Apache Hive
1 Hive 引言
1.1 简介
hive是facebook开源,并捐献给了apache组织,作为apache组织的顶级项目(hive.apache.org)。 hive是一个基于大数据技术的数据仓库(DataWareHouse)技术,主要是通过将用户书写的SQL语句翻译成MapReduce代码,然后发布任务给MR框架执行,完成SQL 到 MapReduce的转换。可以将结构化的数据文件映射为一张数据库表,并提供类SQL查询功能。
总结
- Hive是一个数据仓库
- Hive构建在HDFS上,可以存储海量数据。
- Hive允许程序员使用SQL命令来完成数据的分布式计算,计算构建在yarn之上。(Hive会将SQL转化为MR操作)
优点:
简化程序员的开发难度,写SQL即可,避免了去写mapreduce,减少开发人员的学习成本缺点:
延迟较高(MapReduce本身延迟,Hive SQL向MapReduce转化优化提交),适合做大数据的离线处理(TB PB级别的数据,统计结果延迟1天产出)
Hive不适合场景:
1:小数据量
2:实时计算
- 数据库 DataBase
- 数据量级小,数据价值高
- 数据仓库 DataWareHouse
- 数据体量大,数据价值低
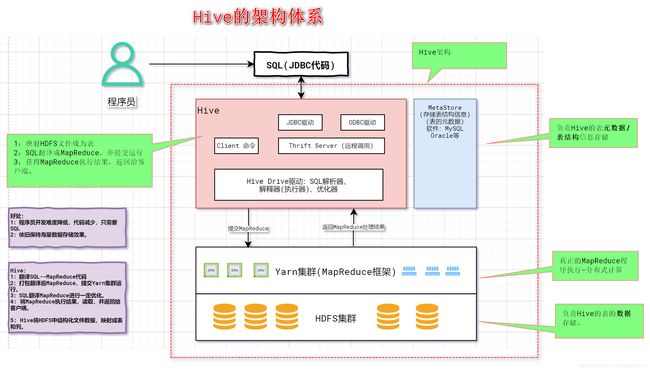
2 Hive 的架构
2.1 简介
HDFS:用来存储hive仓库的数据文件
Yarn:用来完成hive的HQL转化的MR程序的执行
MetaStore:保存管理hive维护的元数据
Hive:用来通过HQL的执行,转化为MapReduce程序的执行,从而对HDFS集群中的数据文件进行统计。
2.2 架构图
3 Hive的安装
# 步骤
1. HDFS(Hadoop2.9.2)
2. Yarn(Hadoop2.9.2)
3. MySQL(5.6)
4. Hive(1.2.1)
虚拟机内存设置至少1G
3.1 安装Mysql
准备工作:将mysql_rpm文件夹上传到/opt/modules目录下
#1. 安装vim
yum install vim
解释:为什么要安装vim,因为mysql本身依赖perl,vim的安装可以解决这些依赖的安装
#2. 卸载mysql自带的mariabd数据库
rpm -e --nodeps mariadb-libs-5.5.56-2.el7.x86_64
解释:centos7自带的mariabd数据库和我们要安装的mysql有冲突
#3. 进入/opt/modules/mysql_rpm文件夹,使用rpm命令安装
rpm -ivh perl-*
rpm -ivh net-tools-2.0-0.22.20131004git.el7.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh mysql-community-*
或者rpm -ivh *
#4. 启动mysql服务
systemctl start mysqld
解释:mysql数据库安装成功他的服务名称叫做mysqld
#5. 登录mysql数据库
#6. 设置root用户的密码和允许远程访问
操作mysql数据库
3.2 安装Hadoop
# 配置hdfs和yarn的配置信息
[root@hive40 ~]# jps
1651 NameNode
2356 NodeManager
2533 Jps
1815 DataNode
2027 SecondaryNameNode
2237 ResourceManager
3.3 安装Hive
3.3.1 上传hive
3.3.2 解压hive
[root@hadoop ~]# tar -zxvf apache-hive-1.2.1-bin.tar.gz -C /opt/installs
[root@hadoop ~]# mv apache-hive-1.2.1-bin hive1.2.1
3.3.3 配置环境变量
export HIVE_HOME=/opt/installs/hive1.2.1
export PATH=$PATH:$HIVE_HOME/bin
3.3.4 加载系统配置生效
[root@hadoop ~]# source /etc/profile
3.3.5 配置hive
hive-env.sh
拷贝一个hive-env.sh:[root@hadoop10 conf]# cp hive-env.sh.template hive-env.sh
# 配置hadoop目录
HADOOP_HOME=/opt/installs/hadoop2.9.2/
# 指定hive的配置文件目录
export HIVE_CONF_DIR=/opt/installs/hive1.2.1/conf/
hive-site.xml
拷贝得到hive-site.xml:[root@hadoop10 conf]# cp hive-default.xml.template hive-site.xml
<configuration>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURLname>
<value>jdbc:mysql://hadoop10:3306/hivevalue>
property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverNamename>
<value>com.mysql.jdbc.Drivervalue>
property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserNamename>
<value>rootvalue>
property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPasswordname>
<value>rootvalue>
property>
configuration>
登录mysql创建hive数据库(使用命令行创建)
create database hive
复制mysql驱动jar到hive的lib目录中
3.4 启动
3.4.1. 启动 hadoop
启动hadoop
# 启动HDFS start-dfs.sh # 启动yarn start-yarn.sh
3.4.2. 初始化hive
初始化元数据:schematool -dbType mysql -initSchema初始化mysql的hivedatabase中的信息。
3.4.3 Hive启动(本地模式)
# 本地模式启动 【管理员模式】
# 启动hive服务器,同时进入hive的客户端。只能通过本地方式访问。
[root@hadoop10 ~]# hive
Logging initialized using configuration in jar:file:/opt/installs/hive1.2.1/lib/hive-common-1.2.1.jar!/hive-log4j.properties
hive>
# 1. 客户端操作之dfs命令
1. 查看dfs中的文件。
dfs -ls /;
2. 查看dfs中 /user 下的文件
dfs -ls /user;
3. 以递归的方式,查看/user下的所有文件
dfs -lsr /user;
# 2.客户端操作之HQL(Hive Query language)
# 1.查看数据库
hive> show databases;
# 2. 创建一个数据库
hive> create database abc;
# 3. 查看database
hive> show databases;
# 4. 切换进入数据库
hive> use abc;
# 5.查看所有表
hive> show tables;
# 6.创建一个表
hive> create table t_user(id string,name string,age int);
# 7. 添加一条数据(转化为MR执行--不让用,仅供测试)
hive> insert into t_user values('1001','zhangsan',20);
# 8.查看表结构
hive> desc t_user;
# 9.查看表的schema描述信息。(表元数据,描述信息)
hive> show create table t_user;
# 明确看到,该表的数据存放在hdfs中。
# 10 .查看数据库结构
hive> desc database abc;
# 11.查看当前库
hive> select current_database();
# 12 其他sql
select * from t_user;
select count(*) from t_user; (Hive会启动MapReduce)
select * from t_user order by id;
3.4.4 Hive启动(客户端)
# 启动hive的服务器,可以允许远程连接方式访问。
// 前台启动
[root@hadoop10 ~]# hiveserver2
// 后台启动
[root@hadoop10 ~]# hiveserver2 &
- beeline客户端(前台启动)
# 启动客户端
[root@hadoop10 ~]# beeline
beeline> !connect jdbc:hive2://hadoop10:10000
回车输入mysql用户名
回车输入mysql密码
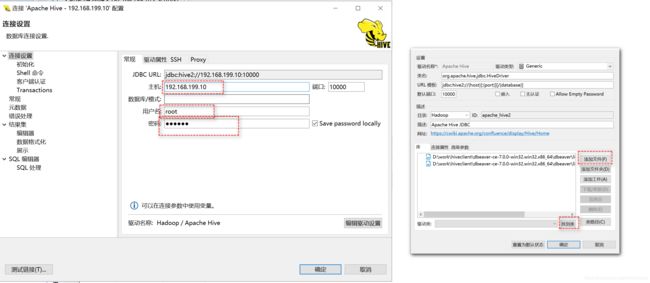
- DBeaver客户端(图形化界面)(后台启动)
# 1: 解压
# 2: 准备dbeaver连接hive的依赖jar
hadoop-common-2.9.2
hive-jdbc-1.2.1-standalone
# 3:启动
3.5 JDBC
# 导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hivegroupId>
<artifactId>hive-jdbcartifactId>
<version>1.2.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoopgroupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-commonartifactId>
<version>2.9.2version>
dependency>
# JDBC操作Hive
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BasicConfigurator.configure();//开启日志
//加载hive驱动
Class.forName("org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver");
//连接hive数据库
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:hive2://hadoop10:10000/abc","root","root");
String sql = "select * from t_user1";
PreparedStatement pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet rs = pstm.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
String id = rs.getString("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
System.out.println(id+":"+name+":"+age);
}
rs.close();
pstm.close();
conn.close();
}
3.6 数据类型
数据类型(
primitive,array,map,struct)
- primitive(原始类型):
hive数据类型 字节 备注 tinyint 1 java-byte 整型 smallint 2 java-short 整型 int 4 java-int 整型 bigint 8 java-long 整型 boolean 布尔 float 4 浮点型 double 8 浮点型 string 字符串 无限制 varchar 字符串 例:varchar(20) 最长20 char 字符串 例:char(20) 定长20 binary 二进制类型 timestamp 时间戳类型 date 日期类型 - array(数组类型):
# 建表 create table t_tab( score array<float>, 字段名 array<泛型> ); - map(key-value类型):MAP
# 建表 create table t_tab( score map<string,float> ); - struct(结构体类型):STRUCT
# 建表 create table t_tab( info struct<name:string,age:int,sex:char(1)>, 列名 struct<属性名:类型,属性名:类型> );
4 Hive数据导入
4.1 自定义分隔符
- 分隔符设计
| 分隔符 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| , | 用来表示每个列的值之间分隔符。 fields |
| - | 用来分割array中每个元素,以及struct中的每个值,以及map中kv与kv之间。 collection items |
| | | 用来分割map的k和v之间 map keys |
| \n | 每条数据分割使用换行。 lines |
- 建表
create table t_person(
id string,
name string,
salary double,
birthday date,
sex char(1),
hobbies array<string>,
cards map<string,string>,
addr struct<city:string,zipCode:string>
) row format delimited
fields terminated by ','--列的分割
collection items terminated by '-'--数组 struct的属性值于值之间 map的kv和kv之间
map keys terminated by '|'-- map的k与v的分割
lines terminated by '\n';--行数据之间的分割
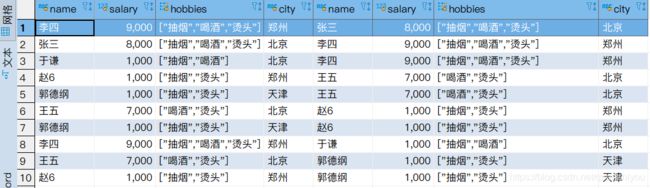
- 测试数据
1,张三,8000.0,2019-9-9,1,抽烟-喝酒-烫头,123456|中国银行-22334455|建设银行,北京-10010
2,李四,9000.0,2019-8-9,0,抽烟-喝酒-烫头,123456|中国银行-22334455|建设银行,郑州-45000
3,王五,7000.0,2019-7-9,1,喝酒-烫头,123456|中国银行-22334455|建设银行,北京-10010
4,赵6,100.0,2019-10-9,0,抽烟-烫头,123456|中国银行-22334455|建设银行,郑州-45000
5,于谦,1000.0,2019-10-9,0,抽烟-喝酒,123456|中国银行-22334455|建设银行,北京-10010
6,郭德纲,1000.0,2019-10-9,1,抽烟-烫头,123456|中国银行-22334455|建设银行,天津-20010
- 导入数据
# 在hive命令行中执行
-- local 代表本地路径,如果不写,代表读取文件来自于HDFS
-- overwrite 是覆盖的意思,可以省略。
load data [local] inpath ‘/opt/datas/person1.txt’ [overwrite] into table t_person;
# 本质上就是将数据上传到hdfs中(数据是受hive的管理)
4.2 JSON分割符
jar添加和数据导入,建表,在beeline里面操作
- 数据
{"id":1,"name":"zhangsan","sex":0,"birth":"1991-02-08"}
{"id":2,"name":"lisi","sex":1,"birth":"1991-02-08"}
- 添加格式解析器的jar(本地客户端命令)
# 在hive的客户端执行(临时添加jar到hive的classpath,有效期本链接内)
add jar /opt/installs/hive1.2.1/hcatalog/share/hcatalog/hive-hcatalog-core-1.2.1.jar
# 补充:永久添加,Hive服务器级别有效。
1. 将需要添加到hive的classpath的jar,拷贝到hive下的auxlib目录下,
2. 重启hiveserver即可。
- 建表
create table t_person2(
id string,
name string,
sex char(1),
birth date
)row format serde 'org.apache.hive.hcatalog.data.JsonSerDe';
- 加载文件数据(本地客户端命令)
# 注意:导入的json数据dbeaver看不了。(因为导入后的表本质上就是该json文件。)
load data local inpath '/opt/person.json' into table t_person2;
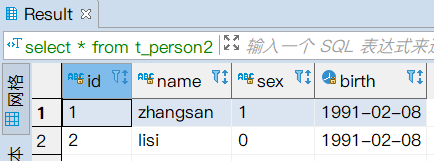
- 查看数据
select * from t_person2;
4.3 正则分隔符
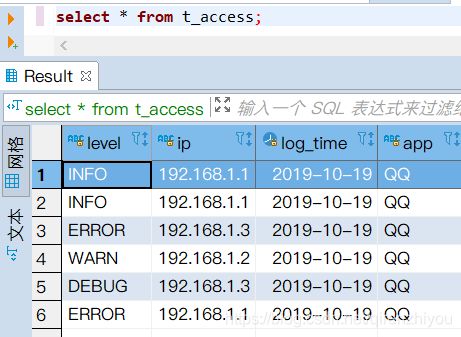
数据:access.log
INFO 192.168.1.1 2019-10-19 QQ com.abc.service.IUserService#login
INFO 192.168.1.1 2019-10-19 QQ com.abc.service.IUserService#login
ERROR 192.168.1.3 2019-10-19 QQ com.abc.service.IUserService#save
WARN 192.168.1.2 2019-10-19 QQ com.abc.service.IUserService#login
DEBUG 192.168.1.3 2019-10-19 QQ com.abc.service.IUserService#login
ERROR 192.168.1.1 2019-10-19 QQ com.abc.service.IUserService#register
建表语句
create table t_access(
level string,
ip string,
log_time date,
app string,
service string,
method string
)row format serde 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.RegexSerDe'--正则表达式的格式转化类
with serdeproperties("input.regex"="(.*)\\s(.*)\\s(.*)\\s(.*)\\s(.*)#(.*)");--(.*) 表示任意字符 \\s表示空格
导入数据
load data local inpath '/opt/access.log' into table t_access;
查看数据
select * from t_access;
5 HQL高级
SQL关键词执行顺序
from > where > group by > having>select>order by>limit注意:sql一旦出现group by,后续的关键词能够操作字段只有(分组依据字段,组函数处理结果)
5.1 HQL高级
5.1.1 条件查询
# 0. 各个数据类型的字段访问(array、map、struct)
select name,salary,hobbies[1],cards['123456'],addr.city from t_person;
# 1. 条件查询:= != >= <=
select * from t_person where addr.city='郑州';
# 2. and or between and
select * from t_person where salary>5000 and array_contains(hobbies,'抽烟');
# 3. order by[底层会启动mapreduce进行排序]
select * from t_person order by salary desc;
# 4. limit(hive没有起始下标)
select * from t_person sort by salary desc limit 5;
# 5. 去重
select distinct addr.city from t_person;
select distinct(addr.city) from t_person;
5.1.2 表连接查询
select ...
from table1 t1 left join table2 t2 on 条件
where 条件
group by
having
1. 查询性别不同,但是薪资相同的人员信息。
select
t1.name,t1.sex,t1.salary,
t2.name,t2.sex,t2.salary
from t_person t1 join t_person t2 on t1.salary = t2.salary
where t1.sex != t2.sex;
2. 查询拥有相同第一爱好且来自不同城市的人信息。
SELECT
t1.name,t1.salary,t1.hobbies,t1.addr.city,
t2.name,t2.salary,t2.hobbies,t2.addr.city
from t_person t1 join t_person t2 on t1.hobbies[0]=t2.hobbies[0]
where t1.addr.city != t2.addr.city;
5.1.3 单行函数
# 单行函数(show functions) 查看所有函数
-- 查看hive系统所有函数
show functions;
1. array_contains(列,值);
select name,hobbies from t_person where array_contains(hobbies,'喝酒');
2. length(列)
select length('123123');
3. concat(列,列)
select concat('123123','aaaa');
4. to_date('1999-9-9')
select to_date('1999-9-9');
5. year(date),month(date),
6. date_add(date,数字)
select name,date_add(birthday,-9) from t_person;
5.1.4 组函数
# 组函数
max、min、sum、avg、count等。
select max(salary) from t_person where addr.city='北京';
select count(id) from t_person;
5.1.5 炸裂函数
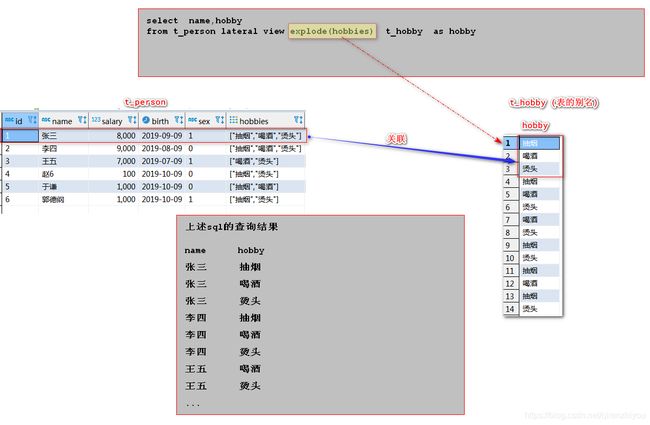
# 炸裂函数(集合函数)
-- 查询所有的爱好,
select explode(hobbies) as hobby from t_person
# lateral view
-- 为指定表,的边缘拼接一个列。(类似表连接)
-- lateral view:为表的拼接一个列(炸裂结果)
-- 语法:from 表 lateral view explode(数组字段) 别名 as 字段名;
-- 查看id,name,爱好。一个爱好一条信息。
select id,name,hobby
from t_person lateral view explode(hobbies) t_hobby as hobby
5.1.6 分组
--分组
--1. group by(查看各个城市的均薪)
select addr.city,avg(salary) from t_person group by addr.city;
--2. having(查看平均工资超过5000的城市和均薪)
select addr.city,avg(salary) from t_person group by addr.city having avg(salary)>5000;
--3. 统计各个爱好的人数
--explod+lateral view
select hobby,count( * )
from t_person lateral view explode(hobbies) t_hobby as hobby
group by hobby;
--4. 统计最受欢迎的爱好TOP1
SELECT hb,count( * ) num
from t_person lateral view explode(hobbies) h as hb
group by hb
order by num desc limit 1;
5.1.7 子查询
# 子查询
-- 统计有哪些爱好,并去重。
select distinct t.hobby from
(select explode(hobbies) as hobby from t_person ) t
5.1.8 行列相转
# 案例表和数据
--## 表(电影观看日志)
create table t_visit_video (
username string,
video_name string,
video_date date
)row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
--## 数据:豆瓣观影日志数据。(用户观影日志数据 按照天存放 1天一个日志文件)
张三,大唐双龙传,2020-03-21
李四,天下无贼,2020-03-21
张三,神探狄仁杰,2020-03-21
李四,霸王别姬,2020-03-21
李四,霸王别姬,2020-03-21
王五,机器人总动员,2020-03-21
王五,放牛班的春天,2020-03-21
王五,盗梦空间,2020-03-21
# collect_list(组函数)
作用:对分组后的,每个组的某个列的值进行收集汇总。
语法:select collect_list(列) from 表 group by 分组列;
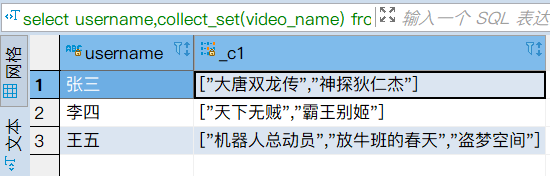
select username,collect_list(video_name) from t_visit_video group by username;
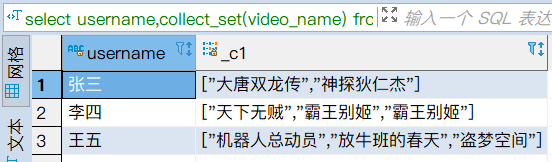
# collect_set(组函数)
作用:对分组后的,每个组的某个列的值进行收集汇总,并去掉重复值。
语法:select collect_set(列) from 表 group by 分组列;
select username,collect_set(video_name) from t_visit_video group by username;
# concat_ws(单行函数)
作用:如果某个字段是数组,对该值得多个元素使用指定分隔符拼接。
select id,name,concat_ws(',',hobbies) from t_person;
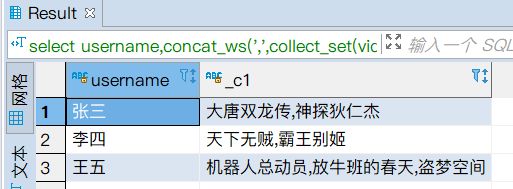
--# 将t_visit_video数据转化为如下图效果
--统计每个人,2020-3-21看过的电影。
select username,concat_ws(',',collect_set(video_name)) from t_visit_video group by username;
5.2 全排序和局部排序
5.2.1 全局排序
# 全局排序
语法:select * from 表 order by 字段 asc|desc;
-- 按照薪资降序排序
select * from t_person order by salary desc;
5.2.2 局部排序
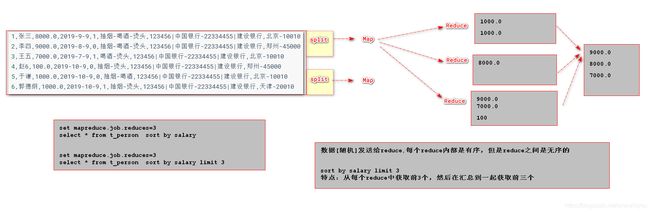
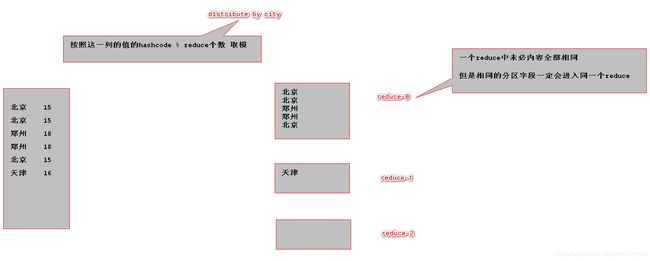
# 局部排序(分区排序)
概念:启动多个reduceTask,对数据进行排序(预排序),局部有序。
局部排序关键词 sort by
默认reducetask个数只有1个,所有分区也只有一个。所以默认和全排序效果一样。
语法:select * from 表 distribute by 分区字段 sort by 字段 asc|desc;
-- 1. 开启reduce个数
-- 设置reduce个数
set mapreduce.job.reduces = 3;
-- 查看reduce个数
set mapreduce.job.reduces;
-- 2. 使用sort by排序 +distribute by 指定分区列。(使用distribute后select就只能*)
-- distribute By:设置分区字段,可以将同一个分区的数据发送到同一个reduce
select * from t_person distribute by addr.city sort by salary desc;
5.2.3 排序总结
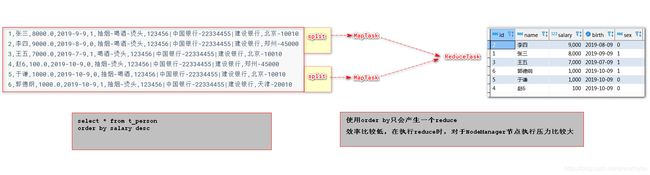
order by:全局排序,只有一个reducer(多个reducer无法保证全局有序),效率不高,对于执行reduce的节点压力较大sort by:局部排序,其在数据进入reducer前完成排序distribute by:分区,按照指定的字段对数据进行划分输出到不同的reduce中- cluster by:除了具有 distribute by 的功能外还兼具 sort by 的功能

6 Hive表分类
4.1 管理表
由Hive全权管理的表所谓的管理表指hive是否具备数据的管理权限,如果该表是管理表,当用户删除表的同时,hive也会将表所对应的数据删除,因此在生产环境下,为了防止误操作,带来数据损失,一般考虑将表修改为非管理表-外部表
总结:Hive的管理,表结构,hdfs中表的数据文件,都归Hive全权管理。---- hive删除管理表,HDFS对应文件也会被删除。
缺点:数据不安全。
4.2 外部表
引用映射HDFS数据作为表管理,但无法删除数据外部表和管理表最大的区别在于删除外部表,只是将MySQL中对应该表的元数据信息删除,并不会删除hdfs上的数据,因此外部表可以实现和第三方应用共享数据。在创建外表的时候需要添加一个关键字"external"即可。create external xxx()…
# 创建外部表
1. 准备数据文件personout.txt
2. 上传至hdfs中,该数据文件必须被放在一个单独的文件夹内。该文件夹内的数据文件被作为表数据
3. 创建表: create external location
在最后使用location 指定hdfs中数据文件所在的文件夹即可。
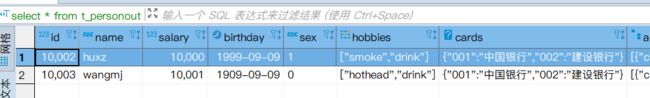
create external table t_personout(
id int,
name string,
salary double,
birthday date,
sex char(1),
hobbies array<string>,
cards map<string,string>,
addr struct<city:string,zipCode:string>
)row format delimited
fields terminated by ',' --列的分割
collection items terminated by '-'--数组 struct的属性 map的kv和kv之间
map keys terminated by '|'
lines terminated by '\n'
location '/file';
4. 查询表数据
4.3 分区表
将表按照某个列(字段)的一定规则进行分区存放,减少海量数据情况下的数据检索范围,提高查询效率;
应用:依据实际业务功能,拿查询条件的列作为分区列来进行分区,缩小MapReduce的扫描范围,提高MapReduce的执行效率
总结:
table中的多个分区的数据是分区管理
1:删除数据按照分区删除。如果删除某个分区,则将分区对应的数据也删除(外部表,数据删除,数据文件依然在)。
2:查询统计,多个分区被一个表管理起来。
select * from 表 where 分区字段为条件。
4.3.1 创建分区表
数据源文件
# 文件"bj.txt" (china bj数据)
1001,张三,1999-1-9,1000.0
1002,李四,1999-2-9,2000.0
1008,孙帅,1999-9-8,50000.0
1010,王宇希,1999-10-9,10000.0
1009,刘春阳,1999-9-9,10.0
# 文件“tj.txt” (china tj数据)
1006,郭德纲,1999-6-9,6000.0
1007,胡鑫喆,1999-7-9,7000.0
建表
create external table t_user_part(
id string,
name string,
birth date,
salary double
)partitioned by(country string,city string)--指定分区列,按照国家和城市分区。
row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
lines terminated by '\n';
创建分区表并导入数据
# 导入china和bj的数据
load data local inpath "/opt/bj.txt" into table t_user_part partition(country='china',city='bj');
# 导入china和heb的数据
load data local inpath "/opt/tj.txt" into table t_user_part partition(country='china',city='tj');
查看分区信息
show partitions t_user_part;
使用分区查询:本质上只要查询条件在存在分区列
select * from t_user_part where city = 'bj'
删除分区信息会连同分区数据一块删除
外部分区表,删除后,hive不管理数据,但是数据文件依然存在
alter table t_user_part drop partition(country='china',city='bj');
添加分区
alter table t_user_part add partition(country='china',city='heb') location '/file/t_user_part/heb';
# 表分类
1. 管理表
hive中table数据和hdfs数据文件都是被hive管理。
2. 外部表--常用--hdfs文件安全。
hive的table数据,如果删除hive中的table,外部hdfs的数据文件依旧保留。
3. 分区表--重要。
将table按照不同分区管理。
好处:如果where条件中有分区字段,则Hive会自动对分区内的数据进行检索(不再扫描其他分区数据),提高hive的查询效率。
7 Hive自定义函数
7.1 内置函数
# 查看hive内置函数
show functions;
# 查看函数描述信息
desc function max;
7.2 自定义函数
UDF(User-Defined-Function):用户自定义函数(单行函数),输入一个数据然后产生一个数据;
UDAF(User-Defined Aggregation Function):用户自定义聚合函数(组函数),多个输入数据然后产生一个输出参数;
UDTF(User-Defined Table-generating Function):用户自定义表生成函数(炸裂函数),输入一行数据生成N行数据
流程:
- 自定义Java类并继承org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.UDF;
- 覆写evaluate函数,evaluate函数支持重载;
- 把程序打包放到hive所在服务器;
- 进入hive客户端,添加jar包;
- 创建关联到Java类的Hive函数;
- Hive命令行中执行查询语句:select id, 方法名(name) from 表名——得出自定义函数输出的结果
用户定义函数-UDF:user-defined function操作作用于单个数据行,并且产生一个数据行作为输出。大多数函数都属于这一类(比如数学函数和字符串函数)。
# 0. 导入hive依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hivegroupId>
<artifactId>hive-execartifactId>
<version>1.2.1version>
dependency>
# 1.定义一个类继承UDF
1. 必须继承UDF
2. 方法名必须是evaluate
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.Description;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.UDF;
@Description(name = "hello",value = "hello(str1,str2)-用来获取 '你好 str1,str2 有美女吗?'的结果"//中文解释会有乱码,最好写英文)
public class HelloUDF extends UDF {
// 方法名必须交evaluate
public String evaluate(String s1,String s2){
return "你好,"+s1+","+s2+"有美女吗?";
}
}
# 2. 配置maven打包环境,打包jar
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
properties>
<build>
<finalName>funcHellofinalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.pluginsgroupId>
<artifactId>maven-jar-pluginartifactId>
<version>2.4version>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>**/function/**include>
includes>
configuration>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
# 打包
mvn package
# 3. 上传linux,导入到函数库中。
# 在hive命令中执行
add jar /opt/app/funcHello.jar; # hive session级别的添加,
delete jar /opt/app/funcHello.jar; # 如果重写,记得删除。
create [temporary] function hello as "function.HelloUDF"; # temporary是会话级别。
# 删除导入的函数
drop [temporary] function hello;
# 4. 查看函数并使用函数
-- 1. 查看函数
desc function hello;
desc function extended hello;
-- 2. 使用函数进行查询
select hello(userid,cityname) from logs;
7.3 pentahu依赖
# 下载
https://public.nexus.pentaho.org/repository/proxied-pentaho-public-repos-group/org/pentaho/pentaho-aggdesigner-algorithm/5.1.5-jhyde/pentaho-aggdesigner-algorithm-5.1.5-jhyde-javadoc.jar
# 放在本地英文目录下
D:\work\pentaho-aggdesigner-algorithm-5.1.5-jhyde-javadoc.jar
# 执行mvn安装本地依赖的命令
D:\work> mvn install:install-file -DgroupId=org.pentaho -DartifactId=pentaho-aggdesigner-algorithm -Dversion=5.1.5-jhyde -Dpackaging=jar -Dfile=pentaho-aggdesigner-algorithm-5.1.5-jhyde-javadoc.jar
8 案例
8.1 列自增长(不确定性函数)
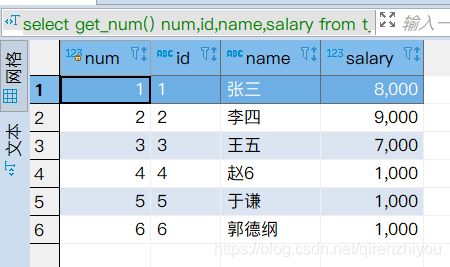
# 定义一个函数 get_number()
select get_num() num,id,name,salary from t_person;
//1. 定义一个java类,继承UDF,书写evaluate方法
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.Description;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.UDF;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
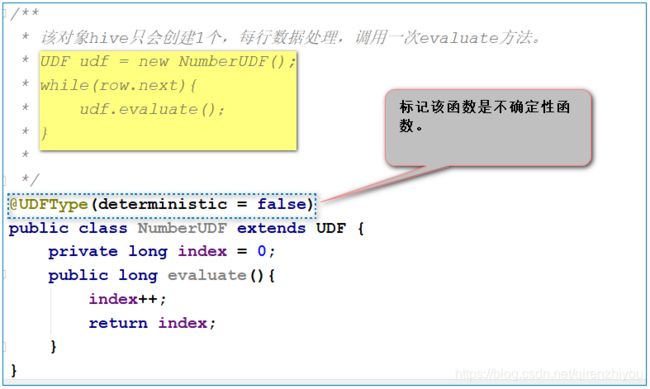
@UDFType(deterministic = false) //输入确定,输出确定的函数,false,因为该函数没有输入,输出结果也会变化。
public class NumberUDF extends UDF {
private long index = 0;
public long evaluate(){
index++;
return index;
}
}
//2. 打包
mvn clean package
//3. 上传linux
//4. 导入到hive的依赖库中
add jar /opt/doc/myhive1.2.jar;
//5. 创建函数
create temporary function get_num as 'function.NumberUDF';
//6. 使用
select get_num() num,id,name,salary from t_person;
8.2 用户自定义函数UDTF
自定义一个 UDTF 实现将一个任意分割符的字符串切割成独立的单词,例如: Line:“hello,world,hadoop,hive” Myudtf(line, “,”)
hello
world
hadoop
hive
代码实现:
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.UDFArgumentException;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.metadata.HiveException;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.udf.generic.GenericUDTF;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.objectinspector.ObjectInspector;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.objectinspector.ObjectInspectorFactory;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.objectinspector.StructObjectInspector;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.objectinspector.primitive.PrimitiveObjectInspectorFactory;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class MyUDTF extends GenericUDTF {
private ArrayList<String> outList = new ArrayList<String>();
@Override
public StructObjectInspector initialize(StructObjectInspector argOIs) throws UDFArgumentException {
//1.定义输出数据的列名和类型
List<String> fieldNames = new ArrayList<String>();
List<ObjectInspector> fieldOIs = new ArrayList<ObjectInspector>();
//2.添加输出数据的列名和类型
fieldNames.add("lineToWord");
fieldOIs.add(PrimitiveObjectInspectorFactory.javaStringObjectInspector);
return ObjectInspectorFactory.getStandardStructObjectInspector(fieldNames, fieldOIs);
}
@Override
public void process(Object[] args) throws HiveException {
//1.获取原始数据
String arg = args[0].toString();
//2.获取数据传入的第二个参数,此处为分隔符
String splitKey = args[1].toString();
//3.将原始数据按照传入的分隔符进行切分
String[] fields = arg.split(splitKey);
//4.遍历切分后的结果,并写出
for (String field : fields) {
//集合为复用的,首先清空集合
outList.clear();
//将每一个单词添加至集合
outList.add(field);
//将集合内容写出
forward(outList);
}
}
@Override
public void close() throws HiveException {
}
}
测试方式同自定义UDF:打包、添加jar、创建函数…
add jar xxxxx.jar;
create temporary function myudtf as "com.abc.function.MyUDTF";
select myudtf(line, ",") word
8.3 表数据转存导入
# 1.将文件数据导入hive表中(重要)
load data local inpath '文件的路径' overwrite into table 表。
# 2.直接将查询结果,放入一个新创建的表中。(执行查询的创建)
create table 表 as select语...
1. 执行select语句
2. 创建一个新的表,将查询结果存入表中。
# 3.将查询结果,导入已经存在表(重要)
insert into 表 select语句...
#覆盖表中的数据
insert overwrite table 表 select语句...
# 4.将HDFS中已经存在文件,导入新建的hive表中
create table Xxx(
...
)row format delimited ba
fields terminated by ','
location 'hdfs的表数据对应的目录'
-- 方式1 [重要]
load data local inpath '/opt/app/t_person.txt' into table t_person
-- 方式2 create table 表名 as select 语句
-- 将查询结果存储到一个新建表(自动创建的)
create table t_person3 as select * from t_person
create table t_person3_2 as select id,name from t_person
create table t_person3_3 as select id,name,salary from t_person where salary > 5000
-- 创建表没有数据
create table t_person3_4 as select id,name,salary from t_person where 1 != 1
-- 方式3 insert into 表名 select 语句 [重要]
-- 实际开发意义:hive数仓分层
-- 将查询结果添加到某张表中,该表需要提前创建好
create table t_person4(
id string,
name string
)row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
-- 向t_person4表中导入数据
insert into t_person4 select id,name from t_person
-- 向表中添加数据 会覆盖原有的数据
insert overwrite table t_person4 select id,name from t_person where salary > 5000
-- 方式4 创建一张表,罩在HDFS现有数据之上
create table t_person5(
id string,
name string,
age int
)row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
location '/file1'
-- location '/文件夹'
将SQL的执行结果插入到另一个表中
create table 表 as select语句
--## 例子:
--统计每个人,2020-3-21看过的电影,将结果存入hive的表:t_video_log_20200321
create table t_video_log_20200321 as select ...;
9 开窗函数(分析函数)
开窗函数:在开窗函数出现之前存在着很多用 SQL 语句很难解决的问题,很多都要通过复杂的相关子查询或者存储过程来完成。
为了解决这些问题,在 2003 年 ISO SQL 标准加入了开窗函数,开窗函数的使用使得这些经典的难题可以被轻松的解决。
目前在 MSSQLServer、Oracle、DB2 等主流数据库中都提供了对开窗函数的支持,MySQL8.0支持。
与聚合函数一样,开窗函数也是对行集组进行聚合计算,但是它不像普通聚合函数那样每组只返回一个值,开窗函数可以为每组返回多个值,因为开窗函数所执行聚合计算的行集组是窗口。在 ISO SQL 规定了这样的函数为开窗函数,在 Oracle 中则被称为分析函数。
1.准备数据
Tom,BeiJing,20,3000
Tim,ChengDu,21,4000
Jim,BeiJing,22,3500
Lily,London,21,2000
John,NewYork,22,1000
YaoMing,BeiJing,20,3000
Swing,London,22,2000
Guo,NewYork,20,2800
YuQian,BeiJing,24,8000
Ketty,London,25,8500
Kitty,ChengDu,25,3000
Merry,BeiJing,23,3500
Smith,ChengDu,30,3000
Bill,BeiJing,25,2000
Jerry,NewYork,24,3300
2.建表/导入数据
create table t_person (
fname string,
fcity string,
fage int,
fsalary int
)row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
load data local inpath '/root/kaichuang.txt' into table t_person;
3.开窗函数的语法
开窗函数格式: 函数名(列) OVER(选项)
OVER 关键字表示把函数当成开窗函数而不是聚合函数。SQL标准允许将所有聚合函数用做开窗函数,使用 OVER 关键字来区分这两种用法。
如果 OVER 关键字后的括号中的选项为空,则开窗函数会对结果集中的所有行进行聚合运算。
PARTITION BY 子句:
开窗函数的 OVER 关键字后括号中的可以使用 PARTITION BY 子句来定义行的分区来供进行聚合计算。与 GROUP BY 子句不同,PARTITION BY 子句创建的分区是独立于结果集的,创建的分区只是供进行聚合计算的,而且不同的开窗函数所创建的分区也不互相影响
ORDER BY子句:
开窗函数中可以在OVER关键字后的选项中使用ORDER BY子句来指定排序规则,而且有的开窗函数还要求必须指定排序规则。使用ORDER BY子句可以对结果集按照指定的排序规则进行排序,并且在一个指定的范围内进行聚合运算
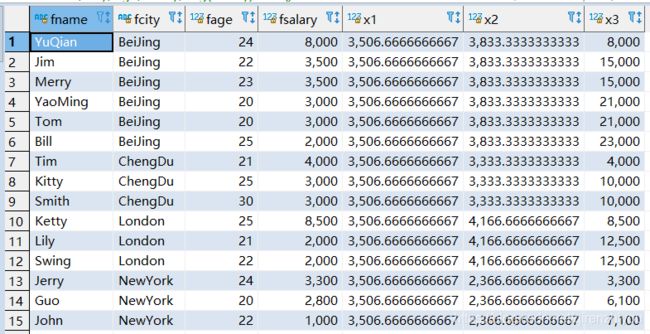
- 排序开窗函数
select
fname,fcity,fage,fsalary,
ROW_NUMBER() over(partition by fcity order by fsalary desc) x1, -- 根据顺序计算
Rank() over(partition by fcity order by fsalary desc) x2, -- 排序相同时会重复,总数不会变
DENSE_RANK () over(partition by fcity order by fsalary desc) x3 -- 排序相同时会重复,总数会减少
from t_person;
- 聚合开窗函数
select
fname,fcity,fage,fsalary,
avg(fsalary) over() x1,
avg(fsalary) over(partition by fcity) x2,
sum(fsalary) over(partition by fcity order by fsalary desc) x3
from t_person;
10 Hive优化
-
MapJoin
如果不指定MapJoin或者不符合MapJoin的条件,那么Hive解析器会将Join操作转换成Common Join,即:在Reduce阶段完成join。容易发生数据倾斜。
可以用MapJoin把小表全部加载到内存在map端进行join,避免reducer处理。 -
行列过滤
列处理:在SELECT中,只拿需要的列,如果有,尽量使用分区过滤,少用SELECT *。
行处理:在分区剪裁中,当使用外关联时,如果将副表的过滤条件写在Where后面,那么就会先全表关联,之后再过滤。 -
采用分桶技术
-
采用分区技术
-
合理设置Map数
- 通常情况下,作业会通过input的目录产生一个或者多个map任务。主要的决定因素有:input的文件总个数,input的文件大小,集群设置的文件块大小。
- 问题2:如果一个任务有很多小文件(远远小于块大小128M),则每个小文件也会被当做一个块,用一个map任务来完成,而一个map任务启动和初始化的时间远远大于逻辑处理的时间,就会造成很大的资源浪费。而且同时可执行的map数是受限的。
- 问题3:是不是保证每个map处理接近128m的文件块,就高枕无忧了?
不一定。比如有一个127m的文件,正常会用一个map去完成,但这个文件只有一个或者两个小字段,却有几千万的记录,如果map处理的逻辑比较复杂,
用一个map任务去做比较耗时 - 问题2和3,采取两种方式来解决:
即减少map数和增加map数
-
小文件进行合并
在Map执行前合并小文件,减少Map数:
CombineHiveInputFormat具有对小文件进行合并的功能(系统默认的格式)
HiveInputFormat没有对小文件合并功能 -
合理设置Reduce数
Reduce个数并不是越多越好- 过多的启动和初始化Reduce也会消耗时间和资源;
- 有多少个Reduce,就会有多少个输出文件,如果生成了很多个小文件,那么如果这些小文件作为下一个任务的输入,则也会出现小文件过多的问题;
- 设置Reduce个数时考虑两个原则:处理大数据量利用合适的Reduce数;使单个Reduce任务处理数据量大小要合适;
-
常用参数
输出合并小文件SET hive.merge.mapfiles = true; -- 默认true,在map-only任务结束时合并小文件 SET hive.merge.mapredfiles = true; -- 默认false,在map-reduce任务结束时合并小文件 SET hive.merge.size.per.task = 268435456; -- 默认256M SET hive.merge.smallfiles.avgsize = 16777216; -- 当输出文件的平均大小小于该值时,启动一个独立的map-reduce任务进行文件merge -
开启map端combiner(不影响最终业务逻辑)
set hive.map.aggr=true; -
压缩
(选择快的)设置map端输出、中间结果压缩。(不完全是解决数据倾斜的问题,但是减少IO读写和网络传输,能提高很多效率) -
开启JVM重用
mapred.job.reuse.jvm.num.tasks = -1默认1,设置为-1表示同一个job下不管有多少task都是只启动一个JVM
默认表示一个task启用一个JVM,这样的话如果小文件过多就会频繁的创建和销毁JVM进程,造成计算资源的浪费。
注意:适用于大量小文件的处理,多个JVM是顺序执行,并不是并行执行