二叉树的先序(preorder),中序(inorder),后序(postorder)的遍历(python)
本篇文章主要是总结二叉树的三种遍历方式,和相关leetcode算法题的解法。
跟线性的数据结构(矩阵,列表,队列,栈···)不同,树的遍历可以有不同的遍历方式。
先序遍历
遍历过程如下:
- 访问根节点,
- 访问当前节点的左子树,
- 访问当前节点的右子树。
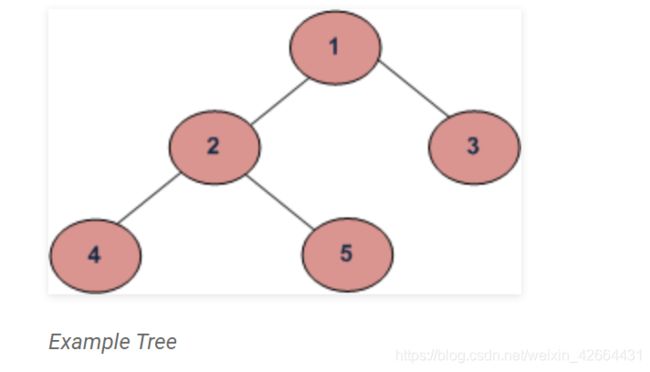
先序遍历的应用场景主要是对树进行复制。对于上面的树,先序遍历的顺序是1 2 4 5 3.
简单的用递归实现一下:
def printPreorder(root):
if root:
print(root.val),
printPreorder(root.left)
printPreorder(root.right)
中序遍历
遍历过程如下:
- 访问左子树,
- 访问根节点,
- 访问右子树。
中序遍历的应用场景主要是在二叉搜索树上,因为返回的节点值是递增的。也可以通过对中序遍历进行变形来返回递减的BST值。在上面的例子中,中序遍历的顺序应该是4 2 5 1 3.
def printInorder(root):
if root:
printInorder(root.left)
print(root.val),
printInorder(root.right)
此处应有一道leetcode算法题lol:
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal(https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/)
用栈的方法来做:
def inorderTraversal(root):
res = []
node_stack = []
p = root
while p or node_stack:
while p:
stack.append(p)
p = p.left
cur_node = node_stack.pop()
res.append(cur_node .val)
p = cur_node .right
return res
还有另外一道类似的题:
95. Binary Search Tree Iterator (https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-search-tree-iterator/),这道题的解决方法其实也是用栈来实现中序遍历。
因为题目相关,在这里简单提及一下迭代器的概念:
迭代是Python最强大的功能之一,是访问集合元素的一种方式。
迭代器是一个可以记住遍历的位置的对象。
迭代器对象从集合的第一个元素开始访问,直到所有的元素被访问完结束。迭代器只能往前不会后退。
迭代器有两个基本的方法:iter() 和 next()。
字符串,列表或元组对象都可用于创建迭代器
详细定义和例子可以查看https://www.runoob.com/python3/python3-iterator-generator.html
后序遍历
遍历过程如下:
- 访问左子树,
- 访问右子树,
- 访问根节点。
后序遍历可以用来对树进行删除。上面的例子用后序遍历的正确顺序是 4 5 2 3 1.。
def printPostorder(root):
if root:
printPostorder(root.left)
printPostorder(root.right)
print(root.val),
leetcode中相关的算法题:
- Binary Tree Postorder Traversal(https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/)
解法如下:
def postorderTraversal(root):
if not root:
return []
res = []
node_stack = [root]
while node_stack:
node = node_stack.pop()
if node.left :
node_stack.append(node.left)
if node.right:
node_stack.append(node.right)
res.append(node.val)
return res[::-1]
另外看到一个比较好的遍历方法,读起来非常清晰易理解且容易实现,来自@henry, 现在摘抄如下
在树的深度优先遍历中(包括前序、中序、后序遍历),递归方法最为直观易懂,但考虑到效率,我们通常不推荐使用递归。
栈迭代方法虽然提高了效率,但其嵌套循环却非常烧脑,不易理解,容易造成“一看就懂,一写就废”的窘况。而且对于不同的遍历顺序(前序、中序、后序),循环结构差异很大,更增加了记忆负担。
因此,我在这里介绍一种“颜色标记法”(瞎起的名字……),兼具栈迭代方法的高效,又像递归方法一样简洁易懂,更重要的是,这种方法对于前序、中序、后序遍历,能够写出完全一致的代码。
其核心思想如下:
使用颜色标记节点的状态,新节点为白色,已访问的节点为灰色。
如果遇到的节点为白色,则将其标记为灰色,然后将其右子节点、自身、左子节点依次入栈。
如果遇到的节点为灰色,则将节点的值输出。
使用这种方法实现的中序遍历如下;如要实现前序、后序遍历,只需要调整左右子节点的入栈顺序即可。
class Solution:
def inorderTraversal(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
WHITE, GRAY = 0, 1
res = []
stack = [(WHITE, root)]
while stack:
color, node = stack.pop()
if node is None: continue
if color == WHITE:
stack.append((WHITE, node.right))
stack.append((GRAY, node))
stack.append((WHITE, node.left))
else:
res.append(node.val)
return res
附上原链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/solution/yan-se-biao-ji-fa-yi-chong-tong-yong-qie-jian-ming/