数据库【嵌套查询】
目录
3.43 嵌套循环
嵌套循环的简单例子:
1.带有in谓词的子查询
[例 3.55] 查询与“刘晨”在同一个系学习的学生。
[例 3.56]查询选修了课程名为“信息系统”的学生学号和姓名。
2.带有比较运算符的子查询
[例 3.57 ]找出每个学生超过他选修课程平均成绩的课程号。
3.带有any(some)或all谓词的子查询
[例 3.58] 查询非计算机科学系中比计算机科学系任意一个学生年龄小的学生姓名和年龄。
[例 3.59] 查询非计算机科学系中比计算机科学系所有学生年龄都小的学生姓名及年龄。
4.带有exists谓词的子查询
[例 3.60]查询所有选修了1号课程的学生姓名。
[例 3.61] 查询没有选修1号课程的学生姓名。
[例 3.62] 查询选修了全部课程的学生姓名。
[例 3.63]查询至少选修了学生201215122选修的全部课程的学生号码。
心得:
3.43 嵌套循环
嵌套循环的简单例子:
select Sname
from Student
where Sno in(
select Sno
from SC
where Cno='2');上面有两个select,第二个循环嵌套在where语句里面。
上层的查询块称为外层查询或父查询。,下层的查询块称为内层查询或子查询。
子查询的select语句中不能使用order by子句,order by语句只能对最终查询结果排序。
1.带有in谓词的子查询
[例 3.55] 查询与“刘晨”在同一个系学习的学生。
分布查询
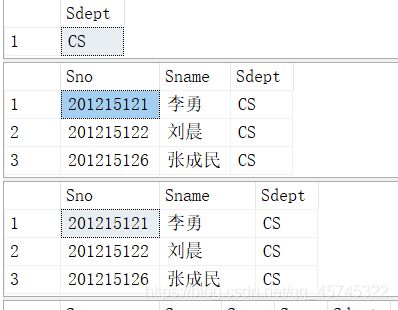
select Sdept
from Student
where Sname='刘晨';
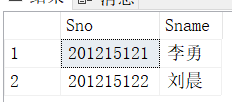
select Sno,Sname,Sdept
from Student
where Sdept='CS';嵌套查询
select Sno,Sname,Sdept
from Student
where Sdept in(
select Sdept
from Student
where Sname='刘晨');在一起运行的结果如下:
也可以使用自身查询来完成该题目:
select s1.Sno,s1.Sname,s1.Sdept
from Student s1,Student s2
where s1.Sdept=s2.Sdept and s2.Sname='刘晨';
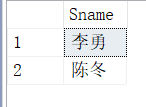
[例 3.56]查询选修了课程名为“信息系统”的学生学号和姓名。
嵌套查询
select Sno,Sname
from Student
where Sno in
(select Sno
from SC
where Cno in
(select Cno
from Course
where Cname='信息系统'
)
);我感觉有点复杂。。。还不如下面的简单易懂。。。
连接查询
select Student.Sno,Sname
from Student,SC,Course
where Student.Sno=Sc.Sno and
SC.Cno=Course.Cno and
Course.Cname='信息系统';
2.带有比较运算符的子查询
[例 3.57 ]找出每个学生超过他选修课程平均成绩的课程号。
这是一个相关子查询。
x,y均是表SC的别名。
select Sno,Cno
from SC x
where Grade>=(select avg (Grade)
from SC y
where y.Sno=x.Sno);3.带有any(some)或all谓词的子查询
使用ANY或ALL谓词时必须同时使用比较运算
语义为:
> ANY 大于子查询结果中的某个值
> ALL 大于子查询结果中的所有值
< ANY 小于子查询结果中的某个值
< ALL 小于子查询结果中的所有值
>= ANY 大于等于子查询结果中的某个值
>= ALL 大于等于子查询结果中的所有值
[例 3.58] 查询非计算机科学系中比计算机科学系任意一个学生年龄小的学生姓名和年龄。
select Sname,Sage
from Student
where Sage< any (select Sage
from Student
where Sdept='CS')
and Sdept<>'CS';--这是父查询块中的条件使用聚集函数的方法。
select Sname,Sage
from Student
where Sage<
(select max(Sage)
from Student
where Sdept='CS')
and Sdept<>'CS';[例 3.59] 查询非计算机科学系中比计算机科学系所有学生年龄都小的学生姓名及年龄。
方法一:用ALL谓词
select Sname,Sage
from Student
where Sage < all
(select Sage
from Student
where Sdept='CS')
and Sdept<>'CS';
方法二:用聚集函数
select Sname,Sage
from Student
where Sage <
(select min(Sage)
from Student
where Sdept='CS')
and Sdept<>'CS';4.带有exists谓词的子查询
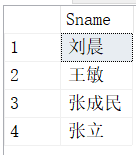
[例 3.60]查询所有选修了1号课程的学生姓名。
select Sname
from Student
where exists
(select *
from SC
where Sno=Student.Sno and Cno='1');
[例 3.61] 查询没有选修1号课程的学生姓名。
select Sname
from Student
where not exists
(select *
from SC
where Sno=Student.Sno and Cno='1');
所有带IN谓词、比较运算符、ANY和ALL谓词的子查询
都能用带EXISTS谓词的子查询 等价替换
[例 3.55]查询与“刘晨”在同一个系学习的学生。
用带EXISTS谓词的子查询替换IN:
select Sno,Sname,Sdept
from Student S1
where exists
(select *
from Student S2
where S2.Sdept=S1.Sdept and
S2.Sname='刘晨');其他方法,可见上方。
[例 3.62] 查询选修了全部课程的学生姓名。
select Sname
from Student
where not exists
(select *
from Course
where not exists
(select *
from SC
where Sno=Student.Sno
and Cno=Course.Cno
)
);
[例 3.63]查询至少选修了学生201215122选修的全部课程的学生号码。
select distinct Sno
from SC SCX
where not exists
(select *
from SC SCY
where SCY.Sno='201215122' and
not exists
(select *
from SC SCZ
where SCZ.Sno=SCX.Sno and
SCZ.Cno=SCY.Cno));
心得:
这个嵌套有点难,(但是大部分的嵌套查询其实都是可以使用其他方法替代的)写的时候,还要不断地看着课本的答案,才能正确的写出来,要好好的学习这个部分。