nginx配置详解
一.nginx常用命令
1.Windows
(1).查看nginx的版本号
nginx -v
(2).启动nginx
start nginx
(3).快速停止或关闭nginx
nginx -s stop
(4).正常停止或关闭nginx
nginx -s quit
(5).配置文件nginx.conf修改重装载命令
nginx -s reload
2.Linux
(1).进入 nginx 目录中
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin
(2).查看 nginx 版本号
./nginx -v
(3).启动 nginx
./nginx
(4).停止 nginx
./nginx -s stop
(5).重新加载 nginx
./nginx -s reload
二.Nginx配置文件(nginx.conf)
1.概述
默认在Linux上安装的Nginx,配置文件在安装的nginx目录下的conf目录下,名字叫做nginx.conf
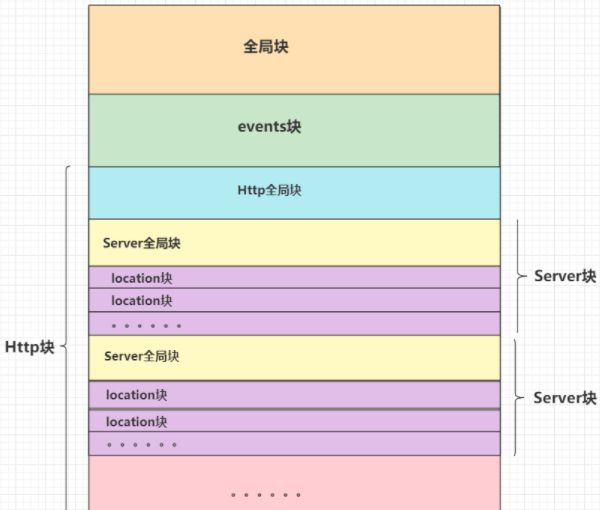
nginx.conf主要由三部分组成: 全局块, events块, http块
2.配置文件结构图解
3.配置文件概览
# 全局快
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# events块
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# http块
http {
#http全局块
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# server块
server {
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# server全局块
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# location块
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# 可以配置多个server块
}... #全局块
events { #events块
...
}
http #http块
{
... #http全局块
server #server块
{
... #server全局块
location [PATTERN] #location块
{
...
}
location [PATTERN]
{
...
}
}
server
{
...
}
... #http全局块
}3.1全局块
就是配置文件从头开始到events块之间的内容,主要设置的是影响nginx服务器整体运行的配置指令,一般有运行nginx服务器的用户组,nginx进程pid存放路径,日志存放路径,配置文件引入,允许生成worker process数等,比如worker_process, 值越大,可以支持的并发处理量也越多,但是还是和服务器的硬件相关
3.2 events块
events 块涉及的指令主要影响 Nginx 服务器与用户的网络连接,常用的设置包括每个进程的最大连接数,是否开启对多 work process下的网络连接进行序列化,是否允许同时接收多个网络连接,选取哪种事件驱动模型来处理连接请求,每个 word process 可以同时支持的最大连接数等。
上述例子就表示每个 work process 支持的最大连接数为 1024.
注意:这部分的配置对 Nginx 的性能影响较大,在实际中应该灵活配置
3.3 http块
包括http全局块,以及多个server块,可以嵌套多个server,配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置。如文件引入,mime-type定义,日志自定义,是否使用sendfile传输文件,连接超时时间,单连接请求数等
3.3.1 http全局块
http 全局块配置的指令包括文件引入、 MIME-TYPE 定义、日志自定义、连接超时时间、单链接请求数上限等。
3.3.2 server块
配置虚拟主机的相关参数,一个http中可以有多个server,这块和虚拟主机有密切关系,虚拟主机从用户角度看,和一台独立的硬件主机是完全一样的,该技术的产生是为了节省互联网服务器硬件成本。每个 http 块可以包括多个 server 块,而每个 server 块就相当于一个虚拟主机,每个 server 块也分为全局 server 块,以及可以同时包含多个 location 块
3.3.2.1 server全局块
最常见的配置是本虚拟机主机的监听配置和本虚拟主机的名称或 IP 配置。
#这一行表示这个server块监听的端口是80,只要有请求访问了80端口,此server块就处理请求
listen 80;
#表示这个server块代表的虚拟主机的名字
server_name localhost;3.3.2.2 location块
配置请求的路由,以及各种页面的处理情况,一个 server 块可以配置多个 location 块.要作用是根据请求地址路径的匹配,匹配成功进行特定的处理,这块的主要作用是基于 Nginx 服务器接收到的请求字符串(例如 server_name/uri-string),对虚拟主机名称(也可以是 IP 别名)之外的字符串(例如 前面的 /uri-string)进行匹配,对特定的请求进行处理。地址定向、数据缓存和应答控制等功能,还有许多第三方模块的配置也在这里进行
# 表示如果请求路径是/就是用这个location块进行处理
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}4.案例讲解
########### 每个指令必须有分号结束。#################
#user administrator administrators; #配置用户或者组,默认为nobody nobody。
#worker_processes 2; #允许生成的进程数,默认为1
#pid /nginx/pid/nginx.pid; #指定nginx进程运行文件存放地址
error_log log/error.log debug; #制定日志路径,级别。这个设置可以放入全局块,http块,server块,级别以此为:debug|info|notice|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg
events {
accept_mutex on; #设置网路连接序列化,防止惊群现象发生,默认为on
multi_accept on; #设置一个进程是否同时接受多个网络连接,默认为off
#use epoll; #事件驱动模型,select|poll|kqueue|epoll|resig|/dev/poll|eventport
worker_connections 1024; #最大连接数,默认为512
}
http {
include mime.types; #文件扩展名与文件类型映射表
default_type application/octet-stream; #默认文件类型,默认为text/plain
#access_log off; #取消服务日志
log_format myFormat '$remote_addr–$remote_user [$time_local] $request $status $body_bytes_sent $http_referer $http_user_agent $http_x_forwarded_for'; #自定义格式
access_log log/access.log myFormat; #combined为日志格式的默认值
sendfile on; #允许sendfile方式传输文件,默认为off,可以在http块,server块,location块。
sendfile_max_chunk 100k; #每个进程每次调用传输数量不能大于设定的值,默认为0,即不设上限。
keepalive_timeout 65; #连接超时时间,默认为75s,可以在http,server,location块。
upstream mysvr {
server 127.0.0.1:7878;
server 192.168.10.121:3333 backup; #热备
}
error_page 404 https://www.baidu.com; #错误页
server {
keepalive_requests 120; #单连接请求上限次数。
listen 4545; #监听端口
server_name 127.0.0.1; #监听地址
location ~*^.+$ { #请求的url过滤,正则匹配,~为区分大小写,~*为不区分大小写。
#root path; #根目录
#index vv.txt; #设置默认页
proxy_pass http://mysvr; #请求转向mysvr 定义的服务器列表
deny 127.0.0.1; #拒绝的ip
allow 172.18.5.54; #允许的ip
}
}
}5.注意事项
(1).$remote_addr 与 $http_x_forwarded_for 用以记录客户端的ip地址
(2).$remote_user :用来记录客户端用户名称
(3).$time_local : 用来记录访问时间与时区
(4).$request : 用来记录请求的url与http协议
(5).$status : 用来记录请求状态;成功是200
(6).$body_bytes_s ent :记录发送给客户端文件主体内容大小
(7).$http_referer :用来记录从那个页面链接访问过来的
(8).$http_user_agent :记录客户端浏览器的相关信息
(9).惊群现象:一个网路连接到来,多个睡眠的进程被同时叫醒,但只有一个进程能获得链接,这样会影响系统性能
(10).每个指令必须有分号结束
6.常用配置案例
6.1文件上传大小
http {
# 设置nginx文件上传大小限制
client_max_body_size 200M;
client_body_buffer_size 50M;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
}6.2 http 转 https
方式①:http端口
server {
rewrite ^(.*)$ https://$host$1 permanent;
}方式②:同时http、https端口
server {
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl;
server_name localhost;
if ($scheme = http) {
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
}redirect重定向https跳转http问题,报错“400 Bad Request: The plain HTTP request was sent to HTTPS port”
解决方法:
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto https;
proxy_pass http://172.17.x.xxx:8081;
proxy_redirect http:// https://;实现流程是根据nginx的不同执行阶段,来完成Location http到https
1)proxy_pass执行前,先设置了request head host 为https外网访问的域名+端口
2)proxy_pass执行后,tomcat结果返回response
3)proxy_redirect修改response中的location中的协议http为https外网访问的协议。
注:redirect重定向主要是通过访问nginx服务的请求head项来决定的,默认是http协议,域名是通过读取host地址,默认host中不包括访问端口
方式③:错误页从定向
server {
listen 8001 ssl;
server_name localhost;
error_page 497 https://$host:8009$uri?$args;
}6.3 隐藏版本号
http {
server_tokens off;
} 6.4.负载均衡(upstream)
upstream xxx.com {
ip_hash;
server 192.168.8.11:80;
server 192.168.8.12:80 down;
server 192.168.8.13:8009 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=20s;
server 192.168.8.146:8080;
}注意:当负载调度算法为ip_hash时,后端服务器在负载均衡调度中的状态不能是weight和backup
upstream是Nginx的HTTP Upstream模块,这个模块通过一个简单的调度算法来实现客户端IP到后端服务器的负载均衡
在上面的设定中,通过upstream指令指定了一个负载均衡器的名称xxx.com,这个名称可以任意指定,在后面需要的地方直接调用即可。
Nginx的负载均衡模块目前支持4种调度算法,下面进行分别介绍,其中后两项属于第三方的调度方法
轮询(默认):每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端某台服务器宕机,故障系统被自动剔除,使用户访问不受影响;
Weight:指定轮询权值,Weight值越大,分配到的访问机率越高,主要用于后端每个服务器性能不均的情况下;
ip_hash:每个请求按访问IP的hash结果分配,这样来自同一个IP的访客固定访问一个后端服务器,有效解决了动态网页存在的session共享问题;
fair:比上面两个更加智能的负载均衡算法。此种算法可以依据页面大小和加载时间长短智能地进行负载均衡,也就是根据后端服务器的响应时间来分配请求,响应时间短的优先分配。Nginx本身是不支持fair的,如果需要使用这种调度算法,必须下载Nginx的upstream_fair模块;
url_hash:按访问url的hash结果来分配请求,使每个url定向到同一个后端服务器,可以进一步提高后端缓存服务器的效率。Nginx本身是不支持url_hash的,如果需要使用这种调度算法,必须安装Nginx 的hash软件包。
在HTTP Upstream模块中,可以通过server指令指定后端服务器的IP地址和端口,同时还可以设定每个后端服务器在负载均衡调度中的状态。常用的状态有:
down:表示当前的server暂时不参与负载均衡;
backup:预留的备份机器。当其他所有的非backup机器出现故障或者忙的时候,才会请求backup机器,因此这台机器的压力最轻;
max_fails:允许请求失败的次数,默认为1。当超过最大次数时,返回proxy_next_upstream 模块定义的错误;
fail_timeout:在经历了max_fails次失败后,暂停服务的时间。max_fails可以和fail_timeout一起使用
6.5 禁止文件缓存
开发环境可使用
location ~* \.(js|css|png|jpg|gif)$ {
add_header Cache-Control no-store;
}6.6 防盗链
防止文件被其他网站使用
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|png)$ {
# 只允许 192.168.0.1 请求资源
valid_referers none blocked 192.168.0.1;
if ($invalid_referer) {
rewrite ^/ http://$host/logo.png;
}
}6.7文件压缩
server {
# 开启gzip 压缩
gzip on;
# 设置gzip所需的http协议最低版本 (HTTP/1.1, HTTP/1.0)
gzip_http_version 1.1;
# 设置压缩级别,压缩级别越高压缩时间越长 (1-9)
gzip_comp_level 4;
# 设置压缩的最小字节数, 页面Content-Length获取
gzip_min_length 1000;
# 设置压缩文件的类型 (text/html)
gzip_types text/plain application/javascript text/css;
}6.8 指定定错误页面
# 根据状态码,返回对于的错误页面
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /source/error_page;
}6.9解决跨域
现在http://xx_domain对https://github.com发起请求一定会出现跨域。
## 配置反向代理的参数
server {
listen 8080;
server_name xx_domain
## 1. 用户访问 http://xx_domain,则反向代理到 https://github.com
location / {
proxy_pass https://github.com;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
# 传递域名
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
# 传递ip
proxy_set_header X-Scheme $scheme;
# 传递协议
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}6.10其他
server {
# 监听端口 HTTPS
listen 443 ssl;
server_name xxx.com;
# 配置域名证书
ssl_certificate C:\WebServer\Certs\certificate.crt;
ssl_certificate_key C:\WebServer\Certs\private.key;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_protocols SSLv2 SSLv3 TLSv1;
ssl_ciphers ALL:!ADH:!EXPORT56:RC4+RSA:+HIGH:+MEDIUM:+LOW:+SSLv2:+EXP; ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
root /data/www/;
location ~ .*\.(php|php5)?$ {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi.conf;
}
# 配置地址拦截转发,解决跨域验证问题
location /oauth/ {
proxy_pass https://localhost:13580/oauth/;
proxy_set_header HOST $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}