ortools解决tsp_ortools系列:VRP问题
ortools系列:VRP问题
VRP问题
车辆路径问题是旅行商问题的推广。在VRP中,目标是为向不同地点交付货物或服务的车队找到最优路线集。VRP最初是由Dantzig和Ramser在1959年提出的。
与TSP类似,VRP也可以用分配给边缘的距离的图来表示。
如果您试图找到一组总距离最小、对车辆没有附加约束的路线,那么最优解决方案是将所有位置分配给一辆车,其余位置空闲。在这种情况下,问题归结为TSP。
一个更有趣的问题是最小化所有车辆的最长路线距离的长度,或最长旅行时间的路线的消耗时间。VRPs还可以对车辆有额外的限制—例如,对每辆车访问的地点数量或每条路线的长度的下限和上限。
在以后的文章中,我们还会讲车辆有容量约束和时间窗口的VRP问题。
- 容量约束:车辆行驶路线上各个地点的总需求不能超过其容量。例如,需求可能是车辆必须交付到每个位置的包裹的大小,其中所有包裹的总大小不能超过车辆的承载能力。
- 时间窗口:每个位置必须在一个时间窗口[ai, bi]内服务,等待时间是允许的。
- 位置对之间的优先关系:例如,位置j在位置i之前不能被访问。
最小化最长的单一路径
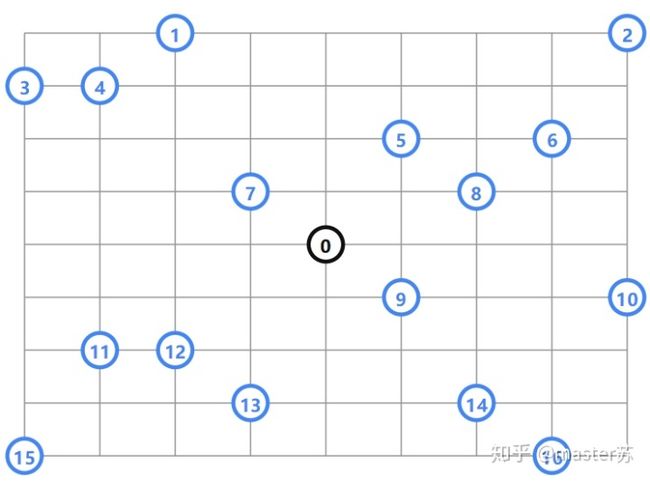
在下面的例子中,一个公司需要访问由相同矩形块组成的城市中的一些客户位置。下图是该城市的示意图,公司位置用黑色标示,参观地点用蓝色标示。
定位坐标
[(456, 320), # location 0
(228, 0), # location 1
(912, 0), # location 2
(0, 80), # location 3
(114, 80), # location 4
(570, 160), # location 5
(798, 160), # location 6
(342, 240), # location 7
(684, 240), # location 8
(570, 400), # location 9
(912, 400), # location 10
(114, 480), # location 11
(228, 480), # location 12
(342, 560), # location 13
(684, 560), # location 14
(0, 640), # location 15
(798, 640)] # location 16在这里我们根据上面的坐标算出不同位置之间的距离,距离函数使用曼哈顿距离:|x1 - x2| + |y1 - y2|.
好,基本问题都解释清楚了,我们还是直接看代码吧:
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
# 定义这个VRP问题的数据,使用字典结构存储
def create_data_model():
"""Creates the data for the example."""
data = {}
# Array of distances between locations.
_distances =
[
[0, 548, 776, 696, 582, 274, 502, 194, 308, 194, 536, 502, 388, 354, 468, 776, 662],
[548, 0, 684, 308, 194, 502, 730, 354, 696, 742, 1084, 594, 480, 674, 1016, 868, 1210],
[776, 684, 0, 992, 878, 502, 274, 810, 468, 742, 400, 1278, 1164, 1130, 788, 1552, 754],
[696, 308, 992, 0, 114, 650, 878, 502, 844, 890, 1232, 514, 628, 822, 1164, 560, 1358],
[582, 194, 878, 114, 0, 536, 764, 388, 730, 776, 1118, 400, 514, 708, 1050, 674, 1244],
[274, 502, 502, 650, 536, 0, 228, 308, 194, 240, 582, 776, 662, 628, 514, 1050, 708],
[502, 730, 274, 878, 764, 228, 0, 536, 194, 468, 354, 1004, 890, 856, 514, 1278, 480],
[194, 354, 810, 502, 388, 308, 536, 0, 342, 388, 730, 468, 354, 320, 662, 742, 856],
[308, 696, 468, 844, 730, 194, 194, 342, 0, 274, 388, 810, 696, 662, 320, 1084, 514],
[194, 742, 742, 890, 776, 240, 468, 388, 274, 0, 342, 536, 422, 388, 274, 810, 468],
[536, 1084, 400, 1232, 1118, 582, 354, 730, 388, 342, 0, 878, 764, 730, 388, 1152, 354],
[502, 594, 1278, 514, 400, 776, 1004, 468, 810, 536, 878, 0, 114, 308, 650, 274, 844],
[388, 480, 1164, 628, 514, 662, 890, 354, 696, 422, 764, 114, 0, 194, 536, 388, 730],
[354, 674, 1130, 822, 708, 628, 856, 320, 662, 388, 730, 308, 194, 0, 342, 422, 536],
[468, 1016, 788, 1164, 1050, 514, 514, 662, 320, 274, 388, 650, 536, 342, 0, 764, 194],
[776, 868, 1552, 560, 674, 1050, 1278, 742, 1084, 810, 1152, 274, 388, 422, 764, 0, 798],
[662, 1210, 754, 1358, 1244, 708, 480, 856, 514, 468, 354, 844, 730, 536, 194, 798, 0]
]
data["distances"] = _distances
data["num_locations"] = len(_distances) # 有几个节点
data["num_vehicles"] = 4 # 有几辆车
data["depot"] = 0 # 仓库索引,我们假设所有的车辆都从同一地点出发,也就是车场。
# 或者,你可以允许车辆在任何位置启动和结束。
return data
# 计算距离的回调函数,和之前的routing问题一样的
def create_distance_callback(data):
"""Creates callback to return distance between points."""
distances = data["distances"]
def distance_callback(from_node, to_node):
"""Returns the manhattan distance between the two nodes"""
return distances[from_node][to_node]
return distance_callback
def add_distance_dimension(routing, distance_callback):
"""Add Global Span constraint"""
distance = 'Distance'
maximum_distance = 3000 # 每辆车能形式的最大距离
routing.AddDimension(
distance_callback,
0, # null slack
maximum_distance,
True, # 从累积到零,意思应该和“走了这么久还剩多少汽油”差不多吧
distance)
distance_dimension = routing.GetDimensionOrDie(distance)
# Try to minimize the max distance among vehicles.
# 尽量减少车辆之间的最大距离。
distance_dimension.SetGlobalSpanCostCoefficient(100)
# 打印每辆车的路线(访问的位置),以及路线的距离。
# 请注意,这些距离包括从仓库到路线中第一个位置的距离以及从最后一个位置返回到仓库的距离。
# IndexToNode, NextVar 函数和前面的tsp问题是相同的意思
def print_solution(data, routing, assignment):
"""Print routes on console."""
total_distance = 0
for vehicle_id in range(data["num_vehicles"]):
index = routing.Start(vehicle_id)
plan_output = 'Route for vehicle {}:n'.format(vehicle_id)
route_dist = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
node_index = routing.IndexToNode(index)
next_node_index = routing.IndexToNode(
assignment.Value(routing.NextVar(index)))
route_dist += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(node_index, next_node_index, vehicle_id)
plan_output += ' {0} ->'.format(node_index)
index = assignment.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
plan_output += ' {}n'.format(routing.IndexToNode(index))
plan_output += 'Distance of route: {}mn'.format(route_dist)
print(plan_output)
total_distance += route_dist
print('Total distance of all routes: {}m'.format(total_distance))
# 主函数
def main():
# 创建数据集
data = create_data_model()
# Create Routing Model
# 创建路由模型
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(
data["num_locations"],
data["num_vehicles"],
data["depot"])
# 提供距离回调,以便解决程序可以计算位置之间的距离。
distance_callback = create_distance_callback(data)
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(distance_callback)
# 添加距离维度
add_distance_dimension(routing, distance_callback)
# Setting first solution heuristic (cheapest addition).
# 必须指定启发式方法来找到第一个解决方案
search_parameters = pywrapcp.RoutingModel.DefaultSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC) # pylint: disable=no-member
# 求解问题
assignment = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
if assignment:
print_solution(data, routing, assignment)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
# 结果
Route for vehicle 0:
0 -> 8 -> 6 -> 2 -> 5 -> 0
Distance of route: 1552m
Route for vehicle 1:
0 -> 7 -> 1 -> 4 -> 3 -> 0
Distance of route: 1552m
Route for vehicle 2:
0 -> 9 -> 10 -> 16 -> 14 -> 0
Distance of route: 1552m
Route for vehicle 3:
0 -> 12 -> 11 -> 15 -> 13 -> 0
Distance of route: 1552m
Total distance of all routes: 6208m注意函数添加距离维度(Add a distance dimension),
要解决这个VRP,需要创建一个距离维度,它计算每辆车沿其路线行驶的累计距离。然后,将成本设置为每条路线总距离的最大值。关于距离信息可以参考vrp_dimension_details.
若要添加距离维度,请使用求解器的AddDimension方法。下面的代码为距离创建一个维度,并设置累计距离成本。
def add_distance_dimension(routing, distance_callback):
"""Add Global Span constraint"""
distance = 'Distance'
maximum_distance = 3000 # 每辆车能形式的最大距离
routing.AddDimension(
distance_callback,
0, # null slack
maximum_distance,
True, # 从累积到零,意思应该和“走了这么久还剩多少汽油”差不多吧
distance)
distance_dimension = routing.GetDimensionOrDie(distance)
# Try to minimize the max distance among vehicles.
# 尽量减少车辆之间的最大距离。
distance_dimension.SetGlobalSpanCostCoefficient(100)下面是求解的结果:
看起来也不难呢,但是我想说的是,如果有1000个节点会怎样?欢迎大家讨论讨论。
参考
- allow-vehicles-to-start-and-end-any-location
- google_ortools_guide
大家看完记得关注点赞.
master苏.