【Spring源码】 BeanFactory和FactoryBean是什么?
1、前言
面试官:“看过Spring源码吧,简单说说Spring中BeanFactory和FactoryBean的区别是什么?”
大神仙:“BeanFactory是bean工厂,FactoryBean是工厂bean”。
这么回答,等于面试官问你Spring是什么,你回答这个单词翻译叫春天。
2、ChitGPT的回答
首先看下C知道(ChitGPT)的回答
没错,基本上已经给出了答案。
那么接下来,我们来详细看下他们分别是什么。
3、什么是BeanFactory?
其实BeanFactory回答是bean工厂也没毛病,确实是。但是却没回答到本质。
我们知道,Spring其中一个核心功能就是IoC。Spring创建bean,使用的是经典的工厂模式,那么这一系列的bean工厂,就是IoC容器或称为对象工厂。
我们先来看下Spring源码中对于BeanFactory的注释:
/**
* // 访问Spring bean容器的根接口
* The root interface for accessing a Spring bean container.
*
* ......
*
* // 这个接口是由拥有许多bean定义的对象实现的,每个bean定义都由一个String名称唯一标识。
* // 根据bean定义,工厂将返回包含对象的独立实例(原型设计模式),或者返回单个共享实例(单例设计模式的高级替代方案,在单例设计模式中,
* // 实例在工厂范围内是单例)。将返回哪种类型的实例取决于bean工厂配置。
* This interface is implemented by objects that hold a number of bean definitions,
* each uniquely identified by a String name. Depending on the bean definition,
* the factory will return either an independent instance of a contained object
* (the Prototype design pattern), or a single shared instance (a superior
* alternative to the Singleton design pattern, in which the instance is a
* singleton in the scope of the factory). Which type of instance will be returned
* depends on the bean factory configuration: the API is the same. Since Spring
* 2.0, further scopes are available depending on the concrete application
* context (e.g. "request" and "session" scopes in a web environment).
*
* ......
*
* // 通常,BeanFactory将加载存储在配置源(如XML文档)中的bean定义,并使用{@code org.springframework。Beans}包来配置bean。
* // 但是,实现可以直接在Java代码中返回它根据需要创建的Java对象。对于如何存储定义没有限制:LDAP、RDBMS、XML、属性文件等等。
* // 鼓励实现支持bean之间的引用(依赖注入)。
*
Normally a BeanFactory will load bean definitions stored in a configuration
* source (such as an XML document), and use the {@code org.springframework.beans}
* package to configure the beans. However, an implementation could simply return
* Java objects it creates as necessary directly in Java code. There are no
* constraints on how the definitions could be stored: LDAP, RDBMS, XML,
* properties file, etc. Implementations are encouraged to support references
* amongst beans (Dependency Injection).
*
* ......
* // Bean工厂实现应该尽可能支持标准的Bean生命周期接口。完整的初始化方法集及其标准顺序为:
*
Bean factory implementations should support the standard bean lifecycle interfaces
* as far as possible. The full set of initialization methods and their standard order is:
*
* - BeanNameAware's {@code setBeanName}
*
- BeanClassLoaderAware's {@code setBeanClassLoader}
*
- BeanFactoryAware's {@code setBeanFactory}
*
- EnvironmentAware's {@code setEnvironment}
*
- EmbeddedValueResolverAware's {@code setEmbeddedValueResolver}
*
- ResourceLoaderAware's {@code setResourceLoader}
* (only applicable when running in an application context)
*
- ApplicationEventPublisherAware's {@code setApplicationEventPublisher}
* (only applicable when running in an application context)
*
- MessageSourceAware's {@code setMessageSource}
* (only applicable when running in an application context)
*
- ApplicationContextAware's {@code setApplicationContext}
* (only applicable when running in an application context)
*
- ServletContextAware's {@code setServletContext}
* (only applicable when running in a web application context)
*
- {@code postProcessBeforeInitialization} methods of BeanPostProcessors
*
- InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
*
- a custom {@code init-method} definition
*
- {@code postProcessAfterInitialization} methods of BeanPostProcessors
*
*
* On shutdown of a bean factory, the following lifecycle methods apply:
*
* - {@code postProcessBeforeDestruction} methods of DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors
*
- DisposableBean's {@code destroy}
*
- a custom {@code destroy-method} definition
*
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 13 April 2001
* @see BeanNameAware#setBeanName
* @see BeanClassLoaderAware#setBeanClassLoader
* @see BeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory
* @see org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware#setEnvironment
* @see org.springframework.context.EmbeddedValueResolverAware#setEmbeddedValueResolver
* @see org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware#setResourceLoader
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisherAware#setApplicationEventPublisher
* @see org.springframework.context.MessageSourceAware#setMessageSource
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext
* @see org.springframework.web.context.ServletContextAware#setServletContext
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization
* @see InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition#getInitMethodName
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeDestruction
* @see DisposableBean#destroy
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition#getDestroyMethodName
*/
public interface BeanFactory {
......
}可以看到,BeanFactory是一个接口类,且是最顶层的一个接口类,其中定义了IoC容器的基本功能规范,用来更好的管理(或者说约束)实现类对于bean的管理,如实例化,定位,配置对应以及创建对象间依赖等。
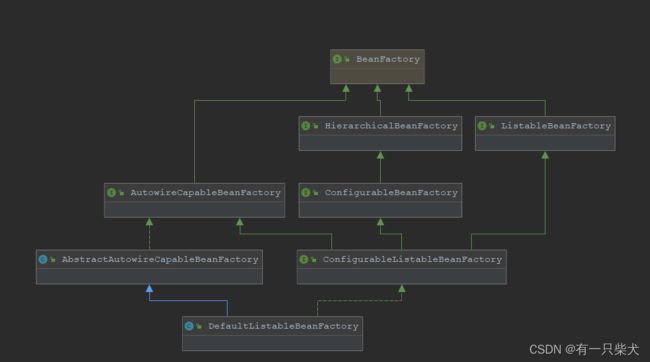
BeanFactory有三个比较重要的接口子类:AutowireCapableBeanFactory,ListableBeanFactory,HierarchicalBeanFactory。BeanFactory有一个默认的实现类是DefaultListableBeanFactory。
在Spring中,DefaultListableBeanFactory被作为一个默认的IoC容器来使用。
来看下类图:
简化一下:
- AutowireCapableBeanFactory:表示Bean的自动装配规则
- ListableBeanFactory:表示Bean可列表化
- HierarchicalBeanFactory:表示Bean有继承关系
这三个接口共同定义了Bean的集合,Bean之间的关系,以及Bean的行为。而BeanFactory是IoC容器最基本的接口类。
再来看下BeanFactory源码内容:
public interface BeanFactory {
// 对FactoryBean的转义定义,因为如果使用bean的名字检索FactoryBean得到的对象是工厂生成的对象,
// 如果需要得到工厂本身,需要转义
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
// 根据bean的名字,获取在IOC容器中得到bean实例
Object getBean(String var1) throws BeansException;
// 根据bean的名字和Class类型来得到bean实例,增加了类型安全验证机制。
T getBean(String var1, Class var2) throws BeansException;
Object getBean(String var1, Object... var2) throws BeansException;
T getBean(Class var1) throws BeansException;
T getBean(Class var1, Object... var2) throws BeansException;
ObjectProvider getBeanProvider(Class var1);
ObjectProvider getBeanProvider(ResolvableType var1);
// 提供对bean的检索,看看是否在IOC容器有这个名字的bean
boolean containsBean(String var1);
// 根据bean名字得到bean实例,并同时判断这个bean是不是单例
boolean isSingleton(String var1) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isPrototype(String var1) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String var1, ResolvableType var2) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String var1, Class var2) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
// 得到bean实例的Class类型
@Nullable
Class getType(String var1) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
// 得到bean的别名,如果根据别名检索,那么其原名也会被检索出来
String[] getAliases(String var1);
}
在BeanFactory中只对IoC容器的基本行为做了定义,通过实现该接口可以实现不同的Bean检索方法。在Spring中也提供了许多IoC容器的实现,如GenericApplicationContext,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext等。
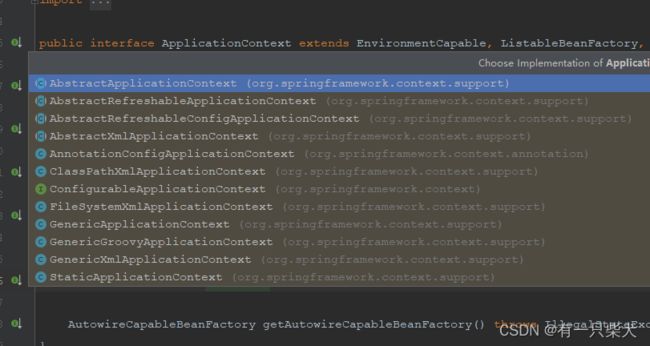
但是在Spring中,是不允许我们直接使用BeanFactory的,他给我们提供了ApplicationContext接口继承BeanFactory接口,同时进行了很多扩展:如实现国际化(实现MessageSource接口),访问资源(实现ResourcePatternResolver接口),支持应用事件(实现ApplicationEventPublisher接口)。
以下为ApplicationContext子类继承图:
4、什么是FactoryBean?
FactoryBean是一个工厂Bean。也是一个接口,该接口提供了一个工厂方法,用来返回其他Bean实例。
来看下注释:
/**
* // 由{@link BeanFactory}中使用的对象实现的接口,这些对象本身就是单个对象的工厂。
* // 如果一个bean实现了这个接口,那么它将被用作要公开的对象的工厂,而不是直接用作将自己公开的bean实例。
* Interface to be implemented by objects used within a {@link BeanFactory} which
* are themselves factories for individual objects. If a bean implements this
* interface, it is used as a factory for an object to expose, not directly as a
* bean instance that will be exposed itself.
*
* // 注意:实现该接口的bean不能作为普通bean使用。
* // FactoryBean是以bean风格定义的,但是为bean引用公开的对象({@link #getObject()})始终是它创建的对象。
* NB: A bean that implements this interface cannot be used as a normal bean.
* A FactoryBean is defined in a bean style, but the object exposed for bean
* references ({@link #getObject()}) is always the object that it creates.
* ......
*
* // 该接口在框架本身中被大量使用,例如用于AOP {@link org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean}。
* // 它也可以用于定制组件;但是,这只在基础结构代码中常见。
*
This interface is heavily used within the framework itself, for example for
* the AOP {@link org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean} or the
* {@link org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean}. It can be used for
* custom components as well; however, this is only common for infrastructure code.
* ......
*
* // 最后,FactoryBean对象参与了包含BeanFactory的bean创建的同步。
* // 除了在FactoryBean本身(或类似)内进行惰性初始化之外,通常不需要内部同步。
*
Finally, FactoryBean objects participate in the containing BeanFactory's
* synchronization of bean creation. There is usually no need for internal
* synchronization other than for purposes of lazy initialization within the
* FactoryBean itself (or the like).
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 08.03.2003
* @param the bean type
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory
* @see org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean
* @see org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean
*/
public interface FactoryBean {
......
}
但从官方给的注释上也能看出,FactoryBean其实就是个Bean,是在IoC容器的基础上给Bean的实现加上了一个简单的工厂模式和装饰模式,是一个用于生产Bean对象的工厂Bean。用户通过实现该接口,可以通过getObject()方法获取对象。
public interface FactoryBean {
// 获取容器管理的对象实例
@Nullable
T getObject() throws Exception;
// 获取Bean工厂创建的对象类型
@Nullable
Class getObjectType();
// Bean工厂创建的对象是否单例模式,
// 如果是,则整个容器中只有一个实例对象,每次请求都返回同一个实例对象
default boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
} 5、小结
BeanFactory:
- 是所有Spring中IoC容器的顶级接口,为Spring的容器定义了一套规范,并提供像getBean()方法从容器中获取Bean实例;
- 负责生产和管理Bean的一个工厂;
- 在产生Bean实例的同时,还提供了DI的能力;
FactoryBean:
- 实际上就是个bean,相当于普通的Bean的实现加上了简单工厂模式和装饰模式;
- 动态生成某一个类别的Bean实例;
- getObject() 获取的是FactoryBean的getObject()返回的对象,而不是FactoryBean本身,如果要获取FactoryBean对象,需要在id前加一个&;