毕业设计-基于 MATLAB 的图像去雾技术研究
目录
前言
课题背景和意义
实现技术思路
一、常用图像去雾算法
二、基于 MATLAB 的图像去雾系统
三、图像质量评价
部分源代码
实现效果图样例
最后
前言
大四是整个大学期间最忙碌的时光,一边要忙着备考或实习为毕业后面临的就业升学做准备,一边要为毕业设计耗费大量精力。近几年各个学校要求的毕设项目越来越难,有不少课题是研究生级别难度的,对本科同学来说是充满挑战。为帮助大家顺利通过和节省时间与精力投入到更重要的就业和考试中去,学长分享优质的选题经验和毕设项目与技术思路。
对毕设有任何疑问都可以问学长哦!
选题指导: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37340229/article/details/128243277
大家好,这里是海浪学长毕设专题,本次分享的课题是
基于 MATLAB 的图像去雾技术研究
课题背景和意义
实现技术思路
一、常用图像去雾算法
直方图均衡化算法原理
图像直方图表示的是图像中每一灰度级出现的概率情况。假设一幅图像具有 N 个像素,r k 表示第 k 个灰度级对应的灰度,L 表示灰度级个数,nk 表示灰度 r k 的像素个数,则直方图可定义为:
![]()
多尺度 Retinex(MSR)算法原理
Retinex 理论即视网膜大脑皮层理论,该理论认为物体色彩主要取决于物体表面对红绿蓝 3 种光线的反射能力,不受光线的反射强度和光照非均匀性的影响,成像过程可表示为:
![]()
式中,I ( x,y ) 表示原始图像,R ( x,y ) 表示反射图像,L( x,y ) 表示入射光照图像。Retinex 算法的 原理是分离图像中的入射光照分量,保留能反映图像细节信息的反射分量。进行对数 运算,有
采用高斯环绕函数与原始图像的卷积来对入射光照分量进行估计,则第 i 条颜色通道经 SSR 算法处理后得到的反射分量 rSSRi ( x,y )可表示为:
为弥补该算法尺度单一、难以平衡图像动态范围压缩能力和色彩保真性的缺点, 提出了 MSR 算法,该算法的实质是对多个不同尺度的 SSR 算法结果的加权平均,可表示为
暗通道先验去雾算法原理
![]()
暗通道先验理论即在绝大多数户外无雾图像非天空区域内,总有大量像素在某个颜色通道上具有很小的亮度值,这个颜色通道即是暗通道。对于非天空区域的清晰无雾图像 J ( x ),其暗通道 J dark ( x )强度值总是趋近于 0,即
![]()
式中,J c ( y )表示图像 J 的 R、G、B 3 个通道中的某个通道,Ω( x )表示以像素 x 为中心的窗口区域。 假设大气光值 A 是已知的,估计初始透射率
引入参数 ω 使复原后的图像保留一定的雾感避免出现失真,复原无雾图像
二、基于 MATLAB 的图像去雾系统
全局直方图均衡化算法:
多尺度 Retinex 算法:
暗通道先验算法:
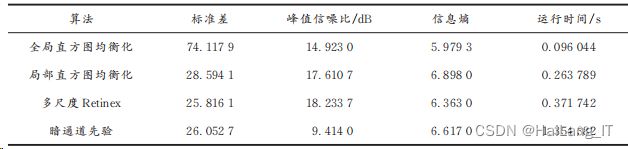
三、图像质量评价
# Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation.
# Licensed under the MIT License.
import os.path
import io
import zipfile
from data.base_dataset import BaseDataset, get_params, get_transform, normalize
from data.image_folder import make_dataset
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from data.Load_Bigfile import BigFileMemoryLoader
from data.Load_Bigfilev2 import BigFileMemoryLoaderv2
from io import BytesIO
import os
import glob
import cv2, math
import random
import numpy as np
import h5py
import os
from PIL import Image
import scipy.io
def pil_to_np(img_PIL):
'''Converts image in PIL format to np.array.
From W x H x C [0...255] to C x W x H [0..1]
'''
ar = np.array(img_PIL)
if len(ar.shape) == 3:
ar = ar.transpose(2, 0, 1)
else:
ar = ar[None, ...]
return ar.astype(np.float32) / 255.
def np_to_pil(img_np):
'''Converts image in np.array format to PIL image.
From C x W x H [0..1] to W x H x C [0...255]
'''
ar = np.clip(img_np * 255, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
if img_np.shape[0] == 1:
ar = ar[0]
else:
ar = ar.transpose(1, 2, 0)
return Image.fromarray(ar)
def synthesize_salt_pepper(image,amount,salt_vs_pepper):
## Give PIL, return the noisy PIL
img_pil=pil_to_np(image)
out = img_pil.copy()
p = amount
q = salt_vs_pepper
flipped = np.random.choice([True, False], size=img_pil.shape,
p=[p, 1 - p])
salted = np.random.choice([True, False], size=img_pil.shape,
p=[q, 1 - q])
peppered = ~salted
out[flipped & salted] = 1
out[flipped & peppered] = 0.
noisy = np.clip(out, 0, 1).astype(np.float32)
return np_to_pil(noisy)
def synthesize_gaussian(image,std_l,std_r):
## Give PIL, return the noisy PIL
img_pil=pil_to_np(image)
mean=0
std=random.uniform(std_l/255.,std_r/255.)
gauss=np.random.normal(loc=mean,scale=std,size=img_pil.shape)
noisy=img_pil+gauss
noisy=np.clip(noisy,0,1).astype(np.float32)
return np_to_pil(noisy)
def synthesize_speckle(image,std_l,std_r):
## Give PIL, return the noisy PIL
img_pil=pil_to_np(image)
mean=0
std=random.uniform(std_l/255.,std_r/255.)
gauss=np.random.normal(loc=mean,scale=std,size=img_pil.shape)
noisy=img_pil+gauss*img_pil
noisy=np.clip(noisy,0,1).astype(np.float32)
return np_to_pil(noisy)
def synthesize_low_resolution(img):
w,h=img.size
new_w=random.randint(int(w/2),w)
new_h=random.randint(int(h/2),h)
img=img.resize((new_w,new_h),Image.BICUBIC)
if random.uniform(0,1)<0.5:
img=img.resize((w,h),Image.NEAREST)
else:
img = img.resize((w, h), Image.BILINEAR)
return img
def convertToJpeg(im,quality):
with BytesIO() as f:
im.save(f, format='JPEG',quality=quality)
f.seek(0)
return Image.open(f).convert('RGB')
def blur_image_v2(img):
x=np.array(img)
kernel_size_candidate=[(3,3),(5,5),(7,7)]
kernel_size=random.sample(kernel_size_candidate,1)[0]
std=random.uniform(1.,5.)
#print("The gaussian kernel size: (%d,%d) std: %.2f"%(kernel_size[0],kernel_size[1],std))
blur=cv2.GaussianBlur(x,kernel_size,std)
return Image.fromarray(blur.astype(np.uint8))
def perlin_noise(im,varargin):
"""
This is the function for adding perlin noise to the depth map. It is a
simplified implementation of the paper:
an image sunthesizer
Ken Perlin, SIGGRAPH, Jul. 1985
The bicubic interpolation is used, compared to the original version.
Reference:
HAZERD: an outdoor scene dataset and benchmark for single image dehazing
IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Sep 2017
The paper and additional information on the project are available at:
https://labsites.rochester.edu/gsharma/research/computer-vision/hazerd/
If you use this code, please cite our paper.
Input:
im: depth map
varargin{1}: decay term
Output:
im: result of transmission with perlin noise added
Authors:
Yanfu Zhang: [email protected]
Li Ding: [email protected]
Gaurav Sharma: [email protected]
Last update: May 2017
:return:
"""
# (h, w, c) = im.shape
# i = 1
# if nargin == 1:
# decay = 2
# else:
# decay = varargin{1}
# l_bound = min(h,w)
# while i <= l_bound:
# d = imresize(randn(i, i)*decay, im.shape, 'bicubic')
# im = im+d
# i = i*2
# im = c(im);
# return im
pass
def srgb2lrgb(I0):
gamma = ((I0 + 0.055) / 1.055)**2.4
scale = I0 / 12.92
return np.where (I0 > 0.04045, gamma, scale)
def lrgb2srgb(I1):
gamma = 1.055*I1**(1/2.4)-0.055
scale = I1 * 12.92
return np.where (I1 > 0.0031308, gamma, scale)
#return : depth matrix
def get_depth(depth_or_trans_name):
#depth_or_trans_name为mat类型文件或者img类型文件地址
data = scipy.io.loadmat(depth_or_trans_name)
depths = data['imDepth'] #深度变量
#print(data.keys()) #打印mat文件中所有变量
depths = np.array(depths)
return depths
def irregular_hole_synthesize(img,mask):
img_np=np.array(img).astype('uint8')
mask_np=np.array(mask).astype('uint8')
mask_np=mask_np/255
img_new=img_np*(1-mask_np)+mask_np*255
hole_img=Image.fromarray(img_new.astype('uint8')).convert("RGB")
return hole_img,mask.convert("L")
def zero_mask(size):
x=np.zeros((size,size,3)).astype('uint8')
mask=Image.fromarray(x).convert("RGB")
return mask
def hazy_simu(img_name,depth_or_trans_name,airlight=0.76,is_imdepth=1): ##for outdoor
"""
This is the function for haze simulation with the parameters given by
the paper:
HAZERD: an outdoor scene dataset and benchmark for single image dehazing
IEEE Internation Conference on Image Processing, Sep 2017
The paper and additional information on the project are available at:
https://labsites.rochester.edu/gsharma/research/computer-vision/hazerd/
If you use this code, please cite our paper.
IMPORTANT NOTE: The code uses the convention that pixel locations with a
depth value of 0 correspond to objects that are very far and for the
simulation of haze these are placed a distance of 2 times the visual
range.
Authors:
Yanfu Zhang: [email protected]
Li Ding: [email protected]
Gaurav Sharma: [email protected]
Last update: May 2017
python version update : Aug 2021
Authors :
Haoying Sun : [email protected]
parse inputs and set default values
Set default parameter values. Some of these are used only if they are not
passed in
:param img_name: the directory and name of a haze-free RGB image, the name
should be in the format of ..._RGB.jpg
:param depth_name: the corresponding directory and name of the depth map, in
.mat file, the name should be in the format of ..._depth.mat
:param save_dir: the directory to save the simulated images
:param pert_perlin: 1 for adding perlin noise, default 0
:param airlight: 3*1 matrix in the range [0,1]
:param visual_range: a vector of any size
:return: image name of hazy image
"""
# if random.uniform(0, 1) < 0.5:
visual_range = [0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1] # visual range in km #可自行调整,或者使用range函数设置区间,此时需要修改beta_param,尚未研究
beta_param = 3.912 #Default beta parameter corresponding to visual range of 1000m
A = airlight
#print('Simulating hazy image for:{}'.format(img_name))
VR = random.choice(visual_range)
#print('Viusal value: {} km'.format(VR) )
#im1 = cv2.imread(img_name)
img_pil = pil_to_np(img_name)
#convert sRGB to linear RGB
I = srgb2lrgb(img_pil)
if is_imdepth:
depths = depth_or_trans_name
d = depths/1000 # convert meter to kilometer
if depths.max()==0:
d = np.where(d == 0,0.01, d) ####
else:
d = np.where(d==0,2*VR,d)
#Set regions where depth value is set to 0 to indicate no valid depth to
#a distance of two times the visual range. These regions typically
#correspond to sky areas
#convert depth map to transmission
beta = beta_param / VR
beta_return = beta
beta = np.ones(d.shape) * beta
transmission = np.exp((-beta*d))
transmission_3 = np.array([transmission,transmission,transmission])
#Obtain simulated linear RGB hazy image.Eq. 3 in the HazeRD paper
Ic = transmission_3 * I + (1 - transmission_3) * A
else:
Ic = pil_to_np(depth_or_trans_name) * I + (1 - pil_to_np(depth_or_trans_name)) * A
# convert linear RGB to sRGB
I2 = lrgb2srgb(Ic)
haze_img = np_to_pil(I2)
# haze_img = np.asarray(haze_img)
# haze_img = cv2.cvtColor(haze_img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# haze_img = Image.fromarray(haze_img)
return haze_img,airlight,beta_return
def hazy_reside_training(img_name,depth_or_trans_name,is_imdepth=1):
"""
RESIDE的 training中:A :(0.7, 1.0) , beta:(0.6, 1.8)
:param img_name:
:param depth_or_trans_name:
:param pert_perlin:
:param is_imdepth:
:return:
"""
beta = random.uniform(0.6, 1.8)
beta_return = beta
airlight = random.uniform(0.7, 1.0)
A = airlight
#print('Viusal value: {} km'.format(VR) )
#im1 = cv2.imread(img_name)
img_pil = pil_to_np(img_name)
#convert sRGB to linear RGB
I = srgb2lrgb(img_pil)
if is_imdepth:
depths = depth_or_trans_name
#convert depth map to transmission
if depths.max()==0:
d = np.where(depths == 0,1, depths)
else:
d = depths / depths.max()
d = np.where(d == 0, 1, d)
beta = np.ones(d.shape) * beta
transmission = np.exp((-beta*d))
transmission_3 = np.array([transmission,transmission,transmission])
#Obtain simulated linear RGB hazy image.Eq. 3 in the HazeRD paper
Ic = transmission_3 * I + (1 - transmission_3) * A
else:
Ic = pil_to_np(depth_or_trans_name) * I + (1 - pil_to_np(depth_or_trans_name)) * A
# convert linear RGB to sRGB
I2 = lrgb2srgb(Ic)
#I2 = cv2.cvtColor(I2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
haze_img = np_to_pil(I2)
# haze_img = np.asarray(haze_img)
# haze_img = cv2.cvtColor(haze_img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# haze_img = Image.fromarray(haze_img)
return haze_img,airlight,beta_return
def hazy_reside_OTS(img_name,depth_or_trans_name,is_imdepth=1):
"""
RESIDE的 OTS中:A [0.8, 0.85, 0.9, 0.95, 1] , beta:[0.04, 0.06, 0.08, 0.1, 0.12, 0.16, 0.2]
:param img_name:
:param depth_or_trans_name:
:param pert_perlin:
:param is_imdepth:
:return:
"""
beta = random.choice([0.04, 0.06, 0.08, 0.1, 0.12, 0.16, 0.2])
beta_return = beta
airlight = random.choice([0.8, 0.85, 0.9, 0.95, 1])
#print(beta)
#print(airlight)
A = airlight
#print('Viusal value: {} km'.format(VR) )
#im1 = cv2.imread(img_name)
#img = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(img_name), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
img_pil = pil_to_np(img_name)
#convert sRGB to linear RGB
I = srgb2lrgb(img_pil)
if is_imdepth:
depths = depth_or_trans_name
#convert depth map to transmission
if depths.max()==0:
d = np.where(depths == 0, 1, depths)
else:
d = depths/(depths.max())
d = np.where(d == 0, 1, d)
beta = np.ones(d.shape) * beta
transmission = np.exp((-beta*d))
transmission_3 = np.array([transmission,transmission,transmission])
#Obtain simulated linear RGB hazy image.Eq. 3 in the HazeRD paper
Ic = transmission_3 * I + (1 - transmission_3) * A
else:
Ic = pil_to_np(depth_or_trans_name) * I + (1 - pil_to_np(depth_or_trans_name)) * A
# convert linear RGB to sRGB
I2 = lrgb2srgb(Ic)
haze_img = np_to_pil(I2)
#haze_img = np.asarray(haze_img)
#haze_img = cv2.cvtColor(haze_img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
#haze_img = Image.fromarray(haze_img)
return haze_img,airlight,beta_return
def online_add_degradation_v2(img,depth_or_trans):
noise = 0
task_id=np.random.permutation(4)
if random.uniform(0,1)<0.3:
noise = 1
#print('noise')
for x in task_id:
#为增加更多变化,随机进行30%的丢弃,即<0.7
if x==0 and random.uniform(0,1)<0.7:
img = blur_image_v2(img)
if x==1 and random.uniform(0,1)<0.7:
flag = random.choice([1, 2, 3])
if flag == 1:
img = synthesize_gaussian(img, 5, 50) # Gaussian white noise with σ ∈ [5,50]
if flag == 2:
img = synthesize_speckle(img, 5, 50)
if flag == 3:
img = synthesize_salt_pepper(img, random.uniform(0, 0.01), random.uniform(0.3, 0.8))
if x==2 and random.uniform(0,1)<0.7:
img=synthesize_low_resolution(img)
if x==3 and random.uniform(0,1)<0.7:
img=convertToJpeg(img,random.randint(40,100))
#JPEG compression whose level is in the range of [40,100]
add_haze = random.choice([1,2,3])
if add_haze == 1:
img, airlight, beta = hazy_reside_OTS(img, depth_or_trans)
elif add_haze == 2:
img, airlight, beta = hazy_simu(img, depth_or_trans)
else:
img, airlight, beta = hazy_reside_training(img, depth_or_trans)
# else:
# if add_haze < 0.1:
# img = hazy_reside_OTS(img, depth_or_trans)
# elif add_haze > 0.1 and add_haze < 0.2:
# img = hazy_simu(img, depth_or_trans)
# else:
# img = hazy_reside_training(img, depth_or_trans)
return img#,noise,airlight,beta
class UnPairOldPhotos_SR(BaseDataset): ## Synthetic + Real Old
def initialize(self, opt):
self.opt = opt
self.isImage = 'domainA' in opt.name
self.task = 'old_photo_restoration_training_vae'
self.dir_AB = opt.dataroot
if self.isImage:
self.load_npy_dir_depth=os.path.join(self.dir_AB,"VOC_RGB_Depthnpy.bigfile")
self.load_img_dir_RGB_old=os.path.join(self.dir_AB,"Real_RGB_old.bigfile")
self.load_img_dir_clean=os.path.join(self.dir_AB,"VOC_RGB_JPEGImages.bigfile")
self.loaded_npys_depth=BigFileMemoryLoaderv2(self.load_npy_dir_depth)
self.loaded_imgs_RGB_old=BigFileMemoryLoader(self.load_img_dir_RGB_old)
self.loaded_imgs_clean=BigFileMemoryLoader(self.load_img_dir_clean)
else:
# self.load_img_dir_clean=os.path.join(self.dir_AB,self.opt.test_dataset)
self.load_img_dir_clean=os.path.join(self.dir_AB,"VOC_RGB_JPEGImages.bigfile")
self.loaded_imgs_clean=BigFileMemoryLoader(self.load_img_dir_clean)
self.load_npy_dir_depth=os.path.join(self.dir_AB,"VOC_RGB_Depthnpy.bigfile")
self.loaded_npys_depth=BigFileMemoryLoaderv2(self.load_npy_dir_depth)
####
print("-------------Filter the imgs whose size <256 in VOC-------------")
self.filtered_imgs_clean=[]
self.filtered_npys_depth = []
for i in range(len(self.loaded_imgs_clean)):
img_name,img=self.loaded_imgs_clean[i]
npy_name, npy = self.loaded_npys_depth[i]
h,w=img.size
if h<256 or w<256:
continue
self.filtered_imgs_clean.append((img_name,img))
self.filtered_npys_depth.append((npy_name, npy))
print("--------Origin image num is [%d], filtered result is [%d]--------" % (
len(self.loaded_imgs_clean), len(self.filtered_imgs_clean)))
## Filter these images whose size is less than 256
# self.img_list=os.listdir(load_img_dir)
self.pid = os.getpid()
def __getitem__(self, index):
is_real_old=0
sampled_dataset=None
sampled_depthdataset = None
degradation=None
if self.isImage: ## domain A , contains 2 kinds of data: synthetic + real_old
P=random.uniform(0,2)
if P>=0 and P<1:
#if random.uniform(0,1)<0.5:
# buyao huidutu
#sampled_dataset=self.loaded_imgs_L_old
#self.load_img_dir=self.load_img_dir_L_old
sampled_dataset = self.loaded_imgs_RGB_old
self.load_img_dir = self.load_img_dir_RGB_old
# else:
# sampled_dataset=self.loaded_imgs_RGB_old
# self.load_img_dir=self.load_img_dir_RGB_old
is_real_old=1
if P>=1 and P<2:
sampled_dataset=self.filtered_imgs_clean
self.load_img_dir=self.load_img_dir_clean
sampled_depthdataset=self.filtered_npys_depth
self.load_npy_dir=self.load_npy_dir_depth
degradation=1
else:
sampled_dataset=self.filtered_imgs_clean
self.load_img_dir=self.load_img_dir_clean
sampled_depthdataset = self.filtered_npys_depth
self.load_npy_dir = self.load_npy_dir_depth
sampled_dataset_len=len(sampled_dataset)
#print('sampled_dataset_len::::',sampled_dataset_len)
index=random.randint(0,sampled_dataset_len-1)
img_name,img = sampled_dataset[index]
# print(img_name)
# print(img)
# print(index)
#print(npy_name)
#print(npy)
if degradation is not None:
npy_name, npy = sampled_depthdataset[index]
img=online_add_degradation_v2(img,npy)
path=os.path.join(self.load_img_dir,img_name)
# AB = Image.open(path).convert('RGB')
# split AB image into A and B
# apply the same transform to both A and B
# if random.uniform(0,1) <0.1:
# img=img.convert("L")
# img=img.convert("RGB")
# ## Give a probability P, we convert the RGB image into L
A=img
w,h=A.size
if w<256 or h<256:
A=transforms.Scale(256,Image.BICUBIC)(A)
## Since we want to only crop the images (256*256), for those old photos whose size is smaller than 256, we first resize them.
transform_params = get_params(self.opt, A.size)
A_transform = get_transform(self.opt, transform_params)
B_tensor = inst_tensor = feat_tensor = 0
A_tensor = A_transform(A)
input_dict = {'label': A_tensor, 'inst': is_real_old, 'image': A_tensor,
'feat': feat_tensor, 'path': path}
return input_dict
def __len__(self):
return len(self.loaded_imgs_clean) ## actually, this is useless, since the selected index is just a random number
def name(self):
return 'UnPairOldPhotos_SR'
class PairOldPhotos(BaseDataset):
def initialize(self, opt):
self.opt = opt
self.isImage = 'imagegan' in opt.name
self.task = 'old_photo_restoration_training_mapping'
self.dir_AB = opt.dataroot
if opt.isTrain:
self.load_img_dir_clean= os.path.join(self.dir_AB, "VOC_RGB_JPEGImages.bigfile")
self.loaded_imgs_clean = BigFileMemoryLoader(self.load_img_dir_clean)
self.load_npy_dir_depth= os.path.join(self.dir_AB, "VOC_RGB_Depthnpy.bigfile")
self.loaded_npys_depth = BigFileMemoryLoaderv2(self.load_npy_dir_depth)
print("-------------Filter the imgs whose size <256 in VOC-------------")
self.filtered_imgs_clean = []
self.filtered_npys_depth = []
for i in range(len(self.loaded_imgs_clean)):
img_name, img = self.loaded_imgs_clean[i]
npy_name, npy = self.loaded_npys_depth[i]
h, w = img.size
if h < 256 or w < 256:
continue
self.filtered_imgs_clean.append((img_name, img))
self.filtered_npys_depth.append((npy_name, npy))
print("--------Origin image num is [%d], filtered result is [%d]--------" % (
len(self.loaded_imgs_clean), len(self.filtered_imgs_clean)))
else:
self.load_img_dir=os.path.join(self.dir_AB,opt.test_dataset)
self.loaded_imgs=BigFileMemoryLoader(self.load_img_dir)
self.load_depth_dir = os.path.join(self.dir_AB, opt.test_depthdataset)
self.loaded_npys = BigFileMemoryLoaderv2(self.load_depth_dir)
self.pid = os.getpid()
def __getitem__(self, index):
if self.opt.isTrain:
img_name_clean,B = self.filtered_imgs_clean[index]
npy_name_depth,D = self.filtered_npys_depth[index]
path = os.path.join(self.load_img_dir_clean, img_name_clean)
if self.opt.use_v2_degradation:
A=online_add_degradation_v2(B,D)
### Remind: A is the input and B is corresponding GT
else:
if self.opt.test_on_synthetic:
img_name_B,B=self.loaded_imgs[index]
npy_name_D,D=self.loaded_npys[index]
A=online_add_degradation_v2(B,D)
A.save('../mybig_data/' + index + '.jpg')
img_name_A=img_name_B
path = os.path.join(self.load_img_dir, img_name_A)
else:
img_name_A,A=self.loaded_imgs[index]
img_name_B,B=self.loaded_imgs[index]
path = os.path.join(self.load_img_dir, img_name_A)
# if random.uniform(0,1)<0.1 and self.opt.isTrain:
# A=A.convert("L")
# B=B.convert("L")
# A=A.convert("RGB")
# B=B.convert("RGB")
# ## In P, we convert the RGB into L
##test on L
# split AB image into A and B
# w, h = img.size
# w2 = int(w / 2)
# A = img.crop((0, 0, w2, h))
# B = img.crop((w2, 0, w, h))
w,h=A.size
if w<256 or h<256:
A=transforms.Scale(256,Image.BICUBIC)(A)
B=transforms.Scale(256, Image.BICUBIC)(B)
# apply the same transform to both A and B
transform_params = get_params(self.opt, A.size)
A_transform = get_transform(self.opt, transform_params)
B_transform = get_transform(self.opt, transform_params)
B_tensor = inst_tensor = feat_tensor = 0
A_tensor = A_transform(A)
B_tensor = B_transform(B)
input_dict = {'label': A_tensor, 'inst': inst_tensor, 'image': B_tensor,
'feat': feat_tensor, 'path': path}
return input_dict
def __len__(self):
if self.opt.isTrain:
return len(self.filtered_imgs_clean)
else:
return len(self.loaded_imgs)
def name(self):
return 'PairOldPhotos'
#del
class PairOldPhotos_with_hole(BaseDataset):
def initialize(self, opt):
self.opt = opt
self.isImage = 'imagegan' in opt.name
self.task = 'old_photo_restoration_training_mapping'
self.dir_AB = opt.dataroot
if opt.isTrain:
self.load_img_dir_clean= os.path.join(self.dir_AB, "VOC_RGB_JPEGImages.bigfile")
self.loaded_imgs_clean = BigFileMemoryLoader(self.load_img_dir_clean)
print("-------------Filter the imgs whose size <256 in VOC-------------")
self.filtered_imgs_clean = []
self.filtered_npys_depth = []
for i in range(len(self.loaded_imgs_clean)):
img_name, img = self.loaded_imgs_clean[i]
npy_name, npy = self.loaded_npys_depth[i]
h, w = img.size
if h < 256 or w < 256:
continue
self.filtered_imgs_clean.append((img_name, img))
self.filtered_npys_depth.append((npy_name, npy))
print("--------Origin image num is [%d], filtered result is [%d]--------" % (
len(self.loaded_imgs_clean), len(self.filtered_imgs_clean)))
else:
self.load_img_dir=os.path.join(self.dir_AB,opt.test_dataset)
self.loaded_imgs=BigFileMemoryLoader(self.load_img_dir)
self.load_depth_dir = os.path.join(self.dir_AB, opt.test_depthdataset)
self.loaded_npys = BigFileMemoryLoaderv2(self.load_depth_dir)
self.loaded_masks = BigFileMemoryLoader(opt.irregular_mask)
self.pid = os.getpid()
def __getitem__(self, index):
if self.opt.isTrain:
img_name_clean,B = self.filtered_imgs_clean[index]
npy_name_depth, D = self.filtered_npys_depth[index]
path = os.path.join(self.load_img_dir_clean, img_name_clean)
A=online_add_degradation_v2(B,D)
B=transforms.RandomCrop(256)(B)
### Remind: A is the input and B is corresponding GT
else:
img_name_A,A=self.loaded_imgs[index]
img_name_B,B=self.loaded_imgs[index]
path = os.path.join(self.load_img_dir, img_name_A)
#A=A.resize((256,256))
A=transforms.CenterCrop(256)(A)
B=A
if random.uniform(0,1)<0.1 and self.opt.isTrain:
A=A.convert("L")
B=B.convert("L")
A=A.convert("RGB")
B=B.convert("RGB")
## In P, we convert the RGB into L
if self.opt.isTrain:
mask_name,mask=self.loaded_masks[random.randint(0,len(self.loaded_masks)-1)]
else:
mask_name, mask = self.loaded_masks[index%100]
mask = mask.resize((self.opt.loadSize, self.opt.loadSize), Image.NEAREST)
if self.opt.random_hole and random.uniform(0,1)>0.5 and self.opt.isTrain:
mask=zero_mask(256)
if self.opt.no_hole:
mask=zero_mask(256)
A,_=irregular_hole_synthesize(A,mask)
if not self.opt.isTrain and self.opt.hole_image_no_mask:
mask=zero_mask(256)
transform_params = get_params(self.opt, A.size)
A_transform = get_transform(self.opt, transform_params)
B_transform = get_transform(self.opt, transform_params)
if transform_params['flip'] and self.opt.isTrain:
mask=mask.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
mask_tensor = transforms.ToTensor()(mask)
B_tensor = inst_tensor = feat_tensor = 0
A_tensor = A_transform(A)
B_tensor = B_transform(B)
input_dict = {'label': A_tensor, 'inst': mask_tensor[:1], 'image': B_tensor,
'feat': feat_tensor, 'path': path}
return input_dict
def __len__(self):
if self.opt.isTrain:
return len(self.filtered_imgs_clean)
else:
return len(self.loaded_imgs)
def name(self):
return 'PairOldPhotos_with_hole'实现效果图样例
图像去雾前后对比:
我是海浪学长,创作不易,欢迎点赞、关注、收藏、留言。
毕设帮助,疑难解答,欢迎打扰!