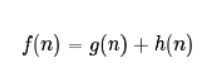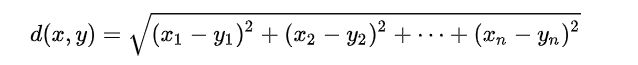[基于Python的数据结构与算法] 图
[基于Python的数据结构与算法] 图
1.图
1.1 图的定义
| 基本概念 | |
|---|---|
| 顶点/边/权重 | 基本组成部分 |
| 度 | deg(v);入度indeg(v)、出度outdeg(v)是输入边、输出边的数目 |
| 路径 | 边连接的顶点序列 |
| 环 | 起点终点相同的路径 |
| 路径长度 | 无权重:路径边数之和 有权重:路径上边的权重之和 |
| 邻接矩阵 | 以二维矩阵的形式储存权重![[基于Python的数据结构与算法] 图_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/e25895eda6ae4482aefb69dbb3e06b23.jpg) |
| 邻接表 | 以字典的形式储存权重![[基于Python的数据结构与算法] 图_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/e354bfec89ec4cef91f1134345fd90bc.jpg) |
| 图的分类 | |
|---|---|
| 边单向/双向 | 有向图(所有边都是单向的)/无向图 |
| 是否有环 | 有环图/无环图 |
| 邻接矩阵空位多/边稀少 | 稀疏图 |
| 任意两点都是连通的图 | 连通图 |
| 其他概念 | |
|---|---|
| 生成树 | 具有无向连通图G 的全部顶点,但边数最少的连通子图(即任意两顶点之间有且仅有一条通路) |
| 最小生成树 | 权值最小的生成树 |
1.2 图的实现
Vertex类:使用字典connectedTo记录每个顶点的邻接表
Graph类:使用字典vertList记录顶点(键是顶点id,值是顶点对象)
对图类中的两个顶点进行连边操作(addEdge),即对顶点对象(addNeighbor)
class Vertex:
def __init__(self, key):
self.__id = key
self.__connectedTo = {}
def addNeighbor(self, nbr, weight = 0):
self.connectedTo[nbr] = weight
def getConnections(self):
return self.connectedTo.keys()
def getId(self):
return self.id
def getWeight(self, nbr):
return self.connectedTo[nbr]
def __str__(self):
return str(self.id) + 'connectedTo:' + str([x.id for x in self.connectedTo])
class Graph:
def __init__(self):
self.__vertList = {}
self.__numVertices = 0
def addVertex(self, key):
self.numVertices += 1
newVertex = Vertex(key)
self.vertList[key] = newVertex
return newVertex
def addEdge(self, f, t, cost = 0):
if f not in self.vertList:
newVertex = Vertex(f)
if t not in self.vertList:
newVertex = Vertex(t)
self.vertList[f].addNeighbor(self.vertList[t], cost)
def getVertex(self, n):
if n in self.vertList:
return self.vertList[n]
else:
return None
def getVertices(self):
return self.vertList.keys()
def __contains__(self, n):
return n in self.vertList
def __iter__(self);
return iter(self.vertList.values())
1.3 宽度优先搜索 BFS
BFS特性
-
BFS访问完所有与起点s相距为k的顶点之后再去访问与其相距为k+1的顶点(广搜)
-
BFS由队列辅助实现
-
BFS以每次生成一层的方式构建一棵树,它会在访问任意一个孙节点之前将起点的所有子节点都添加进来
-
为了记录进度,BFS会将顶点标记成白色、灰色或黑色。
颜色 意义 白色 在构建时,所有顶点都被初始化成白色,代表该顶点没有被访问过。 灰色 当顶点第一 次被访问时,它就会被标记为灰色。 黑色 当BFS完成对该顶点的访问之后, 它就会被标记为黑色。
BFS实现
- 给定图G和起点 s,BFS从起点s开始
- 当前顶点标记为灰色,放入Queue(此队列储存所有灰色顶点,表示待访问)中
- 遍历邻接表,将所有白色相邻顶点标记为灰色,依次放入Queue
- 当前顶点标记为黑色,访问完毕
- 继续访问位于Queue头部的下一个顶点,重复该四步直到Queue为空
-
Vertex类新增属性distance、predecessor、color用来表示顶点的路径长度、上一顶点、颜色状态
class Vertex: def __init__(self, key): self.__id = key self.__connectedTo = {} self.__distance = 0 self.__predecessor = None self.__color = 'white' def setDistance(self, dis): self.__distance = dis def setPred(self, ver): self.__predecessor = ver def setColor(self, color): self.__color = color def getDistance(self): return self.__distance def getPred(self): return self.__predecessor def getColor(self): return self.__color -
以上类可通过调用第三方库实现,得到BFS算法
from pythonds.graphs import Graph, Vertex from pythonds.graphs import Queue #BFS算法实现 def BFS(self, start): start.setDistance(0) start.setPred(None) vertQueue = Queue( ) vertQueue.enqueue(start) while vertQueue.size() > 0: currentVert = vertQueue.dequeue ( ) for nbr in currentVert.getConnections(): if nbr.getColor() == 'white': nbr.setColor('gray') nbr.setDistance(currentVert.getDistance() + 1) nbr.setPred(currentVert) vertQueue.enqueue(nbr) currentVert.setColor('black')
BFS性能分析
| BFS | |
|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | O(V) |
| 时间复杂度 | O(V+E) |
1.4 深度优先搜索 DFS
DFS特性
-
DFS尽可能深地搜索树的分支(深搜)
-
DFS通过递归回溯隐式地使用栈
-
一次深度优先搜索甚至能够创建多棵深度优先搜索树,称为深度优先森林
-
为了记录进度,DFS会将顶点标记成白色、灰色或黑色,同BFS
DFS实现(通用DFS)
-
给定图G和起点 s,DFS从起点s开始
- 当前顶点标记为灰色,遍历其邻接表中的相邻顶点
- 检查相邻顶点的颜色状态,对白色顶点进行递归调用,重复以上操作
-
直到最后的顶点无相邻白色顶点,层层回溯
from pythonds.graphs import Graph
class DFSGraph(Graph):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__ ()#继承父类构造函数中的内容,且子类可在父类的基础上补充
self.time = 0#记录最短路径长度
def DFS(self):
#遍历图中所有顶点,确保深度优先森林中的所有顶点都在考虑范围内,而不会有被遗漏的顶点
for aVertex in self:
aVertex. setColor('white')
aVertex. setPred(-1)
for aVertex in self:
if aVertex.getColor() == 'white':
self.DFSvisit(aVertex)
def DFSvisit(self, startVertex):
startVertex.setColor('gray')
self.time += 1
startVertex.setDiscovery(self.time)
for nextVertex in startVertex.getConnections():
if nextVertex.getColor( ) == "white':
nextVertex.setPred(startVertex)
self.DFSvisit(nextVertex)
startVertex.setColor('black')
self.time += 1
startVertex.setFinish(self.time)
DFS性能分析
| DFS | |
|---|---|
| 时间复杂度 | O(V + E) |
骑士周游问题(Warnsdorff算法)
[ 问题描述 ]
取一块国际象棋8×8的棋盘和一颗骑士棋子(马),在骑士的走法规范下,找到一系列合适的路径,使得骑士对棋盘上的每一格刚好都只
访问一次。
[ 算法实现 ]
from pythonds.graphs import Graph, Vertex
def knightTour(n, path, u, limit):
'''
n 是搜索树的当前深度;
path 是到当前为止访问过的顶点列表;
u 是正在访问的顶点;
limit 是顶点总数。
'''
#顶点正在被访问:标记为灰色,加入路径列表
u.setColor('gray')
path.append(u)
if n < limit:
#获取该顶点相邻顶点列表
nbrlist = list(u.getConnections())
i= 0
done = False
#1.相邻顶点列表第一项符合条件,进行下一顶点递归调用
#2.回溯时返回此步,依次索引相邻列表顶点
while i < len(nbrlist) and not done:
if nbrList[i].getColor() == 'white' :
done = knightTour(n+1, path, nbrList[i], limit)
i += 1
'''
若该顶点是死路(无出边指向顶点len(nbrlist) = 0/相邻顶点无白色nbrList[i].getColor() != 'white')
准备回溯(重新标记为灰色,移出路径列表)
结束该次调用,回到上一层调用
'''
if not done:
path.pop( )
u.setColor('white')
else:
'''
搜索树的当前深度(n) = 顶点总数(limit),
完成一次周游。
'''
done = True
return done
算法改进:
为了保证接下来要访问的顶点有最少的合理走法,每次选择下一个要访问的顶点至关重要。如果选择优先访问合理走法最少的顶点,则骑士优可以先访问棋盘边缘的格子。这样做保证了骑士能够尽早访问难以到达的角落,并且在需要的时候通过 中间的格子跨越到棋盘的另一边。而不是在周游的前期就访问位于棋盘中间的格子,因而被困在棋盘的一边,而无法到达另一边的那些没访问过的格子。
利用这类知识来加速算法被称为启发式搜索算法(heuristic),本例中启发式算法被称为Warnsdorff算法。
而DFS与BFS被称为盲目式搜索算法。
def Warnsdorff(n):
resList = [ ]
for v in n.getConnections():
if v.getColor() == 'white' :
C = 0
for W in v.getConnections() :
if w.getColor() == 'white' :
C += 1
resList. append((c, v))
resList.sort(key = lambda x: x[0])
orderByAvail = [y[1] for y in resList]
return orderByAvail
1.5 最短路径问题/寻路算法
1.5.1 Dijkstra算法
采用贪心模式。类似于BFS,用于解决有权重的图。时间复杂度为O((V + E)logV)
from pythonds.graphs import PriorityQueue, Graph, Vertex
# Vertex类中的distance属性初始值默认设置无穷大(实际一般将其设为一个大于所有可能出现的实际距离的值)
def Dijkstra(aGraph, start):
pq = PriorityQueue()
start.setDistance(0)
pq.buildHeap([(v, v.getDistance()) for v in aGraph])
while not pq.isEmpty():
currentVert = pq.delMin()
for nextVert in currentVert.getConnections() :
newDist = currentVert.getDistance() + currentVert.getweight(nextVert)
if newDist < nextVert.getDistance():
nextVert.setDistance(newDist)
nextVert.setPred(currentVert)
pq.decreaseKey(nextVert, newDist) #此方法将新产生/更新后的(路径, 节点)键值对添加到优先队列中
以此图为例分析 Dijkstra算法 实现过程
- pq = [(0, u), (SysMaxInit, v), (SysMaxInit, w), (SysMaxInit, x)] 进入循环前
- pq = [(1, x), (2, v), (5, w)] 结束第一次循环
- pq = [(2, v), (2, y), (4, w)] 结束第二次循环
- pq = [(2, y), (4, w)] 结束第三次循环
- pq = [(4, w), (3, z)] 结束第四次循环
- pq = [(3, z)] 结束第五次循环
- pq = [] 跳出循环
1.5.2 贪婪最佳优先搜索算法(Greedy Best-First Search,GBFS)
from pythonds.graphs import PriorityQueue, Graph, Vertex
def GBFS(start, goal):
frontier = PriorityQueue()
frontier. insert((start, 0))
came_from = dict() #记录上一顶点,跟踪路径
cost_so_far = dict()
came_from[start] = None
cost_so_far[start] = 0
while not frontier. isEmpty():
current = frontier. delMin()
if current == goal:
break
for next in current. getConnections():
if next not in cost_so_far: #相当于a*的h(n),每个顶点是一定的,无需比较更新
cost_so_far[next] = new_cost
priority = new_cost + heuristic(goal, next) #启发函数,具体意义见a*
frontier.put((next, priority))
came_from[next] = current
1.5.3 A*算法
一种启发式算法,每个顶点的优先级基于如下函数:
- f(n)/cost 是 顶点n的综合代价。下一个要遍历的顶点就是综合优先级最高(代价值最小)的顶点。
- g(n) /g-cost 是 顶点n距离起点的实际代价。
- 如果 g(n)为0,即只计算任意顶点 n 到目标的估计代价 h(n),而不计算顶点 n 距离起点的实际代价,则算法转化为使用贪心策略最佳搜索算法(GBFS),速度最快,但可能得不出最优解
- h(n)/h-cost 是 顶点 n 到目标的估计代价,也就是A*算法的启发函数。
- 如果h(n)为0,即只计算顶点 n 距离起点的实际代价g(n),而不计算顶点 n 到目标的估计代价,则算法转化为Dijkstra算法,此时需要计算最多的顶点
- 如果h(n)不大于顶点 n 到目标的实际距离,则一定可以求出最优解,而且 h(n)越小,需要计算的节点越多,算法效率越低
常用的启发函数有:
-
曼哈顿距离(Manhattan distance)—— 如果图形中只允许朝上下左右四个方向移动
-
欧几里得距离(Euclidean distance)—— 如果图形中允许朝任何方向移动
A*算法代码实现
from pythonds.graphs import PriorityQueue
def a_star(graph, start, goal):
frontier = PriorityQueue()
frontier. insert((start, 0))
came_from = dict() #记录上一顶点,跟踪路径,最短路径再不断更新
cost_so_far = dict() #记录每一次遍历时顶点g(n)的状态,以便更新
came_from[start] = None
cost_so_far[start] = 0
while not frontier. isEmpty():
current = frontier. delMin()
if current == goal:
break
for next in current. getConnections():
new_cost = cost_so_far[current] + current. getWeight(next)
if next not in cost_so_far or new_cost < cost_so_far[next]:
#每个顶点的h(n)是一定的,因此每次只需重新计算比较g(n)
cost_so_far[next] = new_cost
#而优先队列中的优先级由h(n)和g(n)共同决定,PriorityQueue记录顶点f(n)的状态
priority = new_cost + heuristic(goal, next)
frontier.put((next, priority))
came_from[next] = current
参考资料
-
维基百科
-
python数据结构与算法分析第2版
-
算法可视化讲解网站-RedBlogGames
-
知乎-路径规划之A算法 及其算法实现 Github-aAlgorithm
重新计算比较g(n)
cost_so_far[next] = new_cost
#而优先队列中的优先级由h(n)和g(n)共同决定,PriorityQueue记录顶点f(n)的状态
priority = new_cost + heuristic(goal, next)
frontier.put((next, priority))
came_from[next] = current
### 参考资料
- 维基百科
- python数据结构与算法分析第2版
- [算法可视化讲解网站-RedBlogGames](https://www.redblobgames.com/)
- [知乎-路径规划之A*算法](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/54510444) 及其算法实现 [Github-a*Algorithm](https://github.com/paulQuei/a-star-algorithm)
![[基于Python的数据结构与算法] 图_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/517c8daebd02441790864db5e12ee4fb.jpg)
![[基于Python的数据结构与算法] 图_第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/46c134b029934587ad89b7777b29146a.jpg)
![[基于Python的数据结构与算法] 图_第5张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/0c1c79c7b9204bc6a3d2522c8a1a5ca9.jpg)
![[基于Python的数据结构与算法] 图_第6张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/8972e95fc1b64715a46b65b056ff3147.jpg)
![[基于Python的数据结构与算法] 图_第7张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/e6f6458fba3847f69f9a7745b1777f3b.jpg)