChange(rpcClient, configChangeListenRequest);
if (removeSuccess) {
for (CacheData cacheData : removeListenCaches) {
synchronized (cacheData) {
if (cacheData.getListeners().isEmpty()) {
ClientWorker.this
.removeCache(cacheData.dataId, cacheData.group, cacheData.tenant);
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("async remove listen config change error ", e);
}
try {
Thread.sleep(50L);
} catch (InterruptedException interruptedException) {
//ignore
}
}
}
if (needAllSync) {
lastAllSyncTime = now;
}
//If has changed keys,notify re sync md5.
if (hasChangedKeys) {
// 这个代码之前看过了,listenExecutebell.offer(bellItem);可以直接触发之前的那个循环,默认情况是每五秒执行一次的
notifyListenConfig();
}
}
因为前面一个ConfigServices里面有一个ClientWorker,一个ClientWorker里面可以有多个namespace相同,group不同或者dataid不同的文件,然后每3000个做了分片
所以这里的逻辑大概就是,把每一个ConfigServices里面的所有文件按照批次进行发送,是按照taskid来控制的,taskid是之前构造的,每3000个文件都公用一个taskid,是一种分片的处理,然后服务端一次性告诉客户端有哪些文件发送了改变,客户端一次根据改变的文件名称来获取文件内容
然后看核心8的refreshContentAndCheck
private void refreshContentAndCheck(String groupKey, boolean notify) {
if (cacheMap.get() != null && cacheMap.get().containsKey(groupKey)) {
CacheData cache = cacheMap.get().get(groupKey);
refreshContentAndCheck(cache, notify);
}
}
refreshContentAndCheck方法,当服务端告诉客户端哪个文件发送了改变,那么客户端就发起请求
private void refreshContentAndCheck(CacheData cacheData, boolean notify) {
try {
// 核心1,这个方法之前看过,获取远程配置文件的内容
ConfigResponse response = getServerConfig(cacheData.dataId, cacheData.group, cacheData.tenant, 3000L,
notify);
// 核心2
cacheData.setContent(response.getContent());
cacheData.setEncryptedDataKey(response.getEncryptedDataKey());
if (null != response.getConfigType()) {
cacheData.setType(response.getConfigType());
}
if (notify) {
LOGGER.info("[{}] [data-received] dataId={}, group={}, tenant={}, md5={}, content={}, type={}",
agent.getName(), cacheData.dataId, cacheData.group, cacheData.tenant, cacheData.getMd5(),
ContentUtils.truncateContent(response.getContent()), response.getConfigType());
}
// 核心3
cacheData.checkListenerMd5();
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("refresh content and check md5 fail ,dataId={},group={},tenant={} ", cacheData.dataId,
cacheData.group, cacheData.tenant, e);
}
}
核心2也很关键,不仅设置了内容,而且改变了md5值
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
this.md5 = getMd5String(this.content);
}
核心3
void checkListenerMd5() {
for (ManagerListenerWrap wrap : listeners) {
if (!md5.equals(wrap.lastCallMd5)) {
safeNotifyListener(dataId, group, content, type, md5, encryptedDataKey, wrap);
}
}
}
wrap.lastCallMd5为之前的md5,md5为现在的md5,如果加载到新的内容,则会调用上面setContent同时修改md5值,导致两个值不一样
private void safeNotifyListener(final String dataId, final String group, final String content, final String type,
final String md5, final String encryptedDataKey, final ManagerListenerWrap listenerWrap) {
final Listener listener = listenerWrap.listener;
if (listenerWrap.inNotifying) {
LOGGER.warn(
"[{}] [notify-currentSkip] dataId={}, group={}, md5={}, listener={}, listener is not finish yet,will try next time.",
name, dataId, group, md5, listener);
return;
}
Runnable job = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
ClassLoader myClassLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
ClassLoader appClassLoader = listener.getClass().getClassLoader();
try {
if (listener instanceof AbstractSharedListener) {
AbstractSharedListener adapter = (AbstractSharedListener) listener;
adapter.fillContext(dataId, group);
LOGGER.info("[{}] [notify-context] dataId={}, group={}, md5={}", name, dataId, group, md5);
}
// Before executing the callback, set the thread classloader to the classloader of
// the specific webapp to avoid exceptions or misuses when calling the spi interface in
// the callback method (this problem occurs only in multi-application deployment).
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(appClassLoader);
ConfigResponse cr = new ConfigResponse();
cr.setDataId(dataId);
cr.setGroup(group);
cr.setContent(content);
cr.setEncryptedDataKey(encryptedDataKey);
configFilterChainManager.doFilter(null, cr);
String contentTmp = cr.getContent();
listenerWrap.inNotifying = true;
// 核心1
listener.receiveConfigInfo(contentTmp);
// compare lastContent and content
if (listener instanceof AbstractConfigChangeListener) {
Map data = ConfigChangeHandler.getInstance()
.parseChangeData(listenerWrap.lastContent, content, type);
ConfigChangeEvent event = new ConfigChangeEvent(data);
((AbstractConfigChangeListener) listener).receiveConfigChange(event);
listenerWrap.lastContent = content;
}
listenerWrap.lastCallMd5 = md5;
.....
}
这里就是一个对之前保存到CacheData中的listener的回调,调用到receiveConfigInfo方法,传递了文件的内容
之前的listener被包装为的是DelegatingEventPublishingListener,所以调用到DelegatingEventPublishingListener的receiveConfigInfo
public void receiveConfigInfo(String content) {
onReceived(content);
publishEvent(content);
}
看onReceived
private void onReceived(String content) {
delegate.receiveConfigInfo(content);
}
做了个委派模式的委派
之前的回调方法,就是根据拿到的内容,替换了spring environment中的对应的propertySources
Listener listener = new AbstractListener() {
@Override
public void receiveConfigInfo(String config) {
String name = nacosPropertySource.getName();
NacosPropertySource newNacosPropertySource = new NacosPropertySource(
dataId, groupId, name, config, type);
newNacosPropertySource.copy(nacosPropertySource);
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment
.getPropertySources();
// replace NacosPropertySource
propertySources.replace(name, newNacosPropertySource);
}
};
实现了服务端内容修改时,客户端动态感知并且修改spring environment中对应的propertiesSource
然后看publishEvent(content);发布了一个spring的事件,事件类NacosConfigReceivedEvent
private void publishEvent(String content) {
NacosConfigReceivedEvent event = new NacosConfigReceivedEvent(configService,
dataId, groupId, content, configType);
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(event);
}
这个NacosConfigReceivedEvent是被NacosValueAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类监听的
public void onApplicationEvent(NacosConfigReceivedEvent event) {
// 核心1
for (Map.Entry<String, List<NacosValueTarget>> entry : placeholderNacosValueTargetMap
.entrySet()) {
String key = environment.resolvePlaceholders(entry.getKey());
String newValue = environment.getProperty(key);
if (newValue == null) {
continue;
}
List<NacosValueTarget> beanPropertyList = entry.getValue();
for (NacosValueTarget target : beanPropertyList) {
String md5String = MD5Utils.md5Hex(newValue, "UTF-8");
boolean isUpdate = !target.lastMD5.equals(md5String);
if (isUpdate) {
target.updateLastMD5(md5String);
Object evaluatedValue = resolveNotifyValue(target.nacosValueExpr, key, newValue);
if (target.method == null) {
// 核心2
setField(target, evaluatedValue);
}
else {
setMethod(target, evaluatedValue);
}
}
}
}
}
NacosValueAnnotationBeanPostProcessor这个类是处理@NacosValue注解的,核心1里面存储了所有有@NacosValue并且需要自动刷新的(autoRefreshed = true)字段,遍历所有,然后从spring的environment中重新获取值,如果不一样则在核心2处反射进行赋值即可
需要注意这里的处理必须有两个前提
- 全局配置nacos.config.auto-refresh=true
- 字段autoRefreshed = true
注意这里没有看到对@Value注解做动态赋值的处理
到这里还要分析一下这个循环的逻辑,因为外面是一个延迟线程池,0秒循环,但是会依次从阻塞队列拿数据,超时时间是5秒,所以默认是每5秒进入一次executeConfigListen方法
看executeConfigListen方法后面的逻辑,这段代码的逻辑是从远程查询一次后,如果没有查询到变化则设置cacheData的syncWithServer参数为true
for (CacheData cacheData : listenCaches) {
String groupKey = GroupKey
.getKeyTenant(cacheData.dataId, cacheData.group, cacheData.getTenant());
if (!changeKeys.contains(groupKey)) {
//sync:cache data md5 = server md5 && cache data md5 = all listeners md5.
synchronized (cacheData) {
if (!cacheData.getListeners().isEmpty()) {
cacheData.setSyncWithServer(true);
continue;
}
}
}
cacheData.setInitializing(false);
}
然后再看executeConfigListen上面的控制代码,当syncWithServer是true的时候可以进入,上面的逻辑从服务端查询一次没变化时设置为了true,然后会检查一下本地md5值,这是一种常规的检查机制,大概是为了容错吧
然后看这个!needAllSync,ALL_SYNC_INTERNAL=5分钟,这里的意思是当上一次查询到当前时间小于5分钟时执行continue,也就不会走下面的查询远程配置的逻辑了
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
boolean needAllSync = now - lastAllSyncTime >= ALL_SYNC_INTERNAL;
for (CacheData cache : cacheMap.get().values()) {
synchronized (cache) {
//check local listeners consistent.
if (cache.isSyncWithServer()) {
cache.checkListenerMd5();
if (!needAllSync) {
continue;
}
}
。。。。。。
也就是说这里的逻辑是
1、先全局调用一次服务端,根据taskId批量调用,如果查询到有配置文件修改了,那么依次获取配置即可
2、如果没获取到,那么设置syncWithServer=true
3、syncWithServer=true时,只有每隔5分钟才会全局检查一次远程配置
那么这里就有个问题了,如果远程配置我们进行了手动修改,那么客户端是如何感知的呢
这里就要继续看这里的一个核心方法了,executeConfigListen的RpcClient创建逻辑
RpcClient rpcClient = ensureRpcClient(taskId);
ConfigChangeBatchListenResponse configChangeBatchListenResponse = (ConfigChangeBatchListenResponse) requestProxy(
rpcClient, configChangeListenRequest);
看ensureRpcClient方法
private RpcClient ensureRpcClient(String taskId) throws NacosException {
synchronized (ClientWorker.this) {
Map<String, String> labels = getLabels();
Map<String, String> newLabels = new HashMap<String, String>(labels);
newLabels.put("taskId", taskId);
RpcClient rpcClient = RpcClientFactory
.createClient(uuid + "_config-" + taskId, getConnectionType(), newLabels);
if (rpcClient.isWaitInitiated()) {
// 核心1
initRpcClientHandler(rpcClient);
rpcClient.setTenant(getTenant());
rpcClient.clientAbilities(initAbilities());
rpcClient.start();
}
return rpcClient;
}
}
看initRpcClientHandler
private void initRpcClientHandler(final RpcClient rpcClientInner) {
/*
* Register Config Change /Config ReSync Handler
*/
rpcClientInner.registerServerRequestHandler((request) -> {
if (request instanceof ConfigChangeNotifyRequest) {
ConfigChangeNotifyRequest configChangeNotifyRequest = (ConfigChangeNotifyRequest) request;
LOGGER.info("[{}] [server-push] config changed. dataId={}, group={},tenant={}",
rpcClientInner.getName(), configChangeNotifyRequest.getDataId(),
configChangeNotifyRequest.getGroup(), configChangeNotifyRequest.getTenant());
String groupKey = GroupKey
.getKeyTenant(configChangeNotifyRequest.getDataId(), configChangeNotifyRequest.getGroup(),
configChangeNotifyRequest.getTenant());
CacheData cacheData = cacheMap.get().get(groupKey);
if (cacheData != null) {
// 核心1
cacheData.setSyncWithServer(false);
notifyListenConfig();
}
return new ConfigChangeNotifyResponse();
}
return null;
});
。。。。。
这个registerServerRequestHandler传入的lambda表达式,当服务端配置修改时最终会触发到这里
这里服务端通知客户端的代码比较多,大概逻辑是这样的,因为nacos2.x基于grpc,是支持长连接流的方式,服务端可以随时给客户端发消息,当服务端修改配置时就会给客户端推送配置变更的消息,然后客户端强制触发上面的循环,然后会触发executeConfigListen这个方法,从而进行配置的重新获取
核心1设置了cacheData的syncWithServer=false,并且调用了notifyListenConfig(),这个方法之前看过了,相当于直接触发之前那个5秒的循环,直接执行executeConfigListen()方法,然后因为syncWithServer=false,所以可以执行到下面的全局检查配置逻辑,做到了服务端修改配置,客户端进行动态感知
public void notifyListenConfig() {
listenExecutebell.offer(bellItem);
}
到这里environment中的propertiesSource可以做到动态更改了,那么@NacosValue的字段也可以动态更改了,但是@NacosValue并不方便,正常来说使用@Value注解会更好,假设后续动态配置中心使用了别的,比如Apollo,那么这些代码至少是不需要改的
总结
- nacos-config-spring-boot-starter可以实现对@NacosValue注解属性的动态更改,默认无法支持@Value注解的动态更改
- spring cloud nacos需要在类上标记@RefreshScope,可以实现@Value注解属性的动态更改
本文源码流程较为复杂,但是较为重要的逻辑还是可以理清的,源码的内容看起来相对枯燥,最好是需要实践打断点的形式比较容易看懂
基于源码的理解,如果要让nacos-config-spring-boot-starter实现对@Value注解属性的动态更改也不难,可以利用其中的一下监听机制的扩展实现,下一节就讲一下如何实现这个功能