python数据分析基础(三)--- 基于列表的排队与叫号系统
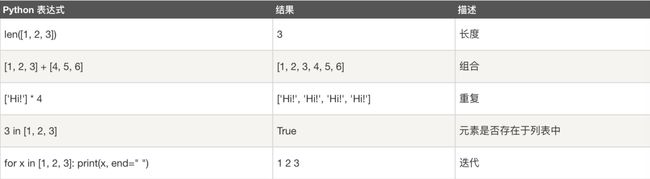
序列是Python中最基本的数据结构。序列中的每个元素都分配一个数字它的位置,索引,第一个索引是0,第二个索引是1,依此类推。 Python有6个序列的内置类型,但最常见的是列表和元组。 序列都可以进行的操作包括索引,切片,加,乘,检查成员。 此外,Python已经内置确定序列的长度以及确定最大和最小的元素的方法
列表是最常用的Python数据类型,它可以作为一个方括号 内的逗号分隔值出现。 列表的数据项不需要具有相同的类型。
1、创建列表
创建一个列表,只要把逗号分隔的不同的数据项使用方括号 括起来即可。如下所示: list1 = ['Google', ’Python3', 2019, 2022] list2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ] list3 = ["a", "b", "c", "d"] 与字符串的索引一样,列表索引从0开始。列表可以进行截取、组合等
2、访问列表中的值
使用下标索引来访问列表中的值,同样你也可以使用方括号的形式截取字符, 如下所示: list1 = ['Google', ’Python3', 2019, 2022]; list2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ]; print ("list1[0]: ", list1[0]) print ("list2[1:5]: ", list2[1:5])
以上实例输出结果: list1[0]: Google list2[1:5]: [2, 3, 4, 5]
3、更新列表 append()
list = ['Google', ’Python3', 2019, 2022]; print ("第三个元素为 : ", list[2]) list[2] = 2001 print ("更新后的第三个元素为 : ", list[2])
输出结果: 第三个元素为 : 2019 更新后的第三个元素为 : 2001
4、删除列表元素 del()
list = ['Google', ’Python3', 2019, 2022]; print ("原始列表 : ", list) del list[2] print ("删除第三个元素 : ", list)
输出结果: 原始列表 : ['Google', ’Python3', 2019, 2022] 删除第三个元素 : ['Google', ’Python3', 2022]
5、python列表脚本操作符
Python列表脚本操作符 列表对 + 和 * 的操作符与字符串相似。+ 号用于组合列表, * 号用于重复列表。
6、python列表的截取与拼接
7、嵌套列表
嵌套列表 使用嵌套列表即在列表里创建其它列表,例如:
示例:
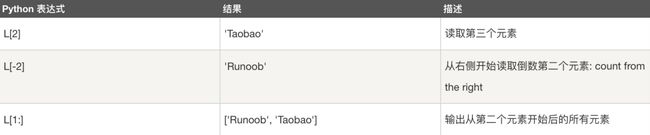
L=['Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao', 5]
print(L[0])
print(L[0][0])
print(L[0][-1])
print(L[-1])
print(L[-2])
print(L[-3])
a = L*5
print(a)
print(a[1:])
print(a[1:7:2]) # 取值范围为1到7,步长为2
print(a[1:8:2])
print(a[1:8:1])
print(a[1:8:3])
print(a[8:1:-3])
print(a[8:1:])
print(a[1:8:])
print(a[::]) # 默认从第一个取到最后一个,步长为1
print(a[:])a = ['a', 'b', 'cdefg']
n = [1, 2, 3]
print(a+n) # 列表的内嵌
x = [a, n]
print(x)
print(len(x))
print(len(x[0]))
print(len(x[1]))
print(len(x[0][2]))
print(max(x[0][2]))
print(min(x[0][2]))['a', 'b', 'cdefg', 1, 2, 3]
[['a', 'b', 'cdefg'], [1, 2, 3]]
2
3
3
5
g
c
基于列表的排队与叫号系统
#import sys
a = 0
b = 0
c = 0
list_A = []
list_B = []
list_C = []
pos_dict = {"BankService": list_A,
"InsureService": list_B,
"FinanceService": list_C}
def append_queue():
"""
:排队系统
:return:
"""
global a, b, c
while True:
choice = int(input('请选择业务类型:1.银行卡业务 2.社保卡业务 3.金融卡业务 4.退出 \n')) # 把输入的数据强制转换为整数
if choice == 1:
a += 1
A_num = "A" + str(a)
list_A.append(A_num)
pos_dict["BankService"] = list_A
print("你的排队号码是A%d,当前你选择的是银行卡业务。\n" % a)
elif choice == 2:
b += 1
B_num = "B" + str(b)
list_B.append(B_num)
pos_dict["InsureService"] = list_B
print("你的排队号码是B%d,当前你选择的是社保卡业务。\n" % b)
elif choice == 3:
c += 1
C_num = "C" + str(c)
list_C.append(C_num)
pos_dict["FinanceService"] = list_C
print("你的排队号码是B%d,当前你选择的是金融卡业务。\n" % c)
else:
# sys.exit() and break
return
def pop_queue():
"""
:叫号系统
:return:
"""
while True:
choice = int(input('请输入当前窗口类型:1.银行卡业务 2.社保卡业务 3.金融卡业务 4.退出 \n'))
if choice == 1:
if len(list_A) == 0:
print("目前银行卡业务窗口空闲,无人排队")
else:
pop_num = list_A.pop(0)
print("请%s号客户前往银行卡业务窗口办理业务,当前排队人数为%d人\n" % (pop_num, len(list_A)))
elif choice == 2:
if len(list_B) == 0:
print("目前社保卡业务窗口空闲,无人排队")
else:
pop_num = list_B.pop(0)
print("请%s号客户前往社保卡业务窗口办理业务,当前排队人数为%d人\n" % (pop_num, len(list_B)))
elif choice == 3:
if len(list_C) == 0:
print("目前金融卡业务窗口空闲,无人排队")
else:
pop_num = list_C.pop(0)
print("请%s号客户前往金融卡业务窗口办理业务,当前排队人数为%d人\n" % (pop_num, len(list_C)))
else:
return
if __name__ == '__main__':
"""
主程序
"""
while True:
choice = int(input('请选择您需求:1.取号 2.叫号 3.退出 \n'))
if choice == 1:
append_queue()
elif choice == 2:
pop_queue()
else:
break