聊聊Spring事件及其应用
在 JDK 中已经提供相应的自定义事件发布功能的基础类:
java.util.EventObject类 :自定义事件类型java.util.EventListener接口:事件的监听器
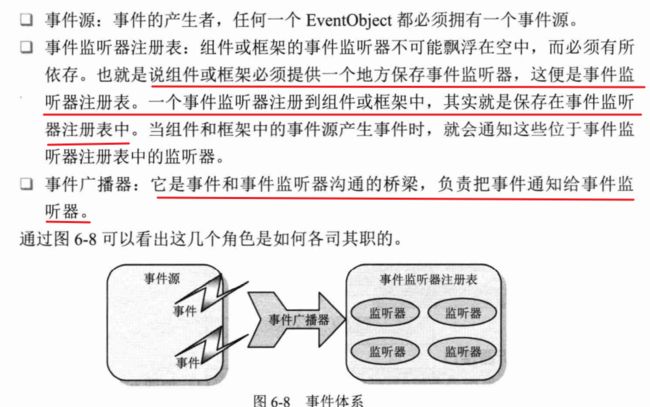
首先了解几个概念:
Spring 事件类结构
1. 事件类
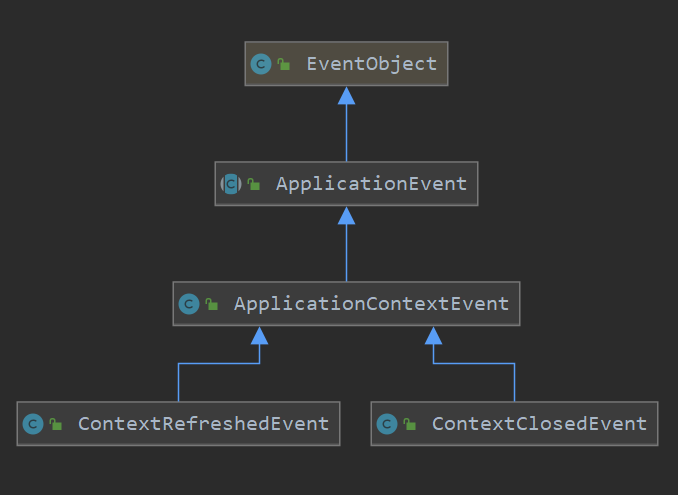
事件类也就是定义发送的内容,比如可以通过继承ApplicationContextEvent来自定义一个特定事件类。
1.1 ApplicationEvent类
首先是继承 EventObject的ApplicationEvent,通过source来指定事件源:
public abstract class ApplicationEvent extends EventObject {
/**
* Constructs a prototypical Event.
*
* @param source The object on which the Event initially occurred.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if source is null.
*/
public ApplicationEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
}
1.2 ApplicationContextEvent类
是主要的容器事件,它有容器启动、刷新、停止以及关闭各种事件的子类。
public class ApplicationContextEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
/**
* Constructs a prototypical Event.
*
* @param source The object on which the Event initially occurred.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if source is null.
*/
public ApplicationContextEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
/**
* Get the ApplicationContext that the event was raised for.
*/
public final ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return (ApplicationContext) getSource();
}
}
public class ContextClosedEvent extends ApplicationContextEvent{
/**
* Constructs a prototypical Event.
*
* @param source The object on which the Event initially occurred.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if source is null.
*/
public ContextClosedEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
}
public class ContextRefreshedEvent extends ApplicationContextEvent{
/**
* Constructs a prototypical Event.
*
* @param source The object on which the Event initially occurred.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if source is null.
*/
public ContextRefreshedEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
}
我们可以通过继承该类来实现,特定的事件类型需求,比如要实现一个邮件发送事件。只需要继承ApplicationContextEvent即可:
public class MailSendEvent extends ApplicationContextEvent {
private String msg;
public MailSendEvent(Object source, String msg) {
super(source);
this.msg = msg;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
}
同时ApplicationContextEvent也有特定的几个子类,来表示容器启动、刷新、停止以及关闭事件:
2.事件监听器
事件监听器接口中,只定义了一个方法:onApplicationEvent(E event)该方法接收ApplicationEvent事件对象,在该方法中编写事件的响应处理逻辑。
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener {
/**
* 接收ApplicationEvent 事件对象
* 在该方法中编写事件的响应处理逻辑
* @param event
*/
void onApplicationEvent(E event);
}
我们同样也可以实现该接口来实现特定的事件监听器功能,比如邮件发送的监听器:
public class MailSenderListener implements ApplicationListener<MailSendEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MailSendEvent event) {
System.out.println("邮件发送器的 resource:" + event.getSource() + "邮件发送器的 msg:" + event.getMsg());
}
}
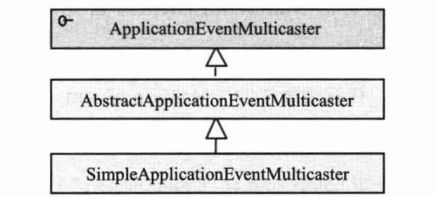
3.事件广播器
事件广播器负责将事件通知监听器注册表中的事件监听器,然后再由事件监听器分别对事件进行响应。Spring中定义了如下接口:
public interface ApplicationEventMulticaster {
/**
* 添加事件监听器
* @param listener
*/
void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener);
/**
* 移除事件监听器
* @param listener
*/
void removeApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener);
/**
* 广播事件
* @param event
*/
void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event);
}
及其简单实现类SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster:
public class SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster extends AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster{
public SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
}
/**unchecked 表示告诉编译器忽略指定的警告,不用再编译完成后出现警告信息*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
for (ApplicationListener applicationListener : getApplicationListeners(event)) {
applicationListener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
}
}
4.事件发布者
它本身作为事件源,会在合适的时点,将相应事件发布给对应的事件监听器:
public interface ApplicationEventPublisher {
/**
* 通知监听者并发布事件
* @param event
*/
void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event);
}
在Spring容器事件中,ApplicationContext接口定义继承了ApplicationEventPublisher接口,所以实际上AbstractApplicationContext在事件中承担了事件发布者的角色。
但是在实际上具体实现事件的发布和事件监听器注册方面,将功能转接给ApplicationEventMulticaster接口,最终具体实现则放在AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster的实现类中:
Spring 事件类的应用
那么在Spring中,事件类到底是如何运行的呢?首先我们会在xml配置文件中配置相应的ApplicationListener类型的监听器,因此在容器启动后,这些类型的bean会被ApplicationContext容器所识别,它们负责监听容器内发布的对应的ApplicationEvent类型的事件。
<bean class="cn.ethan.springframework.test.event.ContextRefreshedEventListener"/>
<bean class="cn.ethan.springframework.test.event.MailSenderListener"/>
<bean class="cn.ethan.springframework.test.event.ContextClosedEventListener"/>
在AbstractApplicationContext的refresh()方法中可以看到自动注册的内容:
public void refresh() throws BeansException {
// 6. 初始化事件发布者
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 7. 注册事件监听器
registerListeners();
// 9. 发布容器刷新完成事件
finishRefresh();
}
private void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, applicationEventMulticaster);
}
private void registerListeners() {
Collection<ApplicationListener> applicationListeners = getBeansOfType(ApplicationListener.class).values();
for (ApplicationListener listener : applicationListeners) {
applicationEventMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
private void finishRefresh() {
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
}
public void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
applicationEventMulticaster.multicastEvent(event);
}
所以在ApplicationContext容器启动时,会自动注册EventListener类型的 Bean,一旦检测到有ApplicationContextEvent类型的事件发布,将通知这些注册到容器的EventListener
应用实例
下面将构建一个发送邮件的Spring事件实例:
1. 邮件发送事件MailSendEvent
public class MailSendEvent extends ApplicationContextEvent {
private String msg;
public MailSendEvent(Object source, String msg) {
super(source);
this.msg = msg;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
}
2.邮件发送事件监听器MailSendListener(邮件发送事件)、ContextRefreshedEventListener(容器刷新事件) 和 ContextClosedEventListener(容器关闭事件)
public class MailSenderListener implements ApplicationListener<MailSendEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MailSendEvent event) {
System.out.println("邮件发送器的 resource:" + event.getSource() + "邮件发送器的 msg:" + event.getMsg());
}
}
public class ContextClosedEventListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextClosedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextClosedEvent event) {
System.out.println("关闭事件:" + this.getClass().getName());
}
}
public class ContextRefreshedEventListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
System.out.println("刷新/打开事件:" + this.getClass().getName());
}
}
这时,将监听器们注入xml文件中:
<bean class="cn.ethan.springframework.test.event.ContextRefreshedEventListener"/>
<bean class="cn.ethan.springframework.test.event.MailSenderListener"/>
<bean class="cn.ethan.springframework.test.event.ContextClosedEventListener"/>
3.邮件发送事件发布者
事件发布者ApplicationEventPublisher,因为前面提到,applicationContext继承了ApplicationEventPublisher,而applicationContext将事件发布功能委托给了ApplicationEventMulticaster,容器在启动开始就会检查是否存在名称为applicationEventMulticaster的 ApplicationEventMulticaster对象实例,如果有就使用提供的实现,没有则默认初始化一个SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster作为将会使用的ApplicationEventMulticaster
/**
* @description: 实现了事件监听器的管理功能
* @author: wjw
* @date: 2022/7/9
*/
public abstract class AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster implements ApplicationEventMulticaster, BeanFactoryAware {
public final Set<ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent>> applicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>();
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
@Override
public void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {
applicationListeners.add((ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent>) listener);
}
@Override
public void removeApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {
applicationListeners.remove(listener);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
/**
* 获得监听器
* @param event
* @return
*/
protected Collection<ApplicationListener> getApplicationListeners(ApplicationEvent event) {
LinkedList<ApplicationListener> allListeners = new LinkedList<>();
for (ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> listener : allListeners) {
if (supportsEvent(listener, event)) {
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
return allListeners;
}
protected boolean supportsEvent(ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> applicationListener, ApplicationEvent event) {
Class<? extends ApplicationListener> listenerClass = applicationListener.getClass();
/**根据不同实例化类型,判断后获取对应目标 class*/
Class<?> targetClass = ClassUtils.isCglibProxyClass(listenerClass) ? listenerClass.getSuperclass() : listenerClass;
Type genericInterface = targetClass.getGenericInterfaces()[0];
Type actualTypeArgument = ((ParameterizedType) genericInterface).getActualTypeArguments()[0];
String className = actualTypeArgument.getTypeName();
Class<?> eventClassName;
try {
eventClassName = Class.forName(className);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new BeansException("wrong event class name: " + className);
}
return eventClassName.isAssignableFrom(event.getClass());
}
}
public class SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster extends AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster{
public SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
}
/**unchecked 表示告诉编译器忽略指定的警告,不用再编译完成后出现警告信息*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
for (ApplicationListener applicationListener : getApplicationListeners(event)) {
applicationListener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
}
}
4.测试验证
public void test_event() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring.xml");
applicationContext.publishEvent(new CustomEvent(applicationContext, 110L, "test!"));
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------------------");
applicationContext.publishEvent(new MailSendEvent(applicationContext, "邮件发送测试"));
applicationContext.registerShutdownHook();
}
刷新/打开事件:cn.ethan.springframework.test.event.ContextRefreshedEventListener$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$2e5c458
-----------------------------------------------------------------
邮件发送器的 resource:cn.ethan.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@5f2050f6邮件发送器的 msg:邮件发送测试
关闭事件:cn.ethan.springframework.test.event.ContextClosedEventListener$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$fbc2c978