SpringBoot入门之一 单体项目
SpringBoot入门之一 单体项目
- 0.学习目标
- 1. 了解SpringBoot
-
- 1.1.什么是SpringBoot
- 1.2.为什么要学习SpringBoot
- 1.3.SpringBoot的特点
- 2.快速入门
-
- 2.1.创建工程
- 2.2.引入依赖
- 2.3.编写HelloWorldController
- 2.4.启动测试
- 2.5.详解
-
- 2.5.1.启动器
- 2.5.2.@EnableAutoConfiguration
- 2.6.入门程序
-
- 2.6.1.@SpringBootApplication
- 2.6.2.@ComponentScan
- 2.6.3.@SpringBootConfiguration
- 源码下载地址
0.学习目标
- 了解SpringBoot的作用
- 掌握java配置的方式
- 了解SpringBoot自动配置原理
- 掌握SpringBoot的基本使用
1. 了解SpringBoot
在这一部分,我们主要了解以下3个问题:
- 什么是SpringBoot
- 为什么要学习SpringBoot
- SpringBoot的特点
1.1.什么是SpringBoot
SpringBoot是Spring项目中的一个子工程,与我们所熟知的Spring-framework 同属于spring的产品:
Spring Boot称为搭建程序的脚手架,只需要“run”就可以非常轻易的狗基建spring应用,大大简化构建庞大的spring项目效率,并且尽可能的减少一切xml配置,做到开箱即用,迅速上手,让我们关注于业务而非配置。
官网
1.2.为什么要学习SpringBoot
java一直被人诟病的一点就是臃肿、麻烦。当我们还在辛苦的搭建项目时,可能Python程序员已经把功能写好了,究其原因主要是两点:
-
复杂的配置
项目各种配置其实是开发时的损耗, 因为在思考 Spring 特性配置和解决业务问题之间需要进行思维切换,所以写配置挤占了写应用程序逻辑的时间。
-
混乱的依赖管理
项目的依赖管理也是件吃力不讨好的事情。决定项目里要用哪些库就已经够让人头痛的了,你还要知道这些库的哪个版本和其他库不会有冲突,这也是件棘手的问题。并且,依赖管理也是一种损耗,添加依赖不是写应用程序代码。一旦选错了依赖的版本,随之而来的不兼容问题毫无疑问会是生产力杀手。
而SpringBoot让这一切成为过去!
1.3.SpringBoot的特点
Spring Boot 主要特征是:
- 创建独立的spring应用程序,使用java -jar xx.jar即可运行.
- 直接内嵌tomcat、jetty和undertow(不需要打包成war包部署)
- 提供了固定化的“starter”配置,以简化构建配置
- 尽可能的自动配置spring和第三方库
- 提供产品级的功能,如:安全指标、运行状况监测和外部化配置等
- 绝对不会生成代码,并且不需要XML配置
总之,Spring Boot为所有 Spring 的开发者提供一个开箱即用的、非常快速的、广泛接受的入门体验
2.快速入门
接下来,我们就来利用SpringBoot搭建一个web工程,体会一下SpringBoot的魅力所在!
本人使用eclipse开发, 需要安装jdk,配置maven
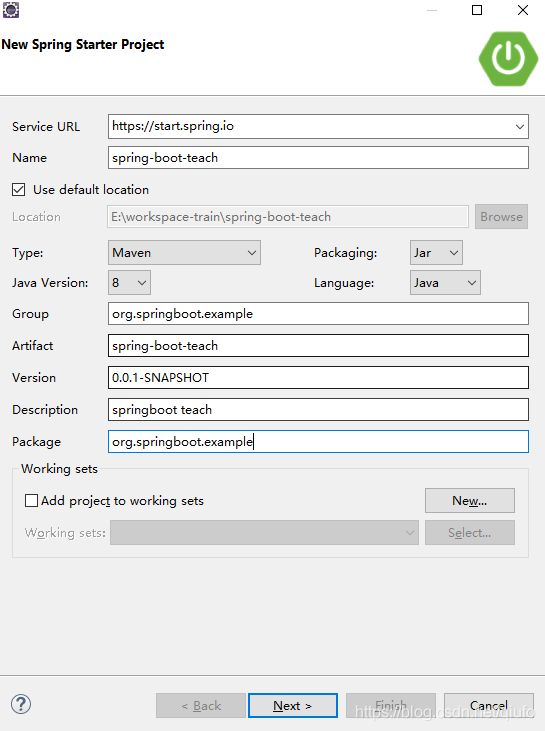
2.1.创建工程
我们先新建一个空的demo工程,如下:
创建以moduel:
public class User {
private String name;
private String passWord;
....
}
目录结构:
2.2.引入依赖
查看pom.xml,我们可以看到SpringBoot的父级依赖spring-boot-starter-parent和自定义添加的spring-boot-starter-web
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.0.0.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<groupId>org.springboot.examplegroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-teachartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<name>spring-boot-teachname>
<description>springboot teachdescription>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintagegroupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engineartifactId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
2.3.编写HelloWorldController
代码:
@RestController
public class HelloWorldController {
@GetMapping("show")
public String test() {
return "hello Spring Boot!";
}
}
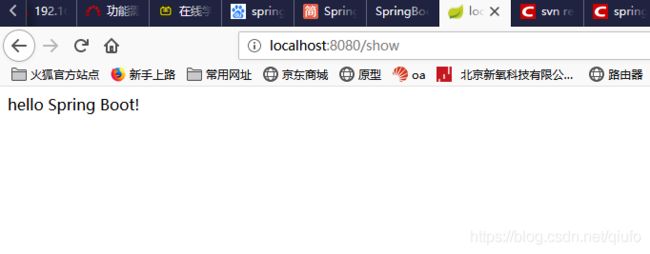
2.4.启动测试
bingo!访问成功!
2.5.详解
入门工程中:pom.xml里引入了启动器的概念以@EnableAutoConfiguration注解。
2.5.1.启动器
为了让SpringBoot帮我们完成各种自动配置,我们必须引入SpringBoot提供的自动配置依赖,我们称为启动器。spring-boot-starter-parent工程将依赖关系声明为一个或者多个启动器,我们可以根据项目需求引入相应的启动器,因为我们是web项目,这里我们引入web启动器:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
dependencies>
需要注意的是,我们并没有在这里指定版本信息。因为SpringBoot的父工程已经对版本进行了管理了。
这个时候,我们会发现项目中多出了大量的依赖:
[INFO] Scanning for projects...
[INFO]
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Building spring-boot-teach 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO]
[INFO] --- maven-dependency-plugin:3.0.1:tree (default-cli) @ spring-boot-teach ---
[INFO] org.springboot.example:spring-boot-teach:jar:0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
[INFO] +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web:jar:2.0.0.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter:jar:2.0.0.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | | +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot:jar:2.0.0.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | | +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-autoconfigure:jar:2.0.0.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | | +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-logging:jar:2.0.0.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | | | +- ch.qos.logback:logback-classic:jar:1.2.3:compile
[INFO] | | | | \- ch.qos.logback:logback-core:jar:1.2.3:compile
[INFO] | | | +- org.apache.logging.log4j:log4j-to-slf4j:jar:2.10.0:compile
[INFO] | | | | \- org.apache.logging.log4j:log4j-api:jar:2.10.0:compile
[INFO] | | | \- org.slf4j:jul-to-slf4j:jar:1.7.25:compile
[INFO] | | +- javax.annotation:javax.annotation-api:jar:1.3.2:compile
[INFO] | | \- org.yaml:snakeyaml:jar:1.19:runtime
[INFO] | +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-json:jar:2.0.0.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | | +- com.fasterxml.jackson.core:jackson-databind:jar:2.9.4:compile
[INFO] | | | +- com.fasterxml.jackson.core:jackson-annotations:jar:2.9.0:compile
[INFO] | | | \- com.fasterxml.jackson.core:jackson-core:jar:2.9.4:compile
[INFO] | | +- com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype:jackson-datatype-jdk8:jar:2.9.4:compile
[INFO] | | +- com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype:jackson-datatype-jsr310:jar:2.9.4:compile
[INFO] | | \- com.fasterxml.jackson.module:jackson-module-parameter-names:jar:2.9.4:compile
[INFO] | +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-tomcat:jar:2.0.0.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | | +- org.apache.tomcat.embed:tomcat-embed-core:jar:8.5.28:compile
[INFO] | | +- org.apache.tomcat.embed:tomcat-embed-el:jar:8.5.28:compile
[INFO] | | \- org.apache.tomcat.embed:tomcat-embed-websocket:jar:8.5.28:compile
[INFO] | +- org.hibernate.validator:hibernate-validator:jar:6.0.7.Final:compile
[INFO] | | +- javax.validation:validation-api:jar:2.0.1.Final:compile
[INFO] | | +- org.jboss.logging:jboss-logging:jar:3.3.2.Final:compile
[INFO] | | \- com.fasterxml:classmate:jar:1.3.4:compile
[INFO] | +- org.springframework:spring-web:jar:5.0.4.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | | \- org.springframework:spring-beans:jar:5.0.4.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | \- org.springframework:spring-webmvc:jar:5.0.4.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | +- org.springframework:spring-aop:jar:5.0.4.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | +- org.springframework:spring-context:jar:5.0.4.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | \- org.springframework:spring-expression:jar:5.0.4.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] \- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test:jar:2.0.0.RELEASE:test
[INFO] +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-test:jar:2.0.0.RELEASE:test
[INFO] +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-test-autoconfigure:jar:2.0.0.RELEASE:test
[INFO] +- com.jayway.jsonpath:json-path:jar:2.4.0:test
[INFO] | +- net.minidev:json-smart:jar:2.3:test
[INFO] | | \- net.minidev:accessors-smart:jar:1.2:test
[INFO] | | \- org.ow2.asm:asm:jar:5.0.4:test
[INFO] | \- org.slf4j:slf4j-api:jar:1.7.25:compile
[INFO] +- junit:junit:jar:4.12:test
[INFO] +- org.assertj:assertj-core:jar:3.9.1:test
[INFO] +- org.mockito:mockito-core:jar:2.15.0:test
[INFO] | +- net.bytebuddy:byte-buddy:jar:1.7.10:test
[INFO] | +- net.bytebuddy:byte-buddy-agent:jar:1.7.10:test
[INFO] | \- org.objenesis:objenesis:jar:2.6:test
[INFO] +- org.hamcrest:hamcrest-core:jar:1.3:test
[INFO] +- org.hamcrest:hamcrest-library:jar:1.3:test
[INFO] +- org.skyscreamer:jsonassert:jar:1.5.0:test
[INFO] | \- com.vaadin.external.google:android-json:jar:0.0.20131108.vaadin1:test
[INFO] +- org.springframework:spring-core:jar:5.0.4.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | \- org.springframework:spring-jcl:jar:5.0.4.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] +- org.springframework:spring-test:jar:5.0.4.RELEASE:test
[INFO] \- org.xmlunit:xmlunit-core:jar:2.5.1:test
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
这些都是SpringBoot根据spring-boot-starter-web这个依赖自动引入的,而且所有的版本都已经管理好,不会出现冲突。
2.5.2.@EnableAutoConfiguration
关于这个注解,官网上有一段说明:
Enable auto-configuration of the Spring Application Context, attempting to guess and configure beans that you are likely to need. Auto-configuration classes are usually applied based on your classpath and what beans you have defined.
简单翻译以下:
开启spring应用程序的自动配置,SpringBoot基于你所添加的依赖和你自己定义的bean,试图去猜测并配置你想要的配置。比如我们引入了
spring-boot-starter-web,而这个启动器中帮我们添加了tomcat、SpringMVC的依赖。此时自动配置就知道你是要开发一个web应用,所以就帮你完成了web及SpringMVC的默认配置了!
@EnableAutoConfiguration 其实也没啥“创意”,各位是否还记得 Spring 框架提供的各种名字为 @Enable 开头的 Annotation 定义?
比如 @EnableScheduling、@EnableCaching、@EnableMBeanExport 等,@EnableAutoConfiguration 的理念和“做事方式”其实一脉相承,简单概括一下就是,借助 @Import 的支持,收集和注册特定场景相关的 bean 定义:
@EnableScheduling 是通过 @Import 将 Spring 调度框架相关的 bean 定义都加载到 IoC 容器。
@EnableMBeanExport 是通过 @Import 将 JMX 相关的 bean 定义加载到 IoC 容器。
而 @EnableAutoConfiguration 也是借助 @Import 的帮助,将所有符合自动配置条件的 bean 定义加载到 IoC 容器,仅此而已!
@EnableAutoConfiguration 作为一个复合 Annotation,其自身定义关键信息如下:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {...}
其中,最关键的要属 @Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class),借助 EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector,@EnableAutoConfiguration 可以帮助 SpringBoot 应用将所有符合条件的 @Configuration 配置都加载到当前 SpringBoot 创建并使用的 IoC 容器,就跟一只“八爪鱼”一样(如图 1 所示)。

借助于 Spring 框架原有的一个工具类:SpringFactoriesLoader 的支持,@EnableAutoConfiguration 可以“智能”地自动配置功效才得以大功告成!
总结,SpringBoot内部对大量的第三方库或Spring内部库进行了默认配置,这些配置是否生效,取决于我们是否引入了对应库所需的依赖,如果有那么默认配置就会生效。
所以,我们使用SpringBoot构建一个项目,只需要引入所需依赖,配置就可以交给SpringBoot处理了。
2.6.入门程序
启动类代码:
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootTeachApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootTeachApplication.class, args);
}
}
启动类上面的注解是@SpringBootApplication,它也是 Spring Boot 的核心注解,
2.6.1.@SpringBootApplication
查看@SpringBootApplication源码
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
Class[] exclude() default {};
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
String[] excludeName() default {};
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages")
String[] scanBasePackages() default {};
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackageClasses")
Class[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {};
}
主要组合包含了以下 3 个注解:
@SpringBootConfiguration:组合了 @Configuration 注解,实现配置文件的功能。
@EnableAutoConfiguration:打开自动配置的功能,也可以关闭某个自动配置的选项,如关闭数据源自动配置功能: @SpringBootApplication(exclude = { DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class })。
@ComponentScan:Spring组件扫描。
2.6.2.@ComponentScan
spring框架除了提供配置方式的注解扫描@ComponentScan。
我们跟进该注解的源码,并没有看到什么特殊的地方。我们查看注释:
大概的意思:
配置组件扫描的指令。提供了类似与
标签的作用通过basePackageClasses或者basePackages属性来指定要扫描的包。如果没有指定这些属性,那么将从声明这个注解的类所在的包开始,扫描包及子包
而我们的@ComponentScan注解声明的类就是main函数所在的启动类,因此扫描的包是该类所在包及其子包。一般启动类会放在一个比较浅的包目录中。
如果我们当前应用没有任何 bean 定义需要通过 @ComponentScan 加载到当前 SpringBoot 应用对应使用的 IoC 容器,那么,除去 @ComponentScan 的声明,当前 SpringBoot 应用依然可以照常运行,功能对等。我们可以手工单个注册,不一定非要通过批量的自动扫描完成,所以说 @ComponentScan 是可有可无的。
2.6.3.@SpringBootConfiguration
@SpringBootConfiguration注解的源码:
我们继续点击查看源码:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
}
通过这段我们可以看出,在这个注解上面,又有一个@Configuration注解。通过上面的注释阅读我们知道:这个注解的作用就是声明当前类是一个配置类,然后Spring会自动扫描到添加了@Configuration的类,并且读取其中的配置信息。而@SpringBootConfiguration是来声明当前类是SpringBoot应用的配置类,项目中只能有一个。所以一般我们无需自己添加。
源码下载地址
https://gitee.com/xiaolaifeng/sample.springboot/tree/master/springboot-teach1