redis源码解析(四)——ziplist
版本:redis - 5.0.4
参考资料:redis设计与实现
文件:src下的ziplist.c ziplist.h
-
- 一、基础知识
-
-
- 1、压缩列表的各个组成部分及详细说明
- 2、列表节点
- 3、encoding
-
- 二、连锁更新
- 三、ziplist.h
- quickList
一、基础知识
压缩列表是Redis为了节约内存而开发的,是由一系列特殊编码的连续内存块组成的顺序性数据结构。一个压缩列表可以包含任意多个节点,每个节点可以保存一个字节数组或者一个整数值(短字符串或小的整数)。
约等于连续内存的双向链表,使用p指针+长度寻址,数据过多时查询性能差
1、压缩列表的各个组成部分及详细说明
ziplist是由以下几部分组成:
| zlbytes | zltail | zllen | entry1 | entry2 | … | entryN | zlend|
* [0f 00 00 00] [0c 00 00 00] [02 00] [00 f3] [02 f6] [ff]
* | | | | | |
* zlbytes zltail zllen "2" "5" end
| 属性 | 类型 | 长度 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| zlbytes | uint32_t | 4字节 | 记录整个压缩列表占用的内存字节数:在对压缩列表进行内存重分配,或者计算zlend的位置时使用 |
| zltail | uint32_t | 4字节 | 记录压缩列表表尾节点距离压缩列表的起始地址有多少个字节:通过这个偏移量,程序无需遍历整个压缩列表就可以确定表尾节点的地址 |
| zllen | uint16_t | 2字节 | 记录了压缩列表包含的节点数量 |
| entryN | 列表节点 | 不定 | 压缩列表包含的各个节点,节点的长度由节点保存的内存决定 |
| zlend | uint8_t | 1字节 | 特殊值oxFF(十进制255),用于标记压缩列表的末尾 |
2、列表节点
typedef struct zlentry {
unsigned int prevrawlensize;//前一节点encoding的长度
unsigned int prevrawlen;//前一个节点的长度,小于254 为一个字节,大于则为五个字节
unsigned int lensize;//当前节点encoding的长度(byte)
unsigned int len;//当前节点长度,使用了多少byte
unsigned int headersize;//prevrawlensize + lensize
unsigned char encoding; /* 数据类型ZIP_STR_* 或ZIP_INT_* 编码格式
However for 4 bits immediate integers this can assume a range of values and must be range-checked. */
unsigned char *p;//指向每一个节点的开始,也就是prevrawlen的位置
} zlentry;
- 存储长度的数值采用小端字节序
- 每个节点大小不同
- 由于存储了每个节点的字节数,无需遍历,用指针p加减字节数,就能让p指向自己需要的地址空间,获得需要的值。
3、encoding
ziplist节约内存很重要的方式就是encoding,我们要弄清楚encoding是什么:
encoding:记录了节点所保存数据的类型以及长度。
- 一字节、两字节或者五字节长,值最高位为00、01、或者10是字节数组编码:这种编码表示节点保存着字节数组,数组长度由编码去掉最高两位的其他位记录。
- 一字节长,值的最高位为11的是整数编码:表示保存的是整数值,整数值类型和长度由编码去除最高两位的其他位记录。
字节数组编码
| 编码 | 编码长度 | 保存的值 |
|---|---|---|
| 00bbbbbb | 1 字节 | 长度小于等于 63 字节的字节数组 |
| 01bbbbbb xxxxxxxx | 2 字节 | 长度小于等于 16383 字节的字节数组 |
| 10______ aaaaaaaa bbbbbbbb cccccccc dddddddd | 5 字节 | 长度小于等于 4294967295 的字节数组 |
整数编码
| 编码 | 编码长度 | 保存的值 |
|---|---|---|
| 11000000 | 1 字节 | int16_t 类型的整数 |
| 11010000 | 1 字节 | int32_t 类型的整数 |
| 11100000 | 1 字节 | int64_t 类型的整数 |
| 11110000 | 1 字节 | 24 位有符号整数 |
| 11111110 | 1 字节 | 8 位有符号整数 |
| 1111xxxx | 1 字节 | 无, 因为编码本身的 xxxx 四个位已经保存了一个介于 0 和12 之间的值 |
二、连锁更新
前提:
每个节点都存储了前一个节点的长度;
根据节点长度不同选择不同字节大小的空来存储长度信息(节省空间);
情景:假设有一个ziplist,存储了几个长度在250到253字节(next的prelen只需要1字节)的节点(只有这几个节点)。现在插入一个大于等于254字节(next的prelen需要5字节)大小的新节点在ziplist头部。
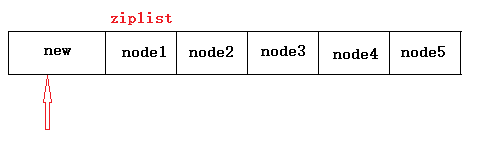
结果:
node1的prelen只有一个字节大小,不够,需要重新申请空间,变成五个字节。申请之后,node1大小超过254,也需要它的下一个节点也需要五个字节来存储它的长度,即node2。
同理,node2申请空间,扩大,则node3也需要,之后node4,node5都需要。
我们只是插入了一个新节点,但是整个list都改变了,每个节点都要重新申请空间。这种连续的多次空间扩展称之为连锁更新。
连锁更新出现的要求:
连续的,多个,长度介于250到253字节的节点;
概率很低,所以连锁更新对ziplist的影响不大
/*
插入节点时, 我们需要将下一个节点的前一节点长度字段设置值为插入节点的长度。
可能会发生这种情况:下一个节点的prelen字段需要增长, 1字节->5字节。
这只发生在有节点插入的情况下 (会导致 realloc 和 memmove)。
当有连续节点大小接近zip _ big _ prvlen时, 这种效果可能会在ziplist中级联,
注意:这种效果也可能发生在反向, 其中prevlen字段所需的字节可能会缩小。
链式的节点 先增长,再缩小会导致频繁的空间resize,因此prevlen字段缩小的情况被故意忽略,
字段长度允许保持大于必要的字节,。
指针p 指向不需要插入后的第一个节点。
*/
unsigned char *__ziplistCascadeUpdate(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p) {
size_t curlen = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl)), rawlen, rawlensize;
size_t offset, noffset, extra;
unsigned char *np;
zlentry cur, next;
//链表不为空
while (p[0] != ZIP_END) {
//获取p所指向的节点的全部信息,存在cur指向的空间中
zipEntry(p, &cur);
rawlen = cur.headersize + cur.len;
rawlensize = zipStorePrevEntryLength(NULL,rawlen);
//没有下一个节点,结束
if (p[rawlen] == ZIP_END) break;
//有下一个节点,取得信息,放在next中
zipEntry(p+rawlen, &next);
//判断next的prevrawlen是否被更改:没有(不发生更新),结束
if (next.prevrawlen == rawlen) break;
//prevrawlen字段需要扩展
if (next.prevrawlensize < rawlensize) {
/* The "prevlen" field of "next" needs more bytes to hold
* the raw length of "cur". */
offset = p-zl;
extra = rawlensize-next.prevrawlensize;
zl = ziplistResize(zl,curlen+extra);
p = zl+offset;
/* Current pointer and offset for next element. */
np = p+rawlen;
noffset = np-zl;
/* Update tail offset when next element is not the tail element. */
if ((zl+intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))) != np) {
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+extra);
}
/* Move the tail to the back. */
memmove(np+rawlensize,
np+next.prevrawlensize,
curlen-noffset-next.prevrawlensize-1);
zipStorePrevEntryLength(np,rawlen);
/* Advance the cursor */
p += rawlen;
curlen += extra;
} else {//需要紧缩
if (next.prevrawlensize > rawlensize) {
/* This would result in shrinking, which we want to avoid.
* So, set "rawlen" in the available bytes. */
zipStorePrevEntryLengthLarge(p+rawlen,rawlen);
} else {
zipStorePrevEntryLength(p+rawlen,rawlen);
}
/* Stop here, as the raw length of "next" has not changed. */
break;
}
}
return zl;
}
/*
指针p指向前一个节点,len为当前长度
如果前一个节点更改大小, 此函数返回编码前一节点长度所需的字节数的差异。
如果需要更多的空间, 该函数返回正数;如果需要较少的空间, 则返回负数; 如果需要相同的空间, 则返回0。
*/
int zipPrevLenByteDiff(unsigned char *p, unsigned int len) {
unsigned int prevlensize;
//编码前一节点长度所需的字节数,存在prevlensize中
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(p, prevlensize);
//zipStorePrevEntryLength(NULL, len):获取编码len长度所需的字节数
return zipStorePrevEntryLength(NULL, len) - prevlensize;
}
三、ziplist.h
//生成
unsigned char *ziplistNew(void);
//把 second 追加到 first, 合并这两个
unsigned char *ziplistMerge(unsigned char **first, unsigned char **second);
//从头或者从尾插入s
unsigned char *ziplistPush(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen, int where);
//获取指定下标的
unsigned char *ziplistIndex(unsigned char *zl, int index);
//下一个节点
unsigned char *ziplistNext(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p);
//前一个节点
unsigned char *ziplistPrev(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p);
//获取
unsigned int ziplistGet(unsigned char *p, unsigned char **sval, unsigned int *slen, long long *lval);
//插入
unsigned char *ziplistInsert(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen);
//删除
unsigned char *ziplistDelete(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char **p);
//从index开始删除num个
unsigned char *ziplistDeleteRange(unsigned char *zl, int index, unsigned int num);
//比较
unsigned int ziplistCompare(unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen);
//查找
unsigned char *ziplistFind(unsigned char *p, unsigned char *vstr, unsigned int vlen, unsigned int skip);
//长度
unsigned int ziplistLen(unsigned char *zl);
//原始长度
size_t ziplistBlobLen(unsigned char *zl);
//打印第一个
void ziplistRepr(unsigned char *zl);
quickList
- ziplist需要连续内存,申请内存效率低
限制ziplist长度和entry大小 - ziplist如何存储大数据
数据分片,多个ziplist - 管理多个ziplist
使用quickList
/* quicklistNode is a 32 byte struct describing a listpack for a quicklist.
* We use bit fields keep the quicklistNode at 32 bytes.
* count: 16 bits, max 65536 (max lp bytes is 65k, so max count actually < 32k).
* encoding: 2 bits, RAW=1, LZF=2.
* container: 2 bits, PLAIN=1 (a single item as char array), PACKED=2 (listpack with multiple items).
* recompress: 1 bit, bool, true if node is temporary decompressed for usage.
* attempted_compress: 1 bit, boolean, used for verifying during testing.
* extra: 10 bits, free for future use; pads out the remainder of 32 bits */
typedef struct quicklistNode {
struct quicklistNode *prev;
struct quicklistNode *next;
unsigned char *entry;
size_t sz; //当前ziplist字节数
unsigned int count : 16;//当前ziplist节点数
unsigned int encoding : 2; /* RAW==1 or LZF==2 */
unsigned int container : 2; /* 数据容器类型 PLAIN==1 or PACKED==2 */
unsigned int recompress : 1; //是否被解压
unsigned int attempted_compress : 1; /* node can't compress; too small */
unsigned int dont_compress : 1; /* prevent compression of entry that will be used later */
unsigned int extra : 9; //预留字段
} quicklistNode;
/* quicklist is a 40 byte struct (on 64-bit systems) describing a quicklist.
* 'count' is the number of total entries.
* 'len' is the number of quicklist nodes.
* 'compress' is: 0 if compression disabled, otherwise it's the number
* of quicklistNodes to leave uncompressed at ends of quicklist.
* 'fill' is the user-requested (or default) fill factor.
* 'bookmarks are an optional feature that is used by realloc this struct,
* so that they don't consume memory when not used. */
typedef struct quicklist {
quicklistNode *head;
quicklistNode *tail;
unsigned long count;//所有ziplist的节点数量
unsigned long len;//ziplist的数量
signed int fill : QL_FILL_BITS;//ziplist的entry上限
unsigned int compress : QL_COMP_BITS; //首尾不压缩的节点数量
unsigned int bookmark_count: QL_BM_BITS;
quicklistBookmark bookmarks[];
} quicklist;
- 中间节点压缩 节省内存