kubeadm,kubevip,containerd部署高可用的kubernetes集群
文章目录
- 环境准备
- 安装 Containerd
- 负载均衡器(kube-vip)
- 初始化控制平面
- 添加control plane node
- 添加work node
- 测试高可用
- Dashboard
- 重新配置前提
单 master 的集群对于生产环境风险太大了,非常有必要做一个高可用的集群,这里的高可用主要是针对 控制面板(master节点)来说的,比如 kube-apiserver、etcd、kube-controller-manager、kube-scheduler 这几个组件,其中 kube-controller-manager 与 kube-scheduler 组件是 Kubernetes 集群自己去实现的高可用( 比如pod本身就可以看成一种高可用方案),当有多个组件存在的时候,会自动选择一个作为 Leader 提供服务,所以不需要我们手动去实现高可用,apiserver 和 etcd 就需要手动去搭建高可用的集群的。高可用的架构有很多,比如典型的 haproxy + keepalived 架构,或者使用 nginx 来做代理实现。
(直接对整个master进行高可用设置)
环境准备
4个节点,都是 Centos 7.6 系统,内核版本:3.10.0-1062.4.1.el7.x86_64,在每个节点上添加 hosts 信息:
vim /etc/hosts
192.168.23.20 api.k8s.local
192.168.23.209 master1
192.168.23.210 master2
192.168.23.211 master3
192.168.23.12 node1
api.k8s.local是vip(192.168.31.10 为 vip,使用域名 api.k8s.local 进行映射。)
节点的 hostname 必须使用标准的 DNS 命名,另外千万不用什么默认的 localhost 的 hostname,会导致各种错误出现的。在 Kubernetes 项目里,机器的名字以及一切存储在 Etcd 中的 API 对象,都必须使用标准的 DNS 命名(RFC 1123)。可以使用命令 hostnamectl set-hostname node1 来修改 hostname。
也就是三个master节点组成的控制面板
紧用防火墙
systemctl disable firewalld
禁用selinux
setenforce 0
sed -ir "/^SELINUX=/c SELINUX=disabled" /etc/selinux/config
由于开启内核 ipv4 转发需要加载 br_netfilter 模块,所以加载下该模块
modprobe br_netfilter
创建/etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf文件,添加如下内容
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
执行如下命令使修改生效
sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
bridge-nf 使得 netfilter 可以对 Linux 网桥上的 IPv4/ARP/IPv6 包过滤。比如,设置net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables=1后,二层的网桥在转发包时也会被 iptables的 FORWARD 规则所过滤。常用的选项包括:
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-arptables:是否在 arptables 的 FORWARD 中过滤网桥的 ARP 包
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables:是否在 ip6tables 链中过滤 IPv6 包
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables:是否在 iptables 链中过滤 IPv4 包
net.bridge.bridge-nf-filter-vlan-tagged:是否在 iptables/arptables 中过滤打了 vlan 标签的包。
安装 ipvs:
cat > /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules <<EOF
#!/bin/bash
modprobe -- ip_vs
modprobe -- ip_vs_rr
modprobe -- ip_vs_wrr
modprobe -- ip_vs_sh
modprobe -- nf_conntrack_ipv4
EOF
chmod 755 /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules && bash /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules && lsmod | grep -e ip_vs -e nf_conntrack_ipv4
上面脚本创建了的/etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules文件,保证在节点重启后能自动加载所需模块。使用lsmod | grep -e ip_vs -e nf_conntrack_ipv4命令查看是否已经正确加载所需的内核模块。
yum install ipset ipvsadm -y
yum install chrony -y
systemctl enable chronyd
systemctl start chronyd
chronyc sources
swapoff -a
sed -ir "/ swap / s/^\(.*\)$/#\1/" /etc/fstab
swappiness 参数调整,修改/etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf添加下面一行:
vm.swappiness=0
执行 sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf 使修改生效
安装 Containerd
各个节点上安装 Containerd。
由于 containerd 需要调用 runc,所以我们也需要先安装 runc,不过 containerd 提供了一个包含相关依赖的压缩包 cri-containerd-cni- V E R S I O N . {VERSION}. VERSION.{OS}-${ARCH}.tar.gz,可以直接使用这个包来进行安装。首先从 release 页面下载相应的版本的压缩包,当前为 1.5.5 版本:
rpm -qa | grep libseccomp
libseccomp-devel-2.3.1-4.el7.x86_64
libseccomp-2.3.1-4.el7.x86_64
rpm -e libseccomp-devel-2.3.1-4.el7.x86_64 --nodeps
rpm -e libseccomp-2.3.1-4.el7.x86_64 --nodeps
#下载高于2.4以上的包
wget http://rpmfind.net/linux/centos/8-stream/BaseOS/x86_64/os/Packages/libseccomp-2.5.1-1.el8.x86_64.rpm
#安装
rpm -ivh libseccomp-2.5.1-1.el8.x86_64.rpm
wget https://github.com/containerd/containerd/releases/download/v1.5.5/cri-containerd-cni-1.5.5-linux-amd64.tar.gz
# 如果有限制,也可以替换成下面的 URL 加速下载
# wget https://download.fastgit.org/containerd/containerd/releases/download/v1.5.5/cri-containerd-cni-1.5.5-linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar -C / -xzf cri-containerd-cni-1.5.5-linux-amd64.tar.gz
将 /usr/local/bin 和 /usr/local/sbin 追加到 ~/.bashrc 文件的 PATH 环境变量中
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin
source ~/.bashrc
containerd 的默认配置文件为 /etc/containerd/config.toml,我们可以通过如下所示的命令生成一个默认的配置:
mkdir -p /etc/containerd
containerd config default > /etc/containerd/config.toml
对于使用 systemd 作为 init system 的 Linux 的发行版,使用 systemd 作为容器的 cgroup driver 可以确保节点在资源紧张的情况更加稳定,所以推荐将 containerd 的 cgroup driver 配置为 systemd。
修改前面生成的配置文件 /etc/containerd/config.toml,在 plugins.“io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri”.containerd.runtimes.runc.options 配置块下面将 SystemdCgroup 设置为 true:
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc]
...
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc.options]
SystemdCgroup = true
....
为镜像仓库配置一个加速器,需要在 cri 配置块下面的 registry 配置块下面进行配置 registry.mirrors:
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri"]
...
# sandbox_image = "k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.5"
sandbox_image = "registry.aliyuncs.com/k8sxio/pause:3.5"
...
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.mirrors]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.mirrors."docker.io"]
endpoint = ["https://??????????.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.mirrors."k8s.gcr.io"]
endpoint = ["https://registry.aliyuncs.com/k8sxio"]
???换上你自己阿里源的镜像加速器的网址
containerd 压缩包中包含一个 etc/systemd/system/containerd.service 的文件,这样我们就可以通过 systemd 来配置 containerd 作为守护进程运行了,现在我们就可以启动 containerd 了,直接执行下面的命令即可:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable containerd --now
可以使用 containerd 的本地 CLI 工具 ctr 和 crictl 了
ctr version
crictl version
上面的操作是包括node节点,全部节点都要做
负载均衡器(kube-vip)
(这一节可以先只在一个master节点比如master1上做)
为 apiserver 提供负载均衡器有很多方法,比如传统的 haproxy+keepalived,或者使用 nginx 代理也可以,这里我们使用一个比较新颖的工具 kube-vip。
kube-vip 可以在你的控制平面节点上提供一个 Kubernetes 原生的 HA 负载均衡,我们不需要再在外部设置 HAProxy 和 Keepalived 来实现集群的高可用了。
在以前我们在私有环境下创建 Kubernetes 集群时,我们需要准备一个硬件/软件的负载均衡器来创建多控制面集群,更多的情况下我们会选择使用 HAProxy + Keepalived 来实现这个功能。一般情况下我们创建2个负载均衡器的虚拟机,然后分配一个 VIP,然后使用 VIP 为负载均衡器提供服务,通过 VIP 将流量重定向到后端的某个 Kubernetes 控制器平面节点上。(High Availability高可用)

使用 kube-vip 的话会怎样
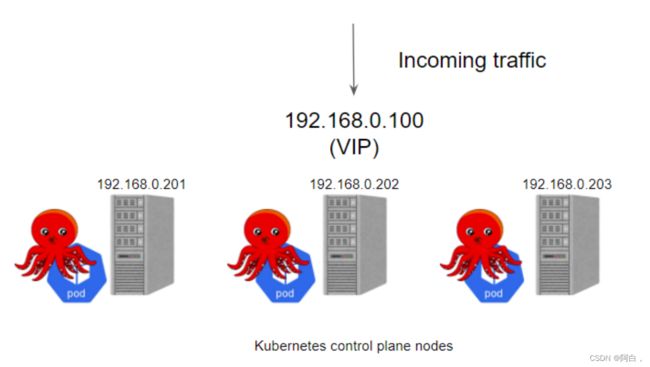
kube-vip 可以通过静态 pod 运行在控制平面节点上,这些 pod 通过 ARP 会话来识别每个节点上的其他主机,我们可以选择 BGP 或 ARP 来设置负载平衡器,这与 Metal LB 比较类似。在 ARP 模式下,会选出一个领导者,这个节点将继承虚拟 IP 并成为集群内负载均衡的 Leader,而在 BGP 模式下,所有节点都会通知 VIP 地址。
集群中的 Leader 将分配 vip,并将其绑定到配置中声明的选定接口上。当 Leader 改变时,它将首先撤销 vip,或者在失败的情况下,vip 将直接由下一个当选的 Leader 分配。当 vip 从一个主机移动到另一个主机时,任何使用 vip 的主机将保留以前的 vip <-> MAC 地址映射,直到 ARP 过期(通常是30秒)并检索到一个新的 vip <-> MAC 映射,这可以通过使用无偿的 ARP 广播来优化。
kube-vip 可以被配置为广播一个无偿的 arp(可选),通常会立即通知所有本地主机 vip <-> MAC 地址映射已经改变。
要使用 kube-vip 来实现集群的高可用,首先在 master1 节点上生成基本的 Kubernetes 静态 Pod 资源清单文件:
mkdir -p /etc/kubernetes/manifests/
# 配置vip地址
export VIP=192.168.23.20
# 设置网卡名称
export INTERFACE=ens33
ctr image pull docker.io/plndr/kube-vip:v0.3.8
# 使用下面的容器输出静态Pod资源清单
ctr run --rm --net-host docker.io/plndr/kube-vip:v0.3.8 vip \
/kube-vip manifest pod \
--interface $INTERFACE \
--vip $VIP \
--controlplane \
--services \
--arp \
--leaderElection | tee /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-vip.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
name: kube-vip
namespace: kube-system
spec:
containers:
- args:
- manager
env:
- name: vip_arp
value: "true"
- name: vip_interface
value: ens33
- name: port
value: "6443"
- name: vip_cidr
value: "32"
- name: cp_enable
value: "true"
- name: cp_namespace
value: kube-system
- name: vip_ddns
value: "false"
- name: svc_enable
value: "true"
- name: vip_leaderelection
value: "true"
- name: vip_leaseduration
value: "5"
- name: vip_renewdeadline
value: "3"
- name: vip_retryperiod
value: "1"
- name: vip_address
value: 192.168.23.20
image: ghcr.io/kube-vip/kube-vip:v0.3.8
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: kube-vip
resources: {}
securityContext:
capabilities:
add:
- NET_ADMIN
- NET_RAW
- SYS_TIME
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
name: kubeconfig
hostNetwork: true
volumes:
- hostPath:
path: /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
name: kubeconfig
status: {}
这里我们将 vip 设置为 192.168.23.20,首先会将 master1 节点选举为 Leader,然后接下来我们使用该 vip 来初始化控制器平台。
初始化控制平面
上面的相关环境配置也完成了,现在我们就可以来安装 Kubeadm 了,我们这里是通过指定 yum 源的方式来进行安装的:
cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg
https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
上面的 yum 源是需要科学上网的,如果不能科学上网的话,我们可以使用阿里云的源进行安装:
cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
repo_gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg
http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
# --disableexcludes 禁掉除了kubernetes之外的别的仓库
yum makecache fast
yum install -y kubelet-1.22.1 kubeadm-1.22.1 kubectl-1.22.1 --disableexcludes=kubernetes
kubeadm version
systemctl enable --now kubelet
"初始化控制平面"这一届到这里是所有节点都要做的
当我们执行 kubelet --help 命令的时候可以看到原来大部分命令行参数都被 DEPRECATED了,这是因为官方推荐我们使用 --config 来指定配置文件,在配置文件中指定原来这些参数的配置,可以通过官方文档 Set Kubelet parameters via a config file 了解更多相关信息,这样 Kubernetes 就可以支持动态 Kubelet 配置(Dynamic Kubelet Configuration)了,参考 Reconfigure a Node’s Kubelet in a Live Cluster。
master1 节点上输出集群初始化默认使用的配置
kubeadm config print init-defaults --component-configs KubeletConfiguration > kubeadm.yaml
然后根据我们自己的需求修改配置,比如修改 imageRepository 指定集群初始化时拉取 Kubernetes 所需镜像的地址,kube-proxy 的模式为 ipvs,另外需要注意的是我们这里是准备安装 flannel 网络插件的,需要将 networking.podSubnet 设置为10.244.0.0/16:
# kubeadm.yaml
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3
bootstrapTokens:
- groups:
- system:bootstrappers:kubeadm:default-node-token
token: abcdef.0123456789abcdef
ttl: 24h0m0s
usages:
- signing
- authentication
kind: InitConfiguration
localAPIEndpoint:
advertiseAddress: 192.168.23.209 # 指定当前节点内网IP
bindPort: 6443
nodeRegistration:
criSocket: /run/containerd/containerd.sock # 使用 containerd的Unix socket 地址
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: master1 #注意节点名称
taints: # 给master添加污点,master节点不能调度应用
- effect: "NoSchedule"
key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/master"
---
apiVersion: kubeproxy.config.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: KubeProxyConfiguration
mode: ipvs # kube-proxy 模式
---
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta3
certificatesDir: /etc/kubernetes/pki
clusterName: kubernetes
controllerManager: {}
dns: {}
etcd:
local:
dataDir: /var/lib/etcd
imageRepository: registry.aliyuncs.com/k8sxio
kind: ClusterConfiguration
kubernetesVersion: 1.22.1
controlPlaneEndpoint: api.k8s.local:6443 # 设置控制平面Endpoint地址
apiServer:
extraArgs:
authorization-mode: Node,RBAC
timeoutForControlPlane: 4m0s
certSANs: # 添加其他master节点的相关信息
- api.k8s.local
- master1
- master2
- master3
- 192.168.23.209
- 192.168.23.210
- 192.168.23.211
networking:
dnsDomain: cluster.local
serviceSubnet: 10.96.0.0/12
podSubnet: 10.244.0.0/16 # 指定 pod 子网
scheduler: {}
---
apiVersion: kubelet.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
authentication:
anonymous:
enabled: false
webhook:
cacheTTL: 0s
enabled: true
x509:
clientCAFile: /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt
authorization:
mode: Webhook
webhook:
cacheAuthorizedTTL: 0s
cacheUnauthorizedTTL: 0s
clusterDNS:
- 10.96.0.10
clusterDomain: cluster.local
cpuManagerReconcilePeriod: 0s
evictionPressureTransitionPeriod: 0s
fileCheckFrequency: 0s
healthzBindAddress: 127.0.0.1
healthzPort: 10248
httpCheckFrequency: 0s
imageMinimumGCAge: 0s
kind: KubeletConfiguration
cgroupDriver: systemd # 配置 cgroup driver
logging: {}
memorySwap: {}
nodeStatusReportFrequency: 0s
nodeStatusUpdateFrequency: 0s
rotateCertificates: true
runtimeRequestTimeout: 0s
shutdownGracePeriod: 0s
shutdownGracePeriodCriticalPods: 0s
staticPodPath: /etc/kubernetes/manifests
streamingConnectionIdleTimeout: 0s
syncFrequency: 0s
volumeStatsAggPeriod: 0s
这里需要注意的是我们在 ClusterConfiguration 块的配置中新增了控制平面的地址以及将 api.k8s.local 这个域名加入到了证书签名中,该域名将映射到 vip:
controlPlaneEndpoint: api.k8s.local:6443 # 设置控制平面Endpoint地址
apiServer:
extraArgs:
authorization-mode: Node,RBAC
timeoutForControlPlane: 4m0s
certSANs: # 添加其他master节点的相关信息
- api.k8s.local
- master1
- master2
- master3
- 192.168.23.209
- 192.168.23.210
- 192.168.23.211
配置文件准备好过后,可以使用如下命令先将相关镜像 pull 下面:
kubeadm config images pull --config kubeadm.yaml
拉取 coredns 镜像的时候出错了,没有找到这个镜像,我们可以手动 pull 该镜像,然后重新 tag 下镜像地址即可:
ctr -n k8s.io i pull docker.io/coredns/coredns:1.8.4
ctr -n k8s.io i tag docker.io/coredns/coredns:1.8.4 registry.aliyuncs.com/k8sxio/coredns:v1.8.4
使用上面的配置文件在 master1 节点上进行初始化
➜ ~ kubeadm init --upload-certs --config kubeadm.yaml
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.22.1
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [api.k8s.local kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local master master1 master2 master3] and IPs [10.96.0.1 192.168.31.31 192.168.31.30 192.168.31.32]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost master] and IPs [192.168.31.31 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost master] and IPs [192.168.31.31 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "sa" key and public key
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests". This can take up to 4m0s
[apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 11.012184 seconds
[upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config-1.22" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster
[upload-certs] Storing the certificates in Secret "kubeadm-certs" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[upload-certs] Using certificate key:
7892cd62c5ab60b28b462af32c7e49aa73d5fd4f723352f3af6546a74e465abc
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node master as control-plane by adding the labels: [node-role.kubernetes.io/master(deprecated) node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers]
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node master as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule]
[bootstrap-token] Using token: abcdef.0123456789abcdef
[bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to get nodes
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster
[bootstrap-token] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace
[kubelet-finalize] Updating "/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf" to point to a rotatable kubelet client certificate and key
[addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
You can now join any number of the control-plane node running the following command on each as root:
kubeadm join api.k8s.local:6443 --token abcdef.0123456789abcdef \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:435fbc28490d1f897337923c19ec27bcf3639e9fe84e8448177777d23cae4176 \
--control-plane --certificate-key 7892cd62c5ab60b28b462af32c7e49aa73d5fd4f723352f3af6546a74e465abc
Please note that the certificate-key gives access to cluster sensitive data, keep it secret!
As a safeguard, uploaded-certs will be deleted in two hours; If necessary, you can use
"kubeadm init phase upload-certs --upload-certs" to reload certs afterward.
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join api.k8s.local:6443 --token abcdef.0123456789abcdef \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:435fbc28490d1f897337923c19ec27bcf3639e9fe84e8448177777d23cae4176
这里初始化的 --upload-certs 标志用来将在所有控制平面实例之间的共享证书上传到集群。然后根据安装提示拷贝 kubeconfig 文件:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
接着我们可以根据上面的提示添加其他的控制平面节点。
添加control plane node
对于每个其他控制平面节点,执行先前在第一个节点 master1 上的 kubeadm init 输出提供的 join 命令来添加控制平面节点:
kubeadm join api.k8s.local:6443 --token abcdef.0123456789abcdef --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:435fbc28490d1f897337923c19ec27bcf3639e9fe84e8448177777d23cae4176 --control-plane --certificate-key 7892cd62c5ab60b28b462af32c7e49aa73d5fd4f723352f3af6546a74e465abc
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[preflight] Reading configuration from the cluster...
[preflight] FYI: You can look at this config file with 'kubectl -n kube-system get cm kubeadm-config -o yaml'
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks before initializing the new control plane instance
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[download-certs] Downloading the certificates in Secret "kubeadm-certs" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost master2] and IPs [192.168.31.32 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost master2] and IPs [192.168.31.32 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [api.k8s.local kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local master1 master2 master3] and IPs [10.96.0.1 192.168.31.32 192.168.31.30 192.168.31.31]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Valid certificates and keys now exist in "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Using the existing "sa" key
[kubeconfig] Generating kubeconfig files
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[check-etcd] Checking that the etcd cluster is healthy
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[kubelet-start] Waiting for the kubelet to perform the TLS Bootstrap...
[etcd] Announced new etcd member joining to the existing etcd cluster
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for "etcd"
[etcd] Waiting for the new etcd member to join the cluster. This can take up to 40s
The 'update-status' phase is deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Currently it performs no operation
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node master2 as control-plane by adding the labels: [node-role.kubernetes.io/master(deprecated) node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers]
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node master2 as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule]
This node has joined the cluster and a new control plane instance was created:
* Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and approval was received.
* The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details.
* Control plane (master) label and taint were applied to the new node.
* The Kubernetes control plane instances scaled up.
* A new etcd member was added to the local/stacked etcd cluster.
To start administering your cluster from this node, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Run 'kubectl get nodes' to see this node join the cluster.
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
需要注意需要在另外两个节点 master2 和 master3 都执行上面的 join 命令,上面的命令中的 --control-plane 就是通知 kubeadm join 创建一个新的控制平面,–certificate-key 会从集群中的 kubeadm-certs Secret 下载控制平面证书并使用给定的密钥进行解密。
当这两个节点被添加到集群后,我们接下来也需要在当前节点上运行 kube-vip,将当前节点作为 kube-vip 的成员,同样执行下面的命令即可:
# 配置vip地址
➜ ~ export VIP=192.168.23.20
# 设置网卡名称
➜ ~ export INTERFACE=ens33
➜ ~ ctr image pull docker.io/plndr/kube-vip:v0.3.8
# 使用下面的容器输出静态Pod资源清单
➜ ~ ctr run --rm --net-host docker.io/plndr/kube-vip:v0.3.8 vip \
/kube-vip manifest pod \
--interface $INTERFACE \
--vip $VIP \
--controlplane \
--services \
--arp \
--leaderElection | tee /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-vip.yaml
当 kube-vip 的静态 Pod 清单创建完成后,正常将能够看到 kube-vip 的 Pod 会按预期启动并运行:
kubectl get pods -A | grep vip
kube-vip-master1
kube-vip-master2
kube-vip-master3
控制平面节点就都准备好了
kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
master1 Ready control-plane,master 9m18s v1.22.1
master2 Ready control-plane,master 7m11s v1.22.1
master3 Ready control-plane,master 5m9s v1.22.1
添加work node
接下来我们可以将 node1 工作节点加入到集群中,同样使用在 master1 上初始化后的提示 join 命令,记得将 master1 节点上面的 $HOME/.kube/config 文件拷贝到 node 节点对应的文件中,安装 kubeadm、kubelet、kubectl(可选),然后执行上面初始化完成后提示的 join 命令即可:
kubeadm join api.k8s.local:6443 --token abcdef.0123456789abcdef \
> --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:435fbc28490d1f897337923c19ec27bcf3639e9fe84e8448177777d23cae4176
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[preflight] Reading configuration from the cluster...
[preflight] FYI: You can look at this config file with 'kubectl -n kube-system get cm kubeadm-config -o yaml'
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[kubelet-start] Waiting for the kubelet to perform the TLS Bootstrap...
This node has joined the cluster:
* Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and a response was received.
* The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details.
Run 'kubectl get nodes' on the control-plane to see this node join the cluster.
如果忘记了上面的 join 命令可以使用命令 kubeadm token create --print-join-command 重新获取。
kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
master1 Ready control-plane,master 9m18s v1.22.1
master2 Ready control-plane,master 7m11s v1.22.1
master3 Ready control-plane,master 5m9s v1.22.1
node1 NotReady <none> 24s v1.22.1
可以看到是 NotReady 状态,这是因为还没有安装网络插件,接下来安装网络插件flannel:
➜ ~ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
# 如果有节点是多网卡,则需要在资源清单文件中指定内网网卡
# 搜索到名为 kube-flannel-ds 的 DaemonSet,在kube-flannel容器下面
➜ ~ vi kube-flannel.yml
......
containers:
- name: kube-flannel
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.14.0
command:
- /opt/bin/flanneld
args:
- --ip-masq
- --kube-subnet-mgr
- --iface=eth0 # 如果是多网卡的话,指定内网网卡的名称
......
➜ ~ kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml # 安装 flannel 网络插件
文件中的image改成上面这个镜像,除了cni-plugin的镜像不用改,rancher的镜像有点问题
隔一会儿查看 Pod 运行状态
kubectl get pods -n kube-system
全running即可
kubectl get node
当我们部署完网络插件后执行 ifconfig 命令,正常会看到新增的cni0与flannel1这两个虚拟设备,但是如果没有看到cni0这个设备也不用太担心,我们可以观察/var/lib/cni目录是否存在,如果不存在并不是说部署有问题,而是该节点上暂时还没有应用运行,我们只需要在该节点上运行一个 Pod 就可以看到该目录会被创建,并且cni0设备也会被创建出来。
测试高可用
上面我们搭建了3个 master 节点的高可用 Kubernetes 集群,接下来我们来测试下高可用是否生效。
首先查看一个 kube-vip 的 Pod 日志
kubectl logs -f kube-vip-master1 -n kube-system
level=info msg="new leader elected: master3"
可以看到 master3 现在是我们的 Leader,接下来我们将 master3 节点关掉,然后观察另外的 kube-vip 的日志变化
kubectl logs -f kube-vip-master2 -n kube-system
level=info msg="Node [master1] is assuming leadership of the cluster"
(assume假设,leadership领导)
Dashboard
v1.22.1 版本的集群需要安装最新的 2.0+ 版本的 Dashboard:
# 推荐使用下面这种方式
➜ ~ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.3.1/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml
➜ ~ vi recommended.yaml
# 修改Service为NodePort类型
......
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
spec:
ports:
- port: 443
targetPort: 8443
selector:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
type: NodePort # 加上type=NodePort变成NodePort类型的服务
......
在 YAML 文件中可以看到新版本 Dashboard 集成了一个 metrics-scraper 的组件,可以通过 Kubernetes 的 Metrics API 收集一些基础资源的监控信息,并在 web 页面上展示,所以要想在页面上展示监控信息就需要提供 Metrics API,比如安装 Metrics Server。
直接创建:
kubectl apply -f recommended.yaml
新版本的 Dashboard 会被默认安装在 kubernetes-dashboard 这个命名空间下面:
kubectl get pods -n kubernetes-dashboard -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
dashboard-metrics-scraper-856586f554-pllvt 1/1 Running 0 24m 10.88.0.7 master <none> <none>
kubernetes-dashboard-76597d7df5-82998 1/1 Running 0 21m 10.88.0.2 node2 <none> <none>
我们仔细看可以发现上面的 Pod 分配的 IP 段是 10.88.xx.xx,包括前面自动安装的 CoreDNS 也是如此,我们前面不是配置的 podSubnet 为 10.244.0.0/16 吗?我们先去查看下 CNI 的配置文件:
ls -la /etc/cni/net.d/
total 8
drwxr-xr-x 2 1001 docker 67 Aug 31 16:45 .
drwxr-xr-x. 3 1001 docker 19 Jul 30 01:13 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 1001 docker 604 Jul 30 01:13 10-containerd-net.conflist
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 292 Aug 31 16:45 10-flannel.conflist
可以看到里面包含两个配置,一个是 10-containerd-net.conflist,另外一个是我们上面创建的 Flannel 网络插件生成的配置,我们的需求肯定是想使用 Flannel 的这个配置,我们可以查看下 containerd 这个自带的 cni 插件配置:
cat /etc/cni/net.d/10-containerd-net.conflist
{
"cniVersion": "0.4.0",
"name": "containerd-net",
"plugins": [
{
"type": "bridge",
"bridge": "cni0",
"isGateway": true,
"ipMasq": true,
"promiscMode": true,
"ipam": {
"type": "host-local",
"ranges": [
[{
"subnet": "10.88.0.0/16"
}],
[{
"subnet": "2001:4860:4860::/64"
}]
],
"routes": [
{ "dst": "0.0.0.0/0" },
{ "dst": "::/0" }
]
}
},
{
"type": "portmap",
"capabilities": {"portMappings": true}
}
]
}
可以看到上面的 IP 段恰好就是 10.88.0.0/16,但是这个 cni 插件类型是 bridge 网络,网桥的名称为 cni0:
ip a
...
6: cni0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,PROMISC,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 9a:e7:eb:40:e8:66 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.88.0.1/16 brd 10.88.255.255 scope global cni0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 2001:4860:4860::1/64 scope global
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::98e7:ebff:fe40:e866/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
...
bridge网络,你可以想起docker中的bridge模式,就是通过的一个网桥比如docker0这里是cni0网桥进行通信的,通过cni0网桥通信的pod在同一台节点上没问题,但是不能跨节点通信,这就需要网络插件来实现了
但是使用 bridge 网络的容器无法跨多个宿主机进行通信,跨主机通信需要借助其他的 cni 插件,比如上面我们安装的 Flannel,或者 Calico 等等,由于我们这里有两个 cni 配置,所以我们需要将 10-containerd-net.conflist 这个配置删除,因为如果这个目录中有多个 cni 配置文件,kubelet 将会使用按文件名的字典顺序排列的第一个作为配置文件,所以前面默认选择使用的是 containerd-net 这个插件。
mv /etc/cni/net.d/10-containerd-net.conflist /etc/cni/net.d/10-containerd-net.conflist.bak
ifconfig cni0 down && ip link delete cni0
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart containerd kubelet
然后记得重建 coredns 和 dashboard 的 Pod,重建后 Pod 的 IP 地址就正常了:
kubectl get pods -n kubernetes-dashboard -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
dashboard-metrics-scraper-856586f554-tp8m5 1/1 Running 0 42s 10.244.1.6 node2 <none> <none>
kubernetes-dashboard-76597d7df5-9rmbx 1/1 Running 0 66s 10.244.1.5 node2 <none> <none>
kubectl get pods -n kube-system -o wide -l k8s-app=kube-dns
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
coredns-7568f67dbd-n7bfx 1/1 Running 0 5m40s 10.244.1.2 node2 <none> <none>
coredns-7568f67dbd-plrv8 1/1 Running 0 3m47s 10.244.1.4 node2 <none> <none>
查看 Dashboard 的 NodePort 端口:
kubectl get svc -n kubernetes-dashboard
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
dashboard-metrics-scraper ClusterIP 10.99.37.172 <none> 8000/TCP 25m
kubernetes-dashboard NodePort 10.103.102.27 <none> 443:31050/TCP 25m
然后可以通过上面的 31050 端口去访问 Dashboard,要记住使用 https,Chrome 不生效可以使用Firefox 测试,如果没有 Firefox 下面打不开页面,点击页面中的信任证书即可
然后创建一个具有全局所有权限的用户来登录 Dashboard(直接使用cluster-admin):
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: admin
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: admin
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: admin
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
kubectl apply -f admin.yaml
kubectl get secret -n kubernetes-dashboard|grep admin-token
admin-token-lwmmx kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 1d
kubectl get secret admin-token-lwmmx -o jsonpath={.data.token} -n kubernetes-dashboard |base64 -d
# 会生成一串很长的base64后的字符串

用上面的 base64 解码后的字符串作为 token 登录 Dashboard 即可
重新配置前提
如果你的集群安装过程中遇到了其他问题,我们可以使用下面的命令来进行重置:
kubeadm reset
ifconfig cni0 down && ip link delete cni0
ifconfig flannel.1 down && ip link delete flannel.1
rm -rf /var/lib/cni/