【I2C】通用驱动i2c-dev分析
文章目录
- 1. 前言
- 2. i2c-dev驱动的注册过程
- 3. open_i2c_dev函数分析
- 4. set_slave_addr函数分析
- 5. i2c_read_bytes函数分析
1. 前言
前面分析i2c-tool测试工具就是基于drivers/i2c/i2c-dev.c驱动来实现的。i2c-dev驱动在加载时会遍历所有的I2C总线(i2c_bus_type)上所有注册的adapter,并且在linux系统创建对应的字符设备,如:/dev/i2c-0、/dev/i2c-1、/dev/i2c-2等。应用程序通过open打开对应的i2c字符设备,通过ioctl来收发数据。具体的架构如下图:
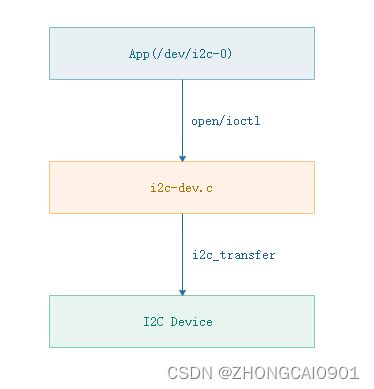
2. i2c-dev驱动的注册过程
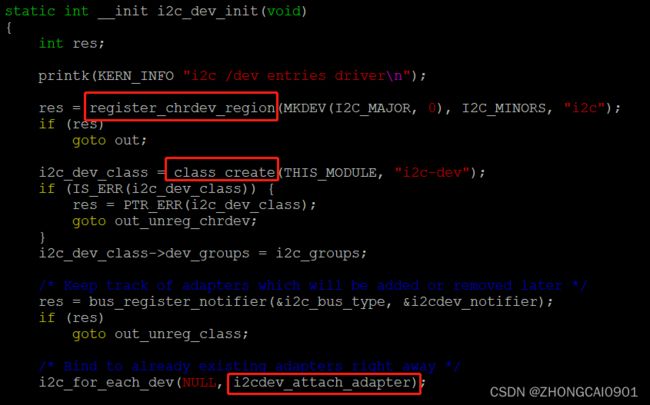
在i2c-dev.c的驱动入口i2c_dev_init函数具体操作如下:
- register_chrdev_region:注册i2c字符设备
- class_create:创建i2c-dev的class,为在linux文件系统中创建字符设备做准备。
- i2cdev_attach_adapter:通过函数
i2c_for_each_dev遍历已经绑定的adapter,有多少个adapter就调用i2cdev_attach_adapter函数几次。
- to_i2c_adapter:通过dev获取对应的i2c adapter。
- cdev_init:它会初始化一个重要的结构体,file_operations。
- dev_set_name:设置device name为
i2c-x,也就是我们在字符设备创建成功后看到的/dev/i2c-x设备。 - cdev_device_add:添加设备到系统,并且创建对应的字符设备到用户空间。
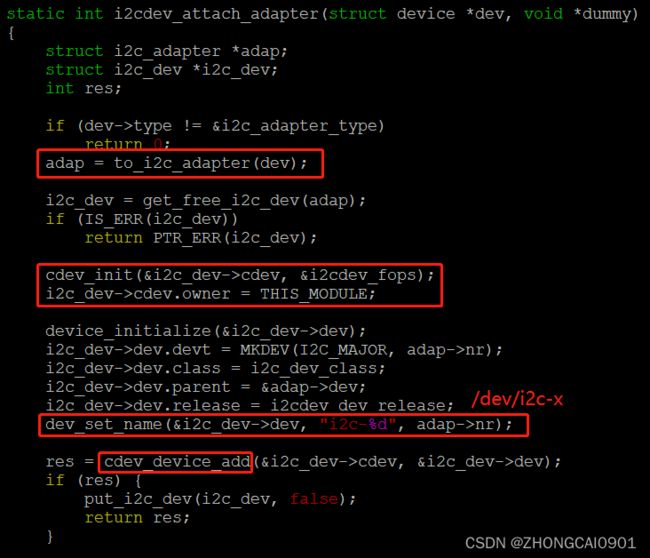
备注:
cdev_device_add这里其实调用了cdev_add和device_add。然而,device_create()是device_register()的封装,而device_register()则是device_add()的封装。
3. open_i2c_dev函数分析
open_i2c_dev是i2c-tool工具open i2c-dev驱动的函数,根据传递的参数最终重要函数应该如下:
file = open("/dev/i2c-0", O_RDWR);
该函数的主要代码如下:
/* File Path = i2c-tools-4.3/tools/i2cbusses.c */
int open_i2c_dev(int i2cbus, char *filename, size_t size, int quiet)
{
int file, len;
len = snprintf(filename, size, "/dev/i2c/%d", i2cbus);
if (len >= (int)size) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s: path truncated\n", filename);
return -EOVERFLOW;
}
file = open(filename, O_RDWR);
if (file < 0 && (errno == ENOENT || errno == ENOTDIR)) {
len = snprintf(filename, size, "/dev/i2c-%d", i2cbus);
if (len >= (int)size) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s: path truncated\n", filename);
return -EOVERFLOW;
}
file = open(filename, O_RDWR);
}
...
return file;
}
应用层调用open后,会对应调用i2c-dev通用驱动的open函数。主要是如下几个步骤:
- to_i2c_adapter:通过minor次设备号,其实这里等同于i2c总线编号。通过它来获取对应总线的adapter。
- kzalloc:申请一个i2c client表示I2C设备,并且初始化该client的name和保存adapter与其建立联系。但是,整个open函数这里没有对I2C地址进行初始化。
- file->private_data:通过private_data保存申请的client地址,为了后面read/write/ioctl可以通过file->private_data很方便的拿到当前dev的client。
/* File Path = kernel/drivers/i2c/i2c-dev.c */
static int i2cdev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
unsigned int minor = iminor(inode);
struct i2c_client *client;
struct i2c_adapter *adap;
adap = i2c_get_adapter(minor);
if (!adap)
return -ENODEV;
/* This creates an anonymous i2c_client, which may later be
* pointed to some address using I2C_SLAVE or I2C_SLAVE_FORCE.
*
* This client is ** NEVER REGISTERED ** with the driver model
* or I2C core code!! It just holds private copies of addressing
* information and maybe a PEC flag.
*/
client = kzalloc(sizeof(*client), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!client) {
i2c_put_adapter(adap);
return -ENOMEM;
}
snprintf(client->name, I2C_NAME_SIZE, "i2c-dev %d", adap->nr);
client->adapter = adap;
file->private_data = client;
return 0;
}
4. set_slave_addr函数分析
open_i2c_dev是i2c-tool工具来设置I2C的设备地址。具体代码如下:
/* File Path = i2c-tools-4.3/tools/i2cbusses.c */
int set_slave_addr(int file, int address, int force)
{
/* With force, let the user read from/write to the registers
even when a driver is also running */
if (ioctl(file, force ? I2C_SLAVE_FORCE : I2C_SLAVE, address) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr,
"Error: Could not set address to 0x%02x: %s\n",
address, strerror(errno));
return -errno;
}
return 0;
}
应用层调用ioctl I2C_SLAVE_FORCE后,会对应调用i2c-dev通用驱动对应的ioctl I2C_SLAVE_FORCE。主要是如下2个步骤:
- client = file->private_data:从private_data中获取当前I2C设备。
- client->addr = arg:设置当前I2C设备的地址信息,方便后面的read/write操作I2C设备。
/* File Path = kernel/drivers/i2c/i2c-dev.c */
static long i2cdev_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
struct i2c_client *client = file->private_data;
unsigned long funcs;
switch (cmd) {
case I2C_SLAVE:
case I2C_SLAVE_FORCE:
if ((arg > 0x3ff) ||
(((client->flags & I2C_M_TEN) == 0) && arg > 0x7f))
return -EINVAL;
if (cmd == I2C_SLAVE && i2cdev_check_addr(client->adapter, arg))
return -EBUSY;
/* REVISIT: address could become busy later */
client->addr = arg;
return 0;
...
}
5. i2c_read_bytes函数分析
i2c_read_bytes这个函数是我自己写的demo code,这里只列了read部分来分析,完整的demo code可以查看上一篇我的博客。主要是如下2个步骤:
- struct i2c_msg messages[2]:定义2个i2c_msg的消息体,并且初始化它。它包含了:I2C的从机设备地址、read/write的flag、数据的长度、存放数据的地址。msg[0]主要是为了发送需要读取从机的哪个寄存器,msg[1]主要的配置读取的数据长度的和存放数据的地址。
- struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data packets:它主要是存放i2c_msg消息地址和i2c_msg消息个数。
- ioctl:通过ioctl发送到内核。
static int i2c_read_bytes(int fd, uint8_t slave_addr, uint8_t reg_addr, uint8_t *values, uint8_t len)
{
uint8_t outbuf[1];
struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data packets;
struct i2c_msg messages[2];
outbuf[0] = reg_addr;
messages[0].addr = slave_addr;
messages[0].flags = 0;
messages[0].len = sizeof(outbuf);
messages[0].buf = outbuf;
/* The data will get returned in this structure */
messages[1].addr = slave_addr;
messages[1].flags = I2C_M_RD/* | I2C_M_NOSTART*/;
messages[1].len = len;
messages[1].buf = values;
/* Send the request to the kernel and get the result back */
packets.msgs = messages;
packets.nmsgs = 2;
if(ioctl(fd, I2C_RDWR, &packets) < 0)
{
printf("Error: Unable to send data");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
应用层调用ioctl I2C_RDWR后,会对应调用i2c-dev通用驱动对应的ioctl I2C_RDWR。它将应用层的数据到拷贝的内核,具体如下:
/* File Path = kernel/drivers/i2c/i2c-dev.c */
case I2C_RDWR: {
struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data rdwr_arg;
struct i2c_msg *rdwr_pa;
//从用户空间拷贝数据到内核空间
copy_from_user(&rdwr_arg,(struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data __user *)arg,sizeof(rdwr_arg));
//分配一块内存空间,将用户空间的数据拷贝进去
rdwr_pa = memdup_user(rdwr_arg.msgs, rdwr_arg.nmsgs * sizeof(struct i2c_msg));
return i2cdev_ioctl_rdwr(client, rdwr_arg.nmsgs, rdwr_pa);
}
static int i2cdev_ioctl_rdwr(struct i2c_client *client, unsigned nmsgs, struct i2c_msg *msgs)
{
***
res = i2c_transfer(client->adapter, msgs, nmsgs);
***
}
总结:其实应用层初始化的i2c_msg就是直接给内核i2c_transfer将I2C消息发送出去的。