本篇接Struts 学习之03Controller(控制器 上)
本打算是写在一起,但很郁闷的是 写了N多的时候,我手痒, 看到电脑插座似呼有些松动,去动了下,结果,瞬间黑屏,电脑重启动,要崩溃了,只好再重新写,激情当然也就减少一大半料~
好了牢骚也不多发了,还是接着Struts 学习之03Controller(控制器 上) 开始创建项目
Step1:我们还是创建一个StrutsProject 并在Struts-config.xml视图中添加一个action form and jsp!具体可参见Struts 学习之01,操作后的struts-cpnfig.xml文件代码如下:
 < struts-config >
< struts-config >
 < data-sources />
< data-sources />
 < form-beans >
< form-beans >
 < form-bean name ="loginForm" type ="fengyan.struts.form.LoginForm" />
< form-bean name ="loginForm" type ="fengyan.struts.form.LoginForm" />
 form-beans >
form-beans >
 < global-exceptions />
< global-exceptions />
 < global-forwards />
< global-forwards />
 < action-mappings >
< action-mappings >
 < action
< action
 attribute ="loginForm"
attribute ="loginForm"
 input ="/login.jsp"
input ="/login.jsp"
 name ="loginForm"
name ="loginForm"
 path ="/login"
path ="/login"
 scope ="request"
scope ="request"
 type ="fengyan.struts.action.LoginAction" >
type ="fengyan.struts.action.LoginAction" >
 < forward
< forward
 name ="ok"
name ="ok"
 path ="/ok.jsp"
path ="/ok.jsp"
 redirect ="true" />
redirect ="true" />
 < forward name ="error" path ="/error.jsp" />
< forward name ="error" path ="/error.jsp" />
 action >
action >
 action-mappings >
action-mappings >
 < message-resources parameter ="fengyan.struts.ApplicationResources" />
< message-resources parameter ="fengyan.struts.ApplicationResources" />
 struts-config >
struts-config >
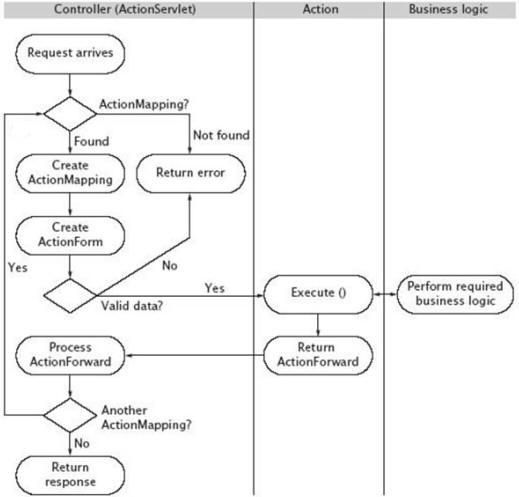
我们现在看上图,其实中间少了一个process方法,其实这里面的过程到了ActionServlet对象后会调用一个RequestProcessor对象,这个可以在struts源代码中可以看到!打开\struts-1.2.9-src\src\share\org\apache\struts\action下的ActionServlet.java (没有的朋友可以到 Apache官方网站上去下载struts是开源,)以下为部分源码:
 ActionServlet.java部分源码
ActionServlet.java部分源码
 public class ActionServlet extends HttpServlet
public class ActionServlet extends HttpServlet


 { //可知它也是继承自HttpServlet类
{ //可知它也是继承自HttpServlet类
 //config属性 指明了struts的配置文件路径
//config属性 指明了struts的配置文件路径
 protected String config = "/WEB-INF/struts-config.xml";
protected String config = "/WEB-INF/struts-config.xml";


 public void init() throws ServletException
public void init() throws ServletException  {
{
 //init()方法在ActionServlet对象加载后立即执行!
//init()方法在ActionServlet对象加载后立即执行!
 // Wraps the entire initialization in a try/catch to better handle
// Wraps the entire initialization in a try/catch to better handle
 // unexpected exceptions and errors to provide better feedback
// unexpected exceptions and errors to provide better feedback
 // to the developer
// to the developer

 try
try  {
{

 /**//*该方法是用来初始化框架的内部消息绑定,这些消息用来输出提示,
/**//*该方法是用来初始化框架的内部消息绑定,这些消息用来输出提示,
 警告,和错误信息到日志文件中,主要操作是:
警告,和错误信息到日志文件中,主要操作是:
 internal=MessageResources.getMessageResources(internalName);
internal=MessageResources.getMessageResources(internalName);
 其中internal是MessageResources的一个实例*/
其中internal是MessageResources的一个实例*/
 initInternal();
initInternal();

 /**//*加载web.xml中定义的不同参数,如config,用以控制ActionServlet
/**//*加载web.xml中定义的不同参数,如config,用以控制ActionServlet
 的不同行为,主要是读取节点中定义的参数*/
的不同行为,主要是读取节点中定义的参数*/
 initOther();
initOther();

 /**//*加载并初始化web.xml文件所定义的servlet名称和servlet映射信息
/**//*加载并初始化web.xml文件所定义的servlet名称和servlet映射信息
 本例中分别是action它映射到
本例中分别是action它映射到
 *.do*/
*.do*/
 initServlet();
initServlet();

 getServletContext().setAttribute(Globals.ACTION_SERVLET_KEY, this);
getServletContext().setAttribute(Globals.ACTION_SERVLET_KEY, this);
 initModuleConfigFactory();
initModuleConfigFactory();
 // Initialize modules as needed
// Initialize modules as needed

 /**//*initModuleConfigFactory()和initModuleConfig("", config):加载并初始化
/**//*initModuleConfigFactory()和initModuleConfig("", config):加载并初始化
 struts-config.xml配置文件,默认配置文件被解析,产生一个ModuleConfig
struts-config.xml配置文件,默认配置文件被解析,产生一个ModuleConfig
 对象于ServletContext 也即为当前Servlet上下文中!*/
对象于ServletContext 也即为当前Servlet上下文中!*/
 ModuleConfig moduleConfig = initModuleConfig("", config);
ModuleConfig moduleConfig = initModuleConfig("", config);

 /**//*struts-config.xml配置文件中的指定的每一个消息资源文件都被 加载
/**//*struts-config.xml配置文件中的指定的每一个消息资源文件都被 加载
 我们这里创建Struts后默认有一个
我们这里创建Struts后默认有一个

 也就是前几篇文章中多次用到的资源文件,是在这里被加载的!*/
也就是前几篇文章中多次用到的资源文件,是在这里被加载的!*/
 initModuleMessageResources(moduleConfig);
initModuleMessageResources(moduleConfig);

 /**//*struts-config.xml配置文件中声明的每一个数据源被加载并且初始化,如果
/**//*struts-config.xml配置文件中声明的每一个数据源被加载并且初始化,如果
 没有配置数据源,则跳过这步!但一般MVC的模型部分主要是由Hibernate
没有配置数据源,则跳过这步!但一般MVC的模型部分主要是由Hibernate
 去完成的!Hibernate配置完了数据源后由Spring去加载,这里跳过,如可能
去完成的!Hibernate配置完了数据源后由Spring去加载,这里跳过,如可能
 我会在以后的文章中写明*/
我会在以后的文章中写明*/
 initModuleDataSources(moduleConfig);
initModuleDataSources(moduleConfig);

 /**//*加载并初始化struts-config.xml配置文件中的指定插件。第一个插件的
/**//*加载并初始化struts-config.xml配置文件中的指定插件。第一个插件的
 init()方法被调用!我在前面的struts 学习之02 中已经用到一个插件!*/
init()方法被调用!我在前面的struts 学习之02 中已经用到一个插件!*/
 initModulePlugIns(moduleConfig);
initModulePlugIns(moduleConfig);
 moduleConfig.freeze();
moduleConfig.freeze();

 Enumeration names = getServletConfig().getInitParameterNames();
Enumeration names = getServletConfig().getInitParameterNames();

 while (names.hasMoreElements())
while (names.hasMoreElements())  {
{
 String name = (String) names.nextElement();
String name = (String) names.nextElement();

 if (!name.startsWith("config/"))
if (!name.startsWith("config/"))  {
{
 continue;
continue;
 }
}
 String prefix = name.substring(6);
String prefix = name.substring(6);
 moduleConfig = initModuleConfig
moduleConfig = initModuleConfig
 (prefix, getServletConfig().getInitParameter(name));
(prefix, getServletConfig().getInitParameter(name));
 initModuleMessageResources(moduleConfig);
initModuleMessageResources(moduleConfig);
 initModuleDataSources(moduleConfig);
initModuleDataSources(moduleConfig);
 initModulePlugIns(moduleConfig);
initModulePlugIns(moduleConfig);
 moduleConfig.freeze();
moduleConfig.freeze();
 }
}

 this.initModulePrefixes(this.getServletContext());
this.initModulePrefixes(this.getServletContext());

 this.destroyConfigDigester();
this.destroyConfigDigester();

 } catch (UnavailableException ex)
} catch (UnavailableException ex)  {
{
 throw ex;
throw ex;

 } catch (Throwable t)
} catch (Throwable t)  {
{

 // The follow error message is not retrieved from internal message
// The follow error message is not retrieved from internal message
 // resources as they may not have been able to have been
// resources as they may not have been able to have been
 // initialized
// initialized
 log.error("Unable to initialize Struts ActionServlet due to an "
log.error("Unable to initialize Struts ActionServlet due to an "
 + "unexpected exception or error thrown, so marking the "
+ "unexpected exception or error thrown, so marking the "
 + "servlet as unavailable. Most likely, this is due to an "
+ "servlet as unavailable. Most likely, this is due to an "
 + "incorrect or missing library dependency.", t);
+ "incorrect or missing library dependency.", t);
 throw new UnavailableException(t.getMessage());
throw new UnavailableException(t.getMessage());
 }
}
 }
}

 //正常的Servlet运行有二个方法,一个是doGet还有一个为doPost
//正常的Servlet运行有二个方法,一个是doGet还有一个为doPost
 //同样我们可以在里面找到这二个方法
//同样我们可以在里面找到这二个方法
 public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
 throws IOException, ServletException
throws IOException, ServletException


 {
{
 process(request, response);
process(request, response);
 }
}
 public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
 throws IOException, ServletException
throws IOException, ServletException


 {
{
 process(request, response);
process(request, response);
 //我们发现它里面的doGet和doPost同时转移提交给了process()方法处理!
//我们发现它里面的doGet和doPost同时转移提交给了process()方法处理!
 //那么我们的重点就放在了process方法
//那么我们的重点就放在了process方法
 }
}
 //接着在里面找到 process方法代码如下
//接着在里面找到 process方法代码如下
 protected void process(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
protected void process(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)

 throws IOException, ServletException
throws IOException, ServletException  {
{

 ModuleUtils.getInstance().selectModule(request, getServletContext());
ModuleUtils.getInstance().selectModule(request, getServletContext());
 ModuleConfig config = getModuleConfig(request);
ModuleConfig config = getModuleConfig(request);
 RequestProcessor processor = getProcessorForModule(config);
RequestProcessor processor = getProcessorForModule(config);
 //上面就是重点,根据config配置文件获取对应的模型,获取到了RequestProcessor对象
//上面就是重点,根据config配置文件获取对应的模型,获取到了RequestProcessor对象


 if (processor == null)
if (processor == null)  {
{
 processor = getRequestProcessor(config);
processor = getRequestProcessor(config);
 }
}

 processor.process(request, response);
processor.process(request, response);

 /**//*最后将请求转交给了RequestProcessor对象的processor方法
/**//*最后将请求转交给了RequestProcessor对象的processor方法
 这也就是从struts1.2起,它里面的控制器这一部分的主要内容已经转移到
这也就是从struts1.2起,它里面的控制器这一部分的主要内容已经转移到
 了RequestProcessor对象中了!自然ActionServlet对象中需要做的就比较
了RequestProcessor对象中了!自然ActionServlet对象中需要做的就比较
 少了*/
少了*/

 }
}
 }
}
我在上面已经做了详细注释,如果对servlet熟习的话,我们知道http请求大多是get/post,同样ActionServlet是从servlet继承来的,通过上面部分源码我们发现,无论是doPost/doGet都是调用的ActionServlet中的process方法,process方法主要的作用就是得到一个相应的ReuestProcessor类或者子类的对象,然后调用这个对象的process方法来处理用户的需求,这样我们将 注意力放在ReuestProcessor上
ReuestProcessor主要执行以下操作:
1.processMultipart(request):对用户的请求进行预处理,如果HttpServletRequest是POST方式,且请求为multipart/form-data,Struts框架将请求对象包装成处理multipart请求专用的请求对象,否则,只是简单的返回原有的请求对象。一般来说除非需要处理文件上传,否则不用关心multipart功能的具体细节。进行包装处理的类是MultipartRequestWrapper类它以用户的请求为包装对象!
2.processPath(request,response):该方法用来从请求URL中获取路径部分,获取到的信息在稍后的步骤中用于选择合适的Struts Action调用,与action标签的path属性相对应!
也就是我们struts-config.xml文件中 它对应于loginForm,
3.processLocale(request,response):处理一些国际化的事物
4.processContent(request,response):设置响应体的编码方式 response.setContentType(contentType);
5.processNoCache(request,response)根据noCache属性的设置调用processNoCache()方法,如果noCache设置为true,则添加合适的响应对象中,使得页面保留浏览器的Cache中。这些响应头包含Pragma,CacheControl和Expries!也就是缓冲区了!
6.processPreprocess(request,response):该方法只是简单的返回一个true值,它是以下方式调用的:
if(!processPreprocess(request,response))return;因此我们可以在processPreprocess方法中进行一点的预处理,如果用户的请求不符号要求的话,我们就让它返回一个false值,这样的话action就不会调用
这里我们在action包下建立一个MyRequestProcessor类,让其继承org.apache.struts.action.RequestProcessor如下图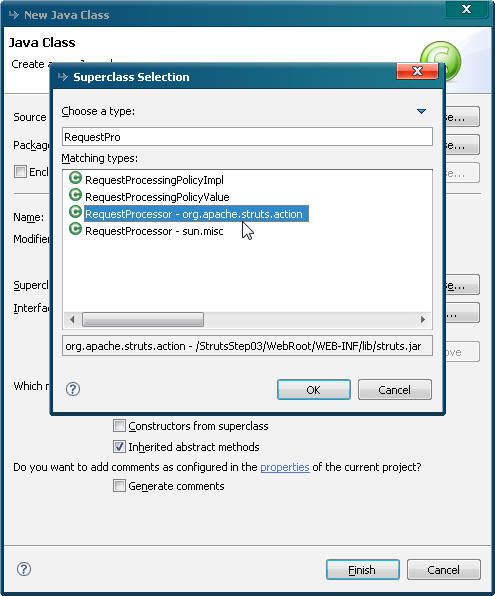
之后我们让该类重写父类方法

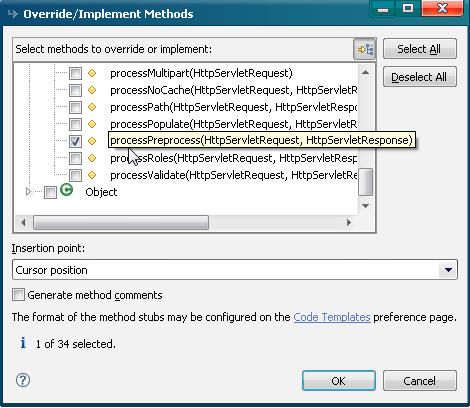
然后我们在processPreprocess方法中简单的修改一下,MyRequestProcessor完整代码如下:
 package fengyan.struts.action;
package fengyan.struts.action;

 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;

 import org.apache.struts.action.RequestProcessor;
import org.apache.struts.action.RequestProcessor;


 public class MyRequestProcessor extends RequestProcessor
public class MyRequestProcessor extends RequestProcessor  {
{

 @Override
@Override

 protected boolean processPreprocess(HttpServletRequest arg0, HttpServletResponse arg1)
protected boolean processPreprocess(HttpServletRequest arg0, HttpServletResponse arg1)  {
{
 //我们简单的让其输出一句话,实际中当然可以根据业务需要来进行处理!
//我们简单的让其输出一句话,实际中当然可以根据业务需要来进行处理!
 System.out.println("楚旋-博客园:http://eflylab.cnblogs.com");
System.out.println("楚旋-博客园:http://eflylab.cnblogs.com");
 return super.processPreprocess(arg0, arg1);
return super.processPreprocess(arg0, arg1);
 //我们可以return false 这样struts-config.xml中的action就不会被调用了
//我们可以return false 这样struts-config.xml中的action就不会被调用了
 }
}
 }
}

这样我们就自己写了一个这样的类,然后我们如何去让其工作呢?当然 我们需要修改struts-config.xml文件,先前的struts-config.xml调用的是系统的的一个processor那么如何使用我们刚刚自定义的呢?我们要加入
节点!我们在后添加如下内容:
 < controller processorClass ="fengyan.struts.action.MyRequestProcessor" >
< controller processorClass ="fengyan.struts.action.MyRequestProcessor" >
 controller >
controller >
这样我们通过修改,就使其不经过原始的processor了,我们可以先运行,效果如下: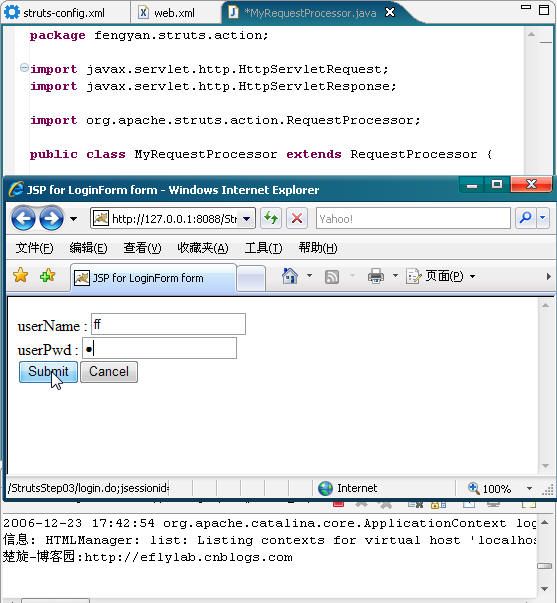
我们可以看到在控制台输出了"楚旋-博客园:http://eflylab.cnblogs.com"表明请求经过了我们的MyRequesProcesor
7. 好了,经过上面processPreprocess预处理之后是processMapping(request,response):它是利用前面所获取的path值,在struts-config.xml中寻找对应的action.即根据path在action-mappings标签中寻找其对应的action,如果找不到则返回一个error
8.processRoles(request,response):通过其名,知道是与角色有关,它是action访问权限的问题!不过可忽略,一般没啥用处!有可能我会在下一篇文章中写出!
9.processActionForm(request,response,mapping):
第一步,查看是否存在着为这个ActionMapping配置的ActionForm,具体查看流程如下:
a:该Action元素的attribute是否为null,如果为null,则返回null;
b:如果attribute不为null,则取得它的name属性,然后根据name的值在中寻找相应的ActionForm,也是通过name属性来配对的,如果找不到的话,则产生错误日志,并且返回null.
第二步:如果存在这样的ActionForm,我们就根据上面的attribute的值,在作用域查看是否存在着这样的ActionForm的实例,如果存在则重复用之,并把它作为返回值,否则的话,就重新创建这个ActionForm的一个实例,并且返回它,最后这个实例将会保存在相应的作用域中
10.processPopulate(request,response,form,mapping)如果存在为ActionMapping配置的ActionForm,则封装请求对象中的数据到ActionForm中,在进行封装之前,先调用ActionForm的reset方法进行属性值的默认化。在Struts 学习之02(验证)中已经用过!
11.processValidate(request,response,form,mapping):如果ActionForm被设置好,并且Action元素的属性validate被设置为true,则进一步调用validate()方法进行规则校验。如果validate方法验证失败,就会保存一个ActionErrors对象到请求区域中,请求就会自动重写向到action映射的input属性所指定的页面中。如果校验通过或在action映射中没有配置ActionForm,则继续处理请求!在Struts 学习之02(验证)中已经用过!
12.processForward(reuest,response,mapping) & processInclude(request,response,mapping):根据action映射是否配置了forward属性或include属性来决定下一步操作。如果配置了任意一个,则相应地调用RequestDispathcher对象的forward方法或include方法,调用后,对客户请求的处理结束。否则,继续处理请求!
13.processActionCreate(request,response,mapping):创建或获取一个Action对象实例处理请求。processActionCreate方法会在缓存中查找是否存在已经创建好的Action实例,如果存在,则重复用之,否则,重新创建并将其存于缓存中。如果该方法返回null,则请求处理结束(注:根据action映射的type属性来寻找对应的Action类)。
14.processActionPerform(request,response,action,form,mapping):调用action实例的execute()方法。也就是为什么我们正常创建一个action时 都会重写它的execute方法!
15.processForwordConfig(request,response,forword):传入action的execute()方法返回的ActionForword对象实例,方法通过检查ActionForword对象实例,决定用redirect或forword方式进行重定向。究竟采用redirect还是forword取决于forword元素的redirect属性值!在前面我们也使用过了!
好了,控制器中篇就先写到这~余下的我会在下一篇中继续!




