@Configuration配置类中若干问题用static解决的源码解析
@Configuration配置类中若干问题用static解决的源码解析
前言
首先感谢A哥对配置类精彩讲解,现我将对@Configuration配置类中若干问题做源码的分析和解读,但一个前提你要对SpringBean的生命周期有个大概的了解,同时对上面A哥的关于@Configuration的文章要有准确的认知,我会用上面的几个案例通过断点的方式,来阐述产生问题的原因
本文内容若没做特殊说明,均基于以下版本:
- JDK:
11 - Spring Framework:
5.2.3.RELEASE
case1
package com.yourbatman.springstatic.demo02;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
class AppConfig {
AppConfig() {
System.out.println("AppConfig init...");
}
@Bean
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor mypostProcessor() {
return new MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor();
}
@Bean
Son son() {
return new Son();
}
@Bean
Parent parent() {
return new Parent(son());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
System.out.println(context.getBean("appConfig").getClass());
}
}
class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor() {
System.out.println("MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor init...");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
}
}
class Parent {
private Son son;
public Parent(Son son) {
this.son = son;
System.out.println("Parent init...");
}
public Son getSon() {
return son;
}
}
class Son {
public Son() {
System.out.println("son init...hashCode() =" + this.hashCode());
}
}
运行输出:
AppConfig init...
MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor init...
7月 20, 2021 1:49:38 下午 org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor enhanceConfigurationClasses
信息: Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition 'appConfig' since its singleton instance has been created too early. The typical cause is a non-static @Bean method with a BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor return type: Consider declaring such methods as 'static'.
son init...hashCode() =375457936
son init...hashCode() =1063980005
Parent init...
class com.yourbatman.springstatic.demo02.AppConfig
这个问题很严重
- AppConfig竟然比MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的初始化时机还早,这本就不合理
- 从
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的日志中可看到:AppConfig配置类enhance增强失败 - Son对象竟然被创建了两个不同的实例,这将会直接导致功能性错误
分析
问题是怎么引起的?我们通过设置断点来找到出错的原因
在AbstratcApplicationContext#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors处设置断点,调试运行 注意beanDefinitionMap中第一个bean定义很重要:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor:这是个非常关键的类,基本上我们自定义的bean都是通过这个类注册的,下面这些注解都是在这个类中处理的
注意beanDefinitionMap中第一个bean定义很重要:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor:这是个非常关键的类,基本上我们自定义的bean都是通过这个类注册的,下面这些注解都是在这个类中处理的
@Configuration
@Component
@PropertySource
@PropertySources
@ComponentScan
@ComponentScans
@Import
@ImportResource
@Bean
F7断点进入invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors,运行至PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors,源码如下:
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
//DefaultListableBeanFactory这个类实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry,这个判断是会进
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
//用一个变量存起来
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
//创建一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor的集合
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//创建一个BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的集合
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//这个时候beanFactoryPostProcessors的集合为空
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
//创建一个BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的集合,表示当前的要执行的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
//从BeanFactory的BeanDefinitionMap中取出实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的类型的键名,
//这个时候只能取出一个,就是ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
//判断是否实现了PriorityOrdered接口,这个时候取出来的是ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
//添加到currentRegistryProcessors集合中去
//getBean的含义:如果容器中这个对象已经创建好了,直接取,如果容器中这个对象没有创建好,那我们就new
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
//存入对应的名字
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
//对BeanDefinition进行排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
//添加到registryProcessors
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
//执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的接口的实现类ConfigurationPostProcessor中的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
//清空当前要执行的集合
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
//再次查找实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的类名
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
//查询出来的如果上次没有执行过同事也是实现Ordered接口的实现类,会进入这个判断
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
//同时添加到当前要执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的集合
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
//同时添加到对应的集合,可以简单说就是执行过的
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
//进行排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
//添加到总的
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
//执行接口中实现类的指定的方法
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
//清除当前的集合
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
//再次查找
boolean reiterate = true;
//这个死循环就能保证所有实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的接口类都会执行
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
//查找实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的实现类
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
//执行所有所有实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
//执行所有所有实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法,这个默认是为空的,
//只有通过调用addBeanFactoryPostProcessor()的BeanFactoryPostProcessor才会在这执行。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
//获取对应实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
// 实现PriorityOrdered和BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类,最先执行
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 实现Ordered和BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类,次之执行
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
// 实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类,最后执行
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
//已经执行过的
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
// 对实现PriorityOrdered和BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类进行排序
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 执行接口的实现方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
// 对实现Ordered和BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类进行排序
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 执行接口对应的方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
// 只实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor的接口的类存入下面的集合。
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
// 执行接口对应的方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
代码1
-
运行到
46行:currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));通过getBean方法得到ConfigurationClassPostProcessor实例,此时查看一级缓存,多了一个ConfigurationClassPostProcessor实例
 2. 运行至
2. 运行至56行:invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);执行ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法,此方法定义配置类中涉及到的BeanDefinition,前面已介绍过了,完了以后,多出三个BeanDefinition(在我们这个例子中是:son,parent,mypostProcessor,注意mypostProcessor的类型是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor)

我们这个例子中没有涉及到实现Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, -
继续运行至
91行,注意我们刚才通过配置类新注册一个BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor名字叫mypostProcessor,通过currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)),我们想创建一个mypostProcessor实例,注意getBean方法,这是BeanFactory非常重要的一个方法,通过他创建Bean的实例,并加入缓存(当然只有单例bean才有缓存), -
但是注意我们这个mypostProcessor的bean定义中的一部分如下:

这意味着mypostProcessor的实例是通过实例工厂方法来创建的,要调用的工厂方法是mypostProcessor方法,工厂对象是appConfig实例,看出问题了吗?我们要调用工厂方法mypostProcessor,必须先有appConfig实例,这是java的基础知识,实例方法必须通过对象的实例来调用,但问题来了:我们的appConfig增强了吗?没有! 对配置类增强在哪执行?如果你理解了A哥以前的文章就知道答案了:在ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#postProcessBeanFactory方法中,就是代码1的
104行,我们现在还没执行到呀! -
我们断点运行到ConstructorResolver#instantiateUsingFactoryMethod,查看代码如下:
 因为factoryBeanName为"appConfig",执行factoryBean = this.beanFactory.getBean(factoryBeanName);获得一个没有增强的appConfig实例
因为factoryBeanName为"appConfig",执行factoryBean = this.beanFactory.getBean(factoryBeanName);获得一个没有增强的appConfig实例
,这个实例将放入容器的缓存,我们要用这个实例都是先从缓存获取这个没有增强的实例,appConfig中的@Bean方法都不会被拦截,这就是我们这个案例出错的根源 -
我们继续单点跟踪到代码1的
104行,我们知道在这对appConfig的class进行增强,但晚了,appConfig的实例已经在没有增强的情况下已经创建了,这地方只是修改了AppConfig类的beanClass而已if (ConfigurationClassUtils.CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL.equals(configClassAttr)) { if (!(beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition)) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition '" + beanName + "' since it is not stored in an AbstractBeanDefinition subclass"); } else if (logger.isInfoEnabled() && beanFactory.containsSingleton(beanName)) { logger.info("Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition '" + beanName + "' since its singleton instance has been created too early. The typical cause " + "is a non-static @Bean method with a BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor " + "return type: Consider declaring such methods as 'static'."); } configBeanDefs.put(beanName, (AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef); }beanFactory.containsSingleton(beanName)为true,容器中已包含"appConfig"实例了,打印运行时的警告信息.appConfig的beanClass被修改了
总结:
造成增强失效的原因:appConfig配置类装配了一个@Bean方法,返回的类型是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,这个BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型bean必须先初始化,而且是通过实例工厂方法来创建实例,实例方法必须通过实例来调用,所有先实例化配置类,但这时postProcessBeanFactory对appConfig增强的代码还没执行,所以实例化了一个没增强的配置类bean,这就是著名的"过早初始化"问题
解决
所有的问题都因实例方法必须通过实例对象来调用,有没有不需要对象实例就可以调用的方法,有呀!静态方法呀,ok,
@Bean
static BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor() {
return new MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor();
}
注意给mypostProcessor方法添加一个static,注意我们这个mypostProcessor的bean定义中的一部分如下:
和以前的比较看出玄机了吗?对,factoryBeanName为空,mypostProcessor为静态方法不需要appConfig的实例,通过类名就可以调用
 factoryBeanName!=null为false,factoryBean=this.beanFactory.getBean(factoryBeanName)不会被调用,所以appConfig不会提前初始化
factoryBeanName!=null为false,factoryBean=this.beanFactory.getBean(factoryBeanName)不会被调用,所以appConfig不会提前初始化
运行的结果:
MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor init...
AppConfig init...
son init...hashCode() =890545344
Parent init...
class com.yourbatman.springstatic.demo02.AppConfig$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$70b3eb50
完美!
修改mypostProcessor方法的返回类型为:BeanFactoryPostProcessor,去掉static,注意BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子接口,这样写是没问题的!
@Bean
BeanFactoryPostProcessor mypostProcessor() {
return new MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor();
}
运行的结果:
AppConfig init...
7月 20, 2021 5:34:34 下午 org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassEnhancer$BeanMethodInterceptor intercept
信息: @Bean method AppConfig.postProcessor is non-static and returns an object assignable to Spring's BeanFactoryPostProcessor interface. This will result in a failure to process annotations such as @Autowired, @Resource and @PostConstruct within the method's declaring @Configuration class. Add the 'static' modifier to this method to avoid these container lifecycle issues; see @Bean javadoc for complete details.
MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor init...
son init...hashCode() =1337192014
Parent init...
class com.yourbatman.springstatic.demo02.AppConfig$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$c49386d
appConfig增强没问题,son()只执行一次,保持单例没问题,AppConfig和MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor实例化的顺序有问题,警告信息说
@Autowired, @Resource , @PostConstruct可能会有问题,哎,“按下了葫芦,起了瓢”,没办法继续挖源码
case2
package com.yourbatman.springstatic.demo03;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
@Configuration
class AppConfig {
@Autowired
private Parent parent;
AppConfig() {
System.out.println("AppConfig init...");
}
@PostConstruct
public void mypostProcessor(){
System.out.println("postconstruct:"+parent);
}
@Bean
BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor() {
return new MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor();
}
@Bean
Son son() {
return new Son();
}
@Bean
Parent parent() {
return new Parent(son());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
System.out.println(context.getBean("appConfig").getClass());
}
}
class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor() {
System.out.println("MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor init...");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
}
}
class Parent {
private Son son;
public Parent(Son son) {
this.son = son;
System.out.println("Parent init...");
}
public Son getSon() {
return son;
}
}
class Son {
public Son() {
System.out.println("son init...hashCode() =" + this.hashCode());
}
}
运行的结果:
AppConfig init...
7月 21, 2021 10:01:07 上午 org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassEnhancer$BeanMethodInterceptor intercept
信息: @Bean method AppConfig.postProcessor is non-static and returns an object assignable to Spring's BeanFactoryPostProcessor interface. This will result in a failure to process annotations such as @Autowired, @Resource and @PostConstruct within the method's declaring @Configuration class. Add the 'static' modifier to this method to avoid these container lifecycle issues; see @Bean javadoc for complete details.
MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor init...
son init...hashCode() =637241618
Parent init...
class com.yourbatman.springstatic.demo02.AppConfig$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$907b6793
出现的问题:
- AppConfig提前于
MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor初始化 @Autowired/@PostConstruct等注解没有生效,这个问题很大
分析
-
代码1运行完
104行后,注意appConfig类已被增强了 -
运行至
165行,执行nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));来初始化mypostProcessor这个bean,同样问题,是通过实例工厂方法来创建mypostProcessor这个bean,实例方法必须通过实例来调用,所有先实例化配置类,但是问题来了,bean的@Autowired需要AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,@Resource和@PostConstruct需要CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,这两个bean是BeanPostProcessor,BeanPostProcessor初始化在refresh方法中的registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)处执行,在invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法后执行,初始化的appConfig的时候这两个bean还没有呢!所以初始化的appConfig中
@Autowired/@PostConstruct等注解没有生效,但appConfig类已被增强 -
通过mypostProcessor()这个实例工厂方法来初始化mypostProcessor这个bean时,将被appConfig增强对象拦截,代码将运行到ConfigurationClassEnhancer.BeanMethodInterceptor中的intercept方法,其中有段代码如下
if (isCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod(beanMethod)) { // The factory is calling the bean method in order to instantiate and register the bean // (i.e. via a getBean() call) -> invoke the super implementation of the method to actually // create the bean instance. if (logger.isInfoEnabled() && BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanMethod.getReturnType())) { logger.info(String.format("@Bean method %s.%s is non-static and returns an object " + "assignable to Spring's BeanFactoryPostProcessor interface. This will " + "result in a failure to process annotations such as @Autowired, " + "@Resource and @PostConstruct within the method's declaring " + "@Configuration class. Add the 'static' modifier to this method to avoid " + "these container lifecycle issues; see @Bean javadoc for complete details.", beanMethod.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName(), beanMethod.getName())); } return cglibMethodProxy.invokeSuper(enhancedConfigInstance, beanMethodArgs); }在执行mypostProcessor方法时,BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanMethod.getReturnType())返回true,打印警告信息
总结
造成这种现象的原因同样是因为appConfig这个配置类"过早的初始化了"
解决
同样给mypostProcessor方法添加static,让mypostProcessor这个bean在不需要appConfig实例的情况下先初始化,而且mypostProcessor()方法是静态的,appConfig增强对象是无法拦截的,intercept方法不会执行,已就不会打印警告信息了
运行结果
MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor init...
AppConfig init...
son init...hashCode() =1030684756
Parent init...
postconstruct:com.yourbatman.springstatic.demo02.Parent@2fb3536e
class com.yourbatman.springstatic.demo02.AppConfig$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$907b6793
完美!
case3
package com.yourbatman.springstatic.demo01;
import lombok.Getter;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
class AppConfig {
AppConfig() {
System.out.println("AppConfig init...");
}
@Bean
Parent parent() {
return new Parent(son());
}
@Bean
Son son() {
return new Son();
}
@Bean
BeanPostProcessor mypostProcessor() {
return new MyBeanPostProcessor();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
}
}
class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
MyBeanPostProcessor() {
System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor init...");
}
}
@Getter
class Parent {
private Son son;
public Parent(Son son) {
this.son = son;
System.out.println("Parent init...");
}
}
class Son {
public Son() {
System.out.println("son init...hashCode() =" + this.hashCode());
}
}
运行的结果:
AppConfig init...
7月 21, 2021 3:47:57 下午 org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate$BeanPostProcessorChecker postProcessAfterInitialization
信息: Bean 'appConfig' of type [com.yourbatman.springstatic.demo01.AppConfig$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$40f6678d] is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors (for example: not eligible for auto-proxying)
MyBeanPostProcessor init...
son init...hashCode() =1594138273
Parent init...
AppConfig和BeanPostProcessor实例化的顺序有问题,信息是什么意思?
分析
-
断点进入AbstractBeanContext#refresh的registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)方法,这个方法是干什么的?顾名思义,是初始化BeanPostProcessor的,在registerBeanPostProcessors方法前面的是invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法,已将我们AppConfig中的mypostProcessor这个Bean的beanDefinition注册进容器中去了,但mypostProcessor还没有初始化
-
进入PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#registerBeanPostProcessors方法,主要代码如下:
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) { String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when // a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when // a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors. int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length; beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount)); // Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, // Ordered, and the rest. List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } // First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); // Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered. List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size()); for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); orderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); // Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors. List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size()); for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors); // Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors. sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors); // Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners, // moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc). beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext)); } 代码2
String[] postProcessorNames保存的是即将要初始化的BeanPostProcessor的名称,在我们这个例子个数是"3",如下:
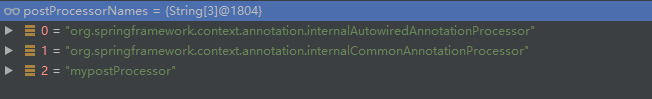
注意有mypostProcessor这个BeanPostProcessor
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount()是已有的BeanPostProcessor数量,在这个例子中是3,+1就是为了后面加入的BeanPostProcessorChecker准备的,beanProcessorTargetCount为目标BeanPostProcessor的数量,在这是7
-
下面的代码是对BeanPostProcessor的分类,当执行到
53行BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);时,当ppName="mypostProcessor"时,同样问题,是通过实例工厂方法来创建mypostProcessor这个bean,实例方法必须通过实例来调用,所有先实例化配置类appConfig -
在先初始化appConfig的过程中,当代码运行至AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean方法中的exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd)这句代码时,在initializeBean方法中有这么一句
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);这句是什么意思?对我的appConfig对象应用所有的BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法
-
进入applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName); if (current == null) { return result; } result = current; } return result; }在for循环中当BeanPostProcessor是前面注册的BeanPostProcessorChecker时,进入BeanPostProcessorChecker的postProcessAfterInitialization方法,代码如下:
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) { if (!(bean instanceof BeanPostProcessor) && !isInfrastructureBean(beanName) && this.beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() < this.beanPostProcessorTargetCount) { if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Bean '" + beanName + "' of type [" + bean.getClass().getName() + "] is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors " + "(for example: not eligible for auto-proxying)"); } } return bean; }注意此时this.beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount()是6,beanPostProcessorTargetCount是7,为什么少一个?**我们的mypostProcessor还没有初始化呀!**所有打印运行时的警告信息,在这里意味我们的appConfig这个bean无法应用于mypostProcessor这个BeanPostProcessor,当然在我们这个例子里,我这个MyBeanPostProcessor什么已没做
总结
造成这种现象的原因同样是因为appConfig这个配置类"过早的初始化了"
解决
不用说了,加static
运行结果:
MyBeanPostProcessor init...
AppConfig init...
son init...hashCode() =363509958
Parent init...
case4
在以前的一个案例中,MapperScannerConfigurer导致properties文件中的参数无法正常解析,我把具体的代码贴出来
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@ComponentScan("demo03.service")
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:database.properties", encoding = "UTF-8")
public class JavaConfig {
@Value(value = "${database.driverClassName}")
private String driverClassName;
@Value(value = "${database.url}")
private String url;
@Value(value = "${database.username}")
private String username;
@Value(value = "${database.password}")
private String password;
@Value(value = "${database.initialSize}")
private String initialSize;
@Value(value = "${database.maxTotal}")
private String maxTotal;
@Value(value = "${database.maxIdle}")
private String maxIdle;
@Value(value = "${database.minIdle}")
private String minIdle;
//定义数据源
@Bean("dataSource")
public BasicDataSource initBasicDataSource() throws Exception {
BasicDataSource dataSource = null;
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.setProperty("driverClassName", driverClassName);
prop.setProperty("url", url);
prop.setProperty("username", username);
prop.setProperty("password", password);
prop.setProperty("initialSize", initialSize);
prop.setProperty("maxTotal", maxTotal);
prop.setProperty("maxIdle", maxIdle);
prop.setProperty("minIdle", minIdle);
dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
return dataSource;
}
//配置SqlSessionFactoryBean
@Bean("sqlSessionFactory")
@Autowired
public SqlSessionFactoryBean initSqlSessionFactoryBean(BasicDataSource dataSource) {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setConfigLocation(new ClassPathResource("mybatis-config.xml"));
return sqlSessionFactoryBean;
}
//配置事务管理器
@Bean
@Autowired
public DataSourceTransactionManager initDataSourceTransactionManager(BasicDataSource dataSource) {
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
//扫描dao包,生成dao接口的代理对象
@Bean
public
MapperScannerConfigurer initMapperScannerConfigurer() {
MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer = new MapperScannerConfigurer();
mapperScannerConfigurer.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName("sqlSessionFactory");
mapperScannerConfigurer.setBasePackage("demo03.dao");
return mapperScannerConfigurer;
}
}
database.properties文件
database.driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
database.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/smbms?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
database.username=root
database.password=1234
#初始化连接:连接池启动时创建的初始化连接数量
database.initialSize=3
#连接池在同一时间能够分配的最大活动连接的数量, 如果设置为非正数则表示不限制
database.maxTotal=8
#连接池中容许保持空闲状态的最大连接数量,超过的空闲连接将被释放,如果设置为负数表示不限制
database.maxIdle=5
#连接池中容许保持空闲状态的最小连接数量,低于这个数量将创建新的连接,如果设置为0则不创建
database.minIdle=3
什么service、dao、mybatis设置等等我都省略了,大家都知道是怎么回事
运行出现异常
50:16.470 [main] INFO o.s.c.a.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor - Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition 'javaConfig' since its singleton instance has been created too early. The typical cause is a non-static @Bean method with a BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor return type: Consider declaring such methods as 'static'.
。。。。。。
。。。。。。
.NullPointerException
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$AutowiredMethodElement
。。。。。。。
大家看到了什么?“Cannot enhance @Configuration…”,什么不是很熟悉,实际上结合case1和case2你就立即明白了.
首先我们看下MapperScannerConfigurer initMapperScannerConfigurer()中的MapperScannerConfigurer 是个什么东东?注意他是一个BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,是不是和case1一样,造成JavaConfig这个配置类在AbstractApplicationContext#refresh#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors中提前初始化,但注意JavaConfig中的@Value注解是需要AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor这个BeanPostProcessor,它在AbstractApplicationContext#refresh#registerBeanPostProcessors中初始化的,registerBeanPostProcessors是在invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors后执行的,所以JavaConfig中的@Value注解是无效的,那么driverClassName等属性是null值,造成在创建"dataSource"时空指针异常