JavaSE基础加强-学习黑马程序员Java基础视频教程(P93开始)
目录
- P0:写在前面的小知识
- P93:下阶段:JavaSE基础加强简介
- P95:static:修饰成员变量、内存机制
- P96:static:修饰成员方法、内存机制
- P97:static:访问的注意事项[拓展、面试]
- P98:static:应用知识-工具类
- P99:static:应用知识-代码块
- P100:static:应用知识-单例模式
- P101:继承:概述、案例
- P102:继承:特点、访问特点、方法重写
- P103:继承:构造器特点、this、super小结
- P105:语法:包、权限修饰符
- P106:语法:final的语法
- P107:语法:常量、常量在开发中的作用
- P108:语法:枚举、枚举作用
- P109:抽象类:概述、案例、特点
- P110:抽象类:模板方法模式
- P111:接口:概述、多实现、多继承
- P112:接口新增方法、注意事项(了解)
- P113:多态的概述,优势,类型转换问题
- P114:多态综合案例
- P115:内部类
- P116:匿名内部类(重点)
- P117:常用API-Object、Objects
- P118:常用API-StringBuilder
- P119:常用API-Math、System、BigDecimal
- P121:日期时间:Date、SimpleDateFormat、Calendar
- P122:JDK开始新增日期API
- P123:包装类
- P124:正则表达式
-
- P124.1 正则表达式的初体验
- P124.2 正则表达式的匹配规则
- P124.3 正则表达式案例
- P124.4 按照正则表达式匹配,分割字符串
- P124.5 爬取信息
- P125:Arrays类
- P126:选择排序、二分查找
-
- P126.1 选择排序
- P126.2 二分查找
- P127:Lambda表达式
-
- P127.1 概念
- P127.2 实例
- P127.3 Lambda表达式的省略规则(进一步简写)
- P129:集合概述、Collection集合的体系特点
-
- P129.1 概述
- P129.2 体系结构
-
- P129.2.1 Collection
- P130:Collection常用API、遍历方式、存储自定义类型的对象
-
- P130.1 常用API
- P130.2 遍历方式
-
- P130.2.1 迭代器 Iterator
- P130.2.2 foreach/增强for循环
- P130.2.3 lambda表达式
- P130.3 Collection集合存储自定义类型的对象
- P131:常见数据结构简介
-
- P131.1 数据结构概述、栈、队列
- P131.2 数组
- P131.3 链表
- P131.4 二叉树、二叉查找树
- P131.5 平衡二叉树
- P131.6 红黑树
- P131:List系列集合、集合的并发修改异常问题
-
- P131.1 List集合特点、特有API
- P131.2 4种遍历方法
- P132.3 ArrayList的底层原理
- P132.4 LinkedList的底层原理
- 补充知识:集合的并发修改异常问题
- P132:泛型深入、自定义泛型、泛型通配符、上下限
学习!!!2022黑马程序员Java学习路线图,好像跟菜鸟教程挺一致的:Java 教程 | 菜鸟教程。
领取方式:关注微信公众号:黑马程序员,回复关键词:领取资源02
在这个博客中黑马程序员Java基础视频教程-课程总结文档,我将徐磊老师写的xmind转为了图片方便观看。
Java入门-学习黑马程序员Java基础视频教程(到P92)
P0:写在前面的小知识
(先记录在这篇博文,到时候与第一篇博文整合到一起)
6.格式化输出(参考链接:Java如何格式化输出?)
- 一般方式:
System.out.println("x = " + x + ", y = " + y); - printf()方式:
System.out.printf("x = %d, y = %f\n", x, y); - format()方式:
System.out.format("x = %d, y = %f\n", x, y);
format与printf是等价的
%d表示整数类型,%f表示浮点数类型。%.2f表示保留小数点后2位
7.类有 5 大成分:成员变量、构造器、方法、代码块、内部类
8.子类对外是一个对象地址,但是内部是分为了两个空间:父类空间super、子类空间this
9.继承
- Java中所有的类都是Object的子类
- 在子类方法中访问成员(成员变量、成员方法)满足:就近原则,使用关键字
super.、this.分别指定访问父类、子类中的成员
10.权限修饰符作用范围:从小打大:private -> 缺省 -> protected ->public
11.一些用在类前的特殊的关键字:final、abstract、interface
- final 与 abstract是互斥关系。final定义的类不能被继承;相反用abstract定义的类必须被继承;final定义的方法不能被重写,abstract定义的方法笔记被重写
- 继承:public 子类名 extends 父类名(只能单继承)
- 实现:public interface 子类名 implement 父类名1,父类名2…(可以多实现)
- 如果一个子类又要继承又要实现,则要先继承后实现,例如:
class Cat extends Animal implements Food{ } - 接口不能实例化、不能创建对象
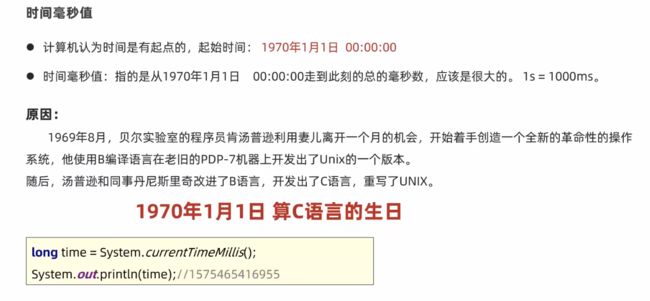
12.时间毫秒值:指从1970年1月1日 00:00:00走到此刻的总的毫秒数。1s=1000ms(1970年1月1日 算C语言的生日,在P119)
11.直接打印集合类,显示的结果是内容;直接打印数组显示的是地址,可用集合类转为字符串Arrays.toString(arr);
12.一个.java文件中可以写多个class,但是只能有一个类的前面加有修饰词public
P93:下阶段:JavaSE基础加强简介
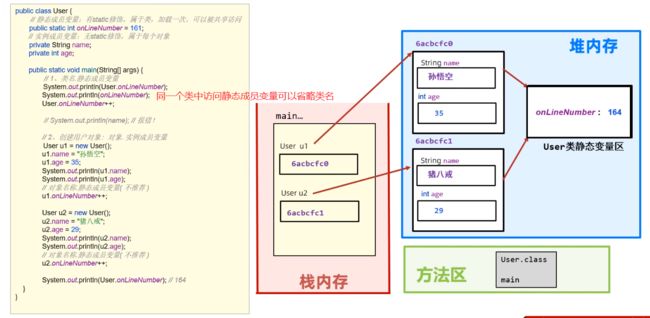
P95:static:修饰成员变量、内存机制
这张图是精髓,注释也要仔细看!
- 同一个类中访问静态成员变量可以省略类名,即通常访问格式为
User.onLineNum,但是可省略写成onLineNum。 - 静态成员变量:有static,属于类,加载一次,可以被共享访问
- 实例成员变量:无static,属于每个对象
P96:static:修饰成员方法、内存机制
P97:static:访问的注意事项[拓展、面试]
static访问注意事项:
- 静态方法只能访问静态的成员,不可以直接访问实例成员(因为实例成员必须由对象触发)
- 实例方法可以访问静态的成员,也可以访问实例成员
- 静态方法中是不可以出现 this 关键字的(this 关键字指明的是当前对象的地址)
- 静态成员只能由类触发;实例成员可由类、对象触发。
P98:static:应用知识-工具类
工具类是什么?
类中都是一些静态方法,每个方法都是以完成一个共用的功能为目的,这个类用来给系统开发人员共同使用的。
使用工具类的好处: 调用方便,提高了代码复用(一次编写,处处可用)
TestDemo.java
package d3_static_test;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = null;
int[] b = {};
int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
System.out.println(ArrayUtils.toString(arr));
System.out.println(ArrayUtils.toString(a));
System.out.println(ArrayUtils.toString(b));
System.out.println("------------------------");
double[] arr2 = {10, 20.5, 30.2, 40.9, 6, 2};
System.out.printf("average = %.2f\n", ArrayUtils.getAverage(arr2));
System.out.println("average = " + ArrayUtils.getAverage(null));
}
}
ArrayUtils.java
package d3_static_test;
public class ArrayUtils {
// 定义一个私有的构造器,表明不能将此类实例化成对象
private ArrayUtils() {
}
// 将整数一维数组转为String类型,格式为[x1, x2, ...]
public static String toString(int[] arr){
if (arr == null){
System.out.println("Array is NULL.");
return null;
}
String s = "[";
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
s += i == arr.length - 1 ? arr[i] : arr[i] + ", ";
}
return s + "]";
}
// 返回将浮点数类型一维数组的平均值(出去最高、最低值)
public static double getAverage(double[] arr){
if (arr == null){
System.out.println("Array is NULL.");
return -1;
}
double max = arr[0], min = arr[0], sum = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max){
max = arr[i];
}
if (arr[i] < min){
min = arr[i];
}
sum += arr[i];
}
return (sum - max - min) / (arr.length - 2);
}
}
P99:static:应用知识-代码块
{}构造代码块(也称实例代码块),用的比较少,还是static {}静态代码块用得比较多,都是执行构造函数之前。- 顺序: 静态代码块 > 构造代码块 > 构造函数,且静态代码块只会在首次调用类的被触发一次,构造代码块会在构造新对象时触发
- 注意: 此代码块中只能写语句,不能写方法
- 静态代码块的特点:如果要在启动系统时对静态资源进行初始化,则建议使用静态代码块完成数据的初始化操作。
package d3_static_test;
public class StaticTestDemo3 {
// 成员变量
private String name;
private static int age = 10;
// 构造函数
StaticTestDemo3(String name){
this.name = name;
System.out.println("========构造函数construct=============");
}
// 构造代码块,执行于构造函数之前
{
String name2 = "long";
System.out.println(name2);
}
// 静态代码块 > 构造代码块 > 构造函数,只调用一次
static {
age++;
System.out.println("age =" + age);
}
// 方法
public void print(){
System.out.println(name + "的年龄是" + age);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StaticTestDemo3 test = new StaticTestDemo3("wu");
StaticTestDemo3 test2 = new StaticTestDemo3("dan");
test.print();
test2.print();
test.print();
}
}
//age =11
//long
//========构造函数construct=============
//long
//========构造函数construct=============
//wu的年龄是11
//dan的年龄是11
//wu的年龄是11
package d3_static_test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class CardTest {
// 1.定义一个静态成员变量,一般使用public共享访问
public static ArrayList<String> cards = new ArrayList<>();
// 2.使用静态代码块,构造56张牌
static {
// 点数
String[] sizes = {"3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10", "J", "Q", "K", "A", "2"};
String[] colors = {"♥", "♠", "♦", "♣"};
for (int i = 0; i < sizes.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < colors.length; j++) {
cards.add(sizes[i] + colors[j]);
}
}
cards.add("小");
cards.add("大");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("新牌为:" + cards); // 在同一个类中,可直接使用静态成员变量
System.out.println("新牌张数为:" + cards.size());
}
}
// 新牌为:[3♥, 3♠, 3♦, 3♣, 4♥, 4♠, 4♦, 4♣, 5♥, 5♠, 5♦, 5♣, 6♥, 6♠, 6♦, 6♣, 7♥, 7♠, 7♦, 7♣, 8♥, 8♠, 8♦, 8♣, 9♥, 9♠, 9♦, 9♣, 10♥, 10♠, 10♦, 10♣, J♥, J♠, J♦, J♣, Q♥, Q♠, Q♦, Q♣, K♥, K♠, K♦, K♣, A♥, A♠, A♦, A♣, 2♥, 2♠, 2♦, 2♣, 小, 大]
// 新牌张数为:54
P100:static:应用知识-单例模式
- 单例:就表示只能拿到一个类、构造器私有、需要内部创建一个静态实例共外部调用(根据实例的构造先后,依次分为饿汉、懒汉单例)
饿汉单例模式
懒汉单例模式
P101:继承:概述、案例
子类对外是一个对象,但是内部是分为了两个空间:父类空间super、子类空间this
P102:继承:特点、访问特点、方法重写
方法重写:
- 子类重写父类方法时,建议对该方法的【声明不变,重新实现】,即方法修饰符、方法名、形参列表等全部都与父类一致,只是在函数体写明新的逻辑代码
- 在需要重写的方法上一行,加上
@Override注解,可以帮助校验重写方法的格式是否正确 + 提高代码的可读性
P103:继承:构造器特点、this、super小结
子类构造器访问父类无参构造器:
- 调用父类无参构造器代码:
super(); - 调用父类有参构造器代码:
super(name, age,...);
如果子类的构造器中没有调用super(name, age,...);,则默认都会自动调用super();。一旦有代码调用了super(name, age,...);,则不会再调用super();
this 和 super
P105:语法:包、权限修饰符
第3栏的【同一个包中其他类】表示:同一个包中的所有类(无关类or子类)
P106:语法:final的语法
public static final修饰的也常称为常量了
P107:语法:常量、常量在开发中的作用
P108:语法:枚举、枚举作用
- 用枚举做信息标志和分类的代码可读性号,入参约束严谨,是最好的信息分类技术
- 但是在实际应用中,可能是因为常量使用比较简单,使用常量的概率会高一些
P109:抽象类:概述、案例、特点
final和abstract是互斥关系
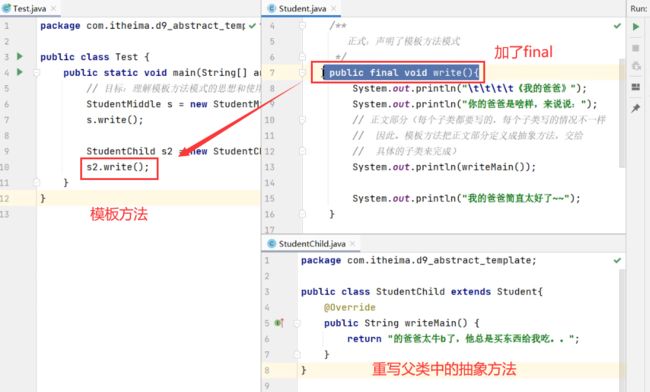
P110:抽象类:模板方法模式
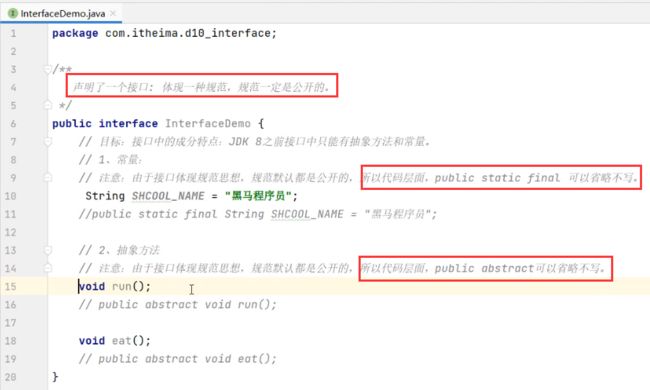
P111:接口:概述、多实现、多继承
P112:接口新增方法、注意事项(了解)
P113:多态的概述,优势,类型转换问题
多态侧重于行为(即方法)
多态的定义: 同类型的对象,执行同一个行为,会表现出不同的特征
P114:多态综合案例
我的代码跟老师的不一样,老师还定义了一个电脑类,然后使用的installUSB,而我是直接定义在这个主代码里面了,emmm~
package d3_interface;
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用多态
USB usb1 = new Mouse("罗技");
USB usb2 = new Keyboard("联想");
System.out.println("----------连接USB设备---------");
usb1.on();
usb2.on();
System.out.println("\n----------使用USB设备---------");
// 先判断数据类型,然后进行强制数据类型转换,并使用实现类的独有功能
useUSB(usb1);
useUSB(usb2);
System.out.println("\n----------断开USB设备---------");
usb1.off();
usb2.off();
}
public static void useUSB(USB usb){
if (usb instanceof Mouse){
Mouse M_usb = (Mouse) usb;
M_usb.click();
}else if(usb instanceof Keyboard){
Keyboard K_usb = (Keyboard) usb;
K_usb.typewriter();
}else{
System.out.println("暂不处理~~");
}
}
}
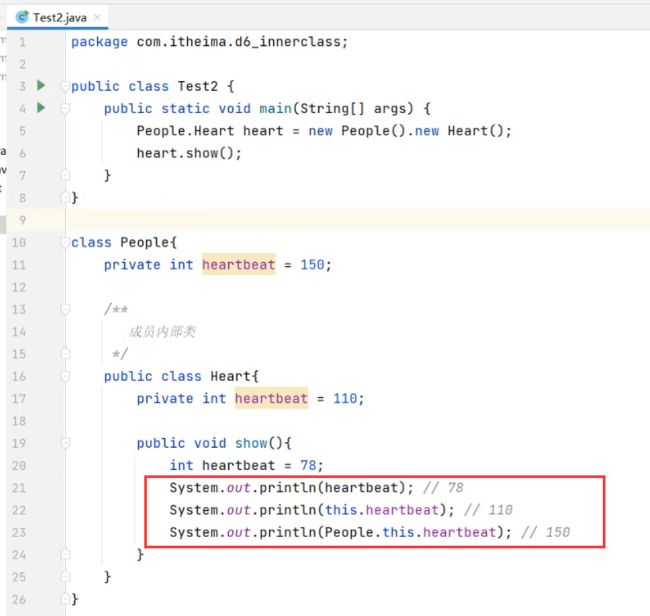
P115:内部类
内部类的分类:
- 静态内部类 [了解]
- 成员内部类(非静态内部类) [了解,有点重要]
- 局部内部类 [鸡肋,了解即可]
- 匿名内部类(重点)
(1) 静态内部类
P116:匿名内部类(重点)
- 匿名内部类的作用:简化代码编写
- 一般的表现形式:作为方法的实参传输
P117:常用API-Object、Objects
- 这两种方法都可以直接用IDEA的快捷键
Alt+Insert生成
Objects
Objects.equals(a, b)对象进行内容比较时,建议使用。因为会更安全、准确Objects.isNull(a)源码是return a == null;
P118:常用API-StringBuilder
- 特点 (先实例化一个对象
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();)- 支持链式编程:
sb.append("abc").append("123").append(3); - 反转 + 链式:
sb.reverse().append("love");
- 支持链式编程:
- 注意
- StringBuilder只是拼接、操作字符串的手段:效率好
- 但是最终还是要恢复成String类型进行后续操作:
String s = sb.toString();
package StringBuilder;
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = null;
int[] arr2 = {};
int[] arr3 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
System.out.println(toString(arr));
System.out.println(toString(arr2));
System.out.println(toString(arr3));
}
public static String toString(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null) {
return null;
} else {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sb.append(arr[i]).append(i == arr.length - 1 ? "" : ", ");
}
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
}
}
// null
// []
// [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
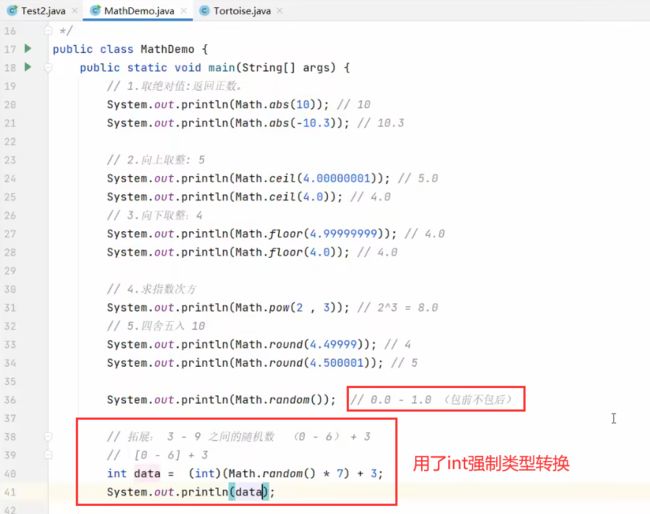
P119:常用API-Math、System、BigDecimal
(1)Math类
- 作用:解决浮点数运算失真的问题
- 注意:(一定要采用调用方法
valueOf()去封装成BigDecimal对象)- 手段:封装浮点型数据为大数据对象
BigDecimal a1 = BigDecimal.valueOf(a); - 目的:转为double继续操作
double rs = a1.doubleValue(); - BigDecimal是一定要精度运算的(因为有时候会遇到除不尽的情况,所以一定要指明精度)
- 手段:封装浮点型数据为大数据对象
❀❀❀❀❀❀❀❀❀❀❀❀❀
❀❀❀❀❀❀❀❀❀❀❀❀❀
不使用float和double进行精确数值计算(参考自代码规范:BigDecimal、int或者long进行精确数值计算)
float和double只能进行较为精确的快速近似的计算,并不能提供完全精确的结果,尤其不适用于货币计算,因为它们不能精确地表示0.1或者10的任何其它负次方。
要进行精确计算就使用BigDecimal、int或者long。
package StringBuilder;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.RoundingMode;
public class TestMain2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("-----------BigDecimal-----------");
BigDecimal a = BigDecimal.valueOf(0.1);
BigDecimal b = BigDecimal.valueOf(0.2);
System.out.println( a + " + " + b + " = " + a.add(b));
System.out.println( a + " - " + b + " = " + a.subtract(b));
System.out.println( a + " * " + b + " = " + a.multiply(b));
System.out.println( a + " / " + b + " = " + a.divide(b));
System.out.println("\n------------double-------------");
double c = 0.1;
double d = 0.2;
System.out.println(c + " + " + d +" = " + (c + d));
System.out.println(c + " - " + d +" = " + (c - d));
System.out.println(c + " * " + d +" = " + (c * d));
System.out.println(c + " / " + d +" = " + (c / d));
System.out.println("\n---------------对于无法除尽的情况-------------");
BigDecimal x = BigDecimal.valueOf(10);
BigDecimal y = BigDecimal.valueOf(3);
// 指定小数点后保留位数 + 采用四舍五入模式
System.out.println("BigDecimal: " + x + " / " + y + " = " + x.divide(y, 2, RoundingMode.HALF_UP));
double xx = 10, yy = 3;
System.out.println("double: " + xx + " / " + yy + " = " + (xx / yy));
}
}
//-----------BigDecimal-----------
//0.1 + 0.2 = 0.3
//0.1 - 0.2 = -0.1
//0.1 * 0.2 = 0.02
//0.1 / 0.2 = 0.5
//
//------------double-------------
//0.1 + 0.2 = 0.30000000000000004
//0.1 - 0.2 = -0.1
//0.1 * 0.2 = 0.020000000000000004
//0.1 / 0.2 = 0.5
//
//---------------对于无法除尽的情况-------------
//BigDecimal: 10 / 3 = 3.33
//double: 10.0 / 3.0 = 3.3333333333333335
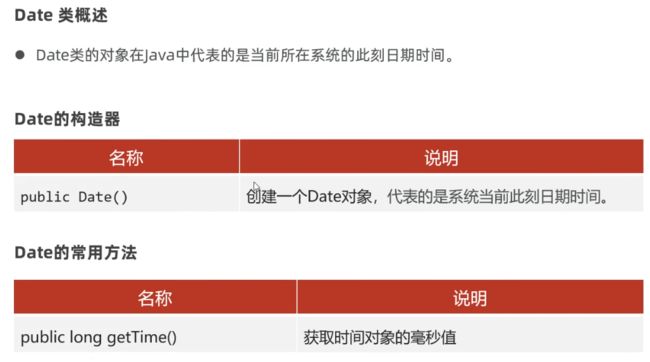
P121:日期时间:Date、SimpleDateFormat、Calendar
- 时间毫秒值(在P119中有讲)还可以用这样计算:
long time = System.currentTimeMillis(); - 格式
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss EEE a表示:日期、时分、星期几、上/下午
(1)Date
Date 常用方法还有:
d1.before(d2)、d1.after(d2) 判断d1、d2的时间先后
package StringBuilder;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestMain3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("当前日期时间为:" + new Date());
// 1小时30分后的日期时间
long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + (90 * 60) * 1000;
Date d = new Date(newTime);
System.out.println("1小时30分后:" + d);
}
}
//当前日期时间为:Mon Jun 13 15:17:50 CST 2022
//1小时30分后:Mon Jun 13 16:47:50 CST 2022
(2)SimpleDateFormat
1. 格式化Date对象为字符串时间
package StringBuilder;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestMain3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.格式化Date SimpleDateFormat 日期 时间 星期几 上/下午
Date d = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss EEE a");
System.out.println(sdf.format(d));
// 2.可以直接格式化时间毫秒值
// 格式121秒后的时间(即 2min + 1s)
long t = System.currentTimeMillis() + 121 * 1000;
System.out.println(sdf.format(t));
}
}
//2022-06-13 15:34:18 周一 下午
//2022-06-13 15:36:19 周一 下午
2. 解析字符串时间为Date对象(面试题)
package StringBuilder;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestMain4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
// 2021年08月06日 11:11:11 往后 2天14小时49分06秒 后的时间是多少
String dateStr = "2021年08月06日 11:11:11";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
Date d = sdf.parse(dateStr);
// 往后走了2天14小时49分06秒 注意最前面将数据类型声明成了 long -> 2L
long t = d.getTime() + (2L * 24 * 60 * 60 + 14 * 60 * 60 + 49 * 60 + 6) * 1000;
// 格式化毫秒值
System.out.println(dateStr);
System.out.println(sdf.format(t));
}
}
//2021年08月06日 11:11:11
//2021年08月09日 02:00:17
练习题
package StringBuilder;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestMain5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
// 1.开始时间、结束时间(秒杀10min)
String startTime = "2021-11-11 00:00:00";
String endTime = "2021-11-11 00:10:00";
// 2.小贾、小皮
String xiaoJia = "2021-11-11 00:03:47";
String xiaoPi = "2021-11-11 00:10:05";
// 3.解析时间
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date start = sdf.parse(startTime);
Date end = sdf.parse(endTime);
Date jia = sdf.parse(xiaoJia);
Date pi = sdf.parse(xiaoPi);
// 4.判断是否在时间范围内
System.out.println("start: " + startTime);
System.out.println("end: " + endTime);
if (jia.after(start) && jia.before(end)) {
System.out.println("小贾:恭喜您成功秒杀!");
} else {
System.out.println("小贾:很遗憾,您未参加上秒杀活动~");
}
if (pi.after(start) && pi.before(end)) {
System.out.println("小皮:恭喜您成功秒杀!");
} else {
System.out.println("小皮:很遗憾,您未参加上秒杀活动~");
}
}
}
(3)Calendar
P122:JDK开始新增日期API
太多API啦!有要用的时候再回来看看老师的视频吧!
1、Duration:用于计算两个“时间”间隔。
2、Period:用于计算两个“日期”间隔。
P123:包装类
为什么提供包装类?
- Java为了实现一切皆对象,为 8 种基本类型提供了对应的引用类型
- 后面的集合和泛型其实也只能支持包装类型,不支持基本数据类型
参考:java基本数据类型所占字节
P124:正则表达式
重点:QQ.matches("\\d{6,20}"
P124.1 正则表达式的初体验
package StringBuilder;
public class TestMain6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:校验QQ号,必须全部数字 6 - 20 位
System.out.println(checkQQ("292938789"));
System.out.println(checkQQ("29293aa89"));
System.out.println(checkQQ(null));
System.out.println(checkQQ("292"));
System.out.println("------------正则表达式-----------");
System.out.println(checkQQ2("292938789"));
System.out.println(checkQQ2("29293aa89"));
System.out.println(checkQQ2(null));
System.out.println(checkQQ2("292"));
}
private static boolean checkQQ2(String QQ) {
return QQ != null && QQ.matches("\\d{6,20}");
}
private static boolean checkQQ(String QQ) {
if (QQ == null || QQ.length() < 6 || QQ.length() > 20) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < QQ.length(); i++) {
if (QQ.charAt(i) < '0' || QQ.charAt(i) > '9') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
P124.2 正则表达式的匹配规则
P124.3 正则表达式案例
package StringBuilder;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestMain7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String phone = checkPhone(sc);
System.out.println("您的手机号码通过校验!" + phone);
String email = checkEmail(sc);
System.out.println("您的Email通过校验!" + email);
String tel = checkTel(sc);
System.out.println("您的Tel通过校验!" + tel);
// 校验金额
String money = checkMoney(sc);
System.out.println("您的Tel通过校验!" + money);
}
// phone:1开头、第二位是[3-9]之间任一数字、剩余还需要输入9位 = 总计11位电话号码
public static String checkPhone(Scanner sc) {
while (true) {
System.out.print("请您输入您的手机号码:");
String phone = sc.next();
if (phone.matches("1[3-9]\\d{9}")) {
return phone;
} else {
System.out.println("格式有误!请重新输入!");
}
}
}
// [email protected] 或者 [email protected]有效
public static String checkEmail(Scanner sc) {
while (true) {
System.out.print("请您输入您的Email:");
String email = sc.next();
if (email.matches("\\w{1,30}@[a-zA-Z0-9]{2,20}(\\.[a-zA-Z0-9]{2,20}){1,2}")) {
return email;
} else {
System.out.println("格式有误!请重新输入!");
}
}
}
// 0开头 + 2~6位数字 + - (可有可无) + 5~20位数字
// 021234567
public static String checkTel(Scanner sc) {
while (true) {
System.out.print("请您输入您的Tel:");
String email = sc.next();
if (email.matches("0\\d{2,6}-?\\d{5,20}")) {
return email;
} else {
System.out.println("格式有误!请重新输入!");
}
}
}
// 有效输入 9、019、0.354 无效输入 0.3.3
public static String checkMoney(Scanner sc) {
while (true) {
System.out.print("请您输入您的Money:");
String money = sc.next();
if (money.matches("\\d+(\\.\\d+)?")) {
return money;
} else {
System.out.println("格式有误!请重新输入!");
}
}
}
}
P124.4 按照正则表达式匹配,分割字符串
- 分割:
String.split("\\w+")-> String[] - 替换:
String.replaceAll("\\w+", " ")-> String
package StringBuilder;
public class TestMain8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String arr = "张三09abc莉莉丝_jxi82啊哈哈9083老师好";
// 分割 返回的是String[] 字符串数组
String[] arr2 = arr.split("\\w+");
System.out.println(print(arr2));
// 替换 返回的是String 字符串
System.out.println(arr.replaceAll("\\w+", " "));
}
public static String print(String[] arr){
StringBuilder rs = new StringBuilder("[");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
rs.append(arr[i]).append(i == arr.length - 1 ? "" : ", ");
}
rs.append("]");
return rs.toString();
}
}
P124.5 爬取信息
P125:Arrays类
package StringBuilder;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class TestMain9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 一般用法
int[] arr = {20, 11, 35, 42, 8, 19};
Arrays.sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // 转为字符串输出
// 对自定义Student类排序
Student[] students = new Student[3];
students[0] = new Student("lwd", 20, 173);
students[1] = new Student("may", 19, 175.5);
students[2] = new Student("love", 22, 175.3);
Arrays.sort(students, new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
//return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge(); // 按照年龄升序
return Double.compare(o2.getHeight(), o1.getHeight()); // 按照身高降序
//return o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName()); //按照姓名升序
}
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(students));
}
}
//[8, 11, 19, 20, 35, 42]
//[Student{name='may', age=19, height=175.5}, Student{name='love', age=22, height=175.3}, Student{name='lwd', age=20, height=173.0}]
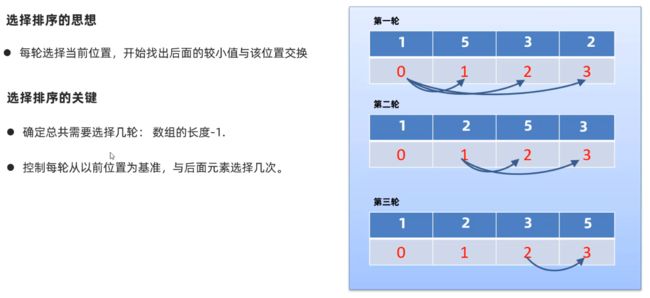
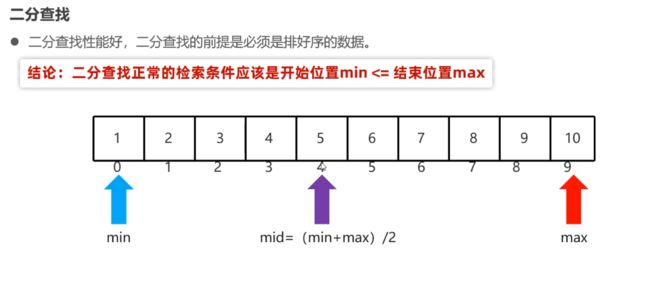
P126:选择排序、二分查找
P126.1 选择排序
P126.2 二分查找
- 前提:必须是排好序的数组
- 检索条件:
开始位置min<=结束位置max - 官方方法调用:
Arrays.binarySearch()
package StringBuilder;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestMain10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 选择排序 小 -> 大
int[] arr = {15, 2, 8, 5, 75, 22, 100, 26, 6, 10};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[i] > arr[j]) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // Arrays.toString打印数组
// 二分查找 -> return index
System.out.print("请输入您想要查找的数据:");
int data = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
int index = binarySearch(arr, data);
if (index == -1) {
System.out.println("查无此元素!");
} else {
System.out.println(data + "的index是:" + index + ",在第" + (index + 1) + "位");
}
}
private static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int data) {
int left = 0, right = arr.length - 1;
int middleIndex;
while (left <= right) {
middleIndex = (left + right) / 2;
if (arr[middleIndex] > data) {
right = middleIndex - 1;
} else if (arr[middleIndex] < data) {
left = middleIndex + 1;
} else {
return middleIndex;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
P127:Lambda表达式
- 当需要用到匿名内部类时,查看源码发现加有
@FunctionalInerface注解的,就可以使用 Lambda 表达式简写(甚至可以先不用直接查看源码,当发现代码变灰了再去查看源码,一般会发现是有注解的)
P127.1 概念
P127.2 实例
P127.3 Lambda表达式的省略规则(进一步简写)
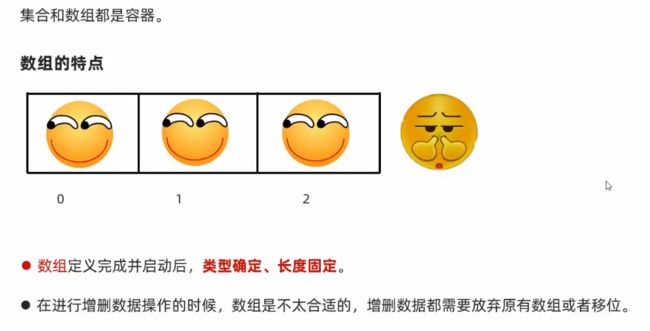
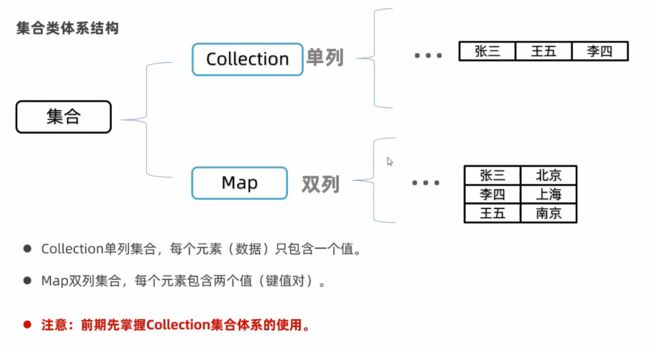
P129:集合概述、Collection集合的体系特点
P129.1 概述
- 集合只能存储对象,不支持基本类型
- 集合和数组都是容器。数组定义之后,数据类型和大小都固定不能做更改;集合数据类型、长度都可以更改。集合作增删改更加方便。
P129.2 体系结构
P129.2.1 Collection
集合对泛型的支持
P130:Collection常用API、遍历方式、存储自定义类型的对象
P130.1 常用API
- 注意,集合转为数组时,使用的
Object[]来接
P130.2 遍历方式
P130.2.1 迭代器 Iterator
- 默认位置:
Iterator得到迭代器对象it = list.iterator(); it,默认指向当前集合的索引位置0 - 如果元素越界,会出现 NosuchElementException 异常
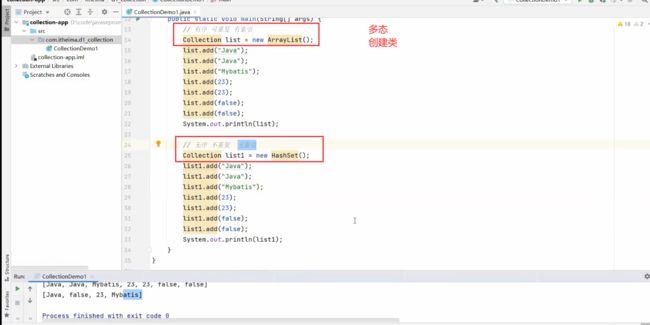
package Collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Test_Iterator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 利用多态创建一个集合对象
Collection<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("张三");
list.add("李四");
list.add("王五");
list.add("六儿");
// 打印集合直接显示时集合内容(而不是集合地址)
System.out.println(list);
// 1.用iterator迭代器进行遍历
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
// 2.foreach 方法
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
P130.2.2 foreach/增强for循环
- 既可以遍历数组,又可以遍历集合
- 遍历过程中,对元素的修改无意义
P130.2.3 lambda表达式
P130.3 Collection集合存储自定义类型的对象
package Collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<Movie> movies = new ArrayList<>();
movies.add(new Movie("《你好,李焕英》", 9.5, "贾玲,张小斐"));
movies.add(new Movie("《唐人街探案》", 8.5, "王宝强,刘昊然"));
movies.add(new Movie("《刺杀小说家》", 8.6, "雷佳音,杨幂"));
// 遍历,采用增强for方式,快捷键 movies.for + Enter
for (Movie movie : movies) {
System.out.println("片名:" + movie.getName());
System.out.println("评分:" + movie.getScore());
System.out.println("主演:" + movie.getActor());
System.out.println("------------------------");
}
}
}
class Movie {
private String name;
private double score;
private String actor;
public Movie() {
}
public Movie(String name, double score, String actor) {
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
this.actor = actor;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
public String getActor() {
return actor;
}
public void setActor(String actor) {
this.actor = actor;
}
}
P131:常见数据结构简介
P131.1 数据结构概述、栈、队列
- 栈:先进后出
- 队列:先进先出
P131.2 数组
P131.3 链表
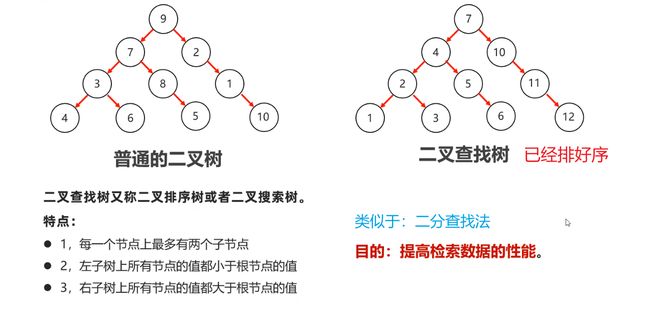
P131.4 二叉树、二叉查找树
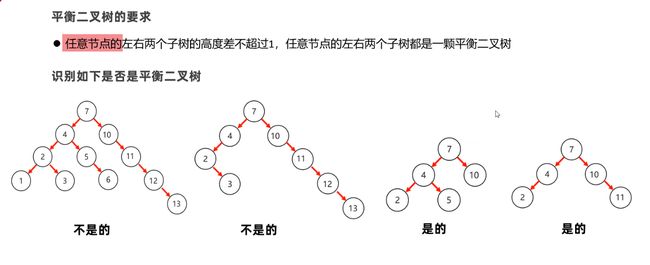
P131.5 平衡二叉树
- 左边高,往右拉(如果直接往右拉不行,则子树内先左拉再右拉)
- 右边高,往左拉(如果直接往左拉不行,则子树内先右拉再左拉)
P131.6 红黑树
P131:List系列集合、集合的并发修改异常问题
P131.1 List集合特点、特有API
P131.2 4种遍历方法
package Collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class TestDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// List
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// add remove set get
list.add("JAVA");
list.add("lwd");
list.add("23");
// remove + return
System.out.println(list.remove(0));
System.out.println(list);
// set + return
System.out.println(list.set(1,"may"));
System.out.println(list);
// get
System.out.println(list.get(0));
// 4种遍历
// 1.for循环
System.out.println("-------------------");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
}
// 2.迭代器
System.out.println();
Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
// 3.foreach
System.out.println();
for(String s:list){
System.out.print(s + " ");
}
// 4.JDK1.8开始之后的Lambda表达式
System.out.println();
list.forEach(s -> System.out.print(s + " "));
}
}
P132.3 ArrayList的底层原理
P132.4 LinkedList的底层原理
- 创建LinkList的时候,尽量不要使用多态的方法,因为要使用LinkList的独有的方法
- LinkList很适合栈和队列
- 入栈:addFirst() <=> push()
- 出栈:removeFirst() <=> pop()
- 入队列:addLast() <=> offerLast() (还是比较常用addLast())
- 出队列:removeFirst() <=> pop()
补充知识:集合的并发修改异常问题
- 当用迭代器,不能直接用list.remove(),而应该用iterator.remove()
- 不能用 增强for、foreach方法 去遍历删除
package Collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class TestDemo_remove {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 构建集合
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("Java");
list.add("Java");
list.add("HTML");
list.add("MySQL");
list.add("Java");
System.out.println(list);
// 有效的两种方法:iterator自带的删除方法 + for遍历删除
// 1.iterator
// Iterator it = list.iterator();
// while (it.hasNext()){
// if (it.next().equals("Java")){
// it.remove();
// }
// }
// System.out.println(list);
// 2.for
// for正向
// for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
// if (list.get(i).equals("Java")) {
// list.remove("Java");
// i--;
// }
// }
// System.out.println(list);
// for 逆向
for (int i = list.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (list.get(i).equals("Java")){
list.remove("Java");
}
}
System.out.println(list);
}
}