机器学习 实验三:K均值聚类
介绍:
在本实验中,将实现K均值聚类算法(K-means)并了解其在数据聚类上的工作原理及图像压缩上的应用。
本次实验需要用到的数据集包括:
- ex3data1.mat -2D 数据集
- hzau.jpeg -用于测试k均值聚类算法图像压缩性能的图像
评分标准如下:
- 要点1:寻找最近类中心点-----------------(20分)
- 要点2:计算均值类中心--------------------(20分)
- 要点3:随机初始化类中心-----------------(10分)
- 要点4:K均值聚类算法---------------------(20分)
- 要点5:图像压缩-----------------------------(30分)
In [1]:
# 引入所需要的库文件
import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
import seaborn as sb
from scipy.io import loadmat
%matplotlib inline1 K均值聚类 K-means Clustering
在本部分实验中,将实现K均值聚类算法。
在每次迭代中,算法主要包含两个部分:寻找最近类中心点和计算均值类中心。
另外,基于初始化的需求,需创建一个选择随机样本并将其用作初始聚类中心的函数。
1.1 寻找最近类中心点
在本部分实验中,我们将为每个样本点寻找离其距离最近的类中心,并将其赋予对应的类。
具体的更新公式如下:
ci:=argminj=1,⋯,K∥xi−μj∥2,ci:=argminj=1,⋯,K‖xi−μj‖2,
其中xixi为第ii个样本点,μjμj为第jj个均值类中心。
**要点 1:** 在下方cell中,请**实现''寻找最近类中心点''的代码**。
In [2]:
# ====================== 在这里填入代码 =======================
def find_closest_centroids(X, centroids):
"""
输入
----------
X : 尺寸为 (m, n)的矩阵,第i行为第i个样本,n为样本的维数。
centroids : 尺寸为 (k, n)的矩阵,其中k为类别个数。
输出
-------
idx : 尺寸为 (m, 1)的矩阵,第i个分量表示第i个样本的类别。
"""
m = X.shape[0]
k = centroids.shape[0]
idx = np.zeros(m,dtype=np.int)
for i in range(m):
minn = 100000
for j in range(k):
dist = np.sum((X[i,:] - centroids[j,:]) ** 2)
if dist < minn:
minn = dist
idx[i] = j
return idx
# ============================================================= 如果完成了上述函数 find_closest_centroids,以下代码可用于测试。如果结果为[0 2 1],则计算通过。
In [3]:
#导入数据
data = loadmat('ex3data1.mat')
X = data['X']
X1=X
initial_centroids = np.array([[3, 3], [6, 2], [8, 5]])
idx = find_closest_centroids(X, initial_centroids)
idx[0:3]Out[3]:
array([0, 2, 1])
In [4]:
#显示并查看部分数据
data2 = pd.DataFrame(data.get('X'), columns=['X1', 'X2'])
data2.head()Out[4]:
| X1 | X2 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.842080 | 4.607572 |
| 1 | 5.658583 | 4.799964 |
| 2 | 6.352579 | 3.290854 |
| 3 | 2.904017 | 4.612204 |
| 4 | 3.231979 | 4.939894 |
In [5]:
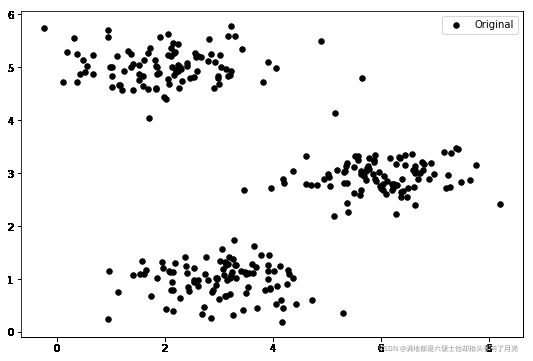
#可视化二维数据
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(9,6))
ax.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], s=30, color='k', label='Original')
ax.legend()
plt.show()
1.2 计算均值类中心
在本部分实验中,我们将每类样本的均值作为新的类中心。
具体的更新公式如下:
μj:=1|Cj|∑i∈Cjxiμj:=1|Cj|∑i∈Cjxi
其中CjCj为第jj类样本点的指标集,|Cj||Cj|为集合CjCj的元素个数。
**要点 2:** 在下方cell中,请**实现''计算均值类中心''的代码**。
In [6]:
# ====================== 在这里填入代码 =======================
def compute_centroids(X, idx, k):
m, n = X.shape
centroids = np.zeros((k, n))
#print(n)
for i in range(k):
num=0
sum=np.zeros(n)
for j in range(m):
if idx[j]==i:
num=num+1
sum[:]=sum[:]+X[j,:]
centroids[i]=sum[:]/num
return centroids
# ============================================================= In [7]:
#测试上述计算均值类中心代码
compute_centroids(X, idx, 3)Out[7]:
array([[2.42830111, 3.15792418],
[5.81350331, 2.63365645],
[7.11938687, 3.6166844 ]])
1.3 随机初始化类中心
随机选择k个样本作为初始类中心。
**要点 3:** 在下方cell中,请**实现''随机初始化类中心''的代码**。具体为随机选择k个样本作为初始类中心。
In [8]:
# ====================== 在这里填入代码 =======================
def init_centroids(X, k):
m, n = X.shape
#j=m/k
#print(j)
idx = np.random.randint(0, m, k)
centroids = np.zeros((k, n))
for i in range(k):
centroids[i,:] = X[idx[i],:]
return centroids
# ============================================================= In [9]:
#测试上述随机初始化类中心代码
init_centroids(X, 3)Out[9]:
array([[3.30063655, 1.28107588],
[1.02285128, 5.0105065 ],
[6.59702155, 3.07082376]])
1.4 实现K均值聚类算法
**要点 4:** 在下方cell中,请通过结合上述步骤**实现''K均值聚类算法''的代码**。
In [10]:
# ====================== 在这里填入代码 =======================
def run_k_means(X, initial_centroids, max_iters):
m, n = X.shape
k = initial_centroids.shape[0]
idx = np.zeros(m)
#centroids = np.zeros((k, n))
centroids =initial_centroids
centroids_last =initial_centroids
for i in range(max_iters):
idx = find_closest_centroids(X, centroids)
centroids = compute_centroids(X, idx, k)
if (centroids==centroids_last).all()==True:
break
centroids_last = compute_centroids(X, idx, k)
return idx, centroids
# ============================================================= 2 将K均值聚类算法应用于数据集1
在本部分实验中,将已实现的K均值聚类算法应用于数据集1,该数据集中的样本维数为2,因此聚类结束后,可通过可视化观察聚类结果。
In [11]:
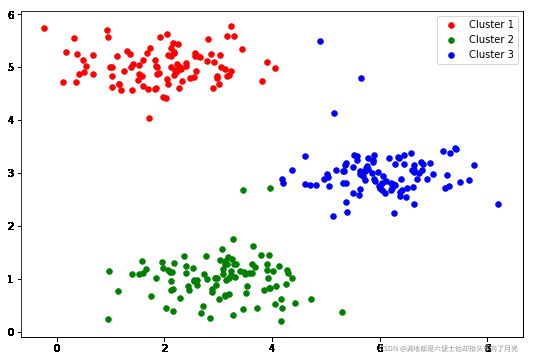
idx, centroids = run_k_means(X, initial_centroids, 10)
# print(centroids)In [12]:
cluster1 = X[np.where(idx == 0)[0],:]
cluster2 = X[np.where(idx == 1)[0],:]
cluster3 = X[np.where(idx == 2)[0],:]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(9,6))
ax.scatter(cluster1[:,0], cluster1[:,1], s=30, color='r', label='Cluster 1')
ax.scatter(cluster2[:,0], cluster2[:,1], s=30, color='g', label='Cluster 2')
ax.scatter(cluster3[:,0], cluster3[:,1], s=30, color='b', label='Cluster 3')
ax.legend()
plt.show()
1.3 将K均值聚类算法应用于图像压缩 Image compression with K-means
In [13]:
#读取图像
A = mpl.image.imread('hzau.jpeg')
A.shapeOut[13]:
(96, 150, 3)
现在我们需要对数据应用一些预处理,并将其提供给K-means算法。
In [14]:
# 归一化图像像素值的范围到[0, 1]
A = A / 255.
# 对原始图像尺寸作变换
X = np.reshape(A, (A.shape[0] * A.shape[1], A.shape[2]))
X.shapeOut[14]:
(14400, 3)
**要点 5:** 在下方cell中,**请利用K均值聚类算法实现图像压缩**。具体方法是将原始像素替换为对应的均值类中心像素。
In [21]:
# ====================== 在这里填入代码 =======================
# 随机初始化类中心
initial_centroids = init_centroids(X, 16)
m=X.shape[0]
idx, centroids = run_k_means(X, initial_centroids, 10)
idx = find_closest_centroids(X, centroids)
#n=centroids.shape[0]
#print(n)
A_compressed=X
for i in range(m):
A_compressed[i,:]=centroids[idx[i],:]
A_compressed = np.reshape(A_compressed, (96, 150,3))
print(A_compressed.shape)
# ============================================================= /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:13: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in true_divide del sys.path[0]
(96, 150, 3)
In [22]:
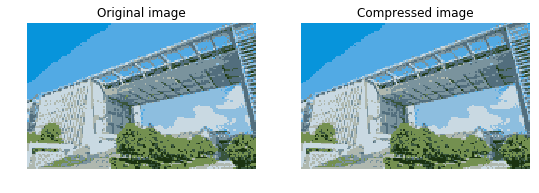
#显示压缩前后的图像
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(9,6))
ax[0].imshow(A)
ax[0].set_axis_off()
ax[0].set_title('Original image')
ax[1].imshow(A_compressed)
ax[1].set_axis_off()
ax[1].set_title('Compressed image')
plt.show()
In [27]:
#计算类中心点
# ====================== 在这里填入代码 =======================
def Manhattan(x, y):
# 定义曼哈顿距离的计算
return np.sum(np.abs(x-y))
def compute_mid(X, idx, k):
m, n = X.shape
centroids = np.zeros((k, n))
for i in range(k):
minn=10000
for j in range(m):
if idx[j]==i:
sum=0
for h in range(m):
if idx[h]==i and j!=h:
sum=sum+Manhattan(X[j,:],X[h,:])
if sumIn [28]:
#实现k中心聚类算法
def run_k_mid(X, initial_centroids, max_iters):
m, n = X.shape
k = initial_centroids.shape[0]
idx = np.zeros(m)
centroids =initial_centroids
centroids_last =initial_centroids
for i in range(max_iters):
idx = find_closest_centroids(X, centroids)
# print(i)
# print(idx)
centroids = compute_mid(X, idx, k)
# print(centroids)
if (centroids==centroids_last).all()==True:
break
centroids_last = compute_mid(X, idx, k)
return idx, centroids
# ============================================================= In [29]:
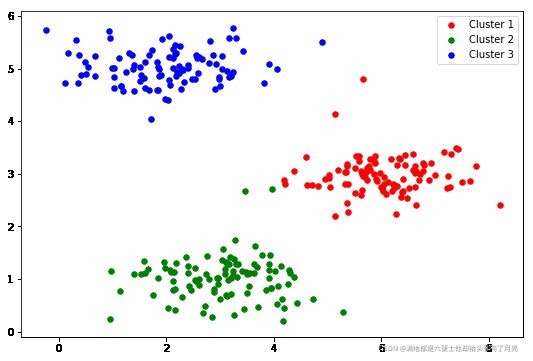
initial_centroids=init_centroids(X1, 3)
# print(initial_centroids)
idx, centroids = run_k_mid(X1, initial_centroids, 10)
# print(idx)
# print(centroids)In [30]:
cluster1 = X1[np.where(idx == 0)[0],:] cluster2 = X1[np.where(idx == 1)[0],:] cluster3 = X1[np.where(idx == 2)[0],:] fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(9,6)) ax.scatter(cluster1[:,0], cluster1[:,1], s=30, color='r', label='Cluster 1') ax.scatter(cluster2[:,0], cluster2[:,1], s=30, color='g', label='Cluster 2') ax.scatter(cluster3[:,0], cluster3[:,1], s=30, color='b', label='Cluster 3') ax.legend() plt.show()
initial_centroids=init_centroids(X1, 3)
# print(initial_centroids)
idx, centroids = run_k_mid(X1, initial_centroids, 10)
# print(idx)
# print(centroids)