Spring实现事务(主要基于XML、注解)
Java知识点总结:想看的可以从这里进入
目录
-
- 15、Spring的事务
-
- 15.1、简介
- 15.2、事务管理器
- 15.3、实现事务
-
- 15.3.1、编程式事务
- 15.3.2、声明式事务
-
- 1、基于XML
- 2、基于注解
15、Spring的事务
15.1、简介
事务是数据库操作的最小工作单元,在大多数情况下事务都要求要么都执成功、要么都不执行(根据实际情况设定,有些事务可能不是这样),它是一组不可再分割的操作集合(工作逻辑单元)。也就是说我们将一组操作看成是多个事务的结合,这些事务只要有一个失败,这次操作就不成功(事务之间就是逻辑与的关系)。而操作失败后,就会产生事务的回滚,将数据返回到操作前的状态。
在Spring中有一个 Spring-tx 的包,其中transaction包提供事务管理的依赖包。

它的内部有三个重要的接口:
- PlatformTransactionManager:平台事务管理器,用于管理事务(实现类DataSourceTransactionManager(配置数据源)、JtaTransactionManager(全局事务管理))
- TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition):获取事务的状态信息
- void commit(TransactionStatus):提交事务
- void rollback(TransactionStatus) :回滚事务
- TransactionDefinition:事务定义的对象,定义了事务的规则,提供获取事务信息的方法。我们配置的事务信息会封装到此对象中。
- String getName():获取事务对象名称
- boolean isReadOnly():事务是否只读
- int getTimeout():事务超时时间
- int getIsolationLevel():事务隔离级别
- int getPropagationBehavior():事务的传播行为
- TransactionStatus:事务的状态,描述某一时间点事务的状态信息
- void flush():刷新事务
- boolean hasSavepoint():是否带有保存点
- boolean isCompleted():事务是否完成
- isNewTransaction():是否是新事务
- isRollbackOnly():获取事务是否回滚
- setRollbackOnly():设置事务回滚

Spring 中提供了以下隔离级别,我们可以根据自身的需求自行选择合适的隔离级别。
方法 说明 ISOLATION_DEFAULT 使用后端数据库默认的隔离级别 ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED 允许读取尚未提交的更改,可能导致脏读、幻读和不可重复读 ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED Oracle 默认级别,允许读取已提交的并发事务,防止脏读,可能出现幻读和不可重复读 ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ MySQL 默认级别,多次读取相同字段的结果是一致的,防止脏读和不可重复读,可能出现幻读 ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE 完全服从 ACID 的隔离级别,防止脏读、不可重复读和幻读 Spring中的事务规则如下:
Spring事务规则 值 描述 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED REQUIRED 表示当前方法必须在事务中运行。如果有事务在进行,就加入当前事务,否则就新建一个事务。 PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS SUPPORTS 表示当前方法不是必须在一个事务中运行。但如果有事务正在进行,就加入事务,否则以非事务的方式运行。 PROPAGATION_MANDATORY MANDATORY 表示当前方法必须在一个事务中运行。如果有事务进行,就加入当前事务,否则就抛出异常 PROPAGATION_NESTED NESTED 如果当前方法正有一个事务在运行,则该方法嵌套在正运行的事务中,被嵌套的事务可以独立于事务中进行提交和回滚,但外层事务抛出异常嵌套的事务必须回滚。嵌套事务不影响外层事务。如果没有事务运行则新建一个事务。 PROPAGATION_NEVER NEVER 表示当前方法不应该在事务中运行。如果没有正在运行的事务,则以非事务方式进行。如果有事务存在,则抛出异常 PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW REQUIRES_NEW 表示方法必须运行在自己的事务中。如果没有事务进行,就新建一个事务。如果有一个事务正在运行,则将事务暂时挂起,等到其他事务运行结束。 PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED NOT_SUPPORTED 表示该方法不应在事务中运行。如果有一个事务在运行,则暂时挂起,等待事务运行完毕,以非事务形式运行。如果没有,就以非事务方式执行。
15.2、事务管理器
在Spring中想要使用事务需要配置事务管理器,它是通过PlatformTransactionManager 进行管理的,Spring 为不同的持久化框架或平台( JDBC、Hibernate、JPA 以及 JTA 等)提供了不同的 PlatformTransactionManager 接口实现,这些实现类被称为事务管理器实现。
| 实现类 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager | 使用 Spring JDBC 进行持久化数据时使用。 |
| org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager | 使用 Hibernate 3.0 及以上版本进行持久化数据时使用。 |
| org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager | 使用 JPA 进行持久化时使用。 |
| org.springframework.jdo.JdoTransactionManager | 当持久化机制是 Jdo 时使用。 |
| org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager | 使用 JTA 来实现事务管理,在一个事务跨越多个不同的资源(即分布式事务)使用该实现 |
因为我们连接数据库都是使用mybatis,所以用的最多的是 org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager。需要在XML中配置:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"/>
bean>
beans>
15.3、实现事务
事务管理方式有两种:一种是传统的编程式事务管理(编写代码实现事务,能精确地定义事务的边界),一种是声明式事务管理(以AOP技术实现,无须通过编程的方式管理事务)。
声明式事务管理的优点就是不需要通过编程的方式实现,只需要在配置文件中进行事务的规则声明,就可以将事务应用得到业务逻辑当中,实际上就是将事务切入到业务目标中,它对业务代码没有侵入性,耦合度低,易于维护,所以现在开发基本都使用声明式事务管理。
声明式事事务管理也分为两种:XML文件配置和注解,其中XML文件配置已经很少使用,现在的事务管理都是通过注解:@Transactional来实现的。
15.3.1、编程式事务
实际上就是通过我们自己写程序来实现的,Spring提供的最原始的事务管理方式是基于TransactionDefinition、PlatformTransactionManager、TransactionStatus 编程式事务。而TransactionTemplate的编程式事务管理是使用模板方法设计模式对原始事务管理方式的封装。
我们使用过spring的JdbcTemplate访问数据库,但是他不支持事务,所以spring设置了一个 org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate模板,它是提供事务管理器的模板。它的核心方法是 execute,传入的参数有两种选择:TransactionCallback、TransactionCallbackWithoutResult
//简化程序化事务划分和事务异常处理的模板类。
public class TransactionTemplate extends DefaultTransactionDefinition implements TransactionOperations, InitializingBean {
.....构造方法等省略.....
/** 设置要使用的事务管理策略 */
public void setTransactionManager(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager) {
this.transactionManager = transactionManager;
}
/**返回要使用的事务管理策略。*/
@Nullable
public PlatformTransactionManager getTransactionManager() {
return this.transactionManager;
}
/**中心方法 ,支持实现TransactionCallback接口的事务代码。 */
@Override
@Nullable
public <T> T execute(TransactionCallback<T> action) throws TransactionException {
Assert.state(this.transactionManager != null, "No PlatformTransactionManager set");
//使用自定义的事务管理器
if (this.transactionManager instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) {
return ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) this.transactionManager).execute(this, action);
}
//系统默认的管理器
else {
//获取事务的状态
TransactionStatus status = this.transactionManager.getTransaction(this);
T result;
try {
//回调接口方法
result = action.doInTransaction(status);
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
// 事务代码抛出应用程序异常 -> 回滚
rollbackOnException(status, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// 事务代码抛出异常 ->回滚
rollbackOnException(status, ex);
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(ex, "TransactionCallback threw undeclared checked exception");
}
//提交事务
this.transactionManager.commit(status);
return result;
}
}
/**执行回滚,正确处理回滚异常。 */
private void rollbackOnException(TransactionStatus status, Throwable ex) throws TransactionException {
Assert.state(this.transactionManager != null, "No PlatformTransactionManager set");
logger.debug("Initiating transaction rollback on application exception", ex);
try {
this.transactionManager.rollback(status);
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
}
下面测试一下:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
<bean id="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/>
bean>
beans>
@SpringJUnitConfig(locations = {"classpath:application.xml"})
public class ClassesTest {
@Autowired
private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public List<User> getUser(Integer ... id){
//使用execute方法 操作事务
return transactionTemplate.execute(status -> {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM `user` WHERE user_id = ?";
try {
List<User> userList = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class), id);
System.out.println("事务操作成功");
return userList;
} catch (DataAccessException e) {
//出现异常设置事务的回滚,必须要有回滚
System.out.println("操作失败事务回滚");
status.setRollbackOnly();
}
return null;
});
}
}

[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-vaLy4MeW-1680166773502)(https://yudejava.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/typora/202302281456492.png)]
15.3.2、声明式事务
声明式事务是一种约定性的事务管理,使用事务时,大部分情况是发生异常后,需要回滚,不发生异常时提交事务。基于这点,spring声明式事务规定,业务方法不发生异常时,spring就让事务管理器提交事务,发生异常时,事务管理器回滚事务。
Spring 声明式事务管理是通过 AOP 实现的,其本质是对方法前后进行拦截,然后在目标方法开始之前创建(加入)一个事务,在执行完目标方法后,根据执行情况提交或者回滚事务。声明式事务最大的优点就是对业务代码的侵入性低,可以将业务代码和事务管理代码很好地进行解耦。
1、基于XML
在Spring2.0后,提供了 tx 命名空间来配置事务,通过 tx:advice 元素配置事务的通知,它有两个属性 id(唯一标识)、transaction-manager(指定事务管理器)。有一个子元素 tx:attributes ,通过配置多个 tx:method 来配置事务的细节
| tx:method 的属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| name | 指定那些方法执行事务(支持通配符) |
| propagation | 指定事务的传播行为 |
| isolation | 指定事务的隔离级别 |
| read-only | 指定事务是否只读 |
| timeout | 指定事务的超时时间 |
| rollback-for | 指定触发回滚的异常 |
| no-rollback-for | 指定不触发回滚的异常 |
使用XML配置
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
<tx:advice id="interceptor" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="select*" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="DEFAULT" read-only="false" timeout="-1" no-rollback-for="" rollback-for=""/>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="" expression=""/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="interceptor" pointcut-ref="切点的id"/>
aop:config>
测试一下:有四个用户,让其中一个人赠送积分给另一个人

-
dao操作数据库
public class IntegralTestTransactionalDao { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; /** 获取所有信息*/ public List<Integral> servletIntegral() { String sql = "SELECT id,`name`,integral_num FROM integral"; return jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Integral.class)); } /** 赠送积分*/ public void givingIntegral(int integralNum,int id){ String sql = "update integral set integral_num = integral_num-? where id=?"; jdbcTemplate.update(sql,integralNum,id); } /** 得到积分*/ public void getIntegral(int integralNum,int id){ String sql = "update integral set integral_num = integral_num+? where id=?"; jdbcTemplate.update(sql,integralNum,id); } /** 根据id获取*/ public Integral servletById(int id) { String sql = "select id,`name`,integral_num FROM integral where id =?"; try { return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Integral.class),id); }catch (EmptyResultDataAccessException e){ return null; } } } -
service
public class IntegralTransactionalServiceImpl implements IntegralTestTransactionalService { @Autowired private IntegralTestTransactionalDao dao; @Override public List<Integral> servletIntegral() { return dao.servletIntegral(); } @Override public Integral servletById(int id) { return dao.servletById(id); } @Override public void changeIntegral(int integralNum,Integral integral1,Integral integral2) throws Exception { System.out.println(integral1.getName()+"赠送积分:"+integralNum); dao.givingIntegral(integralNum,integral1.getId()); try { int i = 5/0; } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println(integral2.getName()+"获得积分:"+integralNum); dao.getIntegral(integralNum,integral2.getId()); } } -
不配置注解,测试一下效果
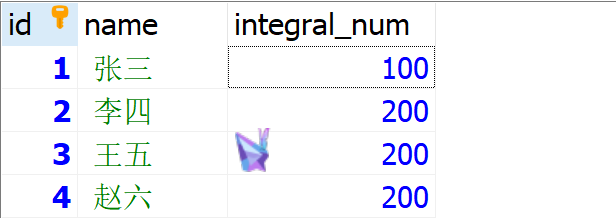
在不配置事务的情况下,张三积分减少,但是王五的并没有获得积分,现在通过XML配置事务:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"/>
bean>
<tx:advice id="interceptor" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="change*" read-only="false"/>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="point" expression="execution(* com.yu.spring.xmltransactional.IntegralTransactionalServiceImpl.changeIntegral(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="interceptor" pointcut-ref="point"/>
aop:config>
beans>
在数据库将数据改成初始状态,再进行测试:我们发现事务回滚了,所有人的积分都没有变化
2、基于注解
想要使用注解实现事务,必须开启事务注解的支持,也是有两种方法进行开启
-
在XML文件中开启:tx 命名空间提供了一个 tx:annotation-driven 的元素,用来开启注解事务,简化 Spring 声明式事务的 XML 配置。
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="事务管理器的id值"/> -
也可以在 @Configuration 的类上添加注解 @EnableTransactionManagement 开启注解支持
使用注解 @Configuration @ComponentScan @EnableTransactionManagement //开启事务 public class SpringConfig { ............ }
Spring 声明式事务编程的核心注解是 @Transactional ,该注解既可以在类上使用,也可以在方法上使用。在类上使用,则表示类中的所有方法都支持事务。在方法上使用,则表示当前方法支持事务。
Spring 容器会查找所有使用了 @Transactional 注解的 Bean,并自动为它们添加事务通知,通知的事务属性则是通过 @Transactional 注解的属性来定义的。
| 事务属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| propagation | 指定事务的传播行为。 |
| isolation | 指定事务的隔离级别。 |
| read-only | 指定是否为只读事务。 |
| timeout | 表示超时时间,单位为“秒”;声明的事务在指定的超时时间后,自动回滚,避免事务长时间不提交会回滚导致的数据库资源的占用。 |
| rollback-for | 指定事务对于那些类型的异常应当回滚,而不提交。 |
| no-rollback-for | 指定事务对于那些异常应当继续运行,而不回滚。 |
测试,还是使用上面XML的例子:
-
先在XML中开启事务注解的支持
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd"> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/> beans> -
dao操作数据
@Repository public class IntegralTestTransactionalDao { ................ } -
编写service(先不加事务注解)
@Service public class IntegralTransactionalServiceImpl implements IntegralTestTransactionalService{ .............................. @Override public void changeIntegral(int integralNum,Integral integral1,Integral integral2) throws Exception { System.out.println(integral1.getName()+"赠送积分:"+integralNum); dao.givingIntegral(integralNum,integral1.getId()); //出错误 try { int i = 5/0; } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println(integral2.getName()+"获得积分:"+integralNum); dao.getIntegral(integralNum,integral2.getId()); } } -
测试
@Test public void annotationtransactionTest() throws Exception { List<Integral> list1 = service.servletIntegral(); list1.forEach(i -> System.out.println(i.getName()+"有积分:"+i.getIntegralNum())); Integral user1 = service.servletById(1); Integral user2 = service.servletById(3); if(user1!=null && user2!=null){ service.changeIntegral(100,user1,user2); } List<Integral> list2 = service.servletIntegral(); list2.forEach(i -> System.out.println(i.getName()+"有积分:"+i.getIntegralNum())); }
我们发现在没有添加事务的时候,出现错误后,张三的积分减少了,但是王五并没有获得积分。现在对service方法添加 @Transactional
@Override
//开启事务
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,timeout = 10,readOnly = false)
public void changeIntegral(int integralNum,Integral integral1,Integral integral2) throws Exception {
System.out.println(integral1.getName()+"赠送积分:"+integralNum);
dao.givingIntegral(integralNum,integral1.getId());
try {
int i = 5/0;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(integral2.getName()+"获得积分:"+integralNum);
dao.getIntegral(integralNum,integral2.getId());
}
此时进行测试,在出现异常后,事务回滚了,2人的积分都没有发生变化