apache-common-pool2简单使用和源码分析
为什么要用连接池
相关jdbc客户端连接服务端过程
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test" ;
String username = "root" ;
String password = "root" ;
try{
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url , username , password ) ;
}catch(SQLException se){
System.out.println("数据库连接失败!");
se.printStackTrace() ;
}
一次客户端sql执行过程
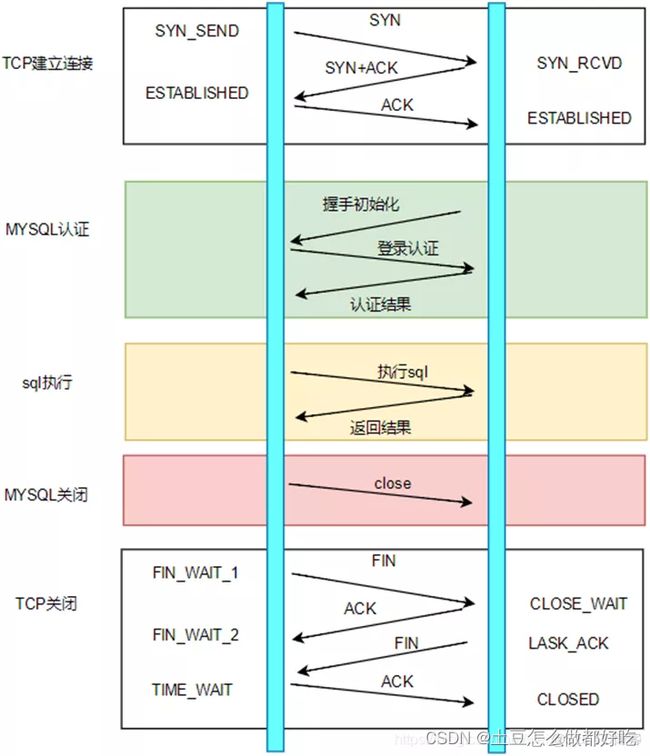
TCP建立连接的三次握手(客户端与MySQL服务器的连接基于TCP协议)
- MySQL认证的三次握手
- 真正的SQL执行
- MySQL的关闭
- TCP的四次握手关闭
假如一个对象创建耗时 500 毫秒,而我们调用它的方法仅耗时 10 毫秒,这种情况每次使用都 new 的话性价比很低,相当于每次都要耗费550 毫秒。
对象池就是为了解决此类问题而诞生的,对于这些昂贵的对象来说,提前创建若干个对象用对象池管理起来,用的时候从对象池借来一个,用完后归还 可以大大提升性能。
apache-common-pool2是什么
apache-common-pool2是一个对象池管理框架,任何需要对象池这种概念的都可以利用这个框架来实现,例如redis的客户端jedis和dbcp都是基于common-pool2实现的。
如何使用
引入依赖
org.apache.commons
commons-pool2
2.7.0
01自定义对象工厂实现BasePooledObjectFactory,重写 create() 和wrap()
public class SimplePooledObjectFactory extends BasePooledObjectFactory<ComplexObject> {
@Override
public SftpClient create() throws Exception {
return new SftpClient(sftpPoolProperties);
}
@Override
public ComplexObject create() {
// 随机指定一个名称,用于区分ComplexObject
String name = "test" + ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100);
return new ComplexObject(name);
}
@Override
public PooledObject<ComplexObject> wrap(ComplexObject obj) {
// 使用默认池化对象包装ComplexObject
return new DefaultPooledObject(obj);
}
}
02 创建对象池
public class SimplePool {
private final GenericObjectPool<ComplexObject> internalPool;
public SftpPool(Proproties p) {
this.internalPool = new GenericObjectPool<>(new SimplePooledObjectFactory (),SimplePooledObjectFactory.getConfig(p));
}
public ComplexObject borrowObject() {
try {
return this.internalPool.borrowObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new PoolException("获取连接对象失败!",e);
}
}
@PreDestroy
public void close() {
try {
this.internalPool.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new PoolException("销毁对象池失败!",e);
}
}
public void invalidateObject(ComplexObject obj) {
try {
this.internalPool.invalidateObject(obj);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new PoolException("销毁连接对象失败!",e);
}
}
public void returnObject(ComplexObject obj) {
try {
this.internalPool.returnObject(obj);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new PoolException("回收连接对象失败!",e);
}
}
03 对象池配置
private GenericObjectPoolConfig<SftpClient> getPoolConfig(Properties p) {
GenericObjectPoolConfig<SftpClient> config = new GenericObjectPoolConfig<>();
config.setMinIdle(p.getMinIdle());
config.setMaxIdle(p.getMaxIdle());
config.setMaxTotal(p.getMaxActive());
config.setMaxWaitMillis(p.getMaxWait());
config.setTestOnBorrow(p.isTestOnBorrow());
config.setTestOnReturn(p.isTestOnReturn());
config.setTestWhileIdle(p.isTestWhileIdle());
config.setTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis(p.getTimeBetweenEvictionRuns());
return config;
}
04 api调用
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 创建配置对象
SimplePool pool = new SimplePool(new Properties);
//借用对象
pool.borrowObject();
//归还对象
pool.returnObject();
}
至此commmon-pool2的对象池使用演示结束,common-pool2还吃支持key-value的对象池KeyedObjectPool,以支持多客户端,具体的使用方式可以自行探索
源码解析(基于obejectPool)
对象池里3个重点组件
01
对象池(ObjectPool):
用于管理池中的所有对象,对于每个对象的操作会代理给 ObjectFactory。ObjectPool 有多个实现,GenericObjectPool 提供了多种配置选项,包括限制空闲或活动实例的数量、在实例处于池中空闲时将其逐出等。从版本 2 开始,GenericObjectPool 还提供了废弃实例跟踪和删除功能。SoftReferenceObjectPool 可以根据需要增长,但允许垃圾收集器根据需要从池中逐出空闲实例。


对象池相关api
- borrowObject:从对象池中获取对象
- returnObject:把对象归还给对象池
- invalidateObject:清理作废一个对象(释放池中一个资源)
- addObject:往对象池中添加一个对象
- getNumIdle:获取空闲对象的数量
- getNumActive:获取活跃对象的数量
- clear:目的是为了清理所有空闲对象
- close:关闭连接池,释放所有池中的资源。
02
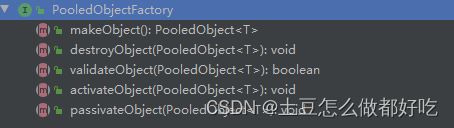
对象工厂(PooledObjectFactory):
负责对象的创建,验证,销毁,ObjectPool 对于每个对象的核心操作会代理给 PooledObjectFactory。
- makeObject 制造对象
- destroyObject 销毁对象
- validateObject 验证对象
- activateObject 激活对象
- passivateObject 钝化对象
03
池化的对象(PooledObject):
用于包装实际的对象,提供一些附件的功能。如 Commons-Pool 自带的 DefaultPooledObject 会记录对象的创建时间,借用时间,归还时间,对象状态等,PooledSoftReference 使用 Java 的软引用来持有对象,便于 JVM 内存不够时回收对象。当然我们也可以实现 PooledObject 接口来定义我们自己的对象包装器。
PooledObject有多种状态,在不同的环节或经过处理后状态会发生变化:
| 状态 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| IDLE | 空闲 |
| ALLOCATED | 在使用 |
| EVICTION | 位于队列中,当前正在测试,可能会被回收 |
| EVICTION_RETURN_TO_HEAD | 不在队列中,当前正在测试,可能会被回收。从池中借出对象时需要从队列出移除并进行测试 |
| VALIDATION | 位于队列中,当前正在验证 |
| VALIDATION_PREALLOCATION | 不在队列中,当前正在验证。当对象从池中被借出,在配置了testOnBorrow的情况下,对像从队列移除和进行预分配的时候会进行验证 |
| VALIDATION_RETURN_TO_HEAD | 不在队列中,正在进行验证。从池中借出对象时,从队列移除对象时会先进行测试。返回到队列头部的时候应该做一次完整的验证 |
| INVALID | 回收或验证失败,将销毁 |
| ABANDONED | 即将无效 |
| RETURN | 返还到池中 |
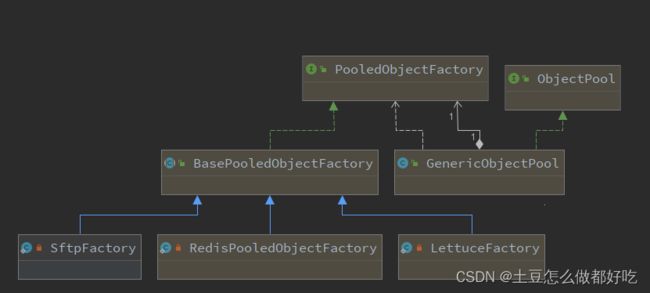
对象池关系图解析
我们对象池关系图可以看到,objectPool是一个抽象接口,具体的实现方式
- ErodingObjectPool 对象池工具类, 返回一个当不再需要空闲对象时,自适应减小其大小的对象池
- GenericObjectPool 通用对象池 目前常用的实现接口,本文重点介绍
- ProxiedObjectPool 代理对象池
- SynchronizedObjectPool 对象池工具类,提高操作时+锁
- SoftReferenceObjectPool 软引用对象池,包裹软引用对象
重点:GenericObjectPool 通用对象池
构造一
public GenericObjectPool(PooledObjectFactory<T> factory, GenericObjectPoolConfig<T> config) {
super(config, "org.apache.commons.pool2:type=GenericObjectPool,name=", config.getJmxNamePrefix());
this.factoryType = null;
this.maxIdle = 8;
this.minIdle = 0;
this.allObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap();
this.createCount = new AtomicLong(0L);
this.makeObjectCount = 0L;
this.makeObjectCountLock = new Object();
this.abandonedConfig = null;
if (factory == null) {
this.jmxUnregister();
throw new IllegalArgumentException("factory may not be null");
} else {
this.factory = factory;
//对象列表的存储容器使用的是双向并发阻塞队列,该阻塞队列同时支持FIFO和FILO两种操作方式,即可以从队列的头和尾同时操作(插入/删除);并且,该阻塞队列是支持线程安全。还有,LinkedBlockingDeque还是可选容量的(防止过度膨胀),即可以指定队列的容量。如果不指定,默认容量大小等于Integer.MAX_VALUE
// config.getFairness()是否公平,内部使用retrantLock实现阻塞
this.idleObjects = new LinkedBlockingDeque(config.getFairness());
this.setConfig(config);
}
}
构造二
public GenericObjectPool(PooledObjectFactory<T> factory, GenericObjectPoolConfig<T> config, AbandonedConfig abandonedConfig) {
this(factory, config);
this.setAbandonedConfig(abandonedConfig);
}
借对象
public T borrowObject(long borrowMaxWaitMillis) throws Exception {
.......省略
while(p == null) {
boolean create = false;
//从空闲队列获取
p = (PooledObject)this.idleObjects.pollFirst();
if (p == null) {
//没有获取到就创建
p = this.create();
if (p != null) {
//创建成功
create = true;
}
}
//当对象池没有空闲对象时,新的获取对象的请求是否阻塞(true 阻塞,配置了maxWaitMillis 才生效;
// false 连接池没有资源立马抛异常)
//默认值 DEFAULT_BLOCK_WHEN_EXHAUSTED = true
if (blockWhenExhausted) {
if (p == null) {
//borrowMaxWaitMillis 默认=-1
if (borrowMaxWaitMillis < 0L) {
//一直等待直到有空闲对象
p = (PooledObject)this.idleObjects.takeFirst();
} else {
//在指定的等待时间等待可用元素,超时返回Null
p = (PooledObject)this.idleObjects.pollFirst(borrowMaxWaitMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
//返回null
if (p == null) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("Timeout waiting for idle object");
}
//没有对象可用,也没有设置没有对象可用时等待,抛出异常
} else if (p == null) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("Pool exhausted");
}
//获取到的对象属于不可用状态
if (!p.allocate()) {
p = null;
}
//获取到对象
if (p != null) {
try {
//激活对象
this.factory.activateObject(p);
} catch (Exception var15) {
try {
//异常销毁
this.destroy(p);
} catch (Exception var14) {
}
//置为null
p = null;
if (create) {
//如果此元素时本次创建获取的,抛出激活不了对象异常
NoSuchElementException nsee = new NoSuchElementException("Unable to activate object");
nsee.initCause(var15);
throw nsee;
}
}
//判断连接对象是否可用
if (p != null && this.getTestOnBorrow()) {
boolean validate = false;
Throwable validationThrowable = null;
try {
//验证连接是否可用
validate = this.factory.validateObject(p);
} catch (Throwable var13) {
PoolUtils.checkRethrow(var13);
validationThrowable = var13;
}
//如果连接不可用
if (!validate) {
try {
//销毁
this.destroy(p);
//销毁连接次数+1
this.destroyedByBorrowValidationCount.incrementAndGet();
} catch (Exception var12) {
}
p = null;
if (create) {
NoSuchElementException nsee = new NoSuchElementException("Unable to validate object");
nsee.initCause(validationThrowable);
throw nsee;
}
}
}
}
}
更新获取对象的耗时
this.updateStatsBorrow(p, System.currentTimeMillis() - waitTime);
return p.getObject();
}
创建对象
private PooledObject<T> create() throws Exception {
int localMaxTotal = this.getMaxTotal();
//获取最大创建对象数,如果没有设置,默认Integer.maxvalue()
if (localMaxTotal < 0) {
localMaxTotal = 2147483647;
}
long localStartTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
//最大等待时间
long localMaxWaitTimeMillis = Math.max(this.getMaxWaitMillis(), 0L);
Boolean create = null;
while(create == null) {
//创建对象lock
synchronized(this.makeObjectCountLock) {
//创建次数+1
long newCreateCount = this.createCount.incrementAndGet();
//如果创建次数>最大允许创建次数
if (newCreateCount > (long)localMaxTotal) {
//不再创建,创建次数-1
this.createCount.decrementAndGet();
//创建对象次数=0
if (this.makeObjectCount == 0L) {
//不再创建
create = Boolean.FALSE;
} else {
//可能在创建过程中,等待
this.makeObjectCountLock.wait(localMaxWaitTimeMillis);
}
} else {
//创建次数+1
++this.makeObjectCount;
//允许创建
create = Boolean.TRUE;
}
}
//如果在等待创建,设置了最大等待时间,并且当前耗时>=等待时间,返回null,不再创建
if (create == null && localMaxWaitTimeMillis > 0L && System.currentTimeMillis() - localStartTimeMillis >= localMaxWaitTimeMillis) {
create = Boolean.FALSE;
}
}
if (!create) {
return null;
} else {
boolean var22 = false;
AbandonedConfig ac;
label190: {
PooledObject p;
try {
var22 = true;
//创建对象
p = this.factory.makeObject();
//创建完成校验,如果失败
if (this.getTestOnCreate()) {
if (!this.factory.validateObject(p)) {
this.createCount.decrementAndGet();
ac = null;
var22 = false;
break label190;
}
var22 = false;
} else {
var22 = false;
}
} catch (Throwable var27) {
this.createCount.decrementAndGet();
throw var27;
} finally {
//没有创建成功对象解锁
if (var22) {
synchronized(this.makeObjectCountLock) {
--this.makeObjectCount;
this.makeObjectCountLock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
//解锁
synchronized(this.makeObjectCountLock) {
--this.makeObjectCount;
this.makeObjectCountLock.notifyAll();
}
//给对象+回收配置
ac = this.abandonedConfig;
if (ac != null && ac.getLogAbandoned()) {
p.setLogAbandoned(true);
p.setRequireFullStackTrace(ac.getRequireFullStackTrace());
}
//创建次数+1
this.createdCount.incrementAndGet();
//添加到对象池
this.allObjects.put(new IdentityWrapper(p.getObject()), p);
return p;
}
//对象校验失败,释放锁
synchronized(this.makeObjectCountLock) {
--this.makeObjectCount;
this.makeObjectCountLock.notifyAll();
return ac;
}
}
}
还对象
public void returnObject(T obj) {
PooledObject<T> p = (PooledObject)this.allObjects.get(new IdentityWrapper(obj));
//没有获取到对象
if (p == null) {
//如果对象没有回收配置
if (!this.isAbandonedConfig()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Returned object not currently part of this pool");
}
} else {
//标记归还状态
this.markReturningState(p);
long activeTime = p.getActiveTimeMillis();
//配置了,返回时校验,同时校验不通过
if (this.getTestOnReturn() && !this.factory.validateObject(p)) {
try {
//销毁对象
this.destroy(p);
} catch (Exception var10) {
this.swallowException(var10);
}
try {
//如果没有空闲对象,确保有一个空闲对象
this.ensureIdle(1, false);
} catch (Exception var9) {
this.swallowException(var9);
}
//更新活动时间
this.updateStatsReturn(activeTime);
} else {
try {
//钝化对象,自我实现
this.factory.passivateObject(p);
} catch (Exception var12) {
this.swallowException(var12);
try {
//钝化出错,销毁对象
this.destroy(p);
} catch (Exception var8) {
this.swallowException(var8);
}
try {
//如果没有空闲对象,确保有一个空闲对象
this.ensureIdle(1, false);
} catch (Exception var7) {
this.swallowException(var7);
}
//更新累计活动时间
this.updateStatsReturn(activeTime);
return;
}
//将对象变为空闲状态
if (!p.deallocate()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Object has already been returned to this pool or is invalid");
} else {
//获取最大空闲数
int maxIdleSave = this.getMaxIdle();
//如果对象池已经关闭,或者最大空闲数>-1 同时最大空闲数<=空闲数
if (this.isClosed() || maxIdleSave > -1 && maxIdleSave <= this.idleObjects.size()) {
try {
//销毁对象
this.destroy(p);
} catch (Exception var11) {
this.swallowException(var11);
}
} else {
//否则就将此对象添加到空闲队列
if (this.getLifo()) {
this.idleObjects.addFirst(p);
} else {
this.idleObjects.addLast(p);
}
//如果池子关闭了,清空
if (this.isClosed()) {
this.clear();
}
}
//更新累计活动时间
this.updateStatsReturn(activeTime);
}
}
}
}
总结
至此apache-common-pool2的相关的使用和分析结束,对连接池有了更多的理解,个人使用案例参考之前做过另一篇笔记common-pool2实现sftp连接池
官方文档:https://javadoc.io/doc/org.apache.commons/commons-pool2/latest/index.html