Spring框架 Aop 及 Ioc详解
Aop 概念及原理
什么是AOP
-
面向切面编程(方面),利用 AOP 可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得
业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
-
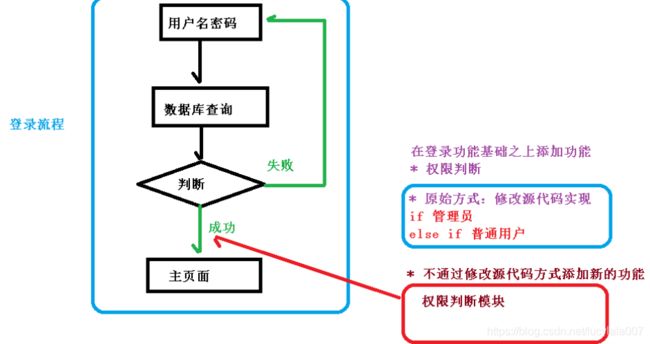
通俗描述:不通过修改源代码方式,在主干功能里面添加新功能
-
使用登录例子说明 AOP
AOP底层原理
Aop底层使用动态代理
有两种情况实现动态代理
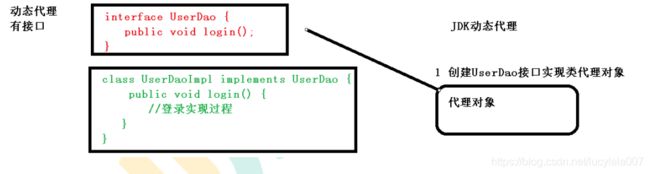
- 第一种 有接口情况,使用JDK动态代理
创建接口实现类代理对象增强类的方法
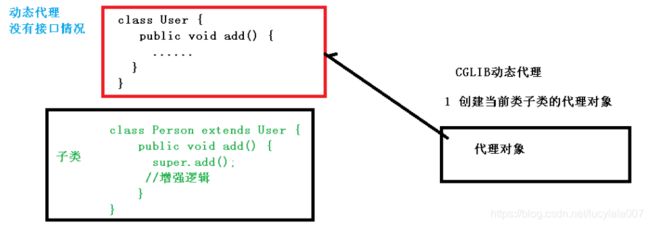
- 第二种 没有接口情况,使用CGLIB动态代理
创建子类的代理对象,增强类的方法
AOP(JDK动态代理)
使用JDK动态代理,使用Proxy类里面的方法创建袋里对象
调用newProxyInstance 方法
方法有三个参数:
第一参数,类加载器
第二参数,增强方法所在的类,这个类实现的接口,支持多个接口
第三参数,实现这个接口 InvocationHandler,创建代理对象,写增强的部分
编写JDK动态代理代码
1.创建接口,定义方法
/**
* @author Coner007
* @creat 2020-12-08-10:27
*/
public interface UserDao {
public int add(int a,int b);
public String update(String id);
}
2.创建接口实现类,实现方法
/**
* @author Coner007
* @creat 2020-12-08-10:28
*/
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) {
System.out.println("add 方法执行了");
return a+b;
}
@Override
public String update(String id) {
System.out.println("update 方法执行了");
return id;
}
}
3.使用Proxy类创建接口代理对象
package com.atguigu.spring5;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class JDKProxy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建接口实现类代理对象
Class[] interfaces = {UserDao.class};
// Proxy.newProxyInstance(JDKProxy.class.getClassLoader(), interfaces, new InvocationHandler() {
// @Override
// public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// return null;
// }
// });
UserDaoImpl userDao = new UserDaoImpl();
UserDao dao = (UserDao)Proxy.newProxyInstance(JDKProxy.class.getClassLoader(), interfaces, new UserDaoProxy(userDao));
int result = dao.add(1,2);
System.out.println("result: "+result);
}
}
//创建袋里对象代码
class UserDaoProxy implements InvocationHandler{
//1 把创建的是谁的代理对象,把谁传递过来
//有参数构造传递
private Object obj;
public UserDaoProxy(Object obj){
this.obj = obj;
}
//增强的逻辑
@Override
public Object invoke(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects) throws Throwable {
//方法之前
System.out.println("方法之前执行..." + method.getName()+ " :传递的参数..."+ Arrays.toString(objects));
//被增强的方法执行
Object res = method.invoke(obj,objects);
//方法之后
System.out.println("方法之后执行...." + obj);
return res;
}
}
AOP操作
1、Spring框架一般都是基于 AspectJ 实现 AOP 操作
(1) AspectJ 不是 Spring 组成部分,独立 AOP 框架,一般把 AspectJ 和 Spirng 框架一起使
用,进行 AOP 操作
2、基于 AspectJ 实现 AOP 操作
(1)基于 xml 配置文件实现
(2)基于注解方式实现(使用)
3、在项目工程里面引入AOP相关依赖
4、切入点表达式
(1)切入点表达式作用:知道对哪个类里面的哪个方法进行增强
(2)语法结构: execution([权限修饰符] [返回类型] [类全路径] [方法名称] (参数列表) )
举例 1:对 com.atguigu.dao.BookDao 类里面的 add 进行增强
execution(* com.atguigu.dao.BookDao.add(…))
举例 2:对 com.atguigu.dao.BookDao 类里面的所有的方法进行增强
execution(* com.atguigu.dao.BookDao.* (…))
举例 3:对 com.atguigu.dao 包里面所有类,类里面所有方法进行增强
execution(* com.atguigu.dao.. (…))
AOP操作(AspectJ注解)
创建类,在类里面定义方法
public class User {
public void add() {
System.out.println("add.......");
}
}
创建增强类(编写增强逻辑)
//增强的类
public class UserProxy {
public void before() {//前置通知
System.out.println("before......");
}
}
进行通知的配置
- 1、在 spring 配置文件中,开启注解扫描
- 2、使用注解创建 User 和 UserProxy 对象
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<context:component-scan basepackage="com.atguigu.spring5.aopanno">context:component-scan>
@Component
public class User {
}
@Component
@Aspect
public class UserProxy {
}
- 在 spring 配置文件中开启生成代理对象
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy>aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
配置不同类型的通知
- 在增强类的里面,在作为通知方法上面添加通知类型注解,使用切入点表达式配置,以及相同切入点提取
/**
* @author Coner007
* @creat 2020-12-08-14:40
*/
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(2)
public class UserProxy {
//相同切入点抽取
@Pointcut(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.spring5.aop_Anno.User.add(..))")
public void pointdemo(){
}
@Before(value = "pointdemo()")
public void before(){
System.out.println("before..........");
}
//后置通知(返回结果后通知,有异常就不通知)
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.spring5.aop_Anno.User.add(..))")
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("afterReturning.........");
}
//最终通知(方法结束之后通知)
@After(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.spring5.aop_Anno.User.add(..))")
public void after() {
System.out.println("after.........");
}
//异常通知
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.spring5.aop_Anno.User.add(..))")
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("afterThrowing.........");
}
//环绕通知
@Around(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.spring5.aop_Anno.User.add(..))")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕之前.........");
//被增强的方法执行
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
//方法有异常也不通知
System.out.println("环绕之后.........");
}
}
有多个增强类多同一个方法进行增强,设置增强类优先级
- 在增强类上面添加注解 @Order(数字类型值),数字类型值越小优先级越高
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(1)
public class PersonProxy
完全使用注解开发
- 创建配置类,不需要创建 xml 配置文件
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.atguigu"})
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
public class ConfigAop {
}
AOP 操作(AspectJ 配置文件)
1、创建两个类,增强类和被增强类,创建方法
2、在 spring 配置文件中创建两个类对象
3、在spring配置文件中创建两个类对象
<bean id="book" class="com.atguigu.spring5.aopxml.Book">bean>
<bean id="bookProxy" class="com.atguigu.spring5.aopxml.BookProxy">bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="p" expression="execution(*
com.atguigu.spring5.aopxml.Book.buy(..))"/>
<aop:aspect ref="bookProxy">
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="p"/>
aop:aspect>
aop:config>
IOC操作Bean管理
基于xml方式注人属性
DI:依赖注入,就是注入属性
第一种注入方式:使用set方法注入
- 创建类,定义属性和对应的set方法
public class Book {
//创建属性
private String bname;
private String bauthor;
//创建属性对应的 set 方法
public void setBname(String bname) {
this.bname = bname;
}
public void setBauthor(String bauthor) {
this.bauthor = bauthor;
}
}
- 在spring配置文件中配置对象创建,配置属性注入
<bean id="book" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Book">
<property name="bname" value="易筋经">property>
<property name="bauthor" value="达摩老祖">property>
bean>
第二种注入方式:使用有参构造进行注入
- 创建类,定义属性,创建属性对应有参数的构造方法
public class Orders {
//属性
private String oname;
private String address;
//有参数构造
public Orders(String oname,String address) {
this.oname = oname;
this.address = address;
}
}
- 在 spring 配置文件中进行配置
<bean id="orders" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Orders">
<constructor-arg name="oname" value="电脑">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="address" value="China">constructor-arg>
bean>
第三种注入方式:名称空间注入
- 使用 p 名称空间注入,可以简化基于 xml 配置方式 ,第一步 添加 p 名称空间在配置文件中
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
- 第二步 进行属性注入,在bean标签里面进行操作
<bean id="book" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Book" p:bname="九阳神功"
p:bauthor="无名氏">bean>
IOC 操作Bean管理(xml注入其他类型属性)
字面量
- null值
<property name="address">
<null/>
property>
- 属性值包括特殊符号
<property name="address">
<value>>]]>value>
property>
注入属性–外部bean
(1)创建两个类 service 类和 dao 类
(2)在 service 调用 dao 里面的方法
(3)在 spring 配置文件中进行配置
public class UserService {
//创建 UserDao 类型属性,生成 set 方法
private UserDao userDao;
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void add() {
System.out.println("service add...............");
userDao.update();
}
}
<bean id="userService" class="com.atguigu.spring5.service.UserService">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDaoImpl">property>
bean>
<bean id="userDaoImpl" class="com.atguigu.spring5.dao.UserDaoImpl">bean>
注入属性–内部Bean
(1)一对多关系:部门和员工
一个部门有多个员工,一个员工属于一个部门
部门是一,员工是多
(2)在实体类之间表示一对多关系,员工表示所属部门,使用对象类型属性进行表示
//部门类
public class Dept {
private String dname;
public void setDname(String dname) {
this.dname = dname;
}
}
//员工类
public class Emp {
private String ename;
private String gender;
//员工属于某一个部门,使用对象形式表示
private Dept dept;
public void setDept(Dept dept) {
this.dept = dept;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
}
(3)在 spring 配置文件中进行配置
<bean id="emp" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Emp">
<property name="ename" value="lucy">property>
<property name="gender" value="女">property>
<property name="dept">
<bean id="dept" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Dept">
<property name="dname" value="安保部">property>
bean>
property>
bean>
注入属性–级联赋值
- 第一种写法
<bean id="emp" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Emp">
<property name="ename" value="lucy">property>
<property name="gender" value="女">property>
<property name="dept" ref="dept">property>
bean>
<bean id="dept" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Dept">
<property name="dname" value="财务部">property>
bean>
- 第二种写法
!在这里插入图片描述
<bean id="emp" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Emp">
<property name="ename" value="lucy">property>
<property name="gender" value="女">property>
<property name="dept" ref="dept">property>
<property name="dept.dname" value="技术部">property>
bean>
<bean id="dept" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Dept">
<property name="dname" value="财务部">property>
bean>
注入属性–集合属性
- 创建类,定义数组、list、map、set 类型属性,生成对应 set 方法
public class Stu {
//1 数组类型属性
private String[] courses;
//2 list 集合类型属性
private List<String> list;
//3 map 集合类型属性
private Map<String,String> maps;
//4 set 集合类型属性
private Set<String> sets;
public void setSets(Set<String> sets) {
this.sets = sets;
}
public void setCourses(String[] courses) {
this.courses = courses;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public void setMaps(Map<String, String> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
}
- 在 spring 配置文件进行配置
<bean id="stu" class="com.atguigu.spring5.collectiontype.Stu">
<property name="courses">
<array>
<value>java 课程value>
<value>数据库课程value>
array>
property>
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>张三value>
<value>小三value>
list>
property>
<property name="maps">
<map>
<entry key="JAVA" value="java">entry>
<entry key="PHP" value="php">entry>
map>
property>
<property name="sets">
<set>
<value>MySQLvalue>
<value>Redisvalue>
set>
property>
bean>
- 在集合里面设置对象类型值
<bean id="course1" class="com.atguigu.spring5.collectiontype.Course">
<property name="cname" value="Spring5 框架">property>
bean>
<bean id="course2" class="com.atguigu.spring5.collectiontype.Course">
<property name="cname" value="MyBatis 框架">property>
bean>
<property name="courseList">
<list>
<ref bean="course1">ref>
<ref bean="course2">ref>
list>
把集合注入部分提取出来
- 在 spring 配置文件中引入名称空间 util
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
- 使用 util 标签完成 list 集合注入提取
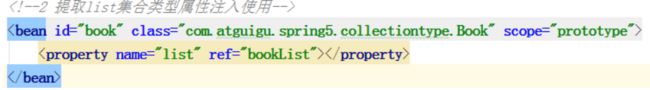
<util:list id="bookList">
<value>易筋经value>
<value>九阴真经value>
<value>九阳神功value>
util:list>
<bean id="book" class="com.atguigu.spring5.collectiontype.Book">
<property name="list" ref="bookList">property>
bean>
单实例还是多实例
如何设置单实例还是多实例
(1)在 spring 配置文件 bean 标签里面有属性(scope)用于设置单实例还是多实例
(2)scope 属性值
第一个值 默认值,singleton,表示是单实例对象
第二个值 prototype,表示是多实例对象
singleton 和 prototype 区别
第一 singleton 单实例,prototype 多实例
第二 设置 scope 值是 singleton 时候,加载 spring 配置文件时候就会创建单实例对象
设置 scope 值是 prototype 时候,不是在加载 spring 配置文件时候创建 对象,在调用
getBean 方法时候创建多实例对象
Bean生命周期
生命周期
- 从对象创建到对象销毁的过程
bean生命周期
- 通过构造器创建 bean 实例(无参数构造)
- 为 bean 的属性设置值和对其他 bean 引用(调用 set 方法)
- 调用 bean 的初始化的方法(需要进行配置初始化的方法)
- bean 可以使用了(对象获取到了)
- 当容器关闭时候,调用 bean 的销毁的方法(需要进行配置销毁的方法)
演示 bean 生命周期
public class Orders {
//无参数构造
public Orders() {
System.out.println("第一步 执行无参数构造创建 bean 实例");
}
private String oname;
public void setOname(String oname) {
this.oname = oname;
System.out.println("第二步 调用 set 方法设置属性值");
}
//创建执行的初始化的方法
public void initMethod() {
System.out.println("第三步 执行初始化的方法");
}
//创建执行的销毁的方法
public void destroyMethod() {
System.out.println("第五步 执行销毁的方法");
}
}
<bean id="orders" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Orders" initmethod="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod">
<property name="oname" value="手机">property>
bean>
@Test
public void testBean3() {
// ApplicationContext context =
// new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean4.xml");
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean4.xml");
Orders orders = context.getBean("orders", Orders.class);
System.out.println("第四步 获取创建 bean 实例对象");
System.out.println(orders);
//手动让 bean 实例销毁
context.close();
}
bean 的后置处理器,bean生命周期有七步
- 通过构造器创建 bean 实例(无参数构造)
- 为 bean 的属性设置值和对其他 bean 引用(调用 set 方法)
- 把 bean 实例传递 bean 后置处理器的方法 postProcessBeforeInitialization
- 调用 bean 的初始化的方法(需要进行配置初始化的方法)
- 把 bean 实例传递 bean 后置处理器的方法 postProcessAfterInitialization
- bean 可以使用了(对象获取到了)
- 当容器关闭时候,调用 bean 的销毁的方法(需要进行配置销毁的方法)
添加后置处理器效果
创建类,实现接口 BeanPostProcessor,创建后置处理器
public class MyBeanPost implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("在初始化之前执行的方法");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("在初始化之后执行的方法");
return bean;
}
}
<bean id="myBeanPost" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.MyBeanPost">bean>
引入外部属性文件配置数据库连接池
直接配置数据库信息
- 配置德鲁伊连接池
- 引入德鲁伊连接池依赖 jar 包
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver">property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/userDb">property>
<property name="username" value="root">property>
<property name="password" value="root">property>
bean>
引入外部属性文件配置数据库连接池
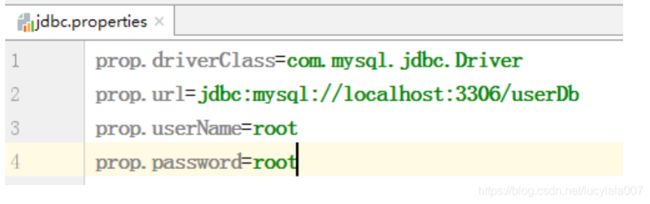
- 创建外部属性文件,properties 格式文件,写数据库信息
把外部 properties 属性文件引入到 spring 配置文件中
- 引入 context 名称空间
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
在 spring 配置文件使用标签引入外部属性文件
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${prop.driverClass}">property>
<property name="url" value="${prop.url}">property>
<property name="username" value="${prop.userName}">property>
<property name="password" value="${prop.password}">property>
bean>
IOC 操作 Bean 管理(基于注解方式)
Spring 针对 Bean 管理中创建对象提供注解
(1)@Component
(2)@Service
(3)@Controller
(4)@Repository
上面四个注解功能是一样的,都可以用来创建 bean 实例
基于注解方式实现对象创建
- 第一步----引入依赖
- 第二步----开启组件扫描
- 第三步----创建类,在类上面添加创建对象注解
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu">context:component-scan>
//在注解里面 value 属性值可以省略不写,
//默认值是类名称,首字母小写
//UserService -- userService
@Component(value = "userService") //
开启组件扫描细节配置
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu" use-defaultfilters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation"
expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
context:component-scan>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation"
expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
context:component-scan>
基于注解方式实现属性注入
(1)@Autowired:根据属性类型进行自动装配
第一步 把 service 和 dao 对象创建,在 service 和 dao 类添加创建对象注解
第二步 在 service 注入 dao 对象,在 service 类添加 dao 类型属性,在属性上面使用注解
@Service
public class UserService {
//定义 dao 类型属性
//不需要添加 set 方法
//添加注入属性注解
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
public void add() {
System.out.println("service add.......");
userDao.add();
}
}
(2)@Qualifier:根据名称进行注入
这个@Qualifier 注解的使用,和上面@Autowired 一起使用
//定义 dao 类型属性
//不需要添加 set 方法
//添加注入属性注解
@Autowired //根据类型进行注入
@Qualifier(value = "userDaoImpl1") //根据名称进行注入
private UserDao userDao;
//(3)@Resource:可以根据类型注入,可以根据名称注入
//@Resource //根据类型进行注入
@Resource(name = "userDaoImpl1") //根据名称进行注入
private UserDao userDao;
//(4)@Value:注入普通类型属性
@Value(value = "abc")
private String name;
完全注解开发
(1)创建配置类,替代 xml 配置文件
@Configuration //作为配置类,替代 xml 配置文件
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.atguigu"})
public class SpringConfig {
}
(2)编写测试类
@Test
public void testService2() {
//加载配置类
ApplicationContext context
= new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService",
UserService.class);
System.out.println(userService);
userService.add();
}
//不需要添加 set 方法
//添加注入属性注解
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
public void add() {
System.out.println(“service add…”);
userDao.add();
}
}
(2)@Qualifier:根据名称进行注入
这个@Qualifier 注解的使用,和上面@Autowired 一起使用
```java
//定义 dao 类型属性
//不需要添加 set 方法
//添加注入属性注解
@Autowired //根据类型进行注入
@Qualifier(value = "userDaoImpl1") //根据名称进行注入
private UserDao userDao;
//(3)@Resource:可以根据类型注入,可以根据名称注入
//@Resource //根据类型进行注入
@Resource(name = "userDaoImpl1") //根据名称进行注入
private UserDao userDao;
//(4)@Value:注入普通类型属性
@Value(value = "abc")
private String name;
完全注解开发
(1)创建配置类,替代 xml 配置文件
@Configuration //作为配置类,替代 xml 配置文件
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.atguigu"})
public class SpringConfig {
}
(2)编写测试类
@Test
public void testService2() {
//加载配置类
ApplicationContext context
= new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService",
UserService.class);
System.out.println(userService);
userService.add();
}
事务操作
(1)事务添加到三层结构里的Service层
(2)在Spring中进行事务管理操作有两种方式
编程式事务管理 和 声明式事务管理(使用)
(3)声明式事务管理
基于注解方式(使用)
基于xml配置文件方式
(4)在Spring中进行声明式事务管理,底层使用AOP原理
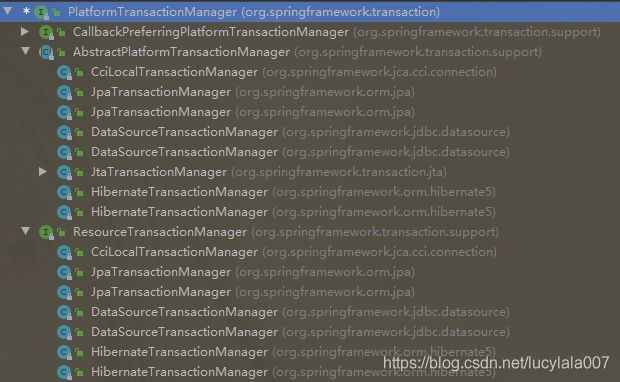
(5)Spring事务管理API
提供一个接口,代表事务管理器,这个接口针对不同的框架提供不同的实现类
注解声明式事务管理
1、在spring配置文件配置事务管理器
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
2、在Springp配置文件引入名称空间 tx ,开启事务注解
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager">tx:annotation-driven>
3、在service类上面(或者service类里面方法上面)添加事务注解
(1)@Transactional,这个注解添加到类上面,也可以添加方法上面
(2)如果把这个注解添加类上面,这个类里面所有的方法都添加事务
(3)如果把这个注解添加方法上面,为这个方法添加事务
@Service
@Transactional
public class UserService {
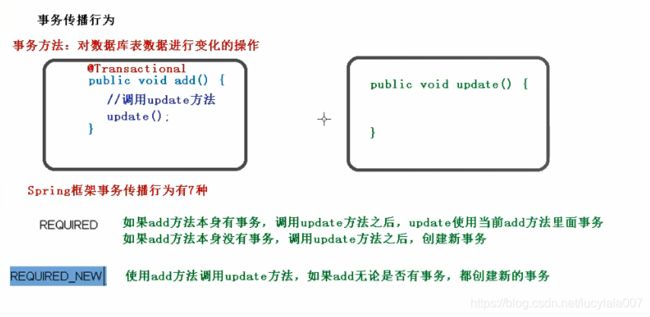
多事务方法直接进行调用,这个过程事务是如何进行管理的
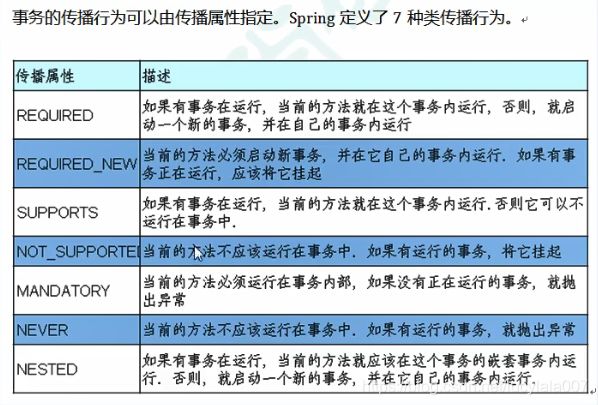
事务的传播行为的七种方式
ioslation: 事务隔离级别
(1)事务有特性成为隔离性,多事务操作之间不会产生影响。不考虑隔离性产生很多问题
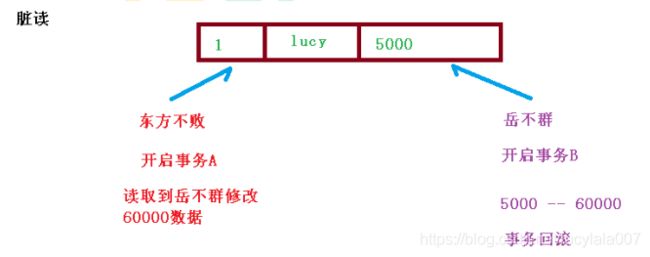
(2)有三个读问题:脏读、不可重复读、虚(幻)读
(3)脏读:一个未提交事务读取到另一个未提交事务的数据
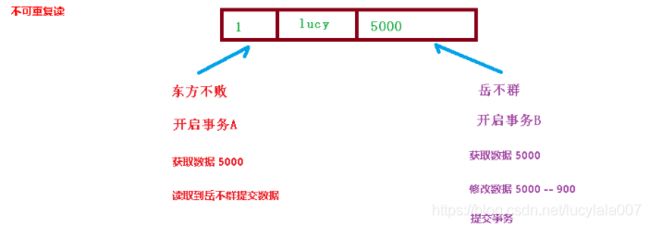
(4)不可重复读:一个未提交事务读取到另一提交事务修改数据
(5)虚读:一个未提交事务读取到另一提交事务添加数据
(6)解决:通过设置事务隔离级别,解决读问题
脏读
不可重复读
幻读
READ UNCOMMITTED(读未提交)
有
有
有
READ COMMITTED(读已提交)
无
有
有
REPEATABLE READ(可重复读)
无
无
有
SERIALIZABLE (串行化)
无
无
无
@Service
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ)
public class UserService {
timeout: 超过时间
(1)事务需要在一定时间内进行提交,如果不提交进行回滚
(2)默认值是-1 ,设置时间以秒单位进行计算
readOnly: 是否只读
(1)读:查询操作,写:添加修改删除操作
(2)readOnly默认值false,表示可以查询,可以添加修改删除操作
(3)设置readOnly值是true,设置成true之后,只能查询
rollbackFor: 回滚
(1)设置出现哪些异常进行事务回滚
noRollbackFor: 不会滚
(1)设置出现哪些异常不进行事务回滚
XML声明式事务管理
在Spring配置文件中进行配置
- 1、配置事务管理器
- 2、配置通知
- 3、配置切入点和切面
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<tx:advice id="txadvice">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="accountMoney" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(* com.atguigu.spring5.service.UserService.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txadvice" pointcut-ref="pt"/>
aop:config>
完全注解声明式事务管理
创建配置类,使用配置类代替xml配置文件
@Configuration //配置类
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.atguigu") //组件扫描
@EnableTransactionManagement //开启事务
public class TxConfig {
//创建数据库连接池
@Bean
public DruidDataSource getDruidDataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql:///user_db");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
return dataSource;
}
//创建JdbcTemplate对象
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
//到ioc容器中根据类型找到dataSource
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
//注入dataSource
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
//创建事务管理器
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager getDataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
}