JAVA并发编程--4.2理解Condition
背景:Condition 多线程条件并发控制,与Lock配合可以实现等待/通知模式;
1 condition 使用demo(生产者与消费者模型):
package org.lgx.bluegrass.bluegrasscoree.util.testcondition;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* @Description TODO
* @Date 2022/11/25 16:19
* @Author lgx
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class TestCondition {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 声明一把lock锁
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 声明队列不为空的条件
Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
// 声明队列不满的条件
Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
// 声明队列的最大长度
int maxSize = 10;
List<String> msg = new ArrayList<>();
// 构造生产者
Producer producer = new Producer(msg, lock, notEmpty, notFull, maxSize);
// 构造消费者
Consumer Consumer = new Consumer(msg, lock, notEmpty, notFull, maxSize);
new Thread(producer).start();
new Thread(Consumer).start();
}
}
// 生产者
class Producer implements Runnable {
private List<String> msg;
private Lock lock;
private Condition notEmpty;
private Condition notFull;
private Integer maxSize;
public Producer(List<String> msg, Lock lock, Condition notEmpty, Condition notFull, Integer maxSize) {
this.msg = msg;
this.lock = lock;
this.notEmpty = notEmpty;
this.notFull = notFull;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
/**
* 生产者产生数据模型
**/
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
// 获取lock 锁,如果获取失败则进入到AQS 同步阻塞队列(双向队列)
lock.lock();
try {
while (msg.size() >= maxSize) {
// 消息已满-- 需要阻塞
System.out.println(" 消息已满-- 需要阻塞");
notFull.await();
}
String msgStr = "写入消息" + UUID.randomUUID();
msg.add(msgStr);
System.out.println(msgStr);
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 生产者产生消息后通知对应的消费者
notEmpty.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 生产者释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 消费者产生数据模型
**/
class Consumer implements Runnable {
private List<String> msg;
private Lock lock;
private Condition notEmpty;
private Condition notFull;
private Integer maxSize;
public Consumer(List<String> msg, Lock lock, Condition notEmpty, Condition notFull, Integer maxSize) {
this.msg = msg;
this.lock = lock;
this.notEmpty = notEmpty;
this.notFull = notFull;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
// 获取lock 锁,如果获取失败则进入到AQS 同步阻塞队列(双向队列)
lock.lock();
try {
while (msg.isEmpty()) {
// 消息队列为空-- 需要阻塞
System.out.println("消息队列为空-- 需要阻塞:");
notEmpty.await();
}
System.out.println("获取消息:" + msg.get(0));
msg.remove(0);
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 消费者消费消息后通知对应的生产者
notFull.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 消费者释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
2 生产者与消费者模型过程分析:
线程获取锁的过程,参考:JAVA并发编程–4.1理解ReentrantLock
2.1 生产者获取lock 锁, 生产消息,当队列满时,调用awaitt() 释放当前线程持有的锁,并阻塞当前线程:
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.await():
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
// 构建Condition单向链表,将当前节点加入到此单向链表中
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
// // 完全释放锁,返回当前线程对锁的重入次数
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
int interruptMode = 0;
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
// 如果当前node 节点只在Condition单向链表 不在AQS 同步阻塞队列中,则返回false,进入此while 循环
LockSupport.park(this);// 挂起档当前的线程
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;.// 当前线程中断则跳出循环
}
// 在AQS 同步队列中唤醒的node 节点去抢占锁
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
if (node.nextWaiter != null) // clean up if cancelled
unlinkCancelledWaiters();// 将Condition单向链表中年已经是取消状态的线程从队列中剔除
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);// 线程中断标记
}
addConditionWaiter:
/**
* Adds a new waiter to wait queue.
* @return its new wait node
*/
private Node addConditionWaiter() {
Node t = lastWaiter;// 最后一个等待节点 初始为null,后续线程进入时 t指向行单向链表的尾节点
// If lastWaiter is cancelled, clean out.
if (t != null && t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) {
unlinkCancelledWaiters();// 清除失效节点
t = lastWaiter;
}
// 构建一个新的节点 static final int CONDITION = -2;
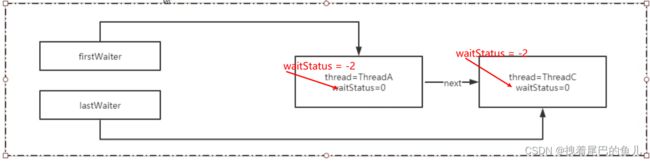
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), Node.CONDITION);
if (t == null)// 第一次 t 为null
firstWaiter = node;// firstWaiter指针指向新创建的node
else // 尾节点的下一节点指向新创建的node 节点;即将 Node 节点加入到单向链表中
t.nextWaiter = node;
lastWaiter = node;// lastWaiter 指针指向新创建的node
return node;
}
第一次:ThreadA(单向链表构建示意)
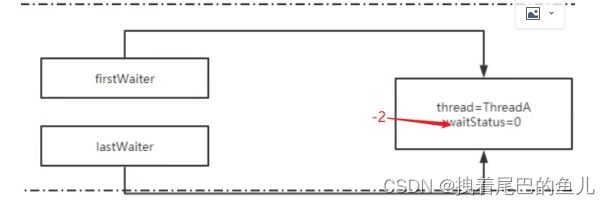
第二个ThreadB(单向链表构建示意)
fullyRelease 完全释放锁 :
final int fullyRelease(Node node) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
// 获取当前lock 的state (锁的次数)
int savedState = getState();
if (release(savedState)) {{// 释放锁
failed = false;// 释放锁成功,失败标识置为false
return savedState;
} else {// 释放失败抛出异常
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)// 如果释放锁失败,则证明释放锁过程中线程出现异常
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;// 将当前condition 单向链表中的改节点置为取消状态
}
}
release(int arg):
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
// 释放锁成功
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);// 唤醒AQS 中的头部节点去抢占锁
return true;
}
return false;
}
unparkSuccessor:
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);// 唤醒线程
}
isOnSyncQueue:是否在AQS同步双向链表中:
/**
* Returns true if a node, always one that was initially placed on
* a condition queue, is now waiting to reacquire on sync queue.
* @param node the node
* @return true if is reacquiring
*/
final boolean isOnSyncQueue(Node node) {
if (node.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION || node.prev == null)
return false;// 当前节点的waitStatus 是CONDITION 或者当前节点的前置节点为空则标明在Condition 单向链表中
if (node.next != null) // If has successor, it must be on queue 不在Condition 单向链表中 已定在AQS队列中
return true;// 挡圈节点不为尾节点返回true
/*
* node.prev can be non-null, but not yet on queue because
* the CAS to place it on queue can fail. So we have to
* traverse from tail to make sure it actually made it. It
* will always be near the tail in calls to this method, and
* unless the CAS failed (which is unlikely), it will be
* there, so we hardly ever traverse much.
*/
return findNodeFromTail(node);
}
findNodeFromTail 遍历AQS队列 寻找node 节点:
/**
* Returns true if node is on sync queue by searching backwards from tail.
* Called only when needed by isOnSyncQueue.
* @return true if present
*/
private boolean findNodeFromTail(Node node) {
Node t = tail;
for (;;) {
if (t == node)
return true;
if (t == null)
return false;
t = t.prev;
}
}
acquireQueued(node, savedState) 当前线程获取锁:
/**
* Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already in
* queue. Used by condition wait methods as well as acquire.
*
* @param node the node
* @param arg the acquire argument
* @return {@code true} if interrupted while waiting
*/
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
// 是否中断标识
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
// 当前节点的前置节点是头结点,则尝试去获取锁
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
// 获取锁成功从AQS中移除改node 节点
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
// 抢占不到锁则挂起当前线程
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);// 从AQS 中移除失效节点
}
}
setHead(node):
private void setHead(Node node) {
head = node;
node.thread = null;
node.prev = null;
}
2.2 消费者获取lock 锁 ,在消费消息后,调用signal() 唤醒生产者:
消费者获取lock 锁, 消费消息,当队列为空时,也会调用awaitt() 释放当前线程持有的锁,并阻塞当前线程:
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer:
signal() 将当前condition队列中的一个头部元素转移至AQS队列中:
/**
* Moves the longest-waiting thread, if one exists, from the
* wait queue for this condition to the wait queue for the
* owning lock.
*
* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if {@link #isHeldExclusively}
* returns {@code false}
*/
public final void signal() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())// 如果当前线程没有获取锁则抛出异常
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
Node first = firstWaiter;// 获取condition队列中的头部节点
if (first != null)
doSignal(first);// 转移改节点至AQS队列
}
doSignal(Node first):
/**
* Removes and transfers nodes until hit non-cancelled one or
* null. Split out from signal in part to encourage compilers
* to inline the case of no waiters.
* @param first (non-null) the first node on condition queue
*/
private void doSignal(Node first) {
do {
if ( (firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null)// condition队列中只有一个节点
lastWaiter = null;
first.nextWaiter = null;// 从condition队列中移除改node 节点
} while (!transferForSignal(first) &&
(first = firstWaiter) != null);
}
transferForSignal(first):
/**
* Transfers a node from a condition queue onto sync queue.
* Returns true if successful.
* @param node the node
* @return true if successfully transferred (else the node was
* cancelled before signal)
*/
final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {
/*
* If cannot change waitStatus, the node has been cancelled.
*/
// 设置node 的waitstate为0,设置失败意味改线程已经被取消
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))
return false;
/*
* Splice onto queue and try to set waitStatus of predecessor to
* indicate that thread is (probably) waiting. If cancelled or
* attempt to set waitStatus fails, wake up to resync (in which
* case the waitStatus can be transiently and harmlessly wrong).
*/
// 将当前node 加入到同步阻塞队列中并返回之前AQS 中tail 节点
Node p = enq(node);
int ws = p.waitStatus;
if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL))
// 如果waitStatus >0 (线程取消状态);或者设置node 的waitStatus 为SIGNAL 失败时 则唤醒之前AQS 中tail 节点线程;
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread);// 优化方式此时唤醒可以使得AQS队列中及时的清除失效节点
消费者线程调用unlock() 方法从AQS 队列中唤醒线程去抢占锁。
3 await 和signal 过程:
(1)生产者(Producer ) 线程A ,线程B,去抢占锁;线程A获取到锁,线程B没有抢占到锁则进入Lock 的AQS(双向链表的阻塞队列) 队列;消费者线程C 没有抢占到锁则进入AQS 队列;
(2)线程A 执行任务后调用signal()/signalAll();此时condition 队列中中没有元素;
(3)线程A 在执行任务过程中,达到一定条件,则调用await() 方法;将当前的node 节点(new Node(Thread.currentThread(), Node.CONDITION))放入到condition 单向队列中;并且完全释放当前持有的lock锁,并且挂起当前的线程;并且从AQS 同步队列中唤醒一个加入时间最早的Node(AQS的header节点)去抢占锁;
(4)线程B 抢占到锁同线程A一样,在达到一定条件,则调用await() 方法;将当前的node 节点(new Node(Thread.currentThread(), Node.CONDITION))放入到condition 单向队列中;并且完全释放锁,并且挂起当前的线程;并且从AQS 同步队列中唤醒一个加入时间最早的Node去抢占锁;
(5)线程C(消费者) 抢占到锁,消费信息后,调用用signal()/signalAll();将位于condition 单向链表中的Node 一个/全部节点转移到AQS(尾插法加入到Lock的同步阻塞队列) 队列中;
(6)线程C(消费者) 业务完成调unlock() 方法,从从AQS 同步队列中唤醒一个加入时间最早的Node(header节点)去抢占锁;
(7)线程A(生产者) 抢占锁,如果抢占到锁则进行执行任务,抢占不到锁则被park,挂起当前线程,等锁的抢占;