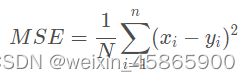Pytorch—nn.MSELoss
MSE:Mean Squared Error 均方误差
含义:均方误差,是预测值与真实值之差的平方和的平均值,即:
但是,在具体的应用中跟定义稍有不同。主要差别是参数的设置,在torch.nn.MSELoss中有一个reduction参数。reduction是维度要不要缩减以及如何缩减主要有三个选项:
‘none’:no reduction will be applied.
‘mean’: the sum of the output will be divided by the number of elements in the output.
‘sum’: the output will be summed.
如果不设置reduction参数,默认是’mean’
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
a = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]], dtype=torch.float)
b = torch.tensor([[3, 5], [8, 6]], dtype=torch.float)
loss_fn1 = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='none')
loss1 = loss_fn1(a.float(), b.float())
print(loss1) # 输出结果:tensor([[ 4., 9.],
# [25., 4.]])
loss_fn2 = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='sum')
loss2 = loss_fn2(a.float(), b.float())
print(loss2) # 输出结果:tensor(42.)
loss_fn3 = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')
loss3 = loss_fn3(a.float(), b.float())
print(loss3) # 输出结果:tensor(10.5000)对于三维输入:
a = torch.randint(0, 9, (2, 2, 3)).float()
b = torch.randint(0, 9, (2, 2, 3)).float()
print('a:\n', a)
print('b:\n', b)
loss_fn1 = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='none')
loss1 = loss_fn1(a.float(), b.float())
print('loss_none:\n', loss1)
loss_fn2 = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='sum')
loss2 = loss_fn2(a.float(), b.float())
print('loss_sum:\n', loss2)
loss_fn3 = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')
loss3 = loss_fn3(a.float(), b.float())
print('loss_mean:\n', loss3)运行结果: