Mybatis架构解析
目录
整体架构层
SqlSession初始化
SQL请求的执行和分发
执行器层和缓存
ps:mybatis 有很多不同的用法,不同的用法对应相同或不同类的不同方法,走不同的分支逻辑,但是它们终究都还是走相同的执行流程,因为不同的写法,用法都是依赖相同的接口,所以如果我们使用mybatis用得比较简单,那么它可能就不会走很多的很长的分支逻辑,比如存储过程,association,类型别名这些东西我们在使用过程中几乎不会用到,自然就不会走到它们的分支处理逻辑,所以我们分析代码的时候不关注它们,它们都只是流程里的细节,但流程是不变的。
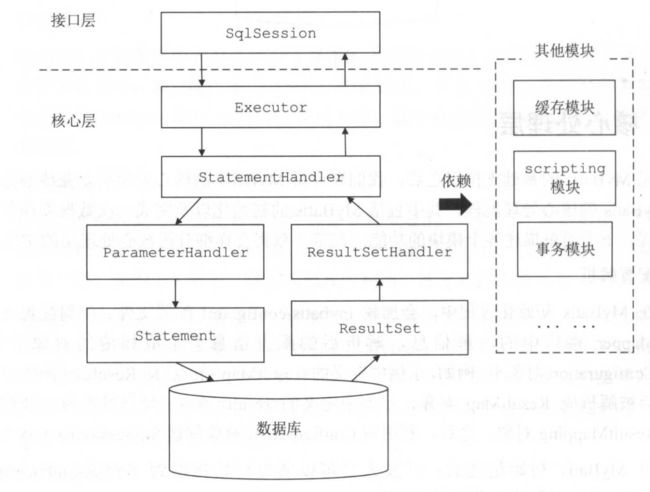
整体架构层
这是mybatis的架构图,层次很清晰,从中我们可以看到 SqlSession 就是mybatis提供给用户层操作数据库的顶级接口。 SqlSession 会调用它的一下层执行器Executor层,执行器Executor层 会调用它的下一层 StatementHandler 层 ,然后 StatementHandler 层会调用它的下一层 ParameterHandler 层 ,ParameterHandler 层会调用它的下一层 Statement 和mysql等数据库进行交互,完成增删改查的操作,返回执行结果,这个执行结果毫无疑问就是 ResultSet ,然后 ResultSetHandler 层会对这个执行结果进行处理,最终返回数据给用户层 。
下面就是一个最简单的例子,我们应用层确实是操作 SqlSession 层来操作mybatis和数据库进行交互的。
@org.junit.Test
public void testQuery() {
try(InputStream inputStream=Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis.xml")) {
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream, "development");
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = mapper.queryUserById(1);
System.out.println(user.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}在 SqlSession 会话层, SqlSession 会调用它的下一层 Executor 执行器去实际执行查询或更新,DefaultSqlSession 是默认的 SqlSession 接口实现类。Executor 有三种具体类型。
executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
executor.update(ms, wrapCollection(parameter));public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private final Configuration configuration;
private final Executor executor;
...
@Override
public void select(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
@Override
public int update(String statement, Object parameter) {
try {
dirty = true;
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.update(ms, wrapCollection(parameter));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error updating database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}在 Executor 执行器层,SimpleExecutor 通过 StatementHandler 创建了一个 Statement 对象,当Statement 对象被创建出来后, StatementHandler 会通过它的update()或 query() 等方法实际执行 SQL语句
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.update(stmt);,并将结果交给 ResultHandler 进行处理 。
handler.update(stmt);public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
public SimpleExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) {
super(configuration, transaction);
}
@Override
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.update(stmt);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
@Override
public List doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
} 在 StatementHandler 层,它会先使用 ParameterHandler 把 Statement中的 "?"占位符替换为实际的参数。
@Override
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}即在 DefaultParameterHandler 中通过反射的方式或类型处理器的方式替换。
public class DefaultParameterHandler implements ParameterHandler {
private final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry;
private final MappedStatement mappedStatement;
private final Object parameterObject;
private final BoundSql boundSql;
private final Configuration configuration;
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
List parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException | SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
} 完成占位符的替换后,StatementHandler 会调用 Statement 执行 sql 命令。
ps.execute();public class PreparedStatementHandler extends BaseStatementHandler {
public PreparedStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
super(executor, mappedStatement, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
}
@Override
public int update(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
ps.execute();
int rows = ps.getUpdateCount();
Object parameterObject = boundSql.getParameterObject();
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator();
keyGenerator.processAfter(executor, mappedStatement, ps, parameterObject);
return rows;
}
@Override
public List query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
ps.execute();
return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}
} Statement 执行完成后,ResultSetHandler 会对 ResultSet 进行处理,
resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps)返回最终结果。我们可以看到都是处理 ResultMap ,ResultMapping ,这些都是mybatis的标签,最终返回一个List
public class DefaultResultSetHandler implements ResultSetHandler {
@Override
public List以上就是mybatis的主要执行流程,中间还有很多细节可以通过看代码,debug跟踪断点的方式去认识mybatis。
SqlSession初始化
XMLConfigBuilder是一个解析mybati xml配置的解析器,xml是一个树形嵌套结构,很好解析,解析完成后生成一个Configuration类,它贯穿了mybatis的整个生命周期。
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}SqlSessionFactory生成后,就会获取一个sqlSession对象,它是java代码操作mybatis的顶级接口,可以通过一个DataSource或Connection来获取。
@Override
public SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, boolean autoCommit) {
return openSessionFromDataSource(execType, null, autoCommit);
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession(Connection connection) {
return openSessionFromConnection(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), connection);
}SQL请求的执行和分发
mybatis 是怎么通过 mapper 接口找到对应的具体sql代码执行的呢?
原来在 mybatis 启动的时候会扫描所有 mapper.xml 文件里的每一个
public class MapperProxy implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (method.isDefault()) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
} 在 MapperMethod 中,它会根据请求类型下发给 sqlSession 去执行。
public class MapperMethod {
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
...
return result;
}
}public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
@Override
public List selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
} mappedStatements 确实是一个Map
public class Configuration {
...
protected final Map mappedStatements = new StrictMap("Mapped Statements collection")
.conflictMessageProducer((savedValue, targetValue) ->
". please check " + savedValue.getResource() + " and " + targetValue.getResource());
...
public MappedStatement getMappedStatement(String id) {
return this.getMappedStatement(id, true);
}
public MappedStatement getMappedStatement(String id, boolean validateIncompleteStatements) {
if (validateIncompleteStatements) {
buildAllStatements();
}
return mappedStatements.get(id);
}
} 总结一下:动态代理proxy会根据请求方法的(select,insert等)类型和(类似com.yzp.demo.mapper.UserMapper.queryUserById)名称去找到要执行的Statement并执行,这个过程就是请求命令的路由分发。
这个过程有点像 open feign 的 ReflectiveFeign 类似,它也是在动态代理中去完成路由分发的逻辑的,另外它们都是使用jdk动态代理。
dispatch 是一个Map,保存了方法和方法处理器的映射关系。
public class ReflectiveFeign extends Feign {
....
static class FeignInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private final Target target;
private final Map dispatch;
FeignInvocationHandler(Target target, Map dispatch) {
this.target = checkNotNull(target, "target");
this.dispatch = checkNotNull(dispatch, "dispatch for %s", target);
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if ("equals".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
Object otherHandler =
args.length > 0 && args[0] != null ? Proxy.getInvocationHandler(args[0]) : null;
return equals(otherHandler);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
return false;
}
} else if ("hashCode".equals(method.getName())) {
return hashCode();
} else if ("toString".equals(method.getName())) {
return toString();
}
return dispatch.get(method).invoke(args);
}
} 执行器层和缓存
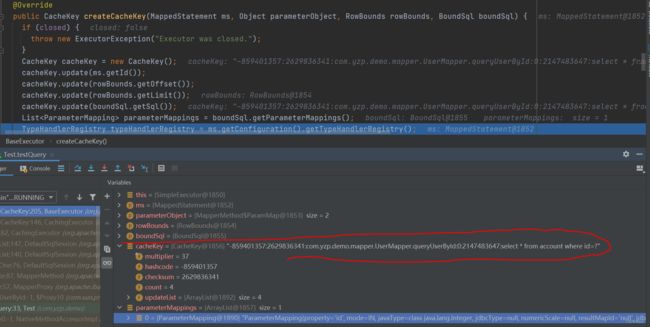
SqlSession会创建一个执行器Executor,分为Simple,Reuse,Batch三种类型,由执行器通过StatementHandler创建Statement对象,Reuse类型的statement可以复用,Simple类型的不可以。其中一级缓存和二级缓存都是在Executor执行器中完成的。一级缓存是一个HashMap,在一个会话里会使用CacheKey来作为键,键的结构如下,可以简单理解为就是一个sql的字符串,最后会生成一个long类型的hash码,debug一下就知道了。
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
}通常我们会关闭一级缓存,因为一级缓存是Session会话级别的,不同的会话的一级缓存互不干扰,这就会导致脏读导致的数据不一致问题。关闭一级缓存则改为statement级即可。
ps:一级缓存:Mybatis的缓存机制详解_cnmeimei的博客-CSDN博客
未完待续