SpringSecurity实战解析
文章目录
- 一、Security认证和原理
-
- 1、认证基本流程
-
- 1.1 表单认证概述
- 1.2 基本流程分析
- 1.3 权限访问流程
- 2、请求间共享认证信息
-
- 2.1 概述
- 2.2 获取认证用户信息
- 3、认证的几种方式
- 4、注解权限
-
- 4.1 概述
- 4.2 @Secured注解使用方式
- 4.3 jsr250Enabled
- 4.4 prePostEnabled 规范(重要)
- 5、自定义认证成功/失败处理器
-
- 5.1 登录处理的方法介绍
- 5.2 成功/失败处理器
- 6、自定义权限处理器
- 二、Security验证码使用
-
- 1、原理概述
- 2、实战
-
- 2.1 验证码图片的生成
- 2.2 自定义验证码过滤器
- 3、session异常问题
- 三、Remember-Me 和注销
-
- 1、Remember-Me 功能概述
-
- 1.1 概述
- 1.2 基本原理
- 2、Remember-Me实战
-
- 2.1 简单加密 Token(基本使用)
- 2.2 持久化 Token(基本使用)
- 3、注销登录
-
- 3.1 概述
- 3.2 自定义登出处理器
- 3.3 安全配置类
- 四、Session 会话管理
-
- 1、Session管理配置
- 2、Session 会话失效处理
-
- 2.1 Session 失效时间
- 2.2 invalidSessionUrl 方法
- 2.3 invalidSessionStrategy 方法
- 3、Session 会话并发控制
-
- 3.1 两种情况分析
- 3.2 自定义统计session使用
- 4、 Redis 共享 Session
-
- 4.1 操作概述
- 4.2 Redis数据解释
- 5、remember-me 失效解释(补充)
- 五、补充与说明
Security入门笔记:Spring Security学习笔记
一、Security认证和原理
Spring Security是一种基于Spring AOP和Servlet Filter的安全框架,其核心是一组过滤器链,实现 Web 请求和方法调用级别的用户鉴权和权限控制
1、认证基本流程
1.1 表单认证概述
Spring Security提供了两种认证方式:HttpBasic 认证和 HttpForm 表单认证。HttpBasic 认证不需要我们编写登录页面,当浏览器请求 URL 需要认证才能访问时,页面会自动弹出一个登录窗口,要求用户输入用户名和密码进行认证。大多数情况下,我们还是通过编写登录页面进行 HttpForm 表单认证(现在默认是这个模式)
1.2 基本流程分析
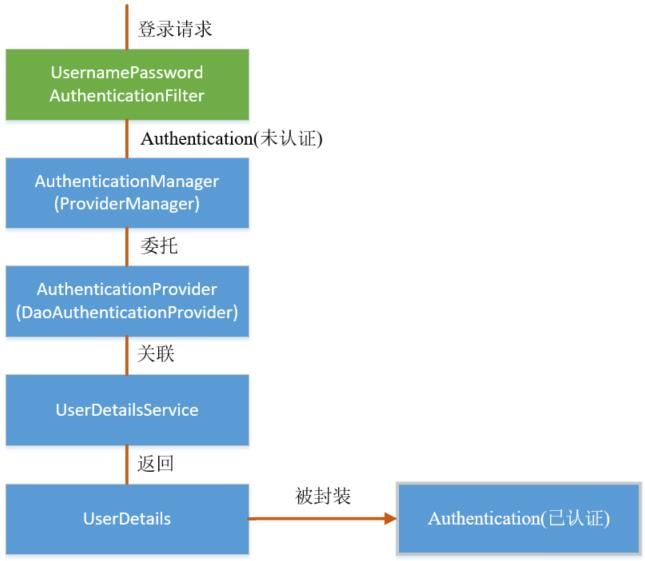
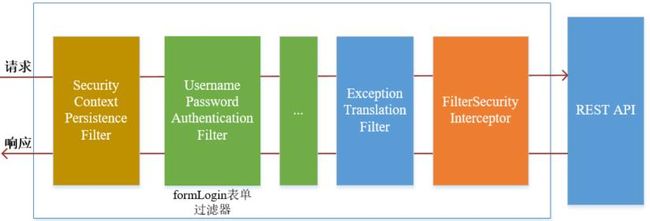
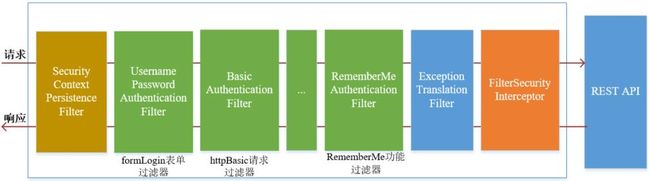
Spring Security采取过滤链实现认证与授权,只有当前过滤器通过,才能进入下一个过滤器
绿色部分是认证过滤器,需要我们自己配置,可以配置多个认证过滤器。认证过滤器可以使用Spring Security提供的认证过滤器,也可以自定义过滤器(例如:验证码验证)。认证过滤器要在configure(HttpSecurity http)方法中配置,没有配置不生效。下面会重点介绍以下三个过滤器:
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器:该过滤器会拦截前端提交的 POST 方式的登录表单请求,并进行身份认证ExceptionTranslationFilter过滤器:该过滤器不需要我们配置,对于前端提交的请求会直接放行,捕获后续抛出的异常并进行处理(例如:权限访问限制)FilterSecurityInterceptor过滤器:该过滤器是过滤器链的最后一个过滤器,根据资源权限配置来判断当前请求是否有权限访问对应的资源。如果访问受限会抛出相关异常,并由ExceptionTranslationFilter过滤器进行捕获和处理
而认证流程是在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器中处理的,具体流程如下所示:
具体的源码相关可以查阅:https://www.cnblogs.com/zongmin/p/13783174.html
1.3 权限访问流程
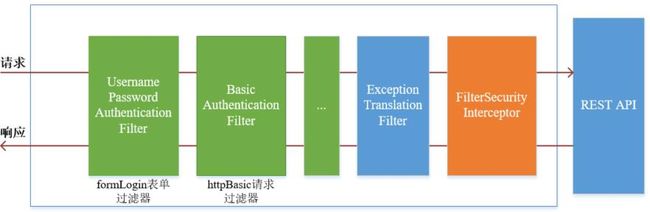
上面介绍了认证流程,下面介绍权限访问流程,主要是对ExceptionTranslationFilter过滤器和FilterSecurityInterceptor过滤器进行介绍
ExceptionTranslationFilter过滤器,该过滤器是用于处理异常的,不需要我们配置,对于前端提交的请求会直接放行,捕获后续抛出的异常并进行处理(例如:权限访问限制)FilterSecurityInterceptor是过滤器链的最后一个过滤器,该过滤器是过滤器链的最后一个过滤器,根据资源权限配置来判断当前请求是否有权限访问对应的资源。如果访问受限会抛出相关异常,最终所抛出的异常会由前一个过滤器ExceptionTranslationFilter进行捕获和处理
需要注意,Spring Security的过滤器链是配置在 SpringMVC 的核心组件 DispatcherServlet 运行之前。也就是说,请求通过Spring Security的所有过滤器,不意味着能够正常访问资源,该请求还需要通过 SpringMVC 的拦截器链
2、请求间共享认证信息
2.1 概述
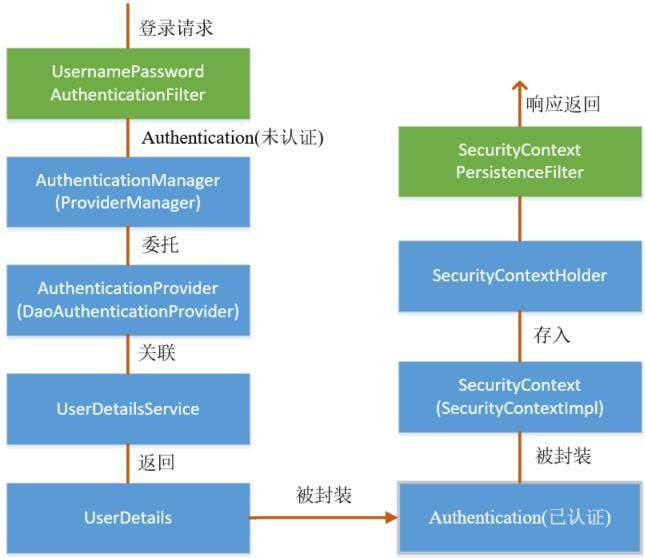
一般认证成功后的用户信息是通过 Session 在多个请求之间共享,Spring Security实现将已认证的用户信息对象 Authentication 与 Session 绑定
2.2 获取认证用户信息
由前文可知,封装了已认证用户信息对象 Authentication 的 SecurityContext 即存储在 SecurityContextHolder 中,也存储在 Session 中,所以这里有几种获取用户数据的方式
// 从 SecurityContextHolder 获取认证用户信息对象 Authentication
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
// 敏感信息 credentials 被去除,principal 存储的为 UserDetails 实现类,可以通过强转获取 UserDetails 对象
// 从 Authentication 中获取 UserDetails
UserDetails user = (UserDetails) authentication.getPrincipal();
// 使用 HttpSession 获取
@GetMapping("/test3")
@ResponseBody
public Object test3(HttpSession session) {
// 获取 Session 获取 SecurityContext
SecurityContext context = (SecurityContext) session.getAttribute("SPRING_SECURITY_CONTEXT");
// 从 Authentication 中获取 UserDetails
UserDetails user = (UserDetails) context.getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
return user;
}
// 最后也是通过request获取用户的session
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) (RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes())).getRequest();
Principal userPrincipal = request.getUserPrincipal();
String userName = userPrincipal.getName();
3、认证的几种方式
创建数据库表和数据
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`username` varchar(50) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户名',
`password` varchar(64) COMMENT '密码',
`mobile` varchar(20) COMMENT '手机号',
`enabled` tinyint NOT NULL DEFAULT '1' COMMENT '用户是否可用',
`roles` text COMMENT '用户角色,多个角色之间用逗号隔开',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `index_username`(`username`),
KEY `index_mobile`(`mobile`)
) COMMENT '用户表';
-- 密码明文都为 123456
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES ('1', 'admin', '$2a$10$JNVWTh5Yq56kJtrCZkcDk.DL/L/i8g3KrTAshcHW3mFf8//lnfG56', '11111111111', '1', 'ROLE_ADMIN,ROLE_USER');
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES ('2', 'user', '$2a$10$JNVWTh5Yq56kJtrCZkcDk.DL/L/i8g3KrTAshcHW3mFf8//lnfG56', '22222222222', '1', 'ROLE_USER');
创建 User 实体类,实现 UserDetails 接口
@Data
public class User implements UserDetails {
private Long id; // 主键
private String username; // 用户名
private String password; // 密码
private String mobile; // 手机号
private String roles; // 用户角色,多个角色之间用逗号隔开
private boolean enabled; // 用户是否可用
private List<GrantedAuthority> authorities; // 用户权限集合
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() { // 返回用户权限集合
return authorities;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() { // 账户是否未过期
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() { // 账户是否未锁定
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() { // 密码是否未过期
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() { // 账户是否可用
return enabled;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) { // equals() 方法一般要重写
return obj instanceof User && this.username.equals(((User) obj).username);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() { // hashCode() 方法一般要重写
return this.username.hashCode();
}
}
创建 CustomUserDetailsService 类,实现 UserDetailsService 接口
@Service
public class CustomUserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//(1) 从数据库尝试读取该用户
User user = userMapper.selectByUsername(username);
// 用户不存在,抛出异常
if (user == null) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户不存在");
}
//(2) 将数据库形式的 roles 解析为 UserDetails 的权限集合
// AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList() 是 Spring Security 提供的方法,用于将逗号隔开的权限集字符串切割为可用权限对象列表
user.setAuthorities(AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList(user.getRoles()));
//(3) 返回 UserDetails 对象
return user;
}
}
最后是自定义认证类(第三种方法选用)
/**
* 自定义认证器
* 验证逻辑,比较传入的 pwd 和 从数据库中拿到的 pwd。
*/
@Component
public class CustomAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
@Autowired
CustomUserDetailsServiceImpl userDetailsService;
/**
* 这里有个循环依赖问题,在配置文件改成spring.main.allow-circular-references: true 即可
* 或者将PasswordEncoder这个bean类单独生成一个文件
*/
@Autowired
BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder;
/**
* @param authentication 验证器
* @return 验证器
* @throws AuthenticationException .
*/
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
// 获取用户名
String account = authentication.getName();
// 获取密码
String password = (String) authentication.getCredentials();
// 记录login请求日志
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) Objects.requireNonNull(RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes())).getRequest();
UserDetails userDetails = userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(account);
boolean checkPassword = bCryptPasswordEncoder.matches(password, userDetails.getPassword());
if (!checkPassword) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("密码不正确,请重新登录!");
}
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(userDetails, password, userDetails.getAuthorities());
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> aClass) {
return true;
}
}
下面是配置文件,我们通过配置文件来选择不同的认证模式
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启 MVC Security 安全配置
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//...
/**
* 自定义数据库验证认证
*/
@Autowired
CustomUserDetailsServiceImpl userDetailsService;
/**
* 自定义登录校验
*/
@Autowired
private CustomAuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider;
//...
/**
* 定制用户认证管理器来实现用户认证
* 内存覆盖
* 最简单是配置文件直接覆盖写
*/
// @Override
// protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
// // 采用内存存储方式,用户认证信息存储在内存中
// auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
// .withUser("admin").password(passwordEncoder()
// .encode("123456")).roles("ADMIN");
// }
/**
* 定制用户认证管理器来实现用户认证
*/
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
// 1、采用内存存储方式,用户认证信息存储在内存中
// auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
// .withUser("admin").password(passwordEncoder()
// .encode("123456")).roles("ROLE_ADMIN");
// 2、不再使用内存方式存储用户认证信息,而是动态从数据库中获取
//auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
// 3、自定义登录验证
auth.authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider);
}
/**
* 定制基于 HTTP 请求的用户访问控制
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//...
// 开启基于 HTTP 请求访问控制
http.authorizeRequests()
// 以下访问不需要任何权限,任何人都可以访问
.antMatchers("/login/page").permitAll()
// 以下访问需要 ROLE_ADMIN 权限
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
// 以下访问需要 ROLE_USER 权限
.antMatchers("/user/**").hasAuthority("ROLE_USER")
// 其它任何请求访问都需要先通过认证
.anyRequest().authenticated();
//...
}
//...
}
此处需要简单介绍下Spring Security的授权方式,在Spring Security中角色属于权限的一部分。对于角色ROLE_ADMIN的授权方式有两种:hasRole("ADMIN")和hasAuthority("ROLE_ADMIN"),这两种方式是等价的。可能有人会疑惑,为什么在数据库中的角色名添加了ROLE_前缀,而 hasRole() 配置时不需要加ROLE_前缀。
hasRole() 在判断权限时会自动在角色名前添加ROLE_前缀,所以配置时不需要添加ROLE_前缀,同时这也要求 UserDetails 对象的权限集合中存储的角色名要有ROLE_前缀。如果不希望匹配这个前缀,那么改为调用 hasAuthority() 方法即可
4、注解权限
4.1 概述
要开启Spring方法级安全,在添加了@Configuration注解的类上再添加@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity注解即可
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled=true)
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
}
其中注解@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity有几个方法:
prePostEnabled****: 确定 前置注解[@PreAuthorize,@PostAuthorize,..]是否启用(常用/重要)securedEnabled****: 确定安全注解[@Secured]是否启用jsr250Enabled****: 确定JSR-250注解 [@RolesAllowed..]是否启用
同一个应用程序中,可以启用多个类型的注解,但是只应该设置一个注解对于行为类的接口或者类
public interface UserService {
List<User> findAllUsers();
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('user')")
void updateUser(User user);
// 下面不能设置两个注解,如果设置两个,只有其中一个生效
// @PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('user')")
@Secured({ "ROLE_user", "ROLE_admin" })
void deleteUser();
}
4.2 @Secured注解使用方式
@Secured注解是用来定义业务方法的安全配置。在需要安全[角色/权限等]的方法上指定 @Secured,并且只有那些角色/权限的用户才可以调用该方法。@Secured缺点(限制)就是不支持Spring EL表达式。不够灵活。并且指定的角色必须以ROLE_开头,不可省略。
在上面的例子中,updateUser 方法只能被拥有user权限的用户调用。deleteUser 方法只能够被拥有admin 或者user 权限的用户调用。而如果想要指定"AND"条件,即调用deleteUser方法需同时拥有ADMIN和DBA角色的用户,@Secured便不能实现。这时就需要使用prePostEnabled提供的注解@PreAuthorize/@PostAuthorize
4.3 jsr250Enabled
@DenyAll****: 拒绝所有访问@RolesAllowed({"USER", "ADMIN"})****: 该方法只要具有"USER","ADMIN"任意一种权限就可以访问。这里可以省略前缀ROLE_,实际的权限可能是ROLE_ADMIN@PermitAll****: 允许所有访问
@GetMapping("test/allow")
@RolesAllowed({"USER","ADMIN"})
public String testAllow() {
return "需要权限";
}
@GetMapping("test/perm")
@PermitAll
public String testPerm() {
return "允许";
}
@GetMapping("test/deny")
@DenyAll
public String testDeny() {
return "拒绝";
}
4.4 prePostEnabled 规范(重要)
该注解更适合方法级的安全,也支持Spring 表达式语言,提供了基于表达式的访问控制。参见常见内置表达式了解支持表达式的完整列表,上面只使用到了一个注解@PreAuthorize,启用prePostEnabled后,提供有四个注解:
@PreAuthorize****: 进入方法之前验证授权。可以将登录用户的roles参数传到方法中验证。
// 只能user角色可以访问
@PreAuthorize ("hasAnyRole('user')")
// user 角色或者 admin 角色都可访问
@PreAuthorize ("hasAnyRole('user') or hasAnyRole('admin')")
// 同时拥有 user 和 admin 角色才能访问
@PreAuthorize ("hasAnyRole('user') and hasAnyRole('admin')")
// 限制只能查询 id 小于 10 的用户
@PreAuthorize("#id < 10")
User findById(int id);
// 只能查询自己的信息
@PreAuthorize("principal.username.equals(#username)")
User find(String username);
// 限制只能新增用户名称为abc的用户
@PreAuthorize("#user.name.equals('abc')")
void add(User user)
@PostAuthorize****: 该注解使用不多,在方法执行后再进行权限验证。 适合验证带有返回值的权限。Spring EL提供 返回对象能够在表达式语言中获取返回的对象returnObject。校验通过就返回,否则表示校验失败,将抛出AccessDeniedException
// 查询到用户信息后,再验证用户名是否和登录用户名一致
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.name == authentication.name")
@GetMapping("/get-user")
public User getUser(String name){
return userService.getUser(name);
}
// 验证返回的数是否是偶数
@PostAuthorize("returnObject % 2 == 0")
public Integer test(){
// ...
return id;
}
@PreFilter****: 对集合类型的参数执行过滤,移除结果为false的元素
// 指定过滤的参数,过滤偶数
@PreFilter(filterTarget="ids", value="filterObject%2==0")
public void delete(List<Integer> ids, List<String> username)
@PostFilter****: 对集合类型的返回值进行过滤,移除结果为false的元素
@PostFilter("filterObject.id%2==0")
public List<User> findAll(){
...
return userList;
}
5、自定义认证成功/失败处理器
5.1 登录处理的方法介绍
此处先对http.formLogin()返回值的主要方法进行说明,这些方法涉及用户登录的处理,具体如下:
loginPage(String loginPage):设置用户登录页面的访问路径,默认为 GET 请求的/login。loginProcessingUrl(String loginProcessingUrl):设置登录表单提交的路径,默认为是 POST 请求的 loginPage() 设置的路径successForwardUrl(String forwordUrl):设置用户认证成功后转发的地址。successHandler(AuthenticationSuccessHandler successHandler):配置用户认证成功后的自定义处理器。defaultSuccessUrl(String defaultSuccessUrl):设置用户认证成功后重定向的地址。这里需要注意,该路径是用户直接访问登录页面认证成功后重定向的路径,如果是其他路径跳转到登录页面认证成功后会重定向到原始访问路径。可设置第二个参数为 true,使认证成功后始终重定向到该地址。failureForwrad(String forwardUrl):设置用户认证失败后转发的地址。failureHandler(AuthenticationFailureHandler authenticationFailureHandler):设置用户登录失败后的自定义错误处理器。failureUrl(String authenticationFailureUrl):设置用户登录失败后重定向的地址,指定的路径要能匿名访问,默认为loginPage() + ?error。usernameParamter(String usernameParamter):设置登录表单中的用户名参数,默认为 username。passwordParamter(String passwordParamter):设置登录表单中的密码参数,默认为 password。
5.2 成功/失败处理器
因为需要用到Jackson,首先对其进行配置
/**
* 统一注解,解决前后端交互 Long 类型精度丢失的问题
*/
@Configuration
public class JacksonConfig {
@Bean
@Primary
public ObjectMapper jacksonObjectMapper(Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder) {
ObjectMapper objectMapper = builder.createXmlMapper(false).build();
// 设置日期转换
objectMapper.setDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
// 设置时区
// objectMapper.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("GMT+8"));
// 序列化时,值为 null 的属性不序列化
// Include.Include.ALWAYS 默认
// Include.NON_DEFAULT 属性为默认值不序列化
// Include.NON_EMPTY 属性为空("" 或 null)都不序列化
// Include.NON_NULL 属性为 null 不序列化
objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL);
// 反序列化时,遇到未知属性的时候不抛出异常
objectMapper.disable(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES);
// 序列化成 json 时,将 Long 转换成 String(防止 js 丢失精度)
// Java 的 Long 能表示的范围比 js 中 number 大,意味着部分数值在 js 会变成不准确的值
SimpleModule simpleModule = new SimpleModule();
simpleModule.addSerializer(Long.class, ToStringSerializer.instance);
simpleModule.addSerializer(Long.TYPE, ToStringSerializer.instance);
objectMapper.registerModule(simpleModule);
return objectMapper;
}
}
自定义失败处理器,这里有个判断原因是可以根据header的信息自定义选择如何跳转。真实环境可以根据自己实际情况进行选择
/**
* 登录失败返回给前端消息
* 继承 SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler 处理器,该类是 failureUrl() 方法使用的认证失败处理器
* 也可以直接实现AuthenticationFailureHandler
*/
@Component
public class CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler extends SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
/**
* 需要在请求的时候加头部信息,否则会认为是表单请求,而不是js请求
*/
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException e) throws IOException, ServletException {
String xRequestedWith = request.getHeader("x-requested-with");
// 判断前端的请求是否为 ajax 请求
if ("JSON".equals(xRequestedWith)) {
Msg msg = null;
if (e instanceof UsernameNotFoundException) {
msg = Msg.fail(CustomExceptionCode.LOGIN_USER_NOT_EXISTED);
} else if (e instanceof BadCredentialsException) {
msg = Msg.fail(CustomExceptionCode.LOGIN_FAILED);
} else if (e instanceof ValidateCodeException) {
// 验证码类型错误
msg = Msg.problem(CustomExceptionCode.LOGIN_VERIFICATION_FAILED.getCode(), e.getMessage());
} else {
msg = Msg.fail(CustomExceptionCode.FAILED);
}
// 认证失败,响应 JSON 数据
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(msg));
}else {
// 以下配置等同于前文的 failureUrl("/login/page?error")
// 认证失败后,重定向到指定地址
// 设置默认的重定向路径
super.setDefaultFailureUrl("/login/page?error");
// 调用父类的 onAuthenticationFailure() 方法
super.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, e);
}
}
}
自定义成功处理器
/**
* 继承 SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler 类,该类是 defaultSuccessUrl() 方法使用的认证成功处理器
* 也可以直接实现AuthenticationSuccessHandler接口类
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler extends SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws ServletException, IOException {
String xRequestedWith = request.getHeader("x-requested-with");
// 判断前端的请求是否为 ajax 请求
if ("JSON".equals(xRequestedWith)) {
// 这里可以进行用户信息的操作
// 认证成功,响应 JSON 数据
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(Msg.success(200,"用户认证成功").add("data",map)));
}else {
// 以下配置等同于前文中的 defaultSuccessUrl("/index")
// 认证成功后,如果存在原始访问路径,则重定向到该路径;如果没有,则重定向 /index
// 设置默认的重定的路径
super.setDefaultTargetUrl("/index");
// 调用父类的 onAuthenticationSuccess() 方法
super.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authentication);
}
}
}
最后配置config
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启 MVC Security 安全配置
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//...
@Autowired
private CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler authenticationSuccessHandler;
@Autowired
private CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler authenticationFailureHandler;
//...
/**
* 定制基于 HTTP 请求的用户访问控制
*
* @param http
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// 启动 form 表单登录
http.formLogin()
// 设置登录页面的访问路径,默认为 /login,GET 请求;该路径不设限访问
.loginPage("/login/page")
// 设置登录表单提交路径,默认为 loginPage() 设置的路径,POST 请求
.loginProcessingUrl("/login/form")
// 设置登录表单中的用户名参数,默认为 username
.usernameParameter("name")
// 设置登录表单中的密码参数,默认为 password
.passwordParameter("pwd")
// 认证成功处理,如果存在原始访问路径,则重定向到该路径;如果没有,则重定向 /index
//.defaultSuccessUrl("/index")
// 认证失败处理,重定向到指定地址,默认为 loginPage() + ?error;该路径不设限访问
//.failureUrl("/login/page?error");
// 不再使用 defaultSuccessUrl() 和 failureUrl() 方法进行认证成功和失败处理,
// 使用自定义的认证成功和失败处理器
.successHandler(authenticationSuccessHandler)
.failureHandler(authenticationFailureHandler);
//...
}
}
6、自定义权限处理器
无权访问自定义处理器
/**
* 认证失败后返回的类
* 也可以直接实现AccessDeniedHandler
*/
@Component
public class CustomAccessDeniedHandler extends AccessDeniedHandlerImpl {
@Autowired
ObjectMapper objectMapper;
/**
* 需要在请求的时候加头部信息,否则会认为是表单请求,而不是js请求
*/
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AccessDeniedException e) throws IOException, ServletException {
String xRequestedWith = request.getHeader("x-requested-with");
// 判断前端的请求是否为 ajax 请求
if ("JSON".equals(xRequestedWith)) {
Msg result = Msg.fail(CustomExceptionCode.LOGIN_NO_ACCESS);
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(result));
}else {
super.handle(request,response,e);
}
}
}
未登录访问处理器
/**
* 自定义未认证访问处理器
* 也可以直接实现AuthenticationEntryPoint
*/
@Component
public class CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint {
@Autowired
ObjectMapper objectMapper;
/**
* 未登录时返回给前端数据,注意这是json数据返回了
*/
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException e) throws IOException, ServletException {
Msg result = Msg.fail(CustomExceptionCode.LOGIN_NEED);
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(result));
}
}
最后将处理器配置到security
// 自定义认证授权失败处理
http.exceptionHandling()
// js请求会覆盖默认
.accessDeniedHandler(accessDeniedHandler)
// 默认授权失败会重定向到登录页
//.accessDeniedPage("/login/page")
// 默认未登录返回的json类
.authenticationEntryPoint(authenticationEntryPoint);
二、Security验证码使用
1、原理概述
在用户登录时,一般通过表单的方式进行登录都会要求用户输入验证码,Spring Security默认没有实现图形验证码的功能,所以需要我们自己实现
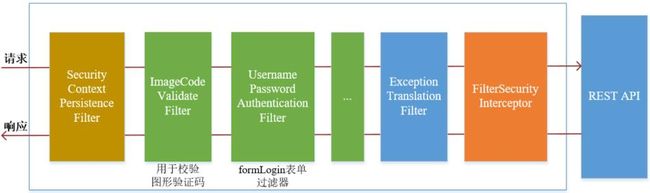
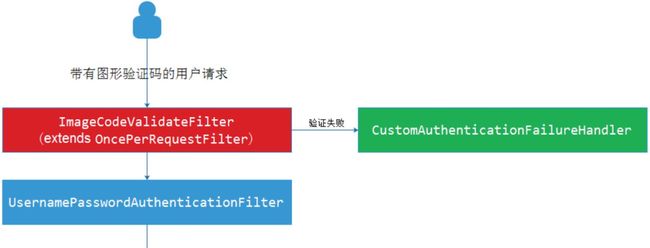
前文中实现的用户名、密码登录是在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器进行认证的,而图形验证码一般是在用户名、密码认证之前进行验证的,所以需要在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器之前添加一个自定义过滤器 ImageCodeValidateFilter,用来校验用户输入的图形验证码是否正确。自定义过滤器继承 OncePerRequestFilter 类,该类是 Spring 提供的在一次请求中只会调用一次的 filter
自定义的过滤器 ImageCodeValidateFilter 首先会判断请求是否为 POST 方式的登录表单提交请求,如果是就将其拦截进行图形验证码校验。如果验证错误,会抛出自定义异常类对象 ValidateCodeException,该异常类需要继承 AuthenticationException 类。在自定义过滤器中,我们需要手动捕获自定义异常类对象,并将捕获到自定义异常类对象交给自定义失败处理器进行处理。
2、实战
2.1 验证码图片的生成
更改安全配置类 SpringSecurityConfig,设置访问/captcha/image不需要任何权限,访问就会出现一个验证码小图片,其他几种验证码可以参考:Java验证码
首先创建验证码的存储类
public class CheckCode implements Serializable {
private String code; // 验证码字符
private LocalDateTime expireTime; // 过期时间
/**
* @param code 验证码字符
* @param expireTime 过期时间,单位秒
*/
public CheckCode(String code, int expireTime) {
this.code = code;
this.expireTime = LocalDateTime.now().plusSeconds(expireTime);
}
public CheckCode(String code) {
// 默认验证码 60 秒后过期
this(code, 60);
}
// 是否过期
public boolean isExpried() {
return this.expireTime.isBefore(LocalDateTime.now());
}
public String getCode() {
return this.code;
}
}
验证码生成类,图片直接返回,结果保存在此次session中
@RestController
@CrossOrigin
public class ValidateController {
public final static String SESSION_KEY_IMAGE_CODE = "SESSION_KEY_IMAGE_CODE";
// 验证码图片边框宽度
private int WIDTH = 120;
// 验证码图片边框高度
private int HEIGHT = 45;
// 验证码有效时间 60s
private int expireIn = 60;
// 普通验证码
private int length = 4; // 验证码位数
@GetMapping("/captcha/image")
public void createCode(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// 设置响应报头信息
response.setHeader("Pragma", "No-cache");
response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache");
response.setDateHeader("Expires", 0);
// 设置响应的MIME类型
response.setContentType("image/jpeg");
//画板
BufferedImage image = new BufferedImage(WIDTH,HEIGHT,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
//画笔
Graphics g = image.getGraphics();
//字体
Font font = new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD,35);
//设置字体
g.setFont(font);
//引入背景图片
g.fillRect(0, 0, WIDTH, HEIGHT);
//随机数
Random random = new Random();
//要随机的字符串
String template = "123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
char tempNum;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++){
//获取随机出的字符
int tempIndex = random.nextInt(template.length()-1);
tempNum = template.charAt(tempIndex);
//拼成字符串
s.append(tempNum);
//设置颜色
Color color = new Color(20+random.nextInt(110),20+random.nextInt(110),random.nextInt(110));
g.setColor(color);
//字母写入图片
g.drawString(String.valueOf(tempNum),25 * i + 12, 32);
}
// 放入session缓存,默认60s过期
CheckCode checkCode = new CheckCode(s.toString().toLowerCase(),expireIn);
HttpSession se = request.getSession();
se.setAttribute(Constants.KAPTCHA_SESSION_KEY, checkCode);
//获取流发送给前台
ServletOutputStream ots = response.getOutputStream();
ImageIO.write(image,"JPEG",ots);
}
}
2.2 自定义验证码过滤器
创建自定义异常类 ValidateCodeException
/**
* 自定义验证码校验错误的异常类,继承 AuthenticationException
*/
public class ValidateCodeException extends AuthenticationException {
public ValidateCodeException(String msg, Throwable t) {
super(msg, t);
}
public ValidateCodeException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
自定义图形验证码校验过滤器 ImageCodeValidateFilter
@Component
public class ImageCodeValidateFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
private String codeParamter = "imageCode"; // 前端输入的图形验证码参数名
@Autowired
private CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler authenticationFailureHandler; // 自定义认证失败处理器
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 非 POST 方式的表单提交请求不校验图形验证码
if ("/login/form".equals(request.getRequestURI()) && "POST".equals(request.getMethod())) {
try {
// 校验图形验证码合法性
validate(request);
} catch (ValidateCodeException e) {
// 手动捕获图形验证码校验过程抛出的异常,将其传给失败处理器进行处理
authenticationFailureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, e);
return;
}
}
// 放行请求,进入下一个过滤器
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
// 判断验证码的合法性
private void validate(HttpServletRequest request) {
// 获取用户传入的图形验证码值
String requestCode = request.getParameter(this.codeParamter);
if(requestCode == null) {
requestCode = "";
}
requestCode = requestCode.trim().toLowerCase();
// 获取 Session
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
// 获取存储在 Session 里的验证码值
CheckCode savedCode = (CheckCode) session.getAttribute(Constants.KAPTCHA_SESSION_KEY);
if (savedCode != null) {
// 随手清除验证码,无论是失败,还是成功。客户端应在登录失败时刷新验证码
session.removeAttribute(Constants.KAPTCHA_SESSION_KEY);
}
// 校验出错,抛出异常
if (StringUtils.isBlank(requestCode)) {
throw new ValidateCodeException("验证码的值不能为空");
}
if (savedCode == null) {
throw new ValidateCodeException("验证码不存在");
}
if (savedCode.isExpried()) {
throw new ValidateCodeException("验证码过期");
}
if (!requestCode.equalsIgnoreCase(savedCode.getCode())) {
throw new ValidateCodeException("验证码输入错误");
}
}
}
更改安全配置类 SpringSecurityConfig,将自定义过滤器添加过滤器链中
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启 MVC Security 安全配置
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//...
@Autowired
private ImageCodeValidateFilter imageCodeValidateFilter; // 自定义过滤器(图形验证码校验)
//...
/**
* 定制基于 HTTP 请求的用户访问控制
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//...
// 将自定义过滤器(图形验证码校验)添加到 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 之前
http.addFilterBefore(imageCodeValidateFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
//...
}
3、session异常问题
可能会出现获取验证码的session和需要输入验证码不是同一个的情况,添加以下代码
@Configuration
public class SpringSessionConfig {
@Bean
public CookieSerializer httpSessionIdResolver() {
DefaultCookieSerializer cookieSerializer = new DefaultCookieSerializer();
// 取消仅限同一站点设置,防止跨域造成的session不一样,这样验证码就会有问题
cookieSerializer.setSameSite(null);
return cookieSerializer;
}
}
三、Remember-Me 和注销
1、Remember-Me 功能概述
1.1 概述
在实际开发中,为了用户登录方便常常会启用记住我(Remember-Me)功能。如果用户登录时勾选了“记住我”选项,那么在一段有效时间内,会默认自动登录,免去再次输入用户名、密码等登录操作。该功能的实现机理是根据用户登录信息生成 Token 并保存在用户浏览器的 Cookie 中,当用户需要再次登录时,自动实现校验并建立登录态的一种机制。Spring Security提供了两种 Remember-Me 的实现方式:
- 简单加密 Token:用散列算法加密用户必要的登录系信息并生成 Token 令牌。
- 持久化 Token:数据库等持久性数据存储机制用的持久化 Token 令牌。
1.2 基本原理
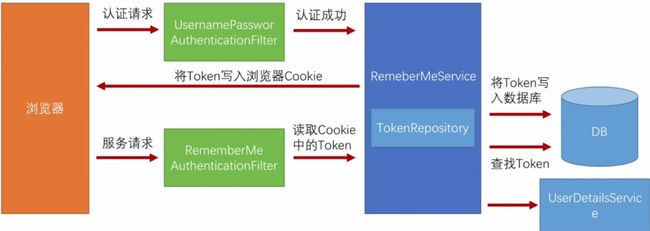
Remember-Me 功能的开启需要在configure(HttpSecurity http)方法中通过http.rememberMe()配置,该配置主要会在过滤器链中添加 RememberMeAuthenticationFilter 过滤器,通过该过滤器实现自动登录。该过滤器的位置在其它认证过滤器之后,其它认证过滤器没有进行认证处理时,该过滤器尝试工作:
注意: Remember-Me 功能是用于再次登录(认证)的,而不是再次请求。工作流程如下:
- 当用户成功登录认证后,浏览器中存在两个 Cookie,一个是 remember-me,另一个是 JSESSIONID。用户再次请求访问时,请求首先被
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter过滤器拦截,该过滤器会根据 JSESSIONID 获取对应 Session 中存储的 SecurityContext 对象。如果获取到的 SecurityContext 对象中存储了认证用户信息对象 Authentiacaion,也就是说线程可以直接获得认证用户信息,那么后续的认证过滤器不需要对该请求进行拦截,remember-me 不起作用。 - 当 JSESSIONID 过期后,浏览器中只存在 remember-me 的 Cookie。用户再次请求访问时,由于请求没有携带 JSESSIONID,SecurityContextPersistenceFilter 过滤器无法获取 Session 中的 SecurityContext 对象,也就没法获得认证用户信息,后续需要进行登录认证。如果没有 remember-me 的 Cookie,浏览器会重定向到登录页面进行表单登录认证;但是 remember-me 的 Cookie 存在,RememberMeAuthenticationFilter 过滤器会将请求进行拦截,根据 remember-me 存储的 Token 值实现自动登录,并将成功登录后的认证用户信息对象 Authentiacaion 存储到 SecurityContext 中。当响应返回时,SecurityContextPersistenceFilter 过滤器会将 SecurityContext 存储在 Session 中,下次请求又通过 JSEESIONID 获取认证用户信息。
**总结:**remember-me 只有在 JSESSIONID 失效和前面的过滤器认证失败或者未进行认证时才发挥作用。此时,只要 remember-me 的 Cookie 不过期,我们就不需要填写登录表单,就能实现再次登录,并且 remember-me 自动登录成功之后,会生成新的 Token 替换旧的 Token,相应 Cookie 的 Max-Age 也会重置。
此处对http.rememberMe()返回值的主要方法进行说明,这些方法涉及 Remember-Me 配置:
rememberMeParameter(String rememberMeParameter):指定在登录时“记住我”的 HTTP 参数,默认为remember-mekey(String key):“记住我”的 Token 中的标识字段,默认是一个随机的 UUID 值tokenValiditySeconds(int tokenValiditySeconds):“记住我” 的 Token 令牌有效期,单位为秒,即对应的 cookie 的 Max-Age 值,默认时间为 2 周userDetailsService(UserDetailsService userDetailsService):指定 Remember-Me 功能自动登录过程使用的 UserDetailsService 对象,默认使用 Spring 容器中的 UserDetailsService 对象tokenRepository(PersistentTokenRepository tokenRepository):指定 TokenRepository 对象,用来配置持久化 TokenalwaysRemember(boolean alwaysRemember):是否应该始终创建记住我的 Token,默认为 falseuseSecureCookie(boolean useSecureCookie):是否设置 Cookie 为安全,如果设置为 true,则必须通过 https 进行连接请求
2、Remember-Me实战
源码分析可以参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/zongmin/p/13783285.html
2.1 简单加密 Token(基本使用)
在用户选择“记住我”登录并成功认证后,Spring Security将默认会生成一个名为 remember-me 的 Cookie 存储 Token 并发送给浏览器;用户注销登录后,该 Cookie 的 Max-Age 会被设置为 0,即删除该 Cookie。Token 值由下列方式组合而成:base64(username + ":" + expirationTime + ":" +md5Hex(username + ":" + expirationTime + ":" + password + ":" + key))
其中,username 代表用户名;password 代表用户密码;expirationTime 表示记住我的 Token 的失效日期,以毫秒为单位;key 表示防止修改 Token 的标识,默认是一个随机的 UUID 值,默认表单如下
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>登录title>
head>
<body>
<h3>表单登录h3>
<form method="post" th:action="@{/login/form}">
<input type="text" name="name" placeholder="用户名"><br>
<input type="password" name="pwd" placeholder="密码"><br>
<input name="imageCode" type="text" placeholder="验证码"><br>
<img th:onclick="this.src='/code/image?'+Math.random()" th:src="@{/code/image}" alt="验证码"/><br>
<div th:if="${param.error}">
<span th:text="${session.SPRING_SECURITY_LAST_EXCEPTION.message}" style="color:red">用户名或密码错误span>
div>
<div><input name="remember-me" type="checkbox">记住我div>
<button type="submit">登录button>
form>
body>
html>
修改安全配置类 SpringSecurityConfig
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启 MVC Security 安全配置
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private CustomUserDetailsServiceImpl userDetailsService;
//...
/**
* 定制基于 HTTP 请求的用户访问控制
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//...
// 开启 Remember-Me 功能
http.rememberMe()
// 指定在登录时“记住我”的 HTTP 参数,默认为 remember-me
.rememberMeParameter("remember-me")
// 设置 Token 有效期为 200s,默认时长为 2 星期
.tokenValiditySeconds(200)
// 指定 UserDetailsService 对象
.userDetailsService(userDetailsService);
// 开启注销登录功能
http.logout()
// 用户注销登录时访问的 url,默认为 /logout
.logoutUrl("/logout")
// 用户成功注销登录后重定向的地址,默认为 loginPage() + ?logout
.logoutSuccessUrl("/login/page?logout");
}
//...
}
2.2 持久化 Token(基本使用)
在用户选择“记住我”成功登录认证后,默认会生成一个名为 remember-me 的 Cookie 储存 Token,并发送给浏览器,具体实现流程如下:
- 用户选择“记住我”功能成功登录认证后,
Spring Security会把用户名 username、序列号 series、令牌值 token 和最后一次使用自动登录的时间 last_used 作为一条 Token 记录存入数据库表中,同时生成一个名为 remember-me 的 Cookie 存储series:token的 base64 编码,该编码为发送给浏览器的 Token - 当用户需要再次登录时,RememberMeAuthenticationFilter 过滤器首先会检查请求是否有 remember-me 的 Cookie。如果存在,则检查其 Token 值中的 series 和 token 字段是否与数据库中的相关记录一致,一致则通过验证,并且系统重新生成一个新 token 值替换数据库中对应记录的旧 token,该记录的序列号 series 保持不变,认证时间 last_used 更新,同时重新生成新的 Token(旧 series : 新 token)通过 Cookie 发送给浏览器,remember-me 的 Cookie 的 Max-Age 也因此重置
- 上述验证通过后,获取数据库中对应 Token 记录的 username 字段,调用 UserDetailsService 获取用户信息。之后进行登录认证,认证成功后将认证用户信息 Authentication 对象存入 SecurityContext
- 如果对应的 Cookie 值包含的 token 字段与数据库中对应 Token 记录的 token 字段不匹配,则有可能是用户的 Cookie 被盗用,这时将会删除数据库中与当前用户相关的所有 Token 记录,用户需要重新进行表单登录
- 如果对应的 Cookie 不存在,或者其值包含的 series 和 token 字段与数据库中的记录不匹配,则用户需要重新进行表单登录。如果用户退出登录,则删除数据库中对应的 Token 记录,并将相应的 Cookie 的 Max-Age 设置为 0
首先创建数据库表 persistent_logins,用于存储自动登录信息
CREATE TABLE `persistent_logins` (
`username` varchar(64) NOT NULL,
`series` varchar(64) PRIMARY KEY,
`token` varchar(64) NOT NULL,
`last_used` timestamp NOT NULL
);
修改安全配置类 SpringSecurityConfig,使用持久化 Token 方式
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启 MVC Security 安全配置
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//...
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource; // 数据源
/**
* 配置 JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl,用于 Remember-Me 的持久化 Token
*/
@Bean
public JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl tokenRepository() {
JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl jdbcTokenRepository = new JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl();
// 配置数据源
jdbcTokenRepository.setDataSource(dataSource);
// 第一次启动的时候可以使用以下语句自动建表(可以不用这句话,自己手动建表,源码中有语句的)
// jdbcTokenRepository.setCreateTableOnStartup(true);
return jdbcTokenRepository;
}
//...
/**
* 定制基于 HTTP 请求的用户访问控制
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//...
// 开启 Remember-Me 功能
http.rememberMe()
// 指定在登录时“记住我”的 HTTP 参数,默认为 remember-me
.rememberMeParameter("remember-me")
// 设置 Token 有效期为 200s,默认时长为 2 星期
.tokenValiditySeconds(200)
// 设置操作数据表的 Repository
.tokenRepository(tokenRepository())
// 指定 UserDetailsService 对象
.userDetailsService(userDetailsService);
// 开启注销登录功能
http.logout()
// 用户注销登录时访问的 url,默认为 /logout
.logoutUrl("/logout")
// 用户成功注销登录后重定向的地址,默认为 loginPage() + ?logout
.logoutSuccessUrl("/login/page?logout");
}
//...
}
3、注销登录
3.1 概述
注销登录需要在安全配置类的configure(HttpSecurity http) 里使用http.logout()配置,该配置主要会在过滤器链中加入 LogoutFilter 过滤器,Spring Security通过该过滤器实现注销登录功能。此处对http.logout()返回值的主要方法进行介绍,这些方法设计注销登录的配置,具体如下:
logoutUrl(String outUrl):指定用户注销登录时请求访问的地址,默认为 POST 方式的/logoutlogoutSuccessUrl(String logoutSuccessUrl):指定用户成功注销登录后的重定向地址,默认为/登录页面url?logoutlogoutSuccessHandler(LogoutSuccessHandler logoutSuccessHandler):指定用户成功注销登录后使用的处理器deleteCookies(String ...cookieNamesToClear):指定用户注销登录后删除的 CookieinvalidateHttpSession(boolean invalidateHttpSession):指定用户注销登录后是否立即清除用户的 Session,默认为 trueclearAuthentication(boolean clearAuthentication):指定用户退出登录后是否立即清除用户认证信息对象 Authentication,默认为 trueaddLogoutHandler(LogoutHandler logoutHandler):指定用户注销登录时使用的处理器
需要注意,Spring Security默认以 POST 方式请求访问/logout注销登录,以 POST 方式请求的原因是为了防止 csrf(跨站请求伪造),如果想使用 GET 方式的请求,则需要关闭 csrf 防护。前面我们能以 GET 方式的请求注销登录,是因为我们在configure(HttpSecurity http)方法中关闭了 csrf 防护
默认配置下,成功注销登录后会进行如下三个操作:
- 删除用户浏览器中的指定 Cookie
- 将用户浏览器中 remember-me 的 Cookie 删除,并清除用户在数据库中 remember-me 的 Token 记录
- 当前用户的 Session 删除,并清除当前 SecurityContext 中的用户认证信息对象 Authentication
- 通知用户浏览器重定向到
/登录页面url?logout
3.2 自定义登出处理器
/**
* 继承 SimpleUrlLogoutSuccessHandler 处理器,该类是 logoutSuccessUrl() 方法使用的成功注销登录处理器
* 也可以直接实现LogoutSuccessHandler
*/
@Component
public class CustomLogoutSuccessHandler extends SimpleUrlLogoutSuccessHandler {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@Override
public void onLogoutSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws ServletException, IOException {
String xRequestedWith = request.getHeader("x-requested-with");
// 判断前端的请求是否为 ajax 请求
if ("JSON".equals(xRequestedWith)) {
// 成功注销登录,响应 JSON 数据
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(Msg.success(200, "注销登录成功!")));
}else {
// 以下配置等同于在 http.logout() 后配置 logoutSuccessUrl("/login/page?logout")
// 设置默认的重定向路径
super.setDefaultTargetUrl("/login/page?logout");
// 调用父类的 onLogoutSuccess() 方法
super.onLogoutSuccess(request, response, authentication);
}
}
}
3.3 安全配置类
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启 MVC Security 安全配置
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//...
@Autowired
private CustomLogoutSuccessHandler logoutSuccessHandler; // 自定义成功注销登录处理器
//...
/**
* 定制基于 HTTP 请求的用户访问控制
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//...
// 开启注销登录功能
http.logout()
// 用户注销登录时访问的 url,默认为 /logout
.logoutUrl("/logout")
// 用户成功注销登录后重定向的地址,默认为 loginPage() + ?logout
//.logoutSuccessUrl("/login/page?logout")
// 不再使用 logoutSuccessUrl() 方法,使用自定义的成功注销登录处理器
.logoutSuccessHandler(logoutSuccessHandler)
// 指定用户注销登录时删除的 Cookie
.deleteCookies("JSESSIONID")
// 用户注销登录时是否立即清除用户的 Session,默认为 true
.invalidateHttpSession(true)
// 用户注销登录时是否立即清除用户认证信息 Authentication,默认为 true
.clearAuthentication(true);
}
//...
}
四、Session 会话管理
1、Session管理配置
Session 会话管理需要在configure(HttpSecurity http)方法中通过http.sessionManagement()开启配置。此处对http.sessionManagement()返回值的主要方法进行说明,这些方法涉及 Session 会话管理的配置,具体如下:
invalidSessionUrl(String invalidSessionUrl):指定会话失效时(请求携带无效的 JSESSIONID 访问系统)重定向的 URL,默认重定向到登录页面invalidSessionStrategy(InvalidSessionStrategy invalidSessionStrategy):指定会话失效时(请求携带无效的 JSESSIONID 访问系统)的处理策略maximumSessions(int maximumSessions):指定每个用户的最大并发会话数量,-1 表示不限数量maxSessionsPreventsLogin(boolean maxSessionsPreventsLogin):如果设置为 true,表示某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求会被拒绝登录;如果设置为 false,表示某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求访问时,其最老会话会在下一次请求时失效并根据 expiredUrl() 或者 expiredSessionStrategy() 方法配置的会话失效策略进行处理,默认值为 falseexpiredUrl(String expiredUrl):如果某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求访问时,其最老会话会在下一次请求时失效并重定向到 expiredUrlexpiredSessionStrategy(SessionInformationExpiredStrategy expiredSessionStrategy):如果某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求访问时,其最老会话会在下一次请求中失效并按照该策略处理请求。注意如果本方法与 expiredUrl() 同时使用,优先使用 expiredUrl() 的配置sessionRegistry(SessionRegistry sessionRegistry):设置所要使用的 sessionRegistry,默认配置的是 SessionRegistryImpl 实现类
2、Session 会话失效处理
当用户的 Session 会话失效(请求携带着无效的 JSESSIONID 访问系统)时,可以制定相关策略对会话失效的请求进行处理
2.1 Session 失效时间
Session 的失效时间配置是 SpringBoot 原生支持的,可以在 配置文件中直接配置
server:
servlet:
# session 失效时间,单位是秒,默认为 30min
# Session 的失效时间至少要 1 分钟,少于 1 分钟按照 1 分钟配置,源码详情TomcatServletWebServerFactory.getSessionTimeoutInMinutes()
session:
timeout: 30m
# JSESSIONID (Cookie)的生命周期,单位是秒,默认为 -1
cookie:
max-age: -1
2.2 invalidSessionUrl 方法
配置 Session 会话失效时重定向到/login/page
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启 MVC Security 安全配置
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//...
/**
* 定制基于 HTTP 请求的用户访问控制
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//...
// 开启 Session 会话管理配置
http.sessionManagement()
// 设置 Session 会话失效时重定向路径,默认为 loginPage()
.invalidSessionUrl("/login/page");
}
//...
}
2.3 invalidSessionStrategy 方法
自定义 Session 会话失效处理策略 CustomInvalidSessionStrategy
/**
* 用户请求携带无效的 JSESSIONID 访问时的处理策略,即对应的 Session 会话失效
*/
@Component
public class CustomInvalidSessionStrategy implements InvalidSessionStrategy {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
private final RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
@Override
public void onInvalidSessionDetected(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// 清除浏览器中的无效的 JSESSIONID
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("JSESSIONID", null);
cookie.setPath(getCookiePath(request));
cookie.setMaxAge(0);
response.addCookie(cookie);
String xRequestedWith = request.getHeader("x-requested-with");
// 判断前端的请求是否为 ajax 请求
if ("JSON".equals(xRequestedWith)) {
// 响应 JSON 数据
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(Msg.fail(CustomExceptionCode.LOGIN_SESSION_EXPIRED)));
}else {
// 重定向到登录页面
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, "/login/page");
}
}
private String getCookiePath(HttpServletRequest request) {
String contextPath = request.getContextPath();
return contextPath.length() > 0 ? contextPath : "/";
}
}
修改安全配置类 SpringSecurityConfig,配置使用自定义的 Session 会话失效处理策略
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启 MVC Security 安全配置
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//...
@Autowired
private CustomInvalidSessionStrategy invalidSessionStrategy; // 自定义 Session 会话失效策略
//...
/**
* 定制基于 HTTP 请求的用户访问控制
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//...
// 开启 Session 会话管理配置
http.sessionManagement()
// 设置 Session 会话失效时重定向路径,默认为 loginPage()
// .invalidSessionUrl("/login/page")
// 配置使用自定义的 Session 会话失效处理策略
.invalidSessionStrategy(invalidSessionStrategy);
}
//...
}
3、Session 会话并发控制
Session 会话并发控制可以限制用户的最大并发会话数量,例如:只允许一个用户在一个地方登陆,也就是说每个用户在系统中只能有一个 Session 会话。在使用 Session 会话并发控制时,最好保证自定义的 UserDetails 实现类重写了 equals() 和 hashCode() 方法
3.1 两种情况分析
- 同一个用户在第二个地方登录,则不允许他二次登录。这里设置
maximumSessions(1)(单用户的 Session 最大并发会话数量)以及maxSessionsPreventsLogin(true)(用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求会被拒绝登录);上述配置限制了同一个用户的二次登陆,但是不建议使用该配置。因为用户一旦被盗号,那真正的用户后续就无法登录,只能通过联系管理员解决,所以如果只能一个用户 Session 登录,一般是新会话登录并将老会话踢下线。 - 如果同一个用户在第二个地方登录,则将第一个踢下线
首先自定义最老会话被踢时的处理策略 CustomSessionInformationExpiredStrategy
/**
* 前提:Session 并发处理的配置为 maxSessionsPreventsLogin(false)
* 用户的并发 Session 会话数量达到上限,新会话登录后,最老会话会在下一次请求中失效,并执行此策略
*/
@Component
public class CustomSessionInformationExpiredStrategy implements SessionInformationExpiredStrategy {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
private final RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
@Override
public void onExpiredSessionDetected(SessionInformationExpiredEvent event) throws IOException {
HttpServletRequest request = event.getRequest();
HttpServletResponse response = event.getResponse();
// 最老会话被踢下线时显示的信息
UserDetails userDetails = (UserDetails) event.getSessionInformation().getPrincipal();
String msg = String.format("用户[%s]在另外一台机器登录,您已下线!", userDetails.getUsername());
String xRequestedWith = event.getRequest().getHeader("x-requested-with");
// 判断前端的请求是否为 ajax 请求
if ("JSON".equals(xRequestedWith)) {
// 认证成功,响应 JSON 数据
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(Msg.problem(400,msg)));
}else {
// 返回到登录页面显示信息
AuthenticationException e = new AuthenticationServiceException(msg);
request.getSession().setAttribute("SPRING_SECURITY_LAST_EXCEPTION", e);
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, "/login/page?error");
}
}
}
修改安全配置类 SpringSecurityConfig,配置最老会话被踢时的处理策略
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启 MVC Security 安全配置
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//...
@Autowired
private CustomSessionInformationExpiredStrategy sessionInformationExpiredStrategy; // 自定义最老会话失效策略
//...
/**
* 定制基于 HTTP 请求的用户访问控制
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//...
// 开启 Session 会话管理配置
http.sessionManagement()
// 设置 Session 会话失效时重定向路径,默认为 loginPage()
// .invalidSessionUrl("/login/page")
// 配置使用自定义的 Session 会话失效处理策略
.invalidSessionStrategy(invalidSessionStrategy)
// 设置单用户的 Session 最大并发会话数量,-1 表示不受限制
.maximumSessions(1)
// 设置为 true,表示某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求会被拒绝登录;
// 设置为 false,表示某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求访问时,其最老会话会在下一次请求时失效
.maxSessionsPreventsLogin(false)
// 设置所要使用的 sessionRegistry,默认为 SessionRegistryImpl 实现类
.sessionRegistry(sessionRegistry())
// 最老会话在下一次请求时失效,并重定向到 /login/page
//.expiredUrl("/login/page");
// 最老会话在下一次请求时失效,并按照自定义策略处理
.expiredSessionStrategy(sessionInformationExpiredStrategy);
}
/**
* 注册 SessionRegistry,该 Bean 用于管理 Session 会话并发控制
*/
@Bean
public SessionRegistry sessionRegistry() {
return new SessionRegistryImpl();
}
/**
* 配置 Session 的监听器(如果使用并发 Sessoion 控制,一般都需要配置)
* 解决 Session 失效后, SessionRegistry 中 SessionInformation 没有同步失效问题
*/
@Bean
public HttpSessionEventPublisher httpSessionEventPublisher() {
return new HttpSessionEventPublisher();
}
//...
}
原理分析可以参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/zongmin/p/13783348.html
3.2 自定义统计session使用
@Controller
public class TestController {
//...
@Autowired
private SessionRegistry sessionRegistry;
//...
@GetMapping("/test4")
@ResponseBody
public Object getOnlineSession() {
// 统计当前用户未过期的并发 Session 数量
UserDetails user = (UserDetails) SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
List<SessionInformation> sessions = this.sessionRegistry.getAllSessions(user, false);
return Msg.success().add("size",sessions.size());
}
@GetMapping("/test5")
@ResponseBody
public Object getOnlineUsers() {
// 统计所有在线用户
List<String> userList = sessionRegistry.getAllPrincipals().stream()
.map(user -> ((UserDetails) user).getUsername())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return Msg.success().add("userList",userList);
}
}
4、 Redis 共享 Session
4.1 操作概述
首先导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commonsgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2artifactId>
<version>2.8.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.sessiongroupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
配置文件进行配置,同时Redis 存储 Session 默认的序列化方式为 JdkSerializationRedisSerializer,所以存入 Session 的对象都要实现 Serializable 接口。因此,要保证前面代码中的验证码 CheckCode 类实现 Serializable 接口
spring:
# Redis 服务器地址
redis:
host: localhost
# Redis 服务器连接端口
port: 6379
# Redis 服务器连接密码(默认无)
password:
# Redis数据库索引(默认为0)
database: 1
lettuce:
pool:
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制),默认 8
max-active: 100
# 连接池大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制),默认 -1
max-wait: PT10S
# 连接池中的大空闲连接 默认 8
max-idle: 10
# 连接池中的小空闲连接 默认 0
min-idle: 1
# 连接超时时间
timeout: PT10S
# 使用 Redis 存储 Session,默认为 none(使用内存存储)
session:
store-type: redis
server:
servlet:
# session 失效时间,单位是秒,默认为 30min
# Session 的失效时间至少要 1 分钟,少于 1 分钟按照 1 分钟配置
session:
timeout: 30m
# JSESSIONID (Cookie)的生命周期,单位是秒,默认为 -1
cookie:
max-age: -1
# 指定存储 SessionId 的 Cookie 名(使用 Redis 存储 Session 后,Cookie 名默认会变为 SESSION)
name: JSESSIONID
最后启动访问即可
4.2 Redis数据解释
一共有三组数据:
-
第一组:string 结构,用于记录指定 Session 的剩余存活时间
spring:session:sessions:9bf69e21-ddd6-4c53-b7e6-976c047158cb就是这个 string 结构的 key,后缀的字符串是 JSEESIONID 的 base64 解码值。其 value 为空,TTL 时间为对应 Session 的剩余存活时间 -
第二组:hash 结构,用于存储指定 Session 的数据
spring:session:sessions:9bf69e21-ddd6-4c53-b7e6-976c047158cb就是这个 hash 结构的 key,后缀的字符串是 JSEESIONID 的 base64 解码值。hash 结构的 value 值本身就是一个 map 集合,分别为 lastAccessedTime(最后访问时间)、creationTime(创建时间)、maxInactiveInterval(最大存活时间)、sessionAttr:属性名(Session 里存储的属性数据) -
第三组:set 结构,用于记录 Session 的过期时间
spring:session:expirations:1602144780000就是这个 set 结构的 key,后缀的字符串是一个整分钟的时间戳,其 value 是一个 set 集合,存的是这个时间戳的分钟内要失效的 Session 对应的 JSEESIONID 的 base64 解码值
5、remember-me 失效解释(补充)
当配置了.maximumSessions(1).maxSessionsPreventsLogin(false)要求只能一个用户 Session 登录时,我们在两个地方使用相同的账号,并且都勾选 remember-me 进行登录。最老会话的下一次请求不但会使老会话强制失效,还会使数据库中所有该用户的所有 remember-me 记录被删除。
五、补充与说明
我的config文件,仅供参考
@Slf4j
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启 MVC Security 安全配置
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
/**
* 登录成功
*/
@Autowired
private CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler authenticationSuccessHandler;
/**
* 登录失败
*/
@Autowired
private CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler authenticationFailureHandler;
/**
* 注销登录
*/
@Autowired
private CustomLogoutSuccessHandler logoutSuccessHandler;
/**
* 自定义 Session 会话失效策略
*/
@Autowired
private CustomInvalidSessionStrategy invalidSessionStrategy;
/**
* 自定义数据库验证认证
*/
@Autowired
CustomUserDetailsServiceImpl userDetailsService;
/**
* 自定义最老会话失效策略
*/
@Autowired
private CustomSessionInformationExpiredStrategy sessionInformationExpiredStrategy;
/**
* 需要登录处理器
*/
@Autowired
private CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint;
/**
* 无权访问
*/
@Autowired
private CustomAccessDeniedHandler accessDeniedHandler;
/**
* 自定义登录校验
*/
@Autowired
private CustomAuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider;
// 自定义过滤器(图形验证码校验)
@Autowired
private ImageCodeValidateFilter imageCodeValidateFilter;
/**
* 密码编码器,密码不能明文存储
*/
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
// 使用 BCryptPasswordEncoder 密码编码器,该编码器会将随机产生的 salt 混入最终生成的密文中
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
/**
* 定制用户认证管理器来实现用户认证
* 内存覆盖
* 最简单是配置文件直接覆盖写
*/
// @Override
// protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
// // 采用内存存储方式,用户认证信息存储在内存中
// auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
// .withUser("admin").password(passwordEncoder()
// .encode("123456")).roles("ADMIN");
// }
/**
* 内存中覆盖默认的用户名与密码
* Security5.7后新的写法
* 和上面一样作用
*/
// @Bean
// public UserDetailsService userDetailsService(){
// InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();
// log.info("Password: {}", passwordEncoder().encode("123456"));
// manager.createUser(User.withUsername("admin").password(passwordEncoder().encode("123456")).authorities("ADMIN").build());
// return manager;
// }
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource; // 数据源
/**
* 配置 JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl,用于 Remember-Me 的持久化 Token
* 每次认证登录会生成一次记录,注销或过期会自动删除
* 下面配置了才用,否则不用
*/
@Bean
public JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl tokenRepository() {
JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl jdbcTokenRepository = new JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl();
// 配置数据源
jdbcTokenRepository.setDataSource(dataSource);
// 第一次启动的时候可以使用以下语句自动建表(可以不用这句话,自己手动建表,源码中有语句的)
// jdbcTokenRepository.setCreateTableOnStartup(true);
return jdbcTokenRepository;
}
/**
* 定制用户认证管理器来实现用户认证
*/
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
// 1、采用内存存储方式,用户认证信息存储在内存中
// auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
// .withUser("admin").password(passwordEncoder()
// .encode("123456")).roles("ROLE_ADMIN");
// 2、不再使用内存方式存储用户认证信息,而是动态从数据库中获取
//auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
// 3、自定义登录验证
auth.authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider);
}
/**
* 定制基于 HTTP 请求的用户访问控制
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// 启动 form 表单登录
http.formLogin()
// 设置登录页面的访问路径,默认为 /login,GET 请求;该路径不设限访问
.loginPage("/login/page")
// 设置登录表单提交路径,默认为 loginPage() 设置的路径,POST 请求
.loginProcessingUrl("/login/form")
// 设置登录表单中的用户名参数,默认为 username
.usernameParameter("name")
// 设置登录表单中的密码参数,默认为 password
.passwordParameter("pwd")
// 认证成功处理,如果存在原始访问路径,则重定向到该路径;如果没有,则重定向 /index
.defaultSuccessUrl("/index")
// 认证失败处理,重定向到指定地址,默认为 loginPage() + ?error;该路径不设限访问
.failureUrl("/login/page?error")
// 不再使用 defaultSuccessUrl() 和 failureUrl() 方法进行认证成功和失败处理,
// 使用自定义的认证成功和失败处理器,可以在自定义那里进行设置,如果js请求就返回json,否则就返回表单(即上面设置的路径)
.successHandler(authenticationSuccessHandler)
.failureHandler(authenticationFailureHandler);
// 开启基于 HTTP 请求访问控制
http.authorizeRequests()
// 以下访问不需要任何权限,任何人都可以访问
.antMatchers("/login/page","/captcha/image").permitAll()
// 对于角色ROLE_ADMIN的授权方式有两种:hasRole("ADMIN")和hasAuthority("ROLE_ADMIN"),这两种方式是等价的。
// 以下访问需要 ROLE_ADMIN 权限
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
// 以下访问需要 ROLE_USER 权限
.antMatchers("/user/**").hasAuthority("ROLE_USER")
// 其它任何请求访问都需要先通过认证
.anyRequest().authenticated();
// 将自定义过滤器(图形验证码校验)添加到 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 之前
http.addFilterBefore(imageCodeValidateFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
// 关闭 csrf 防护
http.csrf().disable();
// 开启 Remember-Me 功能
http.rememberMe()
// 指定在登录时“记住我”的 HTTP 参数,默认为 remember-me
.rememberMeParameter("remember-me")
// 设置 Token 有效期为 200s,默认时长为 2 星期
.tokenValiditySeconds(200)
// 设置操作数据表的 Repository
// .tokenRepository(tokenRepository())
// 指定 UserDetailsService 对象
.userDetailsService(userDetailsService);
// 开启注销登录功能
http.logout()
// 用户注销登录时访问的 url,默认为 /logout
.logoutUrl("/logout")
// 用户成功注销登录后重定向的地址,默认为 loginPage() + ?logout
.logoutSuccessUrl("/login/page?logout")
// 不再使用 logoutSuccessUrl() 方法,使用自定义的成功注销登录处理器
.logoutSuccessHandler(logoutSuccessHandler)
// 指定用户注销登录时删除的 Cookie
.deleteCookies("JSESSIONID")
// 用户注销登录时是否立即清除用户的 Session,默认为 true
.invalidateHttpSession(true)
// 用户注销登录时是否立即清除用户认证信息 Authentication,默认为 true
.clearAuthentication(true);
// 开启 Session 会话管理配置
http.sessionManagement()
// 设置 Session 会话失效时重定向路径,默认为 loginPage()
.invalidSessionUrl("/login/page")
// 配置使用自定义的 Session 会话失效处理策略
.invalidSessionStrategy(invalidSessionStrategy)
// 设置单用户的 Session 最大并发会话数量,-1 表示不受限制
.maximumSessions(1)
// 设置为 true,表示某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求会被拒绝登录;
// 设置为 false,表示某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求访问时,其最老会话会在下一次请求时失效
.maxSessionsPreventsLogin(false)
// 设置所要使用的 sessionRegistry,默认为 SessionRegistryImpl 实现类
.sessionRegistry(sessionRegistry())
// 最老会话在下一次请求时失效,并重定向到 /login/page
.expiredUrl("/login/page")
// 最老会话在下一次请求时失效,并按照自定义策略处理
.expiredSessionStrategy(sessionInformationExpiredStrategy);
// 自定义认证授权失败处理
http.exceptionHandling()
// js请求会覆盖默认
.accessDeniedHandler(accessDeniedHandler)
// 默认授权失败会重定向到登录页
// .accessDeniedPage("/login/page")
// 默认未登录返回的json类
.authenticationEntryPoint(authenticationEntryPoint);
}
/**
* 注册 SessionRegistry,该 Bean 用于管理 Session 会话并发控制
*/
@Bean
public SessionRegistry sessionRegistry() {
return new SessionRegistryImpl();
}
/**
* 配置 Session 的监听器(注意:如果使用并发 Sessoion 控制,一般都需要配置该监听器)
* 解决 Session 失效后, SessionRegistry 中 SessionInformation 没有同步失效的问题
*/
@Bean
public HttpSessionEventPublisher httpSessionEventPublisher() {
return new HttpSessionEventPublisher();
}
/**
* 定制一些全局性的安全配置,例如:不拦截静态资源的访问
*/
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
// 静态资源的访问不需要拦截,直接放行
web.ignoring().antMatchers("/**/*.css", "/**/*.js", "/**/*.png", "/**/*.jpg", "/**/*.jpeg");
}
}
另外Security5.7以后该方法就不推荐了,可以用新版的配置文件方式,更加简洁
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class SecurityConfig {
/**
* 注销成功返回的 JSON 格式数据给前端
*/
@Autowired
private AjaxLogoutSuccessHandler logoutSuccessHandler;
/**
* 无权访问 JSON 格式的数据
*/
@Autowired
private AjaxAccessDeniedHandler ajaxAccessDeniedHandler;
@Autowired
private AjaxAuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint;
@Autowired
private CustomizeSessionInformationExpiredStrategy sessionInformationExpiredStrategy;
@Autowired
private JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter tokenAuthenticationFilter;
@Autowired
private RedisUtils redisUtils;
@Autowired
private LogService logService;
@Autowired
private PowerManagerMapper powerManagerMapper;
@Autowired
private PowerManagerService powerManagerService;
/**
* 注入AuthenticationConfiguration
*/
@Autowired
private AuthenticationConfiguration auth;
/**
* 编写AuthenticationManager的bean
*/
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManager() throws Exception {
return auth.getAuthenticationManager();
}
/**
* 替换旧版本中的configure(HttpSecurity http)方法
*/
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.cors().and().csrf().disable();
http.httpBasic()
.authenticationEntryPoint(authenticationEntryPoint)
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
//自定义放行接口
.antMatchers(
"/swagger**/**",
"/swagger-ui.html",
"/swagger-resources/**",
"/webjars/**",
"/v3/**"
).permitAll()
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and().logout().logoutUrl("/logout")
//登出处理
.logoutSuccessHandler(logoutSuccessHandler)
//添加关于自定义的认证过滤器和自定义的授权过滤器
.and()
.logout().permitAll()//注销行为任意访问
//会话管理
.and().sessionManagement()
//同一账号同时登录最大用户数
.maximumSessions(1)
//会话信息过期策略会话信息过期策略(账号被挤下线)
.expiredSessionStrategy(sessionInformationExpiredStrategy);
//自定义权限拒绝处理类
// 无权访问 JSON 格式的数据
http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedHandler(ajaxAccessDeniedHandler);
// 登录验证
http.addFilter(new TokenLoginFilter(authenticationManager(),redisUtils,logService,powerManagerMapper,powerManagerService)).httpBasic();
// JWT Filter
http.addFilterBefore(tokenAuthenticationFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
return http.build();
}
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
如果想加token验证的话可以参考:Spring Security配置和Spring Security学习笔记
本次Spring Security的Demo代码地址:Security Demo项目
https://blog.csdn.net/2201_75856701/article/details/128676769
https://www.cnblogs.com/zongmin/tag/Spring Security/
https://blog.csdn.net/rq12345688/article/details/125479657
https://blog.csdn.net/lemon_TT/article/details/124675493