机器学习之线性回归、逻辑回归、岭回归和聚类算法
1. 回归算法–线性回归分析
1.1 线性关系模型
-
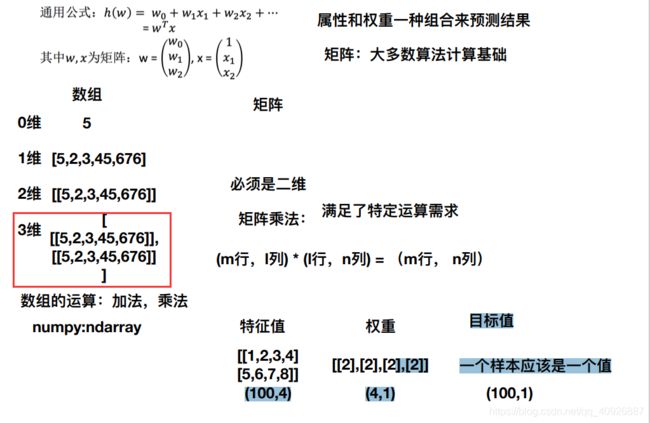
试图学得一个通过属性的线性组合来进行预测的函数:
- ()=_1 _1+_2 _2+…+_ _+
- w为权重,b称为偏置项,可以理解为:_0×1
---------------------------------------------------理解------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------理解------------------------------------------------
1.2 线性回归策略、优化案例
1.2.1 损失函数
预测结果与真实值是有一定的误差
提问:如何去求模型当中的W,使得损失最小?
答:(目的是找到最小损失对应的W值)
相关方法:(1)(2)

1.2.2 相关API
scikit-learn与tensorflow的比较
- scikit-learn:
- 优点:封装好,建⽴模型简单,预测简单
- 缺点:算法的过程,有些参数都在算法API内部优化
- tensorflow:
- 封装⾼低, ⾃⼰实现线性回归,学习率等等
1.3 线性回归实例
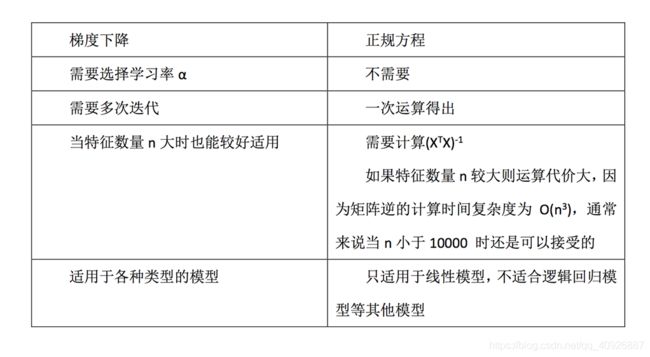
1、sklearn线性回归正规方程、梯度下降API
1.3.1 正规方程求解预测结果
- 注意:
- 0.19版本 转换器,estimator 要求数据必须是⼆维 # y_test.reshape(-1, 1)
- 0.18版本 转换器 estimator 二维、一维数据都可以 # y_train
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
def mylinear():
"""
线性回归直接预测房子价格
:return: None
"""
# 获取数据
lb = load_boston()
# 分割数据集到训练集和测试集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(lb.data, lb.target, test_size=0.25)
print(y_train, y_test)
# 进行标准化处理(?) 目标值处理?
# 特征值和目标值是都必须进行标准化处理, 实例化两个标准化API
std_x = StandardScaler()
x_train = std_x.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = std_x.transform(x_test)
# 目标值
std_y = StandardScaler()
y_train = std_y.fit_transform(y_train.reshape(-1, 1)) # y_train 0.18版本 转换器 estimator 二维数据一维数据都可以
y_test = std_y.transform(y_test.reshape(-1, 1)) # y_test 0.19版本 转换器,estimator 要求数据必须是⼆维
# estimator预测
# 正规方程求解方式预测结果
lr = LinearRegression()
lr.fit(x_train, y_train)
print(lr.coef_)
# 预测测试集的房子价格
y_lr_predict = std_y.inverse_transform(lr.predict(x_test))
print("正规方程测试集里面每个房子的预测价格:", y_lr_predict)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
mylinear()
正规方程测试集里面每个房子的预测价格: [[38.17292549]
[24.38603064]
[19.69435528]
[18.48993572]
......
[33.1439397 ]
[36.34471683]
[25.53738013]]
1.3.2 梯度下降求解预测结果
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, SGDRegressor, Ridge, LogisticRegression
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
def mylinear():
"""
线性回归直接预测房子价格
:return: None
"""
# 获取数据
lb = load_boston()
# 分割数据集到训练集和测试集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(lb.data, lb.target, test_size=0.25)
print(y_train, y_test)
# 进行标准化处理(?) 目标值处理?
# 特征值和目标值是都必须进行标准化处理, 实例化两个标准化API
std_x = StandardScaler()
x_train = std_x.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = std_x.transform(x_test)
# 目标值
std_y = StandardScaler()
y_train = std_y.fit_transform(y_train.reshape(-1, 1)) # y_train 0.18版本 转换器 estimator 二维数据一维数据都可以
y_test = std_y.transform(y_test.reshape(-1, 1)) # y_test 0.19版本 转换器,estimator 要求数据必须是⼆维
# estimator预测
# # 正规方程求解方式预测结果
# lr = LinearRegression()
#
# lr.fit(x_train, y_train)
#
# print(lr.coef_)
#
# # 预测测试集的房子价格
# y_lr_predict = std_y.inverse_transform(lr.predict(x_test))
#
# print("正规方程测试集里面每个房子的预测价格:", y_lr_predict)
# 梯度下降去进行房价预测
sgd = SGDRegressor()
sgd.fit(x_train, y_train)
print(sgd.coef_)
# 预测测试集的房子价格
y_sgd_predict = std_y.inverse_transform(sgd.predict(x_test))
print("梯度下降测试集里面每个房子的预测价格:", y_sgd_predict)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
mylinear()
梯度下降测试集里面每个房子的预测价格: [25.15138165 18.16198705 12.58449378 14.75220226
23.62879777 11.74973668 15.32728958 41.14288107 29.02907643 19.92890793
6.33388839 14.63420966 33.16393357 21.97461105 10.44441454 10.90726611
16.02847717 23.45545813 22.89774722 16.50654202 27.28188056 34.82311791
22.76297694 33.29179225 16.71078919 17.79687416 30.38060444 17.14584607............]
1.3.4 正规方程和梯度下降均方误差比较
-
性能评估API
-
sklearn.metrics.mean_squared_error
-
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, SGDRegressor, Ridge, LogisticRegression
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, classification_report
def mylinear():
"""
线性回归直接预测房子价格
:return: None
"""
# 获取数据
lb = load_boston()
# 分割数据集到训练集和测试集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(lb.data, lb.target, test_size=0.25)
print(y_train, y_test)
# 进行标准化处理(?) 目标值处理?
# 特征值和目标值是都必须进行标准化处理, 实例化两个标准化API
std_x = StandardScaler()
x_train = std_x.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = std_x.transform(x_test)
# 目标值
std_y = StandardScaler()
y_train = std_y.fit_transform(y_train.reshape(-1, 1)) # y_train 0.18版本 转换器 estimator 二维数据一维数据都可以
y_test = std_y.transform(y_test.reshape(-1, 1)) # y_test 0.19版本 转换器,estimator 要求数据必须是⼆维
# estimator预测
# 正规方程求解方式预测结果
lr = LinearRegression()
lr.fit(x_train, y_train)
print(lr.coef_)
# 预测测试集的房子价格
y_lr_predict = std_y.inverse_transform(lr.predict(x_test))
print("正规方程测试集里面每个房子的预测价格:", y_lr_predict)
print("正规方程的均方误差:", mean_squared_error(std_y.inverse_transform(y_test), y_lr_predict))
# # 梯度下降去进行房价预测
sgd = SGDRegressor()
sgd.fit(x_train, y_train.ravel()) # 梯度下降进行预测y_train变成y_train.ravel()否则报错DataConversionWarning但不影响结果
print(sgd.coef_)
# 预测测试集的房子价格
y_sgd_predict = std_y.inverse_transform(sgd.predict(x_test))
print("梯度下降测试集里面每个房子的预测价格:", y_sgd_predict)
print("梯度下降的均方误差:", mean_squared_error(std_y.inverse_transform(y_test), y_sgd_predict))
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
mylinear()
正规方程的均方误差: 27.427941206420243
梯度下降的均方误差: 26.93348926658336
性能评估小结
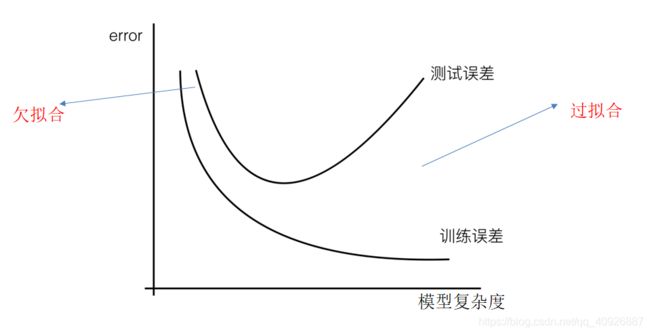
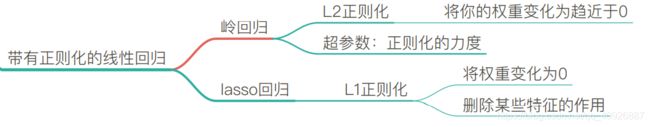
1.3.5 过拟合和欠拟合问题【岭回归】
岭回归算法对比
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, SGDRegressor, Ridge, LogisticRegression
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, classification_report
def mylinear():
"""
线性回归直接预测房子价格
:return: None
"""
# 获取数据
lb = load_boston()
# 分割数据集到训练集和测试集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(lb.data, lb.target, test_size=0.25)
print(y_train, y_test)
# 进行标准化处理(?) 目标值处理?
# 特征值和目标值是都必须进行标准化处理, 实例化两个标准化API
std_x = StandardScaler()
x_train = std_x.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = std_x.transform(x_test)
# 目标值
std_y = StandardScaler()
y_train = std_y.fit_transform(y_train.reshape(-1, 1)) # y_train 0.18版本 转换器 estimator 二维数据一维数据都可以
y_test = std_y.transform(y_test.reshape(-1, 1)) # y_test 0.19版本 转换器,estimator 要求数据必须是⼆维
# estimator预测
# 正规方程求解方式预测结果
lr = LinearRegression()
lr.fit(x_train, y_train)
print(lr.coef_)
# 预测测试集的房子价格
y_lr_predict = std_y.inverse_transform(lr.predict(x_test))
print("正规方程测试集里面每个房子的预测价格:", y_lr_predict)
print("正规方程的均方误差:", mean_squared_error(std_y.inverse_transform(y_test), y_lr_predict))
# 岭回归去进行房价预测
rd = Ridge(alpha=1.0)
rd.fit(x_train, y_train)
print(rd.coef_)
# 预测测试集的房子价格
y_rd_predict = std_y.inverse_transform(rd.predict(x_test))
print("岭回归测试集里面每个房子的预测价格:", y_rd_predict)
print("岭回归的均方误差:", mean_squared_error(std_y.inverse_transform(y_test), y_rd_predict))
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
mylinear()
正规方程测试集里面每个房子的预测价格: [[27.56028957]
岭回归的均方误差: 19.41358615404921
岭回归小结
-
线性回归 LinearRegression与Ridge对比
*岭回归:回归得到的回归系数更符合实际,更可靠。另外,能让估计参数的波动范围变小,变的更稳定。在存在病态数据偏多的研究中有较大的实用价值。
小知识-模型的保存与加载
-
保存和加载的API
- 保存:joblib.dump(rf,‘test.pkl’)
- 加载:estimator = joblib.load(‘test.pkl’) 注意文件格式pkl
代码1
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, SGDRegressor, Ridge, LogisticRegression
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
import joblib
def mylinear():
"""
线性回归直接预测房子价格
:return: None
"""
# 获取数据
lb = load_boston()
# 分割数据集到训练集和测试集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(lb.data, lb.target, test_size=0.25)
print(y_train, y_test)
# 进行标准化处理(?) 目标值处理?
# 特征值和目标值是都必须进行标准化处理, 实例化两个标准化API
std_x = StandardScaler()
x_train = std_x.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = std_x.transform(x_test)
# 目标值
std_y = StandardScaler()
y_train = std_y.fit_transform(y_train.reshape(-1, 1)) # y_train 0.18版本 转换器 estimator 二维数据一维数据都可以
y_test = std_y.transform(y_test.reshape(-1, 1)) # y_test 0.19版本 转换器,estimator 要求数据必须是⼆维
# estimator预测
# 正规方程求解方式预测结果
lr = LinearRegression()
lr.fit(x_train, y_train)
print(lr.coef_)
# 保存训练好的模型
joblib.dump(lr, "./data/tmp/test.pkl")
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
mylinear()
代码2:利用保存好的模型进行预测
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
import joblib
def mylinear():
"""
线性回归直接预测房子价格
:return: None
"""
# 获取数据
lb = load_boston()
# 分割数据集到训练集和测试集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(lb.data, lb.target, test_size=0.25)
print(y_train, y_test)
# 进行标准化处理(?) 目标值处理?
# 特征值和目标值是都必须进行标准化处理, 实例化两个标准化API
std_x = StandardScaler()
x_train = std_x.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = std_x.transform(x_test)
# 目标值
std_y = StandardScaler()
y_train = std_y.fit_transform(y_train.reshape(-1, 1)) # y_train 0.18版本 转换器 estimator 二维数据一维数据都可以
y_test = std_y.transform(y_test.reshape(-1, 1)) # y_test 0.19版本 转换器,estimator 要求数据必须是⼆维
# 预测房价结果
model = joblib.load("./data/tmp/test.pkl")
y_predict = std_y.inverse_transform(model.predict(x_test))
print("保存的模型预测的结果:", y_predict)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
mylinear()
打印输出结果:保存的模型预测的结果: [[18.53694008]
[24.27017922] [21.15654398] [42.80079346]
.......
[28.65321816] [30.93502915] [27.1739603 ]
[31.04974175]]
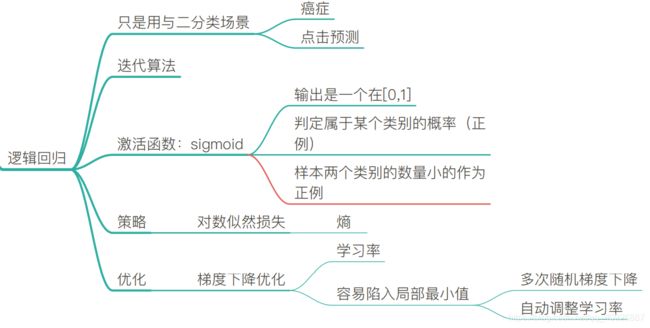
2. 分类算法–逻辑回归分析
-
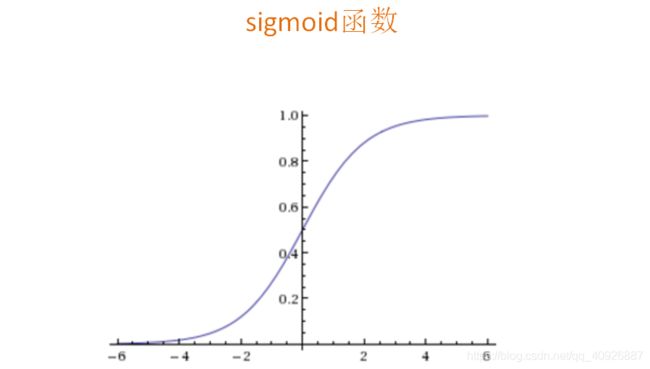
逻辑回归:线性回归的式子作为的输入,解决的二分类问题
- 输入:ℎ()= _0+〖_1 〗_1+_2 _2+…
= ^ (单个样本)
- 输入:ℎ()= _0+〖_1 〗_1+_2 _2+…
-
逻辑回归也是一种自我学习的算法
1.2 逻辑回归的优化与线性回归的比较
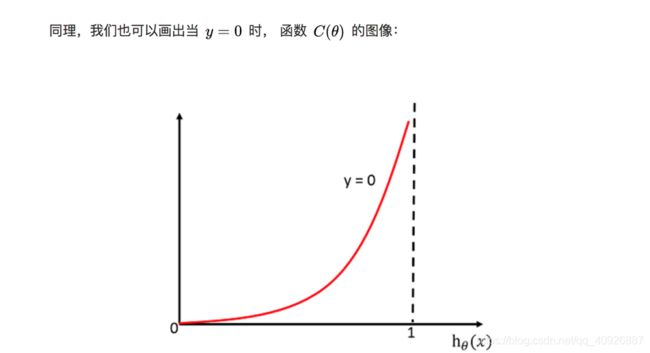
1.2.1 损失函数
-
损失函数(策略):
1.2.2 逻辑回归预测癌症案例
-
良/恶性乳腺癌肿分类流程
- 1、网上获取数据(工具pandas)
- 2、数据缺失值处理、标准化
- 3、LogisticRegression估计器流程
相关API
- sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression(penalty=‘l2’, C = 1.0)
- Logistic回归分类器
- coef_:回归系数
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, classification_report
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
def logistic():
"""
逻辑回归做二分类进行癌症预测(根据细胞的属性特征)
:return: NOne
"""
# 构造列标签名字
column = ['Sample code number','Clump Thickness', 'Uniformity of Cell Size','Uniformity of Cell Shape','Marginal Adhesion', 'Single Epithelial Cell Size','Bare Nuclei','Bland Chromatin','Normal Nucleoli','Mitoses','Class']
# 读取数据
data = pd.read_csv("https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/breast-cancer-wisconsin/breast-cancer-wisconsin.data", names=column)
print(data)
# 缺失值进行处理
data = data.replace(to_replace='?', value=np.nan) # to_replace被替换掉的值,
data = data.dropna()
# 进行数据的分割 特征值:column[1:10] 目标值:data[column[10]
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data[column[1:10]], data[column[10]], test_size=0.25)
# 进行标准化处理
std = StandardScaler()
x_train = std.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = std.transform(x_test)
# 逻辑回归预测
lg = LogisticRegression(C=1.0)
lg.fit(x_train, y_train)
print(lg.coef_)
y_predict = lg.predict(x_test)
print("准确率:", lg.score(x_test, y_test))
print("召回率:", classification_report(y_test, y_predict, labels=[2, 4], target_names=["良性", "恶性"]))
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
logistic()
输出:E:\PycharmProjects\untitled\venv\Scripts\python.exe E:/PycharmProjects/untitled/测试/day_03.py
Sample code number Clump Thickness ... Mitoses Class
0 1000025 5 ... 1 2
1 1002945 5 ... 1 2
2 1015425 3 ... 1 2
3 1016277 6 ... 1 2
4 1017023 4 ... 1 2
.. ... ... ... ... ...
694 776715 3 ... 1 2
695 841769 2 ... 1 2
696 888820 5 ... 2 4
697 897471 4 ... 1 4
698 897471 4 ... 1 4
[699 rows x 11 columns]
[[1.28583635 0.04301273 0.92733399 0.71515282 0.12722421 1.16065635 0.98566744 0.65166086 0.69025379]]
准确率: 0.9824561403508771
召回率: precision recall f1-score support
良性 0.97 1.00 0.99 106
恶性 1.00 0.95 0.98 65
accuracy 0.98 171
macro avg 0.99 0.98 0.98 171
weighted avg 0.98 0.98 0.98 171
Process finished with exit code 0
逻辑回归小结
应用:广告点击率预测、电商购物搭配推荐
优点:适合需要得到一个分类概率的场景
缺点:当特征空间很大时,逻辑回归的性能不是很好
(看硬件能力)
| . | 判别模型 | 生成模型 |
|---|---|---|
| . | 逻辑回归 | 朴素贝叶斯 |
| 解决问题 | 二分类 | 多分类问题 |
| 应用场景 | 癌症、广告点击率、电商购物搭配 | 文本分类 |
| 参数 | 正则化力度 | 没有 |
| 其他 | 判别模型(K-近邻、决策树、随机森林、神经网络) |
3. 聚类算法–K-means原理及案例
3.1 相关API
-
sklearn.cluster.KMeans(n_clusters=8,init=‘k-means++’)
- k-means聚类
- n_clusters:开始的聚类中心数量
- init:初始化方法,默认为’k-means ++’
- 返回值
- labels_:默认标记的类型,可以和真实值比较(不是值比较)
-
如果〖〗_ 小于0,说明_ 的平均距离大于最近的其他簇。
聚类效果不好 -
如果〖〗_ 越大,说明_ 的平均距离小于最近的其他簇。
聚类效果好 -
轮廓系数的值是介于 [-1,1] ,越趋近于1代表内聚度和分离度都相对较优
--------------------------------------------API------------------------------------------
-
sklearn.metrics.silhouette_score(X, labels)
计算所有样本的平均轮廓系数-
X:特征值
-
labels:被聚类标记的目标值
-
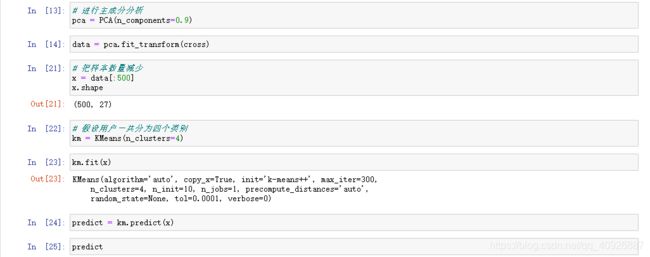
3.2 代码截图
聚类小结
4.小结
到这里,有关机器学习的知识已经学习完了,下面我会继续更新有关深度学习的相关内容。下面是有关机器学习步骤的思维导图,因为是pdf的格式,不方便直接分享,下面是下载链接:
机器学习第二天思维导图
机器学习第三天思维导图