排序算法之冒泡排序(图解)
冒泡排序
- 1.冒泡排序
-
- wikipedia:
- 2.冒泡排序的步骤
-
-
- 第一次迭代
- 之后的迭代
-
- 3.冒泡排序的实现
-
-
- 伪代码
- 助记码
- Python
- Java
- C
- C++
-
- 4.冒泡排序的复杂度
-
-
- 平均复杂度的计算
-
1.冒泡排序
wikipedia:
冒泡排序(英语:Bubble Sort)又称为泡式排序,是一种简单的排序算法。它重复地走访过要排序的数列,一次比较两个元素,如果它们的顺序错误就把它们交换过来。走访数列的工作是重复地进行直到没有再需要交换,也就是说该数列已经排序完成。这个算法的名字由来是因为越小的元素会经由交换慢慢“浮”到数列的顶端。
为什么介绍用“浮”呢?看它的动图应该就可以理解了。
总结一下就是:比较相邻的两个元素然后交换这两者,一直到一整个数列都按照顺序排列。
2.冒泡排序的步骤
可以先看动图,如果动图就能够理解的话,就不需要看下面的步骤了。
如果觉得动图太快,可以按照下面的步骤一步步理解。
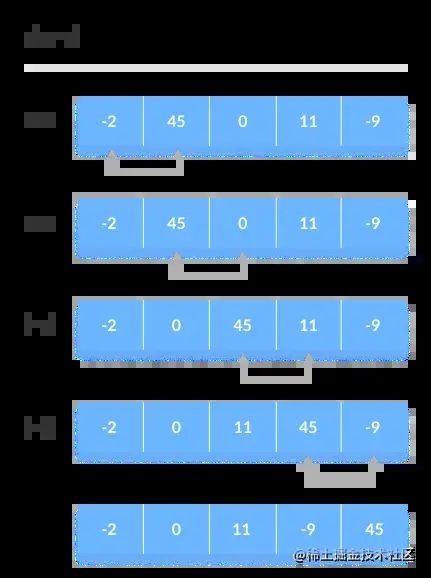
第一次迭代
- 从第一个下标开始,也就是0,比较第一个和第二个元素。
- 如果第一个元素比第二个元素大,那就交换两者。
- 然后比较第二个元素和第三个元素,如果两者也不是升序,那交换两者。
- 一直比较和交换,直到最后。
之后的迭代
冒泡排序就是不断重复迭代的过程,随着不断的交换,大的元素会和动图一样交换到后面,小的元素则会换到前面。下图是第二次迭代。
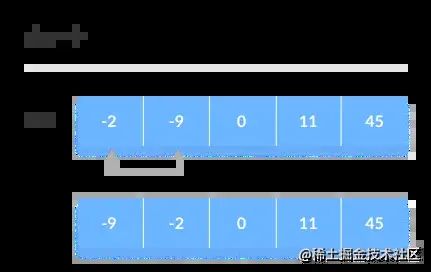
下图是最后一次迭代,当-2和-9交换后,这一整个数组的排序就完成了。
3.冒泡排序的实现
伪代码
function bubble_sort (array, length) {
var i, j;
for(i from 0 to length-1){
for(j from 0 to length-1-i){
if (array[j] > array[j+1])
swap(array[j], array[j+1])
}
}
}
助记码
i∈[0,N-1) //循环N-1遍
j∈[0,N-1-i) //每遍循环要处理的无序部分
swap(j,j+1) //两两排序(升序/降序)
Python
# Bubble sort in Python
def bubbleSort(array):
# loop to access each array element
for i in range(len(array)):
# loop to compare array elements
for j in range(0, len(array) - i - 1):
# compare two adjacent elements
# change > to < to sort in descending order
if array[j] > array[j + 1]:
# swapping elements if elements
# are not in the intended order
temp = array[j]
array[j] = array[j+1]
array[j+1] = temp
data = [-2, 45, 0, 11, -9]
bubbleSort(data)
print('Sorted Array in Ascending Order:')
print(data)
Java
// Bubble sort in Java
import java.util.Arrays;
class Main {
// perform the bubble sort
static void bubbleSort(int array[]) {
int size = array.length;
// loop to access each array element
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++)
// loop to compare array elements
for (int j = 0; j < size - i - 1; j++)
// compare two adjacent elements
// change > to < to sort in descending order
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// swapping occurs if elements
// are not in the intended order
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] data = { -2, 45, 0, 11, -9 };
// call method using class name
Main.bubbleSort(data);
System.out.println("Sorted Array in Ascending Order:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
}
}
C
// Bubble sort in C
#include C++
// Bubble sort in C++
#include 4.冒泡排序的复杂度
| 时间复杂度 | |
|---|---|
| 最优 | O(n) |
| 最坏 | O( n 2 n^2 n2) |
| 平均 | O( n 2 n^2 n2) |
| 空间复杂度 | O(1) |
| 稳定性 | Yes |
平均复杂度的计算
| 循环 | 比较的次数 |
|---|---|
| 1st | (n-1) |
| 2nd | (n-2) |
| 3rd | (n-3) |
| … | … |
| last | 1 |
所以,比较的次数是
(n-1) + (n-2) + (n-3) +.....+ 1 = n(n-1)/2
基本上等于 n 2 n^2 n2