Java遍历Map五种方法
一、Map集合遍历日常开发最常使用,简单总结五种方法差异。
①、Iterator+entrySet写法【推荐JDK8以下】,Map.Entry是Map接口的内部接口,获取迭代器,然后依次取出每个迭代器里面的Map.Entry
Iterator> iterator=map.entrySet().iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Map.Entry entry=iterator1.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey());
System.out.println(entry.getValue());
} ②、Iterator+keyset写法【不推荐,只能获取key,然后通过key获取对应的value,重复计算】
Iterator iterator=map.keySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Integer key=iterator.next();
System.out.println(key);
System.out.println(map.get(key));
} ③、foreach遍历方式【JDK8以下推荐写法】
for(Map.Entry entry:map.entrySet()){
System.out.println(entry.getKey());
System.out.println(entry.getValue());
}; ④:lambda表达式遍历【JDK8推荐写法,简捷】
map.forEach((key,value)->{
System.out.println(key);
System.out.println(value);
});⑤:stream流遍历Map【JDK8不推荐写法,重复计算】
map.entrySet().stream().forEach((Map.Entry entry) -> {
System.out.println(entry.getKey());
System.out.println(entry.getValue());
}); 如果Map集合存在一些中间处理,可以过滤操作,使用流式遍历也很方便。
附【List和Map删除集合元素】,业务实现里面经常需要清理集合中的指定的对象,这里以List和Map为例介绍一下正常的删除方式。
JDK8以下写法,迭代器会动态感知集合的变化。
List list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
Iterator integerIterator=list.iterator();
while(integerIterator.hasNext()){
Integer integer=integerIterator.next();
if(integer.equals(5)){
integerIterator.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(list);
![]()
JDK8及以上的写法,新增一个removeIf方法
list.removeIf(key ->key.equals(4));Map的写法。
JDK1.8一下
Iterator> iterator=map.entrySet().iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Map.Entry entry=iterator.next();
if(entry.getKey().equals("2")){
iterator.remove();
}
} JDK1.8及以上
map.keySet().removeIf(key -> key.equals("3"));【附录 JAVA的ArrayList的遍历方式】
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、普通for循环遍历
List list = getList();
for(int i=0;i iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
// 3、增强for-each遍历,底层通过迭代器遍历实现,迭代器遍历提供容器统一遍历接口
for(String str:list){
System.out.println(str);
}
// 4、Lambda遍历
list.stream().forEach(str->{
System.out.println(str);
});
// 5、ListIterator迭代,前向迭代
ListIterator listIterator = list.listIterator();
while(listIterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(listIterator.next());
}
// 6、ListIterator迭代,反向迭代
while(listIterator.hasPrevious()){
System.out.println(listIterator.previous());
}
}
private static List getList() {
List list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add("Map");
list.add("HashMap");
list.add("LinkedHashMap");
list.add("TreeMap");
list.add("ConcurrentHashMap");
return list;
} 附录:开发中常用的各种类型List集合,util包下
import java.util.Collections;
// 1、空集合,底层自定义一个EmptyList实现,接口空list返回,不像new ArrayList分配不必要的内存空间
Collections.emptyList();
// 2、单值List,底层定义SingletonList,size为1
Collections.singletonList(new Object());
// 3、线程安全的List,底层定义SynchronizedList,方法定义通过synchronized代码实现线程安全,定义了一个SynchronizedCollection
Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
// 4、不可变List,不支持修改,定义一个UnmodifiableCollection,UnmodifiableList
Collections.unmodifiableList(new ArrayList<>());List转换Map整理.
/**
* 转换Map,保存后者
* @return Map
*/
private static Map convertOldValueMap(){
List bookList=new ArrayList<>();
bookList.add(new Book("The King","Tom","1955"));
bookList.add(new Book("The King Tail","Jack","1956"));
bookList.add(new Book("The King Tail","Bean","1957"));
bookList.add(new Book("The King Help","Bean","1957"));
// 注意Key值重复时处理,这里是保存旧的值,之前加入的数据
// Function keyMapper
// Function valueMapper->Function.identity()
// BinaryOperator mergeFunction
return bookList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Book::getReleaseYear, Function.identity(),(oldValue,newValue)->oldValue));
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
class Book{
private String name;
private String author;
private String releaseYear;
} ①、合并不覆盖旧值.
/**
* 转换Map,保存后者
* @return Map
*/
private static Map convertNewValueMap(){
List bookList=new ArrayList<>();
bookList.add(new Book("The King","Tom","1955"));
bookList.add(new Book("The King Tail","Jack","1956"));
bookList.add(new Book("The King Tail","Bean","1957"));
bookList.add(new Book("The King Help","Bean","1957"));
// 注意Key值重复时处理,这里是保存新的值,也就是后面加入的数据
// Function keyMapper
// Function valueMapper->Function.identity()
// BinaryOperator mergeFunction
return bookList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Book::getReleaseYear, Function.identity(),(oldValue,newValue)->newValue));
} ②、合并覆盖旧值.
List对象属性分组过滤
class UserInfo{
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public UserInfo(Long id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserInfo{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
UserInfo userInfo = (UserInfo) o;
return Objects.equals(id, userInfo.id) &&
Objects.equals(name, userInfo.name) &&
Objects.equals(age, userInfo.age);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id, name, age);
}
}List对象去重,记得重写hashcode和equals方法.
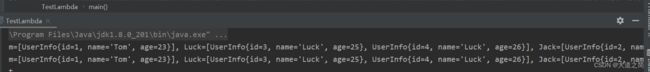
List infoList = userInfoList.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(infoList); List userInfoList=new ArrayList<>();
userInfoList.add(new UserInfo(1L, "Tom", 23));
userInfoList.add(new UserInfo(2L, "Jack", 24));
userInfoList.add(new UserInfo(3L, "Luck", 25));
userInfoList.add(new UserInfo(4L, "Luck", 26));
// Stream属性分组过滤
Map> collect = userInfoList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(UserInfo::getName));
System.out.println(collect); 传统的Map属性分组
Map> result = new HashMap<>();
// 转换
for(UserInfo userInfo:userInfoList){
String name = userInfo.getName();
List list = result.get(name);
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list)){
list = new ArrayList<>();
result.put(name, list);
}
// 存在直接添加list中即可
list.add(userInfo);
}