java第一阶段(day16)超市管理系统
1.创建项目 surpermarmarket
2.引入依赖(4个jar包) surpermarmarket.lib包下
3.写配置文件(创建数据库连接池) surpermarmarket.druid.properties
username=root
password=root
url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/supermarket?characterEncoding=utf-8 (防止乱码)
driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver4.创建包 src.com.javasm.bean等,这里忘记写com.javssm jar文件放到了dir包里
注:路径不要出现java单个的
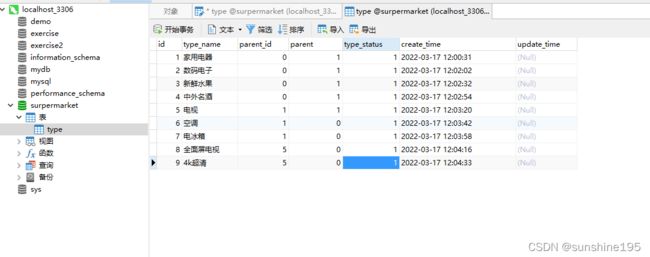
5.建库surpermarmarket,新建第一张表type(商品类型表)
注:字段名里不要带is,尤其是boolean类型的
6.编码工作
6.1写APP接口 surpermarmarket.src.App (客户端)
public class APP {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SupermarketMgr().start();
}
}6.2新建测试类 surpermarmarket.src.SupermarketMgr
含根据登录名选角色方法,登录方法,管理员方法,收银员方法等
public class SupermarketMgr {
public void start() {
login(); //根据登录用户的用户名和密码进行判断是哪个角色
}6.3新建封装录入Scanner的类 util.InputUtil
public class InputUtil {
private InputUtil(){}
private static Scanner input;
static{
input = new Scanner(System.in);
}
public static String inputStr(){
return input.next();
}
public static void close(){
input.close();
}
}6.4新建枚举类,放管理员,收银员账号,密码。 common.RoleEnum
@AllArgsConstructor
@Getter
public enum RoleEnum {
ADMIN("admin","1234"),
CASHIER("cashier","1234");
private final String name;
private final String pass;
}6.5写登录方法,并选择管理员菜单或者收银员菜单
private void login() {
System.out.println("----------------欢迎登录----------------");
System.out.println("请录入用户名:");
String name = InputUtil.inputStr();
System.out.println("请录入密码:");
String pass = InputUtil.inputStr();
if(Objects.equals(name, RoleEnum.ADMIN.getName())&&Objects.equals(pass, RoleEnum.ADMIN.getPass())){
//管理员
adminMenu();
}else if(Objects.equals(name, RoleEnum.CASHIER.getName())&&Objects.equals(pass, RoleEnum.CASHIER.getPass())){
//收银员
cashierMenu();
}else{
InputUtil.close();
throw new RuntimeException("录入用户名或者密码有误,不存在此用户,请联系管理员");
}
}6.6 写管理员菜单---商品类型管理,商品管理,会员管理三个功能
private void adminMenu() {
System.out.println("欢迎你"+RoleEnum.ADMIN.getName());
String str;
do {
System.out.println("1.商品类型管理");
System.out.println("2.商品管理");
System.out.println("3.会员管理");
System.out.println("4.退出");
int choice = InputUtil.inputInt("^[1-4]$","请录入1-4数据:");
switch (choice) {
case 1:
//1.商品类型管理
break;
case 2:
//2.商品管理
break;
case 3:
//3.会员管理
break;
case 4:
//4.退出
System.out.println("程序退出");
return;
}
System.out.println("是否继续操作?y/n");
str = InputUtil.inputStr();
} while (str.equalsIgnoreCase("y"));
}这里需在封装录入的Scanner类中加入输入int型数据方法:
public static int inputInt(String regex, String msg) {
while (true) {
System.out.println(msg);
String str = input.next();
if(str.matches(regex)){
return Integer.parseInt(str);
}
}
}同时在登录入口处给出资源释放:(省去每次用一个菜单,释放一次资源)
public void start() {
login(); //根据登录用户的用户名和密码进行判断是哪个角色
InputUtil.close();
}6.7新建商品类型管理模块(新增,删除,修改,查询,退出) 先新建menu包,包下新建TypeMenu
public class TypeMenu {
public void menu(){
String s;
do {
System.out.println("1.新增类型");
System.out.println("2.删除类型");
System.out.println("3.修改类型");
System.out.println("4.层级查询类型");
System.out.println("5.退出");
int choice = InputUtil.inputInt("^[1-5]$", "请录入1-5的数据:");
switch (choice) {
case 1:
//1.新增类型
break;
case 2:
//2.删除类型
break;
case 3:
//3.修改类型
break;
case 4:
//4.层级查询类型
break;
case 5:
//5.退出
break;
}
System.out.println("是否继续?y/n");
s = InputUtil.inputStr();
} while (Objects.equals(s,"y"));
}
}6.8一般增删改都是看着信息进行,故先完成查询功能。这些需要dao,service,impl,sql等。
在sql包下新建TypeSql
public interface TypeSql {
//查询所有类型的数据
String FIND_ALL_TYPE = "select * from type";
}在bean包逆向引入Type 修改不符合jdbc的字段类型
@Setter
@Getter
@ToString
public class Type {
private Integer id;
private String typeName;
private Integer parentId;
private boolean parent;
private boolean typeStatus;
private java.util.Date createTime;
private java.util.Date updateTime;
}在dao包新建TypeDao
public interface TypeDao {
List findAllType() throws Exception;
} 在dao.impl包下新建TypeDaoImpl
public class TypeDaoImpl implements TypeDao {
@Override
public List findAllType() throws Exception {
return new QueryRunner(数据源).query(TypeSql.FIND_ALL_TYPE,new BeanListHandler<>(Type.class,new BasicRowProcessor(new GenerousBeanProcessor())));
}
} 故此时要建立数据源 在util包下新建DruidUtil
public class DruidUtil {
private DruidUtil(){
}
private static DataSource dataSource;
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src/druid.properties"));
dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static DataSource getDataSource(){
return dataSource;
}
}相应的可增加配置文件的初始值和默认最大值:
username=root
password=root
url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/supermarket?characterEncoding=utf-8
driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
initialSize=5
maxActive=15回到TypeDaoImpl将数据源添加进去:
public class TypeDaoImpl implements TypeDao {
@Override
public List findAllType() throws Exception {
return new QueryRunner(DruidUtil.getDataSource()).query(TypeSql.FIND_ALL_TYPE,new BeanListHandler<>(Type.class,new BasicRowProcessor(new GenerousBeanProcessor())));
}
} 在service包下新建TypeService类:
public interface TypeService {
void findAllType();
}在service包下新建impl包,新建TypeServiceImpl类:
public class TypeServiceImpl implements TypeService {
private static final TypeDao typeDao = new TypeDaoImpl();
@Override
public void findAllType() {
try {
List typeList = typeDao.findAllType();
String str = "|-";
for (Type type : typeList) {
if(type.getParentId().equals(0)){
System.out.println(str+type.getTypeName());
//找指定父类型的子级类型
findChildType(type,"| "+str,typeList);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void findChildType(Type parentType, String s, List typeList) {
for (Type type : typeList) {
if(type.getParentId().equals(parentType.getId())){
System.out.println(s+type.getTypeName());
//如果子级类型是父级类型
if(type.isParent()){
findChildType(type,"| "+s,typeList);
}
}
}
}
} 相应的在TypeMenu类里增加如下语句:
private static final TypeService typeService = new TypeServiceImpl();
private void showTypeByLevel() {
System.out.println("类型信息展示如下:");
typeService.findAllType();
}6.9为了测试管理员菜单下的商品类型管理模块的层级查询功能代码是否正确,先将测试类里的收银员菜单添加。
private void cashierMenu() {
System.out.println("欢迎你"+RoleEnum.CASHIER.getName());
String str;
do {
System.out.println("1.购买管理");
System.out.println("2.订单查询");
System.out.println("3.排行统计");
System.out.println("4.退出");
int choice = InputUtil.inputInt("^[1-4]$","请录入1-4数据:");
switch (choice) {
case 1:
new TypeMenu().menu();
//1.购买管理
break;
case 2:
//2.订单查询
break;
case 3:
//3.排行统计
break;
case 4:
//4.退出
System.out.println("程序退出");
return;
}
System.out.println("是否继续操作?y/n");
str = InputUtil.inputStr();
} while (str.equalsIgnoreCase("y"));
}同时在管理员菜单的switch中的case1下增加:
new TypeMenu().menu();6.10类型的信息一般是不变的,没必要每次查询都掉数据库。可将其放入缓存,每次查前判断缓存是否为空,空则查数据库,并放入缓存,不空则直接查缓存。
缓存优点:提高了查询的性能 缺点:数据库更新,缓存不知道,不能实时同步,每次更新,都要及时更改缓存数据
在TypeServiceImpl中增加缓存,并修改相应查询代码:
private static Map cache = new HashMap<>(16);
@Override
public void findAllType() {
try {
List typeList = (List) cache.get("typeList"); //先从缓存拿数据
if(typeList == null){ //缓存为空
typeList = typeDao.findAllType(); //操作数据库
cache.put("typeList",typeList); //并将数据放入缓存
}
String str = "|-";
for (Type type : typeList) {
if(type.getParentId().equals(0)){
System.out.println(str+type.getId()+":"+type.getTypeName());
//找指定父类型的子级类型
findChildType(type,"| "+str,typeList);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} 6.11接着做管理员菜单下商品类型管理的新增功能:
在TypeMenu的switch的case1:下添加:
addTypeFun();并且在该类里添加该方法,具体些什么还不清楚,先从dao开始写:
//新增
int addType(Type type) throws Exception; //int两层意思:1.受影响记录数(先按这个来) 2.自增id 参数是完整的类型对象在TypeSql中加入新增sql
//新增
String INSERT_TYPE = "insert into type (type_name, parent_id, parent, type_status) values (?,?,?,?)";在daoImpl里:
为避免每次来个方法都new QueryRunner,可将其提出,并初始化。
//新增
@Override
public int addType(Type type) throws Exception {
//只要是新增的都是可用的,故将最后一个属性直接写死,写成1
return queryRunner.update(TypeSql.INSERT_TYPE,type.getTypeName(),type.getParentId(),type.isParent(),1);
}在service中:
int addType(Type type);在serviceImpl中:
异常用@SneakyThrows抛出:
//新增:
@Override
@SneakyThrows
public int addType(Type type) {
return typeDao.addType(type);
}回到TypeMenu,补全新增的方法:
private void addTypeFun() {
Type type = new Type();
System.out.println("请录入新的类型名称:"); //刚才已分析,最后一个属性已写死,只需录入三个属性
String typeName = InputUtil.inputStr();
type.setTypeName(typeName);
typeService.findAllType(); //给该类型指定父级类型,应该看着信息给,故应先查询
System.out.println("请指定该<<"+typeName+">>类型的父级类型:(作为1级类型 请给0)");
int parentId = InputUtil.inputInt(); //这里输入的内容不需要正则,在InputUtil里重载inputInt()的方法
if(parentId==0){
type.setParent(true);
}
type.setParentId(parentId);
typeService.addType(type);
System.out.println("新增<<"+typeName+">>成功");
}在InputUtil里重载inputInt():
public static int inputInt(){
return input.nextInt();
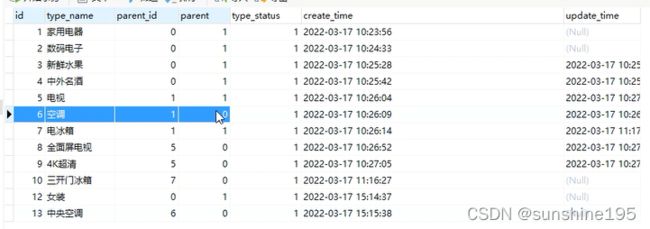
}当新增“中央空调后”,作为父级的空调并没有修改,其列parent数据仍为0,查询时将无法展示其子级中央空调。
故新增时,若为表中原有的类型的子级,且原类型的parent字段数据为0时,需要修改父级的记录:
在TypeMenu的addTypeFun()中删除判断parentId==0的代码,剩余代码为:
private void addTypeFun() {
Type type = new Type();
System.out.println("请录入新的类型名称:"); //刚才已分析,最后一个属性已写死,只需录入三个属性
String typeName = InputUtil.inputStr();
type.setTypeName(typeName);
typeService.findAllType(); //给该类型指定父级类型,应该看着信息给,故应先查询
System.out.println("请指定该<<"+typeName+">>类型的父级类型:(作为1级类型 请给0)");
int parentId = InputUtil.inputInt(); //这里输入的内容不需要正则,在InputUtil里重载inputInt()的方法
type.setParentId(parentId);
typeService.addType(type);
System.out.println("新增<<"+typeName+">>类型成功");
}从新增的类型中可通过parentId找到其父类id,但通过id查找类型的方法还没有,故应先在TypeDao里创建该方法:
//根据id查询类型
Type findTypeById(Integer TypeId) throws Exception;在TypeSql新增sql语句
//根据id查询类型
String FIND_TYPE_BY_ID = "select * from type where id = ? ";在TypeDaoImpl里实现该方法:
@Override
public Type findTypeById(Integer TypeId) throws Exception {
return queryRunner.query(TypeSql.FIND_TYPE_BY_ID,new BeanHandler<>(Type.class, new BasicRowProcessor(new GenerousBeanProcessor())), TypeId);
}找到父级类型的信息后,若父级类型的parent是0,那就要修改其为1.故还要新建修改的方法:
在TypeDao里:
//修改类型信息
int updateTypeById(Type parentType) throws Exception;在TypeSql新增sql语句:
//修改类型信息
String UPDATE_TYPE_BY_ID = "update type set type_name = ?, parent_id = ?, parent = ?, type_status = ? where id = ?";在TypeDaoImpl里实现该方法:
@Override
public int updateTypeById(Type parentType) throws Exception{
return queryRunner.update(TypeSql.UPDATE_TYPE_BY_ID,
parentType.getTypeName(),parentType.getParentId(),parentType.isParent(), parentType.isTypeStatus(),parentType.getId()
);
}回到TypeServiceImpl中,代码修改为:
//新增:
@Override
@SneakyThrows
public int addType(Type type) {
//新增前,要判断指定的父级类型是否作为父类型使用,若不是需要更改该记录
Integer parentId = type.getParentId(); //新增类型的父类型的id
if(parentId!=0){
Type parentType = typeDao.findTypeById(parentId); //根据父类类型id查其parent列是什么,故这里要创建findTypeById()方法
if(!parentType.isParent()){
parentType.setParent(true);
//修改父级类型的数据
typeDao.updateTypeById(parentType);
}
}else type.setParent(true);
return typeDao.addType(type);
}6.12删除类型功能
在TypeMenu里switch中case3中加如下语句:
deleteTypeFun();并在该类中新增该方法。删除也是看着信息删,故删之前可调该类中的层级展示的方法。
private void deleteTypeFun() {
showTypeByLevel();
System.out.println("请录入要删除的类型id:");
int typeId = InputUtil.inputInt();
typeService.deleteType(typeId);
System.out.println("删除类型id<<"+typeId+">>成功");
}在TypeService中创建deleteType()方法:
//删除类型信息
void deleteType(int typeId);在TypeServiceImpl中实现该方法:
//删除
@Override
@SneakyThrows
public void deleteType(int typeId) {
typeDao.deleteTypeById(typeId);
}在TypeDao里补全该方法:
//删除
void deleteTypeById(int typeId) throws Exception;在TypeSql里增加sql语句:
//删除
String DELETE_TYPE_BY_ID = "dalete from type where id = ?";在TypeDaoImpl里实现该方法:
@Override
public void deleteTypeById(int typeId) throws Exception {
queryRunner.update(TypeSql.DELETE_TYPE_BY_ID,typeId);
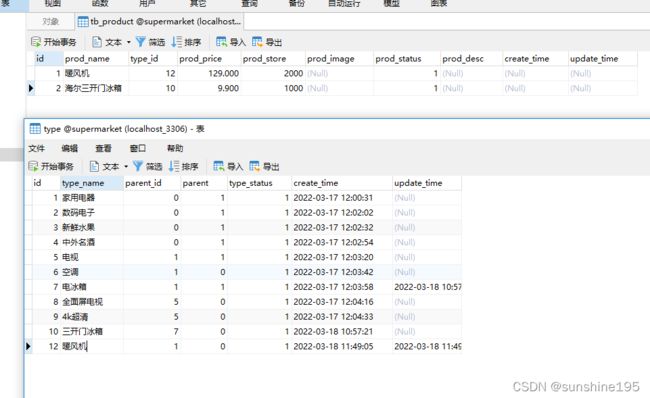
}删除是有要求的:父类类型不能删,即删除前应该判断是否有子级,有子级就不要删了。如何保证它是一个父级,还是查询。 类型是子级的也不能随便删,没有商品关联才可以删,有商品关联也不能删。
如上图,三开门冰箱虽然没有子级,但和商品表有关联,不能删。(删除后商品表中海尔三开门冰箱的type_id的10不知道是谁)
该子级类型是否有商品关联,还是查询,这是商品dao的功能,故在TypeServiceImpl中增加:
private static final ProductDao producyDao = new ProductDaoImpl();在dao包新建ProductDao:
public interface ProductDao {
}在dao.impl包下创建其实现类:
public class ProductDaoImpl implements ProductDao {
@Override
public List findProductByTypeId(int typeId) {
return null;
}
} 在bean包下逆向引入商品表:
在ProductDao新建方法:
//根据类型id查询关联的商品
List findProductByTypeId(int typeId) throws Exception; 在ProductDaoImpl中实现该方法:
public class ProductDaoImpl implements ProductDao {
private static final QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(DruidUtil.getDataSource());
@Override
public List findProductByTypeId(int typeId) throws Exception{
return queryRunner.query(ProductSql.FIND_PRODUCT_BY_TYPE,
new BeanListHandler<>(Product.class,new BasicRowProcessor(new GenerousBeanProcessor())),typeId);
}
} 在sql包下创建ProductSql接口,写商品的sql
public interface ProductSql {
String FIND_PRODUCT_BY_TYPE = "select * from product where type_id=? ";
}在TypeServiceImpl类中,修改deleteType方法:
//删除
@Override
@SneakyThrows
public void deleteType(int typeId) {
Type type = typeDao.findTypeById(typeId); //只要是删除都是有查询的
String typeName = type.getTypeName();
//若类型是作为父级类型使用,不能删除
if(type.isParent()){
System.out.println("<<"+typeName+">>是作为父类型的,无法删除");
return;
}
//若删除子级类型,在没有商品关联时才可删除,有关联不能删除,因此还是要先查询该类型下是否关联商品。
List productList = producyDao.findProductByTypeId(typeId);
if(!productList.isEmpty()){
System.out.println("<<"+typeName+">>关联了具体的商品,无法删除");
return;
}
//到底是否真的删除,看具体需求,仅仅是更改状态还是直接删除这条记录? (目前真的删除)
typeDao.deleteTypeById(typeId);
} 回到TypeMenu中,是否删除,要返回个值来确定,这里暂且用boolean类型(为true,则成功)
private void deleteTypeFun() {
showTypeByLevel();
System.out.println("请录入要删除的类型id:");
int typeId = InputUtil.inputInt();
if (typeService.deleteType(typeId)) {
System.out.println("删除类型id<<"+typeId+">>成功");
}
}相应的在TypeService中修改返回值类型为boolean
//删除类型信息
boolean deleteType(int typeId);在实现类中也相应进行修改:
//删除
@Override
@SneakyThrows
public boolean deleteType(int typeId) {
Type type = typeDao.findTypeById(typeId); //只要是删除都是有查询的
String typeName = type.getTypeName();
//若类型是作为父级类型使用,不能删除
if(type.isParent()){
System.out.println("<<"+typeName+">>是作为父类型的,无法删除");
return false;
}
//若删除子级类型,在没有商品关联时才可删除,有关联不能删除,因此还是要先查询该类型下是否关联商品。
List productList = producyDao.findProductByTypeId(typeId);
if(!productList.isEmpty()){
System.out.println("<<"+typeName+">>关联了具体的商品,无法删除");
return false;
}
//到底是否真的删除,看具体需求,仅仅是更改状态还是直接删除这条记录? (目前真的删除)
typeDao.deleteTypeById(typeId);
return true;
} 6.13接下来就是商品类型管理的修改功能:
在TypeMenu的switch的case3中添加语句,并增加其方法:
updateTypeFun();private void updateTypeFun() {
TypeService typeService = new TypeServiceImpl();
System.out.println("请录入要修改类型的id:");
int typeId = InputUtil.inputInt();
System.out.println("要修改的类型信息如下:");
Type type = typeService.findTypeById(typeId);
System.out.println("请录入要修改的列:1.type_name 2.parent_id 3.parent 4.type_status");
String choiceStr = InputUtil.inputStr();
String[] array = choiceStr.split(",");
for (String s : array) {
int choice = Integer.parseInt(s);
switch (choice){
case 1:
System.out.println("请录入新的type_name");
String newName = InputUtil.inputStr();
type.setTypeName(newName);
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("请录入新的parent_id");
Integer newId = InputUtil.inputInt();
type.setParentId(newId);
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("请录入新的parent");
boolean newParent = InputUtil.inputBoolean();
type.setParent(newParent);
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("请录入新的type_status");
boolean newStatus = InputUtil.inputBoolean();
type.setTypeStatus(newStatus);
break;
}
}
System.out.println(typeService.updateTypeById(type));
System.out.println("修改类型id<<" + typeId + ">>成功");
}在TypeService中新增:
int updateTypeById(Type type);在TypeServiceImpl中新增:
//修改商品类型
@Override
@SneakyThrows
public int updateTypeById(Type type) {
return typeDao.updateTypeById(type);
}在TypeDao中调用updateTypeById()方法。
在TypeDaoImpl中调用updateTypeById()方法。
至此,管理员菜单中商品类型管理模块(增删改查)做完。
6.14接下来写管理员菜单下的商品管理模块,对商品表进行添加,删除,修改,查询等。与商品类型管理模块基本一致。
首先在SupermarketMgr中管理员菜单的switch中的case2 中新增(访问商品菜单的入口):
new ProductMenu().menu();在Menu包下新建ProductMenu类,并新增menu()方法:
public class ProductMenu {
public void menu() {
String s;
do {
System.out.println("---------------------1.新增商品--------------------");
System.out.println("---------------------2.删除商品--------------------");
System.out.println("---------------------3.修改商品--------------------");
System.out.println("---------------------4.分页查询--------------------");
System.out.println("---------------------5.退 出--------------------");
int choice = InputUtil.inputInt("^[1-5]$", "请录入1-5的数据:");
switch (choice) {
case 1:
addProductFun();
break;
case 2:
deleteProductFun();
break;
case 3:
updateProductFun();
break;
case 4:
showProductByPage();
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("程序退出");
return;
}
System.out.println("是否继续操作商品模块?y/n");
s = InputUtil.inputStr();
} while (Objects.equals(s, "y"));
}
}同理先做4.分页查询:
private void showProductByPage() {
System.out.println("目前在售产品信息如下:");
final int size = 2;
int page = 1;
int totalCount = productService.findProductCount();
int totalPage = totalCount / size;
totalPage = (totalCount % size == 0) ? totalPage : totalPage + 1;
do {
System.out.println("第<<" + page + ">>页信息如下:");
List productList = productService.findProductByPage(page, size);
productList.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("是否继续查询其他商品?y/n");
String s = InputUtil.inputStr();
if (Objects.equals("n", s)) {
break;
}
page = continuePage(totalPage);
} while (true);
} 首先需要查询总记录数,才能知道页数,故先求总页数:
在service包下新建ProductService类,并新增求总页数的方法:
int findProductCount();在Service.Impl包下新建ProductServiceImpl类,并实现上述方法:
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public int findProductCount() {
return productDao.findProductCount();
}在dao包下新建ProductDao类,并新增该方法:
int findProductCount() throws Exception;在sql包下新建ProductSql类,并新增查询总记录数的sql:
String FIND_PRODUCT_COUNT = "SELECT count(*) FROM product WHERE prod_status=1";在dao.impl包下新建ProductDaoImpl类,并实现该方法:
@Override
public int findProductCount() throws Exception {
return queryRunner.query(ProductSql.FIND_PRODUCT_COUNT, new ScalarHandler()).intValue();
} 查得总记录数后,就可根据指定页数查询商品信息,在ProductSerive中新增该方法:
List findProductByPage(int page, int size); 在ProductServiceImpl中实现该方法:
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public List findProductByPage(int page, int size) {
return productDao.findProductByPage(page, size);
} 在ProductDao中新增该方法:
List findProductByPage(int page, int size) throws Exception; 在ProductSql中新增该sql:
String FIND_PRODUCT_BY_PAGE = "SELECT * FROM product WHERE prod_status=1 ORDER by id DESC LIMIT ?,?";在ProductDaoImpl中实现该方法:
@Override
public List findProductByPage(int page, int size) throws Exception {
return queryRunner.query(
ProductSql.FIND_PRODUCT_BY_PAGE,
new BeanListHandler<>(Product.class, new BasicRowProcessor(new GenerousBeanProcessor())),
(page - 1) * size, size);
} 以上分页查询,刚打开页面展示的是第一页信息,还应该有个指定页数的方法,故在ProductMenu类中的该分页查询功能中抽出一个指定页数的方法:
private int continuePage(int totalPage) {
for (int pageNum = 1; pageNum <= totalPage; pageNum++) {
System.out.print(pageNum + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("请录入要查看的页数:");
return InputUtil.inputInt();
}至此,分页查询功能结束。
接下来在ProductMenu中做新增和修改商品功能,录入商品所属类型应该看着商品类型进行录入:
private void addProductFun() {
Product product = new Product();
System.out.println("请录入商品的名称:");
product.setProdName(InputUtil.inputStr());
typeService.findAllType();
System.out.println("请选择商品所属类型:");
product.setTypeId(InputUtil.inputInt());
System.out.println("请录入商品库存:");
product.setProdStore(InputUtil.inputInt());
System.out.println("请录入商品单价:");
product.setProdPrice(Double.parseDouble(InputUtil.inputStr()));
System.out.println("请录入商品图片路径:");
product.setProdImage(InputUtil.inputStr());
System.out.println("请录入商品状态: 1. 在售 2. 下架 3.删除");
product.setProdStatus(InputUtil.inputInt());
System.out.println("请录入商品描述:");
product.setProdDesc(InputUtil.inputStr());
System.out.println(productService.addAndUpdateProduct(product));
System.out.println("新增商品<<" + product.getProdName() + ">>成功");
}在ProductService中新增该方法:
int addAndUpdateProduct(Product product);在ProductService中实现该方法:
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public int addAndUpdateProduct(Product product) {
String prodImage = product.getProdImage();
if (!prodImage.isBlank() && !prodImage.startsWith("upload")) {
//商品图片上传
product.setProdImage(FileUtil.uploadProductImage(product.getProdImage()));
}
if (product.getId() == null) {
return productDao.addProduct(product);
}
return productDao.updateProductById(product);
}在ProductDao中创建新增商品方法:
int addProduct(Product product) throws Exception;在ProductSql中增加新增的sql
String ADD_PRODUCT = "INSERT INTO product (prod_name, type_id, prod_price, prod_store, prod_image, prod_status, prod_desc) VALUES (?,?,?,?,?,?,?)";在ProductDaoImpl中实现该方法:
@Override
public int addProduct(Product product) throws Exception {
return queryRunner.update(ProductSql.ADD_PRODUCT,
product.getProdName(),
product.getTypeId(),
product.getProdPrice(),
product.getProdStore(),
product.getProdImage(),
product.getProdStatus(),
product.getProdDesc()
);
}在ProductDao中创建修改商品的方法:
int updateProductById(Product product) throws Exception;在ProductSql中增加修改的sql:
String UPDATE_PRODUCT_BY_ID = "UPDATE product SET prod_name=?, type_id=?, prod_price=?, prod_store=?, prod_image=?, prod_status=?, prod_desc=? WHERE id=?";在ProductDaoImpl中实现该方法:
@Override
public int updateProductById(Product product) throws Exception {
return queryRunner().update(ProductSql.UPDATE_PRODUCT_BY_ID,
product.getProdName(),
product.getTypeId(),
product.getProdPrice(),
product.getProdStore(),
product.getProdImage(),
product.getProdStatus(),
product.getProdDesc(),
product.getId()
);
}至此,新增和修改的方法结束。
接下来是删除商品的功能,在ProductMenu中新增该方法:
private void deleteProductFun() {
System.out.println("请录入要删除的商品id:");
int productId = InputUtil.inputInt();
System.out.println("确认删除吗?y/n");
String str = InputUtil.inputStr();
if (Objects.equals("n", str)) return;
Product product = productService.findProductById(pid);
product.setProdStatus(3);
productService.deleteProduct(productId);
System.out.println("删除id为<<" + pid + ">>商品成功");
}在ProductService中增加删除的方法:
//删除商品
void deleteProduct(int productId);在ProductServiceImpl中实现该方法:
@Override
@SneakyThrows
public void deleteProduct(int productId) {
productDao.deleteProduct(productId);
}在ProductDao中增加该方法:
//删除商品
void deleteProduct(int productId) throws Exception;在ProductSql中增加删除的sql:
String DELETE_PRODUCT ="delete from product where id = ?";在ProductDaoImpl中实现该方法:
@Override
public void deleteProduct(int productId) throws Exception {
queryRunner.update(ProductSql.DELETE_PRODUCT,productId);
}至此,商品管理模块结束。
管理员菜单中的会员管理模块,有添加会员,修改会员,查询会员,会员充值的功能,是对会员信息表的增删改查,和上面两个模块一模一样,这里略。
接下来做收银员部分,收银员菜单有1.购物车模块2.订单查询3.排行统计三个模块。先看第一个模块。
//收银员的模块
private void cashierMenu() {
String str;
do {
System.out.println("1.购物车模块");
System.out.println("2. 订单查询");
System.out.println("3. 排行统计");
System.out.println("4. 退 出");
int choice = InputUtil.inputInt("^[1-4]$", "请录入1-4之间的数据:");
switch (choice) {
case 1:
new CartMenu().menu();
break;
case 2:
break;
case 3:
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("程序退出");
return;
}
System.out.println("是否继续操作收银员模块?y/n");
str = InputUtil.inputStr();
} while (Objects.equals("y", str));
}在Menu包下新建CartMenu类,并新建menu()方法。
public class CartMenu {
public void menu() {
String s;
do {
System.out.println("---------------------1.购买指定商品--------------------");
System.out.println("---------------------2.修改商品数量--------------------");
System.out.println("---------------------3.删除购物车商品--------------------");
System.out.println("---------------------4.查询购物车商品信息--------------------");
System.out.println("---------------------5.支付--------------------");
System.out.println("---------------------6.退 出--------------------");
int choice = InputUtil.inputInt("^[1-6]$", "请录入1-5的数据:");
switch (choice) {
case 1:
buyProductFun();
break;
case 2:
break;
case 3:
break;
case 4:
CartService.showProdList();
break;
case 5:
pay();
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("程序退出");
return;
}
System.out.println("是否继续操作类型模块?y/n");
s = InputUtil.inputStr();
} while (Objects.equals(s, "y"));
}
}先做第一个功能,在该类中创建该方法。(购买商品,并存储到购物车里)
private static ProductService productService = new ProductServiceImpl();
//购物商品 存储购物车
private void buyProductFun() {
//1.查询目前在售的商品-----> 分页展示
int page = 1;
final int size = 2;
int totalCount = productService.findProductCount();
int totalPage = totalCount / size;
totalPage = (totalCount % size) == 0 ? totalPage : totalPage + 1;
do {
System.out.println("第<<" + page + ">>页的数据如下:");
List productList = productService.findProductByPage(page, size);
productList.forEach(System.out::println);
int choice = InputUtil.inputInt("^[1-3]$", "请选择功能: 1. 购买指定的商品 2. 继续分页查询 3.结束购买");
switch (choice) {
case 1:
putProdIntoCart();
break;
case 2:
page = continueShowPage(totalPage);
break;
case 3:
return;
}
} while (true);
} 继续分页查询的方法被抽出来,如下:
private int continueShowPage(int totalPage) {
for (int pageCount = 1; pageCount <= totalPage; pageCount++) {
System.out.print(pageCount + "\t");
}
System.out.println("请录入要查询的页数:");
return InputUtil.inputInt();
}购买指定商品的方法被抽出来,如下:
private void putProdIntoCart() {
System.out.println("请录入要购买的商品id:");
int pid = InputUtil.inputInt();
Product product = productService.findProductById(pid);
System.out.println("购买的商品详情如下:" + product);
String prodName = product.getProdName();
Integer prodStore = product.getProdStore();
System.out.println("请录入要购买的<<" + prodName + ">>数量:");
int buyNum = InputUtil.inputInt();
CartItem cartItem = CartService.getProdById(pid);
int oldNum = 0;
if (cartItem != null) {
oldNum = cartItem.getBuyNum();
}
if (buyNum + oldNum > prodStore) {
System.out.println("<<" + prodName + ">>库存不足 无法购买");
return;
}
//库存ok,可以购买,购买的商品存储在购物车
//题中要求购物车不是一张表,那购物车是一个容器。数组和集合可做容器,排除数组。集合有List,Map,set,其中set一般不用。
//从性能上map更好,若购买同一个商品,只需购买量累加即可,List需要循环遍历然后累加,而Map只需结合key拿value。
//若用List充当购物车,购物车里是购物项(购买的商品,购买数量,小计)以及总金额。在list<>里存product并不合适,只能拿到商品信息,购买量得不到,那就无法求得小计和总计。
//用Map去做,key应为商品id,value若为购买数量,支付成功后更新很多表,如何找到商品库存?求小计单价如何拿?需要根据商品id再查一次。若购物车里存10个商品,买的时候,会先查一次(根据商
// 品id),用来展示商品信息。做支付时,更新表,又要去查。10个商品一共查了20次,效率很低。故value存购买数量,不太合适。value存商品对象,相当于List。此时Map
//和List效果差不多,但Map效率更高。问题是拿不到购买数量,故value中放商品对象不合适。
//最合适的还是放购物项,两个都可以,用Map效率更高。
//List Map(可用来判断之前是否买过,不用遍历,可根据id直接拿,id==null,说明之前没买过)
CartService.addProdToCart(product, buyNum);
} 如上分析,购物车是Map集合,里面存放商品id和购物项。故,在bean包新建CartItem类,表示购物项:
@Setter
@Getter
public class CartItem {
private Product product; //商品信息
private Integer buyNum; //购买数量
private BigDecimal money; //每条购物项(每种商品)的小计
public BigDecimal getMoney() { //小计=数量*单价 小数间不能直接运算,且还是BigDecimal类型,要如下做:
money = new BigDecimal(buyNum.toString()).multiply(new BigDecimal(product.getProdPrice().toString()));
return money;
}
public CartItem(Product product, Integer buyNum) {
this.product = product;
this.buyNum = buyNum;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CartItem{" +
"productId=" + product.getId() +
", productName=" + product.getProdName() +
", productStore=" + product.getProdStore() +
", productPrice=" + product.getProdPrice() +
", buyNum=" + buyNum +
", money=" + getMoney() +
'}';
}
}在Service中新建CartService,去写增加商品到购物车的方法:
public class CartService {
private CartService() { //构造私有化
}
//创建购物车
public static Map cart; //购物车没必要new多次,一个人只有一辆
static {
cart = new HashMap<>(16); //初始化购物车
}
//CartItem对象里有商品对象,购买数量和小计。通过商品对象可拿到商品单价,从而可得小计。故小计money不需要传。
public static void addProdToCart(Product product, Integer buyNum) { //商品添到购物车的静态方法
Integer id = product.getId(); //拿商品id
CartItem item = cart.get(id);
if (item != null) {
//之前买过这个商品
item.setBuyNum(item.getBuyNum() + buyNum);
} else {
//第一次
item = new CartItem(product, buyNum); //CartItem对象
cart.put(id, item); //将商品添加到购物车(商品id和CartItem对象)
}
System.out.println("购买<<" + buyNum + ">>个" + product.getProdName() + "成功");
}
} 回到CartMenu目录,去写4.查询购物车商品信息的功能:
这里直接调CartService.showProdList();
public static void showProdList() {
if (cart.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("购物车目前没有商品");
return;
}
//遍历map
cart.forEach((id, item) -> System.out.println(item)); //对应的item即CartItem,要在该类中重写ToString().
}
public static CartItem getProdById(int pid) { //这个在CartMenu类中购买指定商品的方法中用到
return cart.get(pid);
}购买了指定商品并存在购物车后,就是5.支付。
支付一定是总金额,为购物车小计的累加,故应该在CartService类中增加计算小计累加的方法:
private static BigDecimal totalMoney; //totalMoney必须放到外面声明(不要初始化,要在里面初始化)
public static BigDecimal getTotalMoney() {
totalMoney = new BigDecimal("0"); //初始值给0
cart.forEach((id, item) -> { //这里lamda表示,是匿名内部类,故变量totalMoney必须放到外面声明
totalMoney = totalMoney.add(item.getMoney());
});
return totalMoney;
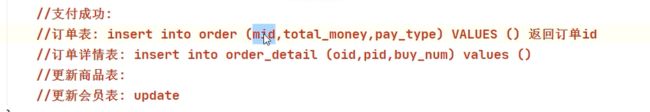
}支付方式有两种,现金支付和余额支付(最好用枚举)。考虑支付成功,需要动哪些表--1.订单表(mid表示会员id,游客的mid值为-1;total_money订单总金额;pay_type支付类型), 2. 订单详情表(oid订单id,pid购买商品的id,buy_num购买数量)。先走订单表,再走订单详情表。3.更新商品表信息。4.若选用余额支付,还要更新会员表。
但这里只有支付功能,支付需要生成订单(在OrderService里,还没创建),就将以上涉及要动的表都放到订单表里编写。写成一个事务。后面生成订单以及动这些表的一系列动作,只调用OrderService的一个方法,addOrder()即可。
选择余额支付,说明是会员,就需要录用户名和密码(前面没有说会员管理功能,这里新建MemberService,要什么方法创建什么方法),也要考虑余额是否大于订单总金额(余额不足可充值,充值就更新会员表的余额,也可转成现金支付,这里只写了现金支付)。这里将余额支付抽成一个方法.
生成订单的方法中,应该传入什么值?看sql语句,会员id,总金额,支付类型。总金额和支付类型都有。会员id呢?若为游客,则为-1,若为会员,应该在抽出的余额支付方法里的新建MemberService类的方法中找到,即在member对象里。如何拿到member对象?提前在余额支付的入口前声明Member member。(意思很简单,但是代码很巧妙,这里逻辑性有点强)
下面写代码:在CartMenu类中:
private Member member;
private void pay() {
OrderService orderService = new OrderServiceImpl();
BigDecimal totalMoney = CartService.getTotalMoney();
System.out.println("一共需要支付:" + totalMoney);
System.out.println("请选择支付方式:");
System.out.println("1.现金支付");
System.out.println("2.余额支付");
int payType = InputUtil.inputInt();
switch (payType) {
case 1:
member = new Member();
member.setId(-1);
break;
case 2:
payType = balancePay(totalMoney);
break;
}
orderService.addOrder(member, totalMoney, payType);
//清空购物车
CartService.cart.clear();
}
private static final MemberService memberService = new MemberServiceImpl();
private int balancePay(BigDecimal totalMoney) {
System.out.println("请录入用户名:");
String name = InputUtil.inputStr();
System.out.println("请录入密码:");
String pass = InputUtil.inputStr();
member = memberService.findMemberByNameAndPass(name, pass);
BigDecimal balance = member.getBalance();
if (balance.compareTo(totalMoney) < 0) {
//余额不足
System.out.println("请使用现金支付");
return 1;
}
return 2;
}这里需要注意一点(在进行余额比较时,balance和totalMoney都是BigDecimal对象,对象不能直接比较。这里用compareTo(BigDecimal val),返回值为int。) 如下测试:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new BigDecimal("100").compareTo(new BigDecimal("200")));
}返回值为-1,代表100比200小。
在service包下创建MemberService类,并增加需要的方法:
public interface MemberService {
Member findMemberByNameAndPass(String name, String pass);
}在Service.impl包下新建其实现类,并重写该方法:
public class MemberServiceImpl implements MemberService {
private static MemberDao memberDao = new MemberDaoImpl();
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public Member findMemberByNameAndPass(String name, String pass) {
return memberDao.findMemberByNameAndPass(name, pass);
}
}在dao包下:
public interface MemberDao {
Member findMemberByNameAndPass(String name, String pass) throws Exception;
void updateMember(Member member) throws Exception;
}在sql包下新建MemberSql类,并增加相关sql(这里将更新会员表的sql也写入):
public interface MemberSql {
String FIND_BY_NAME_PASS = "SELECT * FROM member WHERE name=? and password=?";
String UPDATE_MEMBER = "update member set name=?, password=?, user_image=?, phone=?, balance=?, point=? where id = ?";
}
在dao.impl包下:
public class MemberDaoImpl implements MemberDao {
private static QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(DruidUtil.getDataSource());
@Override
public Member findMemberByNameAndPass(String name, String pass) throws Exception {
return queryRunner.query(
MemberSql.FIND_BY_NAME_PASS,
new BeanHandler<>(Member.class, new BasicRowProcessor(new GenerousBeanProcessor())),
name, pass
);
}
}接下来写创建订单并更新一系列表的操作:
在Service包下创建OrderService类,并增加新增订单的方法:
public interface OrderService {
void addOrder(Member member, BigDecimal totalMoney, int payType);
}在Service.impl包下创建OrderServiceImpl类,实现该方法,并且更新相关表,用事务写:
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
@Override
public void addOrder(Member member, BigDecimal totalMoney, int payType) {
Connection connection = null;
try {
//0. 手动的从池子里面获得一个闲置的可用的连接对象
connection = DruidUtil.getDataSource().getConnection();
//1.关闭事务自动提交
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
OrderDao orderDao = new OrderDaoImpl(connection);
ProductDao productDao = new ProductDaoImpl(connection);
MemberDao memberDao = new MemberDaoImpl(connection);
Integer memberId = member.getId();
//订单表: insert into order (mid,total_money,pay_type) VALUES () 返回订单id
int oid = orderDao.addOrder(memberId, totalMoney, payType);
//订单详情表: insert into order_detail (oid,pid,buy_num) values () 购物项
Set> entrySet = CartService.cart.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry itemEntry : entrySet) {
Integer pid = itemEntry.getKey();
CartItem cartItem = itemEntry.getValue();
Integer buyNum = cartItem.getBuyNum();
orderDao.addOrderAndDetail(oid, pid, buyNum);
//更新商品表:
Product product = cartItem.getProduct();
int newStore = product.getProdStore() - buyNum; //新库存是原库存-购买量
if (newStore == 0) { //新库存为0,被买光
product.setProdStatus(2); //2代表下架,应该放到枚举类中维护
}
product.setProdStore(newStore);
productDao.updateProductById(product);
}
//更新会员表: update
if (memberId != -1) {
member.setBalance(member.getBalance().subtract(totalMoney)); //subtract是减
member.setPoint(member.getPoint()+totalMoney.doubleValue());
memberDao.updateMember(member);
}
//2.提交事务并释放资源
DbUtils.commitAndCloseQuietly(connection);
} catch (Exception e) {
//3.回滚事务并释放资源
e.printStackTrace();
DbUtils.rollbackAndCloseQuietly(connection);
}
}
} 在Dao包下创建OrderDao类:
public interface OrderDao {
int addOrder(Integer memberId, BigDecimal totalMoney, int payType) throws Exception;
void addOrderAndDetail(int oid, int pid, int buyNum) throws Exception;
}在sql包下创建OrderSql类,并增加sql:
public interface OrderSql {
String ADD_ORDER = "INSERT INTO `order` (mid, total_money, pay_type) VALUES (?,?,?)";
String ADD_ORDER_DETAIL = "INSERT INTO order_detail (oid, pid, buy_num) VALUES (?,?,?)";
}在Dao.Impl包下创建OrderDaoImpl类:
public class OrderDaoImpl implements OrderDao {
private Connection connection;
public OrderDaoImpl() {
}
public OrderDaoImpl(Connection connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
@Override
public int addOrder(Integer memberId, BigDecimal totalMoney, int payType) throws Exception {
return new QueryRunner().insert(connection,
OrderSql.ADD_ORDER,
new ScalarHandler(),
memberId,totalMoney,payType).intValue(); //将BigInteger转成int数据
}
@Override
public void addOrderAndDetail(int oid, int pid, int buyNum) throws Exception {
new QueryRunner().update(connection,OrderSql.ADD_ORDER_DETAIL,oid,pid,buyNum);
}
} 更新会员表,在上面已写了一部分,现在还需在MemberDaoImpl写其实现方法(注意,一个事务中写,就不能调用QueryRunner的有参构造,从池子里拿连接了。其连接从service中拿):
private Connection connection;
public MemberDaoImpl(Connection connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
public MemberDaoImpl() { //也要提供无参构造,不然其他地方可能报错
}
@Override
public void updateMember(Member member) throws Exception {
new QueryRunner().update(connection, MemberSql.UPDATE_MEMBER,
member.getName(),
member.getPassword(),
member.getUserImage(),
member.getPhone(),
member.getBalance(),
member.getPoint(),
member.getId()
);
}
对应的ProductDaoImpl类中也应该从servise中拿连接(这里有小问题,看代码):
private Connection connection;
public ProductDaoImpl(Connection connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
public ProductDaoImpl() {
}
@Override
public int updateProductById(Product product) throws Exception {
//这里有问题,若只是一个单独的更新,只是商品表的更新,怎么处理? 再加一个更新方法,连接从池子拿,代码冗余。 只能if判断,下面会说。
return new QueryRunner().update(connection, ProductSql.UPDATE_PRODUCT_BY_ID,
product.getProdName(),
product.getTypeId(),
product.getProdPrice(),
product.getProdStore(),
product.getProdImage(),
product.getProdStatus(),
product.getProdDesc(),
product.getId()
);
}以更新会员表为例,在事务里,则从service拿连接,单独更新会员表,则从池子拿连接。在MemberDaoImpl中只能判断连接,尽管这不是最完美的解决方式:
//"update member set name=?, password=?, user_image=?, phone=?, balance=?, point=? where id = ?";
@Override
public void updateMember(Member member) throws Exception {
if(connection==null){
queryRunner.update(MemberSql.UPDATE_MEMBER,
member.getName(),
member.getPassword(),
member.getUserImage(),
member.getPhone(),
member.getBalance(),
member.getPoint(),
member.getId()
);
return;
}
new QueryRunner().update(connection, MemberSql.UPDATE_MEMBER,
member.getName(),
member.getPassword(),
member.getUserImage(),
member.getPhone(),
member.getBalance(),
member.getPoint(),
member.getId()
);
}至此,收银员部分的购物车模块的支付功能结束。