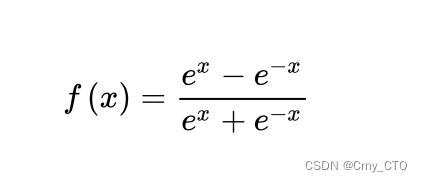Activation Function激活函数 ---饱和激活函数
Activation Function
定义
- 激活函数是在人工神经网络中常用的数学函数。
- 在神经网络中,输入经过权值加权计算并求和之后,需要经过一个函数的作用,这个函数就是激活函数(Activation Function)。
作用
- 在线性变换后,需要对input进行非线性变换,即引入非线性激活函数
- 对每一层的输出做处理,引入非线性因素,使得神经网络可以逼近任意的非线性函数,进而使得添加了激活函数的神经网络可以应用到众多的非线性模型中,从而在非线性领域继续发挥重要作用
增加非线性,帮助nn学习各种现象,增加神经网络的表达能力,从而提高神经网络的性能
例如:
提高模型鲁棒性、
缓解梯度消失问题、
将特征输入映射到新的特征空间
加速模型收敛
- 如果在神经网络中不引入激活函数,
那么在该网络中,每一层的输出都是上一层输入的线性函数,
无论最终的神经网络有多少层,输出都是输入的线性组合;
其一般也只能应用于线性分类问题中,
例如,
多层感知机 (MLP)
Multi-Layer Perceptron
常见激活函数
饱和激活函数
(以Tanh,Sigmoid和hard-Sigmoid函数为主)
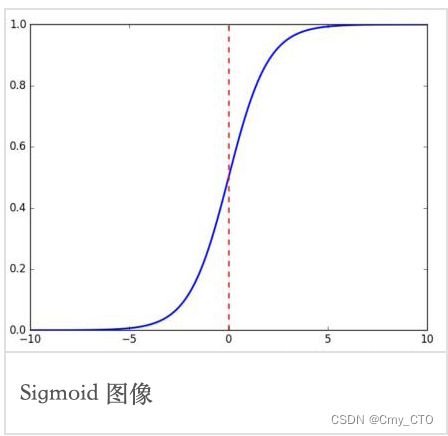
Sigmoid函数
常被用作神经网络的阈值函数,将变量映射到0,1之间
i.e. 将input压缩到 [0,1]
表达式
函数图像
优点:
- 将很大范围内的输入特征值压缩到0~1之间,使得在深层网络中可以保持数据幅度不会出现较大的变化,而Relu函数则不会对数据的幅度作出约束;
- 在物理意义上最为接近生物神经元
- 根据其输出范围,该函数适用于将预测概率作为输出的模型;
缺点:
- 当输入非常大或非常小的时候,输出基本为常数,即变化非常小,进而导致梯度接近于0;
- 输出不是0均值,进而导致后一层神经元将得到上一层输出的非0均值的信号作为输入。随着网络的加深,会改变原始数据的分布趋势;
- 梯度可能会过早消失,进而导致收敛速度较慢,例如与Tanh函数相比,其就比sigmoid函数收敛更快,是因为其梯度消失问题较sigmoid函数要轻一些;
- 、幂运算相对耗时。
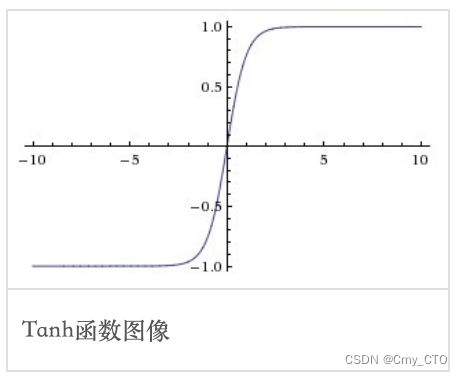
Tanh函数
Tanh是双曲函数中的一个,Tanh()为双曲正切。
在数学中,双曲正切“Tanh”是由基本双曲函数双曲正弦和双曲余弦推导而来。
函数的输出范围在 -1~1 之间
i.e. 将input压缩到 [-1,1]
表达式
函数图像
优点:
- 解决了上述的Sigmoid函数输出不是0均值的问题;
- Tanh函数的导数取值范围在01之间,优于sigmoid函数的00.25,一定程度上缓解了梯度消失的问题;
- Tanh函数在原点附近与y=x函数形式相近,当输入的激活值较低时,可以直接进行矩阵运算,训练相对容易;
缺点:
- 与Sigmoid函数类似,梯度消失问题仍然存在;
- 观察其两种形式的表达式,即2*sigmoid(2x)-1与(exp(x)-exp(x))/(exp(x)+exp(-x)),
(可见,幂运算的问题仍然存在)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
class ActivateFunc():
def __init__(self, x, b=1, lamb=2, alpha=1, a=2):
super(ActivateFunc, self).__init__()
self.x = x
self.b = b
self.lamb = lamb
self.alpha = alpha
self.a = a
def __init__(self, x, b=1, lamb=2, alpha=1, a=2):
super(ActivateFunc, self).__init__()
self.x = x
self.b = b
self.lamb = lamb
self.alpha = alpha
self.a = a
def Sigmoid(self):
y = np.exp(self.x) / (np.exp(self.x) + 1)
y_grad = y*(1-y)
return [y, y_grad]
def Tanh(self):
y = np.tanh(self.x)
y_grad = 1 - y * y
return [y, y_grad]
def Hard_Sigmoid(self):
f = (2 * self.x + 5) / 10
y = np.where(np.where(f > 1, 1, f) < 0, 0, np.where(f > 1, 1, f))
y_grad = np.where(f > 0, np.where(f >= 1, 0, 1 / 5), 0)
return [y, y_grad]
def PlotActiFunc(x, y, title):
plt.grid(which='minor', alpha=0.2)
plt.grid(which='major', alpha=0.5)
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.title(title)
plt.show()
def PlotMultiFunc(x, y):
plt.grid(which='minor', alpha=0.2)
plt.grid(which='major', alpha=0.5)
plt.plot(x, y)
if __name__ == '__main__':
x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.01)
activateFunc = ActivateFunc(x)
activateFunc.b = 1
PlotActiFunc(x, activateFunc.Sigmoid()[0], title='Sigmoid')
PlotActiFunc(x, activateFunc.Tanh()[0], title='Tanh')
PlotActiFunc(x, activateFunc.Hard_Sigmoid()[0], title='Hard_Sigmoid')
plt.figure(1)
PlotMultiFunc(x, activateFunc.Sigmoid()[0])
PlotMultiFunc(x, activateFunc.Hard_Sigmoid()[0])
plt.legend(['Sigmoid', 'Hard-Sigmoid'])
plt.figure(2)
PlotMultiFunc(x, activateFunc.Tanh()[0])
plt.legend(['Tanh'])
plt.show()
未完待续……