D-Bus 详解:从编译到应用
一、简介
D-Bus是一种消息总线系统,是进程间通信 (IPC)的系统。
从体系结构上讲,它分为三层:
- 一个库libdbus,它允许两个应用程序相互连接并交换消息。
- 一个消息总线守护程序的可执行文件dbus-daemon,建立在libdbus之上,多个应用程序可以连接。守护程序可以将消息从一个应用程序路由到零个或多个其他应用程序。
- 基于特定应用程序框架的绑定或包装程序库。例如,libdbus-glib和libdbus-qt。也有Python之类的语言的绑定。这些包装库是大多数人应该使用的API,因为它们简化了D-Bus编程的细节。libdbus旨在作为高级绑定的低级后端。libdbus API的大部分仅对绑定实现有用。(本文不包含该部分)
libdbus仅支持一对一连接,就像原始网络套接字一样。但是不是通过连接发送字节流,而是发送message。消息具有标识消息类型的标头和包含数据有效负载的正文。libdbus还抽象出所使用的数据传输方式(套接字与其他方式),并处理诸如身份验证之类的细节。
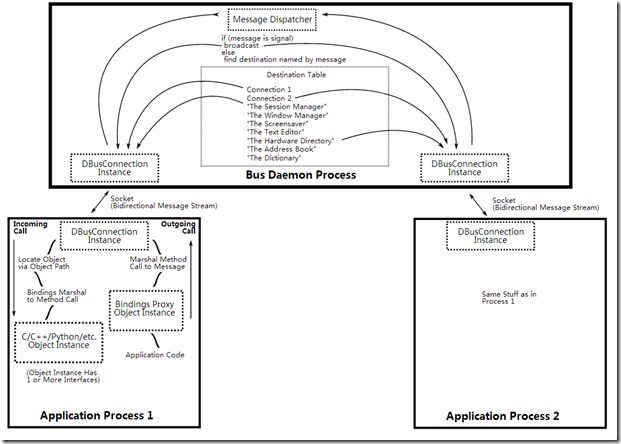
消息总线守护程序构成了一个轮毂。轮毂的每个毂条都是使用libdbus与应用程序的一对一连接。应用程序通过其分支将消息发送到总线守护程序,然后总线守护程序将消息转发到其他已连接的应用程序。可以将守护程序视为路由器。
dbus 低级API实现和D-Bus协议已经进行了数年的严格测试,现在已“定型”。将来的更改将兼容或适当地版本化。
低级libdbus库没有必需的依赖项;总线守护程序唯一需要的依赖项是XML解析器(expat)。特定于特定框架(Qt,GLib,Java,C#,Python等)的更高级别的绑定添加了更多的依赖关系,使用起来更加简单。绑定与底层的libdbus分开发展。对于诸如C#,Java和Ruby之类的语言,D-Bus协议也有一些重新实现,这些不使用libdbus参考实现。
应该注意的是,底层实现并不是主要为应用程序作者设计的。相反,它是约束作者的基础,也是重新实现的参考。如果可以,建议使用更高级别的绑定或实现之一。
D-Bus可以很方便地移植到任何Linux或UNIX版本,并且正在向Windows移植。
二、通信特点
D-BUS是一种低延迟、低开销、高可用性的进程间通信机制。其协议是二进制的,避免序列化的过程,通信效率较高。D-BUS可以提供一些更高层的功能:
- 结构化的名字空间;
- 独立于架构的数据格式;
- 支持消息中的大部分通用数据元素;
- 带有异常处理的通用远程调用接口;
- 支持广播类型的通信。
三、下载
参考实现
dbus(合并了dbus-daemon和libdbus)是D-Bus的参考实现。可以从dbus.freedesktop.org上的发行目录:下载发行的版本,并且在所有主要的Linux发行版中都可用。
http://dbus.freedesktop.org/releases/dbus/
目前的稳定分支是DBUS 1.12.x。这是推荐版本。
目前传统的分支DBUS 1.10.x。仍然提供支持,但仅用于安全修复程序。
较旧的分支(例如1.8.x和1.6.x)已经到期,并且不太可能发布更多版本。
当前的开发分支是 dbus 1.13.x,它将在形成1.14.x稳定分支。开发分支没有安全支持,该版本还包含可能破坏稳定的更改。
完全不支持诸如1.11.x和1.9.x之类的被取代的开发分支,并且以后不会有任何安全修复程序。
绑定和独立实现
绑定和独立的实现从Bindings Page链接到。
绑定包装了libdbus(并因此自动获得了新的身份验证机制和其他对libdbus的添加),而重新实现则从头开始对协议进行编码(从而避免了对libdbus C库的依赖,但必须与新功能保持同步) 。
源代码
在freedesktop.org Gitlab实例上的项目dbus中可获得D-Bus规范的最新版本和参考实现。
https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/dbus/dbus
对于其他实现和绑定,请使用源代码存储库以实现适当的实现。
四、编译
安装cmake
在Ubuntu下直接sudo apt-get install cmake版本较低,。
提示CMake 3.0.2 or higher is required。
官网下载最新版3.17.1,然后解压编译即可
./configure
make
make install
安装expat
下载 expat-2.2.9.tar.gz
官方网站:https://libexpat.github.io/
Linux编译:
./configure --prefix=/home/share/opensource/expat
ARM编译:
./configure --prefix=/home/share/opensource/expat_ql --host=arm-none-linux CC=arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc CXX=arm-none-linux-gnueabi-g++ --enable-shared --enable-static
安装:
make
make install
安装dbus
以dbus-1.12.16版本为例。
下载后解压源代码
tar -zxvf dbus-1.12.16.tar.gz
Linux编译:
./configure --prefix=/home/share/opensource/dbus EXPAT_CFLAGS="-I/home/share/opensource/expat/include" EXPAT_LIBS="-L/home/share/opensource/expat/lib -lexpat"
ARM编译:
./configure --prefix=/home/share/opensource/dbus_ql --host=arm-linux CC=arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc CXX=arm-none-linux-gnueabi-g++ EXPAT_CFLAGS="-I/home/share/opensource/expat_ql/include" EXPAT_LIBS="-L/home/share/opensource/expat_ql/lib -lexpat"
安装:
make
make install
注意:1.8.X版本编译和1.12.16不一致:
Linux:
./configure --prefix=/home/share/opensource/dbus_8_20 \
CFLAGS="-I/home/share/opensource/expat/include" \
LDFLAGS="-L/home/share/opensource/expat/lib -lexpat"
ARM:
./configure --prefix=/home/share/opensource/dbus_ql_8_20 \
--host=arm-linux \
CC=arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc \
CXX=arm-none-linux-gnueabi-g++ --enable-shared --enable-static \
CFLAGS="-I/home/share/opensource/expat_ql/include" \
LDFLAGS="-L/home/share/opensource/expat_ql/lib -lexpat"
生成的bin文件简介
dbus-cleanup-sockets:用于清除目录中的剩余套接字。
dbus-daemon:是D-Bus消息总线守护程序。
dbus-launch:用于从Shell脚本启动dbus-daemon。通常会从用户的登录脚本中调用它。
dbus-monitor:用于监视通过D-Bus消息总线的消息。
dbus-run-session:作为新的D-Bus会话开始一个进程。
dbus-send:用于将消息发送到D-Bus消息总线。
dbus-test-tool:是D-Bus流量生成器和测试工具;它是用于调试和分析D-Bus的多功能工具。
dbus-update-activation-environment:用于更新用于D-Bus会话服务的环境; 在不使用systemd的情况下激活会话服务时,它将更新dbus-daemon --session使用的环境变量列表。
dbus-uuidgen:用于生成通用的唯一ID。
五、API手册
API参考手册,用于参考实现 libdbus:http://dbus.freedesktop.org/doc/api/html/index.html
六、技术实现
D-Bus 本身是构建在 Socket 机制之上。真正的通信还是由 Socket 来完成的。D-Bus 则是在这之上,制定了一些通信的协议,并提供了更高一层的接口,以更方便应用程序之间进行数据的交互。
在D-Bus的体系中,有一个常驻的进程 Daemon,所有进程间的交互都通过它来进行分发和管理。所有希望使用 D-Bus 进行通信的进程,都必须事先连上 Daemon,并将自己的名字注册到 Daemon 上,之后,Daemon会根据需要把消息以及数据发到相应的进程中。
DBUS中主要概念为总线,连接到总线的进程可通过总线接收或传递消息,总线收到消息时,根据不同的消息类型进行不同的处理。DBUS中消息分为四类:
- Method call消息:将触发一个函数调用 ;
- Method return消息:触发函数调用返回的结果;
- Error消息:触发的函数调用返回一个异常 ;
- Signal消息:通知,可以看作为事件消息。
在一台机器上总线守护有多个实例(instance)。这些总线之间都是相互独立的。一个持久的系统总线(system bus)和 很多会话总线(session buses)。
- System Bus:它在引导时就会启动。这个总线由操作系统和后台进程使用,安全性非常好,以使得任意的应用程序不能欺骗系统事件。 它是桌面会话和操作系统的通信,这里操作系统一般而言包括内核和系统守护进程。 这种通道的最常用的方面就是发送系统消息,比如:插入一个新的存储设备;有新的网络连接;等等。
- Session Buses:这些总线当用户登录后启动,属于那个用户私有。它是用户的应用程序用来通信的一个会话总线。 同一个桌面会话中两个桌面应用程序的通信,可使得桌面会话作为整体集成在一起以解决进程生命周期的相关问题。
应用主要包括2方面:函数调用和消息广播
- 函数调用:D-BUS可以实现进程间函数调用,进程A发送函数调用的请求(Method call消息),经过总线转发至进程B。进程B将应答函数返回值(Method return消息)或者错误消息(Error消息)。
- 消息广播:进程间消息广播(Signal消息)不需要响应,接收方需要向总线注册感兴趣的消息类型,当总线接收到“Signal消息”类型的消息时,会将消息转发至希望接收的进程。
1. 基本概念
| A… | is identified by a(n)… | which looks like… | and is chosen by… |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bus | address | unix:path=/var/run/dbus/system_bus_socket |
system configuration |
| Connection | bus name | :34-907 (unique) or com.mycompany.TextEditor (well-known) |
D-Bus (unique) or the owning program (well-known) |
| Object | path | /com/mycompany/TextFileManager |
the owning program |
| Interface | interface name | org.freedesktop.Hal.Manager |
the owning program |
| Member | member name | ListNames |
the owning program |
Address
address是用来标识dbus-daemon的。当一个dbus-daemon运行以后,其他的app该怎么连接到这个dbus-daemon,靠的就是address。
address的格式要求像这样:unix:path=/var/run/dbus/system_bus_socket。
Bus Name
是一个每个应用程序(或是通信对象)用来标识自己。
有两种,一种是“Unique Connection Name”,是以冒号开头的,是全局唯一但人类不友好的命名,一种是“Well-know Name”,人类友好的。
Bus Name 的命名规则是:
- Bus name 就像网址一样,由“.”号分割的多个子字符串组成,每个子字符串都必须至少有一个以上的字符。
- 每个子字符串都只能由“
[A-Z][a-z][0-9]_-”这些 ASCII 字符组成,只有 Unique Name 的子串可以以数字开头。 - 每个 Bus name 至少要有一个“.”和两个子字符串,不能以“.”开头
- Bus name 不能超过 255 个字符
D-Bus Name 是用来给应用程序进行标识自己的,所以每当程序连上 D-Bus Daemon 后,就会分配到一个 Unique Name,同时应用程序还可以要求自己分配另一个 Well-know name (通过 dbus_bus_request_name 函数)。
Interface Name
D-Bus 也有 interface 这个概念,主要是用来为更高一层的框架使用方面而设定的。在 C API 这一层,几乎可以无视这个概念,只需要知道这个一个“字符串”,并在消息匹配是被 D-Bus 使用到,会随着消息在不同的进程之前传递,从进程 A 发送一个消息或是数据到进程 B 时,其中必定会带有一个部分就是这个字符串,至于 B 进程怎么用(或是无视它)都可以。它的命名规则与 D-Bus Name 几乎是一样的,只有一点要注意,interface name 中不能带有“-”字符。
Object Path
D-Bus 中的 object path,与 interface 一样,也只是个概念在更高一层的框架(QT Dbus)中才比较有用,在 C API 这一层,几乎可以无视这个概念,把它当成一个普通的字符串,根据通信的需要,用来做一种标识和区分。Object path 的命名规则是
- object path 可以是任意长度的
- 以’/‘开头,并以以’/'分隔的若干子字符串组成
- 每个子串必须由“[A-Z][a-z][0-9]_”中的字符组成
- 不能有空子串(也就是不能连续两个’/'符)
- 除了“root path”(’/’)之外,不能再有 object path 是以 ‘/’ 结尾的了。
例子:/com/example/MusicPlayer1
Member Name
Member 包含两种类型,一种是 Signal,一种是 Method。
在大多数方面,他们几乎是一样的,除了两点:
- Signal是在总线中进行广播的,而Method是指定发给某个进程的。
- Signal 不会有返回,而 Method 一定会有返回(同步的或是异步的)。
Member name的命名规则是这样的:
- 只能包含“
[A-Z][a-z][0-9]_”这些字符,且不能以数字开头。不能包含“.”。 - 不能超过255个字符
以 C API 的层面来看,Member name最大的作用就是在两个进程间共享“发出的消息的类型信息”。D-Bus 只能以 Signal / Method 来进行消息通信,这两种方式都允许在消息发出之前,在消息中 append 各种类型的数据,当通信的对方收到消息后,它就可以通过 Signal / Method 的名称知道如何把各种数据再解析出来。
2. 通信流程概览
![]()
进程1(Process1)需先连接到总线(dbus_bus_get),其次构造消息(dbus_message_new_signal),然后发送消息(dbus_connection_send)到后台进程。后台进程接收消息,然后根据消息类型对消息进行不同处理(bus_dispatch_matches)。
进程2(Process2)接收消息前需要连接到总线,并告知总线自己希望得到的消息类型(dbus_bus_add_match),然后等待接收消息(dbus_connection_pop_message)。进程2(Process2)收到总线转发的消息时会根据消息类型,做不同的处理(若是信号类型则不需要发送返回值给总线)。
3. 连接到总线
相关接口
typedef enum
{
DBUS_BUS_SESSION, /**< The login session bus */
DBUS_BUS_SYSTEM, /**< The systemwide bus */
DBUS_BUS_STARTER /**< The bus that started us, if any */
} DBusBusType;
DBusConnection *dbus_bus_get (DBusBusType type, DBusError *error) /* 建立和总线的连接 */
int dbus_bus_request_name (DBusConnection *connection,
const char *name,
unsigned int flags,
DBusError *error) /* 注册连接名称 */
void dbus_connection_close (DBusConnection *connection) /* 关闭连接 */
实现示例
首先使用
connection = dbus_bus_get(DBUS_BUS_SESSION, &err);
让应用程序和 D-Bus 之间取得连接。DBUS_BUS_SESSION 表示使用的是Session bus。
之后,使用函数:
ret = dbus_bus_request_name(connection, "hello.world.client",
DBUS_NAME_FLAG_REPLACE_EXISTING, &err);
将自己的进程名字注册到 Daemon 上。DBUS_NAME_FLAG_REPLACE_EXISTING表示使用bus name程序如果已经存在的话,请求替换当前主所有者。
4. 构建数据
相关接口
DBusMessage *dbus_message_new_signal (const char *path,
const char *iface,
const char *name) /* 创建信号类型消息 */
DBusMessage *dbus_message_new_method_call (const char *destination,
const char *path,
const char *iface,
const char *method) /* 创建一个函数调用消息 */
DBusMessage *dbus_message_new_method_return (DBusMessage *method_call) /* 创建返回消息 */
DBusMessage* dbus_message_new_error (DBusMessage *reply_to,
const char *error_name,
const char *error_message);/* 创建Error消息 */
void dbus_message_iter_init_append (DBusMessage *message,
DBusMessageIter *iter) /* 为消息添加参数 */
dbus_bool_t dbus_message_iter_append_basic(DBusMessageIter *iter,
int type,
const void *value);/* 添加具体参数 */
void dbus_message_unref (DBusMessage *message);/* 释放内存 */
实现示例
上文已提到,dbus中包括四种消息。
Method call消息:
msg = dbus_message_new_method_call("hello.world.service",
"/hello/world","hello.world", "add");
dbus_message_iter_init_append(msg, &arg);
dbus_message_iter_append_basic (&arg, DBUS_TYPE_INT32,&a);
dbus_message_iter_append_basic (&arg, DBUS_TYPE_INT32,&b);
Method return消息:
rp = dbus_message_new_method_return(msg);
dbus_message_iter_init_append(rp, &r_arg);
dbus_message_iter_append_basic(&r_arg, DBUS_TYPE_INT32, &sum);
Error消息:
rp = dbus_message_new_error(msg,DBUS_ERROR_FAILED,"test");
根据D-Bus规范中给出的语法,错误名称必须是有效的错误名称。
如果不想编一个错误名,请使用DBUS_ERROR_FAILED “org.freedesktop.DBus.Error.Failed”
Signal消息:
msg = dbus_message_new_signal("/hello", "aa.bb.cc", "alarm_test");
dbus_message_iter_init_append(msg, &arg);
dbus_message_iter_append_basic(&arg, DBUS_TYPE_STRING, &str);
DBusMessage 是 DBus 中的核心数据结构。可以这样理解:DBus中传递消息数据的时候,就是通过它来传递的。对于使用者来说,DBusMessage 中存储了两种重要的信息,一种是为通信机制服务的各种 Name,一种是通信的数据本身。
DBus 提供了一个 DBusMessageIter 的类型,使用这个类型的变量,我们就可以向 DBusMessage 中很容易地加入数据,也可以很容易地从中取出数据。
dbus_message_iter_append_basic函数向 DBusMessageIter 中追加一些“基本类型”(basic)的数据,所谓基本类型的数据,在 DBus 中是这么定义的:
| Conventional Name | Encoding | Alignment |
|---|---|---|
INVALID |
Not applicable; cannot be marshaled. | N/A |
BYTE |
A single 8-bit byte. | 1 |
BOOLEAN |
As for UINT32, but only 0 and 1 are valid values. |
4 |
INT16 |
16-bit signed integer in the message’s byte order. | 2 |
UINT16 |
16-bit unsigned integer in the message’s byte order. | 2 |
INT32 |
32-bit signed integer in the message’s byte order. | 4 |
UINT32 |
32-bit unsigned integer in the message’s byte order. | 4 |
INT64 |
64-bit signed integer in the message’s byte order. | 8 |
UINT64 |
64-bit unsigned integer in the message’s byte order. | 8 |
DOUBLE |
64-bit IEEE 754 double in the message’s byte order. | 8 |
STRING |
A UINT32 indicating the string’s length in bytes excluding its terminating nul, followed by non-nul string data of the given length, followed by a terminating nul byte. |
4 (for the length) |
OBJECT_PATH |
Exactly the same as STRING except the content must be a valid object path (see above). |
4 (for the length) |
SIGNATURE |
The same as STRING except the length is a single byte (thus signatures have a maximum length of 255) and the content must be a valid signature (see above). |
1 |
ARRAY |
A UINT32 giving the length of the array data in bytes, followed by alignment padding to the alignment boundary of the array element type, followed by each array element. |
4 (for the length) |
STRUCT |
A struct must start on an 8-byte boundary regardless of the type of the struct fields. The struct value consists of each field marshaled in sequence starting from that 8-byte alignment boundary. | 8 |
VARIANT |
The marshaled SIGNATURE of a single complete type, followed by a marshaled value with the type given in the signature. |
1 (alignment of the signature) |
DICT_ENTRY |
Identical to STRUCT. | 8 |
UNIX_FD |
32-bit unsigned integer in the message’s byte order. The actual file descriptors need to be transferred out-of-band via some platform specific mechanism. On the wire, values of this type store the index to the file descriptor in the array of file descriptors that accompany the message. | 4 |
结构体消息构建
关于如何便捷传输结构体消息,请参考如下API。
接口:
dbus_bool_t dbus_message_iter_open_container (DBusMessageIter *iter,
int type,
const char *contained_signature,
DBusMessageIter *sub);
dbus_bool_t dbus_message_iter_append_fixed_array (DBusMessageIter *iter,
int element_type,
const void *value,
int n_elements); dbus_bool_t dbus_message_iter_close_container (DBusMessageIter *iter,
DBusMessageIter *sub);
示例:
//将容器类型的值附加到消息。
dbus_message_iter_open_container(&arg,DBUS_TYPE_ARRAY,DBUS_TYPE_BYTE_AS_STRING,&arg_sub);
//将固定长度值块追加到数组。
dbus_message_iter_append_fixed_array(&arg_sub, DBUS_TYPE_BYTE, &req,sizeof(ydsRteRcReq_t));
//关闭附加到消息的容器类型值
dbus_message_iter_close_container(&arg, &arg_sub);
注意:传输数据需要是指针的地址
5. 发送数据
相关接口
dbus_bool_t dbus_connection_send ( DBusConnection *connection,
DBusMessage *message,
dbus_uint32_t *serial) /* 发送消息到总线 */
void dbus_message_unref (DBusMessage *message) /* 释放消息 */
dbus_bool_t dbus_connection_send_with_reply (DBusConnection *connection,
DBusMessage *message,
DBusPendingCall **pending_return,
int timeout_milliseconds) /* 发送消息,等待回复 */
void dbus_connection_flush (DBusConnection *connection); /* 发送消息 */
dbus_connection_flush 这个函数的作用是“Blocks until the outgoing message queue is empty.”,可以简单地理解为调用这个函数可以使用得发送进程一直等消息发送完了才能继续运行。
实现示例
发送Method return/Signa/Error数据
//入队
dbus_connection_send(connection, msg, NULL);
//发送
dbus_connection_flush(connection);
//释放内存
dbus_message_unref(msg);
发送Method call数据,等待回复:
//入队message,等待回复
//param1: 连接描述符
//param2: message
//param3: 相当于一个回调的一个描述符,为了获了返回的消息
//param4: 超时间. -1代表无限
dbus_connection_send_with_reply (connection, msg, &pending, -1);
dbus_connection_flush(connection);
dbus_message_unref(msg);
6. 接收数据
相关接口
void dbus_bus_add_match ( DBusConnection *connection,
const char *rule,
DBusError *error) /* 告知总线感兴趣的消息 */
DBusMessage *dbus_connection_pop_message ( DBusConnection *connection) /* 接收消息 */
void dbus_pending_call_block (DBusPendingCall *pending) /* 阻塞等待返回值 */
DBusMessage *dbus_pending_call_steal_reply (DBusPendingCall *pending) /* 获得返回消息*/
DBusMessage *dbus_connection_pop_message ( DBusConnection *connection) /* 从总线获取消息 */
实现示例
//注册感兴趣的signal
//param1: 连接描述符
//param2: match rule (常用的类型: sender=
// interface=
// type=
// member= )
//param3: err info
//只设置一个type = signal,表示所有信号都接受.也可以加上接口,发送者bus_name
dbus_bus_add_match(connection, "type='signal'", &err);
Signal消息使用dbus_bus_add_match函数向 Daemon 添加匹配信号,让 Daemon 知道自己对这种信号感兴趣。
可以使用下面的函数来进行等待:
//param1: 连接描述符
//param2: 超时时间, -1无限超时时间
dbus_connection_read_write(conn, 0);
//从队列中取出一条消息
msg = dbus_connection_pop_message(conn);
一旦有消息发送过来, 就可以通过 msg 取到相应的数据了。
对Method return消息:
//阻塞,直到接收到一个响应.
dbus_pending_call_block (pending);
//从pending中取出msg
msg = dbus_pending_call_steal_reply (pending);
之后可以进行数据解析。
7. 解析数据
相关接口
dbus_bool_t dbus_message_is_method_call (DBusMessage *message,
const char *iface,
const char *method) /* 判定消息是方法调用 */
dbus_bool_t dbus_message_is_signal (DBusMessage *message,
const char *iface,
const char *signal_name) /* 判断消息是否为信号 */
dbus_bool_t dbus_message_iter_init (DBusMessage *message,
DBusMessageIter *iter) /* 获取参数 */
int dbus_message_iter_get_arg_type (DBusMessageIter *iter);/* 返回参数类型。 */
void dbus_message_iter_get_basic (DBusMessageIter *iter,
void *value);/* 读取基本类型值 */
dbus_bool_t dbus_message_iter_next (DBusMessageIter *iter);/* 下一个参数 */
实现示例
消息判断:
dbus_message_is_signal(msg, "aa.bb.cc", "alarm_test");
dbus_message_is_method_call(msg, "hello.world", "add");
使用dbus_message_is_signal/dbus_message_is_method_call判断消息类型。
消息解析:
if(!dbus_message_iter_init(msg, &arg))
{
printf("no argument!\n");
goto out;
}
if(dbus_message_iter_get_arg_type(&arg) != DBUS_TYPE_INT32)//1
{
printf("argument error\n");
goto out;
}
dbus_message_iter_get_basic(&arg, &a);//2
if(!dbus_message_iter_next(&arg))
{
printf("too few argument!\n");
goto out;
}
dbus_message_iter_get_basic(&arg, &b);
先使用 dbus_messge_iter_init 先把 DBusMessage 对象和从 DBus 总线中取到的 msg 关联起来。
这样,使用1处的函数先取得第一个通信数据中第一个参数的类型,如果类型无误的话可以进而使用2处的函数取得参数值本身。
使用dbus_message_iter_next迭代下一个参数,重复上述步骤。
结构体消息解析
关于如何便捷解析结构体消息,请参考如下API。
接口:
void dbus_message_iter_recurse (DBusMessageIter *iter,
DBusMessageIter *sub);
void dbus_message_iter_get_fixed_array (DBusMessageIter *iter,
void *value,
int *n_elements);
示例:
//从消息读取值时递归到容器值,初始化子迭代器以用于遍历容器的子值。
dbus_message_iter_recurse(&arg, &arg_sub);
//从消息迭代器中读取固定长度值块。
dbus_message_iter_get_fixed_array(&arg_sub,&req,&num);
注意:传输数据需要是指针的地址
七、权限配置文件
D-Bus配置文件 D-Bus消息守护进程的配置文件配置了总线的类型,资源限制,安全参数等。 配置文件的格式并不是标准的一部分,也不保证向后兼容。
标准的系统总线和会话总线在“/etc/dbus-1/system.conf”和“/etc/dbus-1/session.conf”(1.12.16在“/share/dbus-1/system.conf”和“/share/dbus-1/session.conf”)。
上面列出的配置文件可能不应修改。如果需要更改,则应创建/etc/dbus-1/session-local.conf和/或 /etc/dbus-1/system-local.conf对这些文件进行任何所需的更改。
该配置文件的格式就是一个xml文档,且必须有如下类型声明:
根元素
一般为system或session。
在当前位置包含该文件,如果是相对目录,则应为相对于当前配置文件所在目录,有一个选项”ignore_missing=(yes|no)”,默认为yes
在当前位置包含该目录所有的配置文件,目录中文件的包含顺序不定,且只有以”.conf”结尾的文件才会被包含。
daemon运行的用户,可以为用户名或uid,如果守护进程无法切换到该用户就会自动退出,如果有多个配置项,会采用最后一个。
进程成为一个真正的守护进程。
总线监听的地址,地址为包含传输地址加参数/选项的标准D-Bus格式,例如:
<listen>unix:path=/tmp/foolisten>
<listen>tcp:host=localhost,port=1234listen>
指定授权机制。如果不存在,所有已知的机制都被允许。如果有多项配置,则所有列出的机制都被允许。
添加扫描.service文件的目录,Service用于告诉总线如何自动启动一个程序,主要用于每用户的session bus。
设定setuid helper,使用设置的用户启动系统服务的守护进程,一般来说应该是dbus-daemon-launch-helper。 该选项仅用于系统总线。
资源限制一般用于系统总线。 设置资源限制,例如:
<limit name="max_message_size">64limit>
<limit name="max_completed_connections">512limit>
可用的限制名有:
"max_incoming_bytes" : total size in bytes of messages
incoming from a single connection
"max_incoming_unix_fds" : total number of unix fds of messages
incoming from a single connection
"max_outgoing_bytes" : total size in bytes of messages
queued up for a single connection
"max_outgoing_unix_fds" : total number of unix fds of messages
queued up for a single connection
"max_message_size" : max size of a single message in
bytes
"max_message_unix_fds" : max unix fds of a single message
"service_start_timeout" : milliseconds (thousandths) until
a started service has to connect
"auth_timeout" : milliseconds (thousandths) a
connection is given to
authenticate
"max_completed_connections" : max number of authenticated connections
"max_incomplete_connections" : max number of unauthenticated
connections
"max_connections_per_user" : max number of completed connections from
the same user
"max_pending_service_starts" : max number of service launches in
progress at the same time
"max_names_per_connection" : max number of names a single
connection can own
"max_match_rules_per_connection": max number of match rules for a single
connection
"max_replies_per_connection" : max number of pending method
replies per connection
(number of calls-in-progress)
"reply_timeout" : milliseconds (thousandths)
until a method call times out
定义用于一组特定连接的安全策略,策略由和元素组成。 策略一般用于系统总线,模拟防火墙的功能来只允许期望的连接。 当前系统总线的默认策略会阻止发送方法调用和获取总线名字,其他的如消息回复、信号等是默认允许的。
通常来说,最好是保证系统服务尽可能的小,目标程序在自己的进程中运行并且提供一个总线名字来提供服务。 规则使得程序可以设置总线名字,
元素可以有下面四个属性中的一个: context=”(default|mandatory)” at_console=”(true|false)” user=”username or userid” group=”group name or gid”
策略以下面的规则应用到连接:
- 所有 context=”default” 的策略被应用
- 所有 group=”connection’s user’s group” 的策略以不定的顺序被应用
- 所有 user=”connection’s auth user” 的策略以不定顺序被应用
- 所有 at_console=”true” 的策略被应用
- 所有 at_console=”false” 的策略被应用
- 所有 context=”mandatory” 的策略被应用 后应用的策略会覆盖前面的策略。
和出现在元素下面,禁止一些动作,而则创建上面元素的一些例外。 这两个元素可用的属性包括:
send_interface=”interface_name”
send_member=”method_or_signal_name” send_error=”error_name” send_destination=”name” send_type=”method_call” | “method_return” | “signal” | “error” send_path=”/path/name”
receive_interface=”interface_name” receive_member=”method_or_signal_name” receive_error=”error_name” receive_sender=”name” receive_type=”method_call” | “method_return” | “signal” | “error” receive_path=”/path/name”
send_requested_reply=”true” | “false” receive_requested_reply=”true” | “false”
eavesdrop=”true” | “false”
own=”name” own_prefix=”name” user=”username” group=”groupname”
send_destination跟receive_sender是指发送到目的为或者收到来自于该名字的owner,而不是该名字。因此 如果一个连接有三个服务A、B、C,如果拒绝发送到A,那么发送到B和C也不行。 其他的send_*和receive_*则匹配消息头的字段。
在session.conf中:
<busconfig>
<type>sessiontype>
<keep_umask/>
<listen>unix:tmpdir=/tmplisten>
<auth>EXTERNALauth>
<standard_session_servicedirs />
<policy context="default">
<allow send_destination="*" eavesdrop="true"/>
<allow eavesdrop="true"/>
<allow own="*"/>
policy>
<includedir>session.dincludedir>
<include ignore_missing="yes">session-local.confinclude>
<include if_selinux_enabled="yes" selinux_root_relative="yes">contexts/dbus_contextsinclude>
<limit name="max_incoming_bytes">1000000000limit>
<limit name="max_incoming_unix_fds">250000000limit>
<limit name="max_outgoing_bytes">1000000000limit>
<limit name="max_outgoing_unix_fds">250000000limit>
<limit name="max_message_size">1000000000limit>
<limit name="service_start_timeout">120000limit>
<limit name="auth_timeout">240000limit>
<limit name="pending_fd_timeout">150000limit>
<limit name="max_completed_connections">100000limit>
<limit name="max_incomplete_connections">10000limit>
<limit name="max_connections_per_user">100000limit>
<limit name="max_pending_service_starts">10000limit>
<limit name="max_names_per_connection">50000limit>
<limit name="max_match_rules_per_connection">50000limit>
<limit name="max_replies_per_connection">50000limit>
busconfig>
可以看到默认是允许所有消息进行发送的。
在system.conf中:
<busconfig>
<type>systemtype>
<user>messagebususer>
<fork/>
<standard_system_servicedirs/>
<servicehelper>/home/share/opensource/dbus_8_20/libexec/dbus-daemon-launch-helperservicehelper>
<pidfile>/home/share/opensource/dbus_8_20/var/run/dbus/pidpidfile>
<syslog/>
<auth>EXTERNALauth>
<listen>unix:path=/home/share/opensource/dbus_8_20/var/run/dbus/system_bus_socketlisten>
<policy context="default">
<allow user="*"/>
<deny own="*"/>
<deny send_type="method_call"/>
<allow send_type="signal"/>
<allow send_requested_reply="true" send_type="method_return"/>
<allow send_requested_reply="true" send_type="error"/>
<allow receive_type="method_call"/>
<allow receive_type="method_return"/>
<allow receive_type="error"/>
<allow receive_type="signal"/>
<allow send_destination="org.freedesktop.DBus"/>
<deny send_destination="org.freedesktop.DBus"
send_interface="org.freedesktop.DBus"
send_member="UpdateActivationEnvironment"/>
<deny send_destination="org.freedesktop.DBus"
send_interface="org.freedesktop.systemd1.Activator"/>
policy>
<policy user="root">
<allow send_destination="org.freedesktop.DBus"
send_interface="org.freedesktop.systemd1.Activator"/>
policy>
<includedir>system.dincludedir>
<include ignore_missing="yes">system-local.confinclude>
<include if_selinux_enabled="yes" selinux_root_relative="yes">contexts/dbus_contextsinclude>
busconfig>
八、D-Bus会话守护程序
dbus-deamon是一个D-Bus消息总线daemon,运行在后台,它支持两个应用进程间一对一的通信,dbus-deamon也是用libdbus实现的。
系统启动之后,有两个dbus daemon的实例,一个称为system,一个称为session(如果是多个用户,那么会每个用户启动一个),这个实例配置不同,权限也不同。
system 实例使用的配置文件=/etc/dbus-1/system.conf
session实例使用的配置文件=/etc/dbus-1/session.conf
一般来说system daemon,被init script启动,具有root权根,大部分功能用于广播系统事件,比如插拨设备。session daemon用于不同桌面的进程通信或不同进程间的通信。
命令参数
dbus-daemon [--version] [--session] [--system] [--config-file=FILE] [--print-address[=DESCRIPTOR]] [--print-pid[=DESCRIPTOR]] [--introspect] [--address=ADDRESS] [--nopidfile] [--nofork] [--fork] [--systemd-activation]
这些设置选项优先级大于配置文件所配置的
–version:版本
–session:针对每个登录用户,普通用户(普通权限的dbus daemon)
–system:针对系统用户,超级权限(有特权的dbus daemon)
–config-file=FILE:指定dbus daemon相关配置文件位置
–fork:让dbus daemon fork一个进程出来
–nofork:不需要fork
–print-address[=DESCRIPTOR]:打印出dbus daemon监听地址.
–print-pid[=DESCRIPTOR]:打印出dbus daemon pid
–introspect:打印出dbus daemon内部实现的方法
–address:设置监听地址
–nopidfile:不写pid 到文件(配置文件会配置一个文件来记录dbus daemon pid)
–systemd-activation:可能跟systemd启动服务有关
–syslog:强制dbus daemon,用syslog(即会记录log,也会输出到标准输出)
–syslog-only:仅做 syslog
–nosyslog:仅做标准输出
例子
dbus-daemon --session --print-address --nofork --print-pid
开启dbus-daemon session类型,打印出监听地址,打印出pid, 且不做fork
dbus-daemon --session --print-address --fork --print-pid
fork一个进程
dbus-daemon --session --print-address --fork --print-pid --introspect
打印出dbus daemon内部所有的方法
dbus-daemon --session --print-address --fork --print-pid --address=unix:abstract=/tmp/dbus-123456
指定一个监听地址
开机启动
要在系统重新引导时自动启动dbus-daemon,请/etc/rc.d/init.d/dbus从blfs-bootscripts-20200404软件包中安装引导 脚本。(未实践测试,仅记录提供参考,ARM、Linux中已存在dbus-daemon system)
make install-dbus
请注意,此启动脚本仅启动系统范围的 D-Bus守护程序。每个需要访问D-Bus 服务的用户也将需要运行会话守护程序。使用dbus-launch 命令可以使用许多方法来启动会话守护程序 ,如上。
使用dbus-launch指定要运行的程序。(在还使用*–exit-with-session* 参数时)这样做的好处是,当指定的程序停止时,停止会话守护程序。
还可以通过添加以下行来在系统或个人启动脚本中启动会话守护程序:
# Start the D-Bus session daemon
eval `dbus-launch`
export DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS
退出shell时,此方法不会停止会话守护程序,因此应在~/.bash_logout文件中添加以下行:
# Kill the D-Bus session daemon
kill $DBUS_SESSION_BUS_PID
九、应用
完整示例一
与上面实现片段对应的完整代码:
发送方进程
#include 接收方进程
#include 完整示例二
这应该就是使用C API为D-BUS编写一个简单的服务器和客户机所需要的全部。
下面的代码片段来自dbus example.c。
接收信号:dbus-example receive
发送信号:dbus-example send param
监听方法调用:dbus-example listen
调用方法:dbus-example query param
#define DBUS_API_SUBJECT_TO_CHANGE
#include 示例编译
Linux编译
gcc dbus_test.c -o dbus_test -ldbus-1 -lpthread -L/home/share/opensource/dbus/lib -I/home/share/opensource/dbus/include/dbus-1.0
ARM编译
arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc dbus_test.c -o dbus_test -ldbus-1 -lpthread -L/home/share/opensource/dbus_ql/lib -I/home/share/opensource/dbus_ql/include/dbus-1.0
有可能会提示找不dbus-arch-deps.h头文件,在系lib\dbus-1.0\include,然后拷贝到include/dbus-1.0/dbus目录
运行注意事项
需要先将dbus-daemon 运行起来。在ARM中查看进程,如下则已运行,否则需要先启动daemon。
# ps | grep dbus
812 messageb 0:00 /usr/bin/dbus-daemon --system
1210 root 310:00 /usr/bin/dbus-daemon --fork --print-pid 4 --print-address 6 --session
启动dbus-daemon
启动session:
./dbus-daemon --config-file=/etc/dbus-1/session.conf –print-address
设置环境变量DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS,将打印的内容设置成DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS的值就可以了,这样session-bus就可以使用了。
启动system:
./dbus-daemon --config-file=/etc/dbus-1/system.conf --print-address
打印的大致内容是:
unix:path=/var/run/dbus/system_bus_socket,guid=73e31e28f60060659d6ee6005422cb1d
设置环境变量DBUS_SYSTEM_BUS_ADDRESS,需将打印前半部的内容设置成环境变量DBUS_SYSTEM_BUS_ADDRESS=unix:path=/var/run/dbus/system_bus_socket,重启设备或source配置文件一下。
在ARM中运行若提示,则session没有启动,报错:
Using X11 for dbus-daemon autolaunch was disabled at compile time, set your DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS instead
解决方案参考下面链接:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/41242460/how-to-export-dbus-session-bus-address
export $(dbus-launch)
通过dbus-launch程序,会fork一个session回话的daemon,程序即可通过该daemon进行通信。
或者(我是使用的这种)。
eval `dbus-launch --auto-syntax`
要连接到session-bus的程序必须知道DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS的值,因为DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS的值不是唯一的,每次都不一样,每次都要设置DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS的环境变量,虽然可以通过./dbus-launch来启动dbus-daemon,并且dbus-launch自带设置DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS的环境变量的功能,但由于dbus-launch设置的环境变量只在本进程,而且是本次执行中有效。所以一般要通过上述命令来启动dbus-launch,该命令采用eval来执行两次,第一次执行dbus-lauch --auto-syntax,除了启动dbus daemon之外,还输出了下面的内容:
DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS='unix:path=/tmp/dbus-6Z62FMmwf3,guid=5dbd92e4865a3f56880d2120000000d6';
export DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS; DBUS_SESSION_BUS_PID=998;
第二次执行时就将环境变量DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS暴露出去了。之后你就可以启动要连接到session-bus的程序。